
by Sheila Dunning | Aug 13, 2015
 University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
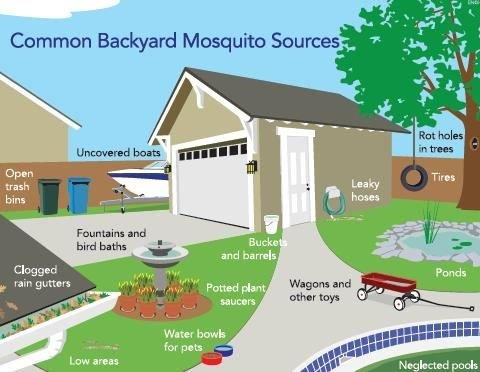
With all the quick afternoon thunderstorms and frequent irrigation events, now is the time to check out where the water is collecting in your yard. The female Culex nigripalpus mosquitoes lay their eggs in temporary flood water pools; even very small ones such as pet watering bowls, bird baths and upturned Magnolia leaves. Dumping out the collection containers every couple of days can greatly reduce the population.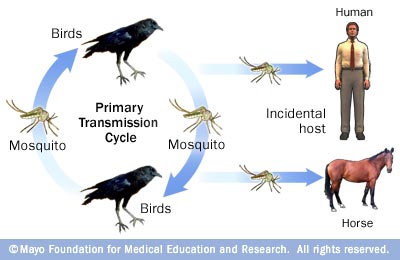
Becoming infected with West Nile Virus is not easy. Mosquitoes usually obtain the virus by feeding on infected wild birds, many of which have migrated from areas that have ongoing West Nile Virus outbreaks. Once the mosquito has drawn infected blood from the bird, the virus goes through a temperature-dependent incubation period within the mosquito. Then, when the infected mosquito “bites” a human or horse the virus mixed in saliva is released into the blood stream of the second host. West Nile Virus is not transmitted from one human to another. Nor is it transmitted from bird to human or from horse to human.
Thanks to a devoted set of researchers and government public health officials, here in Florida we are able to monitor mosquito-borne illnesses quickly and effectively. Additional partners, such as local veterinaries, sentinel bird stations and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) serve as reporters for virus population. Should an individual come across dead birds without an obvious cause, reporting them to the FWC at www.myfwc.com/bird/ is the best thing to do.
 As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:
As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:
Stay indoors at dusk (peak mosquito biting time).
If you must be outside, wear long sleeves and pants and/or mosquito repellents containing the active ingredient DEET.
Repair torn door and window screens.
Remove unnecessary outside water sources.
Flush out water collected in outdoor containers every 3-4 days.
Disturb or remove leaf litter, including roof gutters and covers on outdoor equipment.
For additional information, contact your local Extension office about obtaining a free Florida Resident’s Guide to Mosquito Control.

by Matthew Orwat | Aug 11, 2015
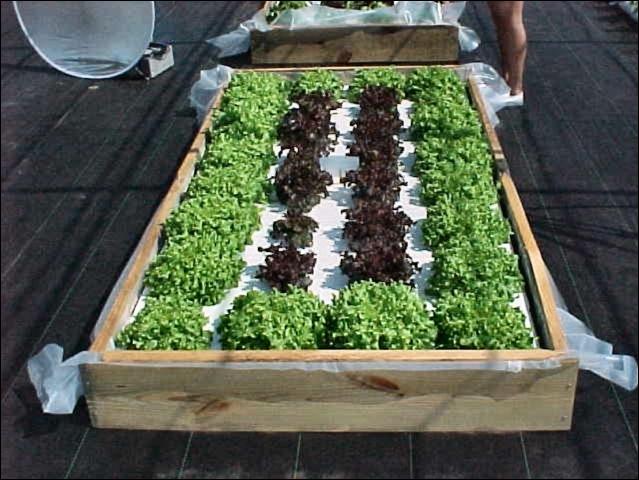
Building a floating hydroponic garden as a fall project could be rewarding and delicious. In the fall, lettuce, cabbage and greens are ideal for floating hydroponic gardens.
Watch a video by UF / IFAS Extension Agents to learn how to construct your own floating hydroponic garden by clicking on the picture below.
The publication, Building a Floating Hydroponic Garden, is also available for those interested in more information.

by Les Harrison | Aug 11, 2015
Weeds are growing everywhere, especially in manicured lawns and landscapes despite the best efforts of owners who have spared no expense to remove the offending flora. Herbicides to control the weeds seem to be less effective as August progresses.
The reality, at least about the herbicides, is different from perceived appearances. Herbicides can be a wonderful tool for the homeowner, if applied properly.
[important]The first point to remember about herbicides is to always, Always, ALWAYS apply them as instructed by the label directions. The oft quoted mantra of “the label is the law” is accurate.[/important]
Herbicides and their labeling are periodically reviewed and assessed to confirm effectiveness against target weeds without damaging the environment. Not following the label directions can have many negative implications for both the environment and the applicator.
Herbicides are either selective or non-selective when killing plants. Non-selective herbicides kill or damage every plant, but selective herbicides target a narrower range of plants.

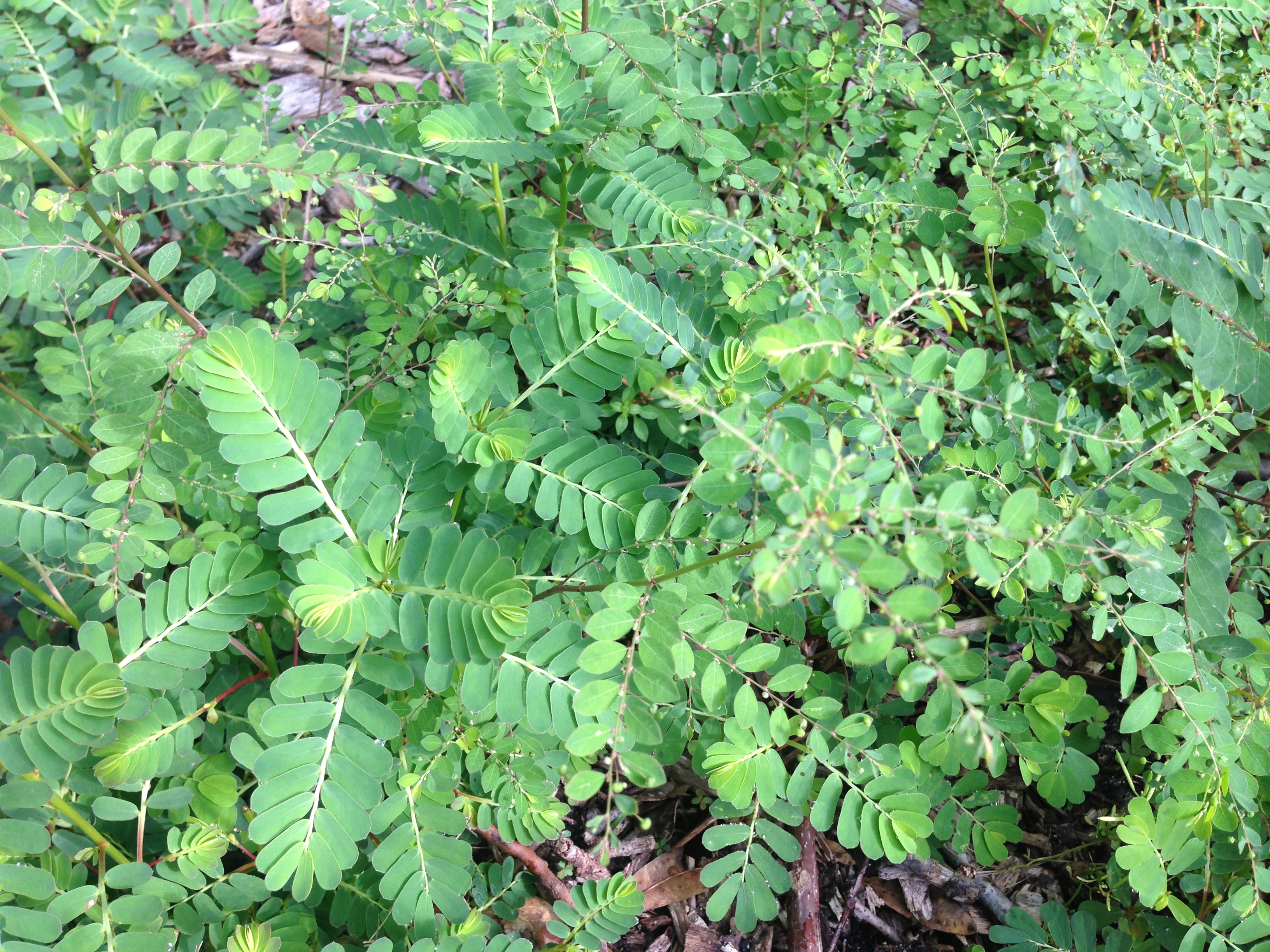
Chamberbitter, a common annual weed. Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
Never apply herbicides when there is a breeze or wind. Herbicide drift can injure or destroy plants that are not the intended target.
High temperatures can contribute to the drift problem by volatizing some of the herbicide spray. Even the lightest air movement will cause drift off the target weeds when this condition exists. Herbicide drift can also be deposited in ponds and streams, harming the aquatic creatures that live there. Some herbicides are toxic to fish, insects and other animals that can be killed by tiny amounts of the active chemical. Additionally, the off target herbicides can kill aquatic plants. When the dead plants decay, they deplete the water of oxygen, again threatening or ending the life of the water’s residents.
Rain or dew resulting from high humidity can negate a herbicide’s application. If a leaf is wet, most or all the herbicide will run off on to the soil where it can leach into the water table.
Unless stated on the label, herbicides work only when the plant is actively growing. A hot, dry week or two can put a plant in drought mode, suspending growth and the herbicide’s effectiveness.
Many weeds have already produced seeds for next spring. Herbicides applied now will not affect the germination of that seed months from now.
The most effective strategy is to mow weeds before they set seed or to collect and destroy those which have already produced seed. Even with 100 percent success at eliminating this year’s weed seed crop, there will be weeds next year.
Some weed seed remain in the soil, sometimes for decades, only to germinate when conditions are perfect for their sprouting. Sickle pod and crotalaria are local examples of long term seed vigor.
Other seed can blow in or be dropped by wild or domestic animals passing through the property. A pre-emergent herbicide which stops germination can help control these latent invaders.
For more information:
Weed Management Guide for Florida Lawns
Gardening Solutions: Weeds

by Roy Carter | Aug 10, 2015
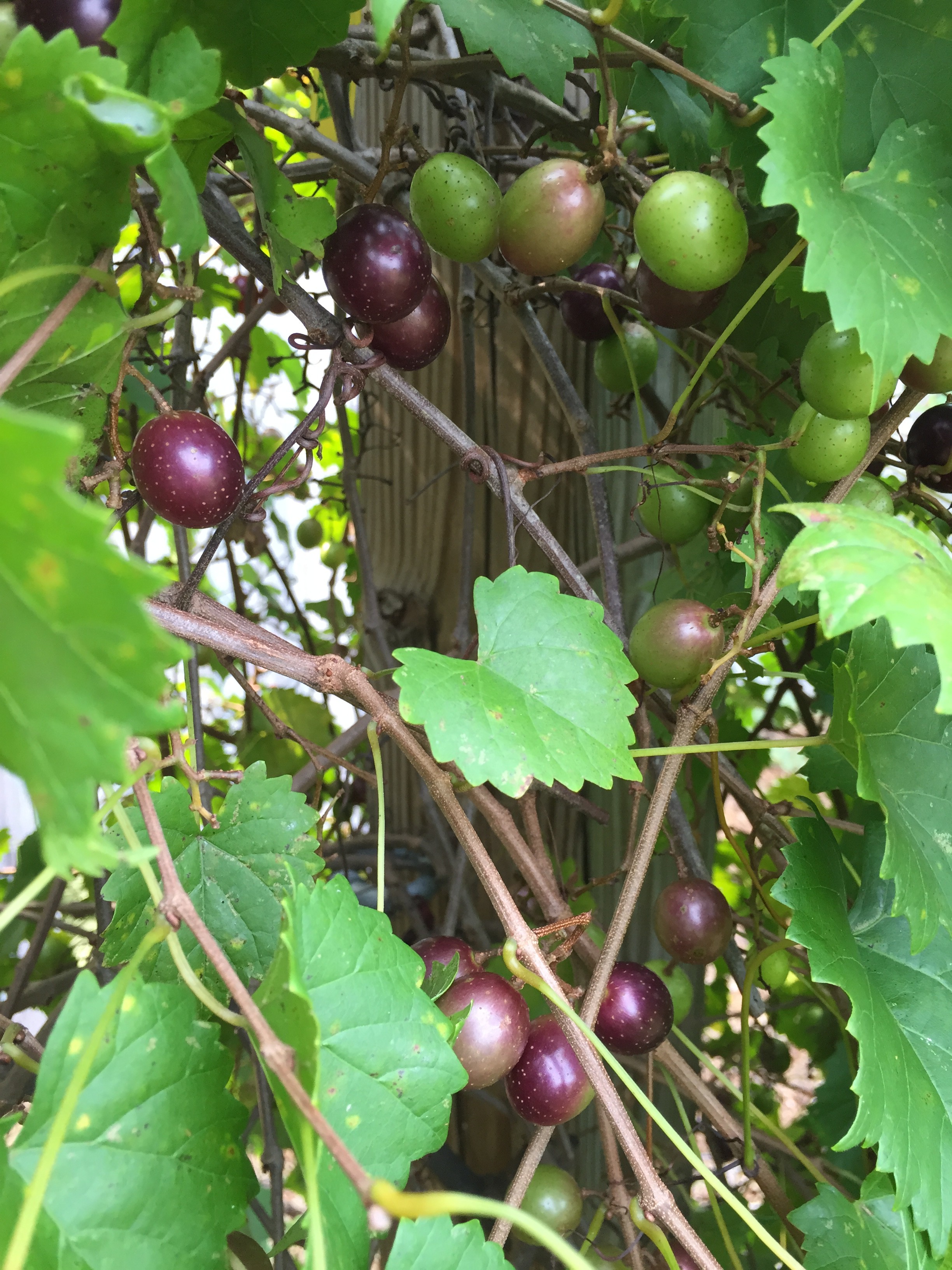
The muscadine grape is a popular fruit that grows very well here in North Florida. It has smaller leaves than bunch grapes and fruit are harvested singly, rather than in bunches. Theses grapes can be enjoyed fresh and also be used for home wine-making. One of the nice things about growing muscadine grapes in Florida is that they’re rarely bothered by insects or diseases. They can easily be grown in your backyard garden.

Muscadine grapes are ripening now! Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
Grapes will grow well in a variety of soils here in North Florida. Upland soils with clay underlying at about three feet are ideal. You should avoid poorly drained soils. If the grapes are grown on soil with very good drainage, they should be set in the ground deeper than they were grown in the nursery on land with a high water table. Grapes should be planted on raised beds at the same depth they were at in the nursery.
During the first year, grapes should be fertilized with a quarter pound of 8-8-8 or 10-10-10 fertilizer, applied in bands about a foot away from the plant, soon after growth begins. Repeat applications in April, July and September. Fertilizer rates increase each year, but they should never exceed six pounds per vine per year.
Weeds can sometimes be a problem with muscadine grapes. To get rid of weeds, you can use a good herbicide, or you can cultivate around the plants. The muscadine grape has a very shallow root system, however, so be careful when you’re weeding around the plants. Mulches can be helpful in controlling weeds, but be sure to leave a circle of at least six inches around each vine uncovered.
Grapes need a generous supply of water to survive here in North Florida. In fact, more first-year grapes die from a lack of water than from any other cause. Make sure the plant receives about an inch of water weekly. Muscadine grapes are rarely bothered by insects or diseases. However, a spray program is advised to protect plants from possible damage by black rot or bitter rot. Spraying should begin when the vines are in bloom, and continue a regular two week intervals until about a week before the harvest. For specific information on the proper spray to use, you should contact your local County Agent.
Muscadine grapes mature in August and early September. If you don’t plan to use them immediately, they should be picked from the vine when ripe and stored at 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
For more information, please see:
The Muscadine Grape
Muscadines Benefit from Timely and Artful Pruning

by Larry Williams | Aug 3, 2015

Damage caused by azalea lace bug. Photo credit: James Castner, UF/IFAS
When azaleas are in a garden, azalea lace bugs are sure to follow. The good news is these insects, that discolor the leaves of azaleas, can be controlled.
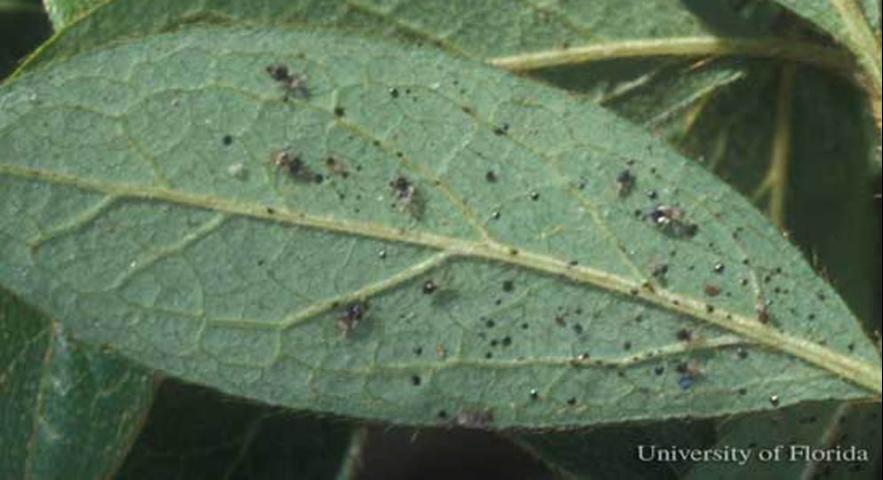
Lace bugs live on the underside of leaves and damage their hosts by piercing leaves with their straw-like mouthparts and removing the plant’s juices. Infested leaves have tiny yellow spots on the top surface and are discolored with dark, varnish-like excrement and old insect parts on the underside. Azalea plants begin to look unhealthy as insect numbers increase through spring and summer.
Azalea lace bugs spend winter as eggs on the underside of azalea leaves. They hatch in early to mid-March and then begin to feed and develop into adults.
Lace bugs complete their first generation by late April. They increase in number throughout the remainder of spring, summer and fall. These insects can complete three to five generations in a single growing season. In late September adult lace bugs, in their final generation of the season, lay eggs that will carry the population through winter.
The key to easily controlling azalea lace bugs is to properly time control efforts.
Inspect plants in early spring to see if insects are present. Look for leaves that are whitish to yellow on the top surface (they may be mottled in appearance) and have small, dark, varnish-like spots on the undersides. If leave damage is heavy continue to check plants every week for small lace bugs, which should begin to be visible in late March through April.
Early to mid spring is the best time to control the first generation of the bugs. Proper insecticide application timing will reduce need for further sprays during the rest of the growing season.
Insecticidal soap, horticultural oil, neem oil and most synthetic insecticides provide good control of lace bugs on azaleas. When using these types of chemicals, make sure to spray the backs of the leaves.

Azalea leaf with lace bugs. Photo Credit: James Castner, UF/IFAS
Systemic insecticides available for use against lace bugs include dinotefuran (Safari), imidacloprid (Bayer Advanced Tree & Shrub Insect Control, Merit) and acephate (Lilly Miller Ready-to-Use Systemic, Orthene). When properly applied, one application may provide season long control.
When using any chemical treatment on plants, it’s best to apply the product during early morning or late evening under cooler temperatures but never during the heat of the day or when the plant is in full sun. And always follow instructions on the pesticide label concerning mixing, application and safety precautions.

 University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
 As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:
As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:







