
by Mary Salinas | Aug 20, 2021
On August 12, 2021, our panel answered questions on a wide variety of landscape topics. Maybe you are asking the same questions, so read on!
Ideas on choosing plants
What are some perennials that can be planted this late in the summer but will still bloom through the cooler months into fall?
Duranta erecta ‘Sapphire Showers’ or ‘Gold Mound’, firespike, Senna bicapsularis, shrimp plant, lion’s ear
Where can native plants be obtained?

Dune sunflower, Helianthus debilis. Photo credit: Mary Salinas UF/IFAS Extension.
Gardening Solutions: Florida Native Plants – see link to FANN: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/native-plants.html
What are some evergreen groundcover options for our area?
Mondo grass, Japanese plum yew, shore juniper, ajuga, ferns such as autumn fern.
What are some ideas for partial morning sun butterfly attracting tall flowers to plant now?
Milkweed, salt and pepper plant, swamp sunflower, dune sunflower, ironweed, porterweed, and salt bush.
I’m interested in moving away from a monoculture lawn. What are some suggestions for alternatives?
Perennial peanut, powderpuff mimosa, and frogfruit.
We are new to Florida and have questions about everything in our landscape.
Florida-Friendly-Landscaping TM Program and FFL Web Apps: https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/
https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/resources/apps/
UF IFAS Gardening Solutions: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/
What are some of the top trends in landscaping today?
Houseplants, edible gardens, native plants, food forests, attracting wildlife, container gardening, and zoysiagrass lawns
Edibles

Artwork broccoli is a variety that produces small heads. Photo credit: Mary Salinas UF/IFAS Extension.
What vegetables are suitable for fall/winter gardening?
Cool Season Vegetables: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/edibles/vegetables/cool-season-vegetables.html
North Florida Gardening Calendar: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP451%20%20%20
Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/vh021
How can I add herbs to my landscape?
Herbs in the Florida Garden: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/edibles/vegetables/herbs.html
My figs are green and hard. When do they ripen?
Why Won’t My Figs Ripen: https://www.lsuagcenter.com/profiles/rbogren/articles/page1597952870939
What is best soil for raised bed vegetable gardens?
Gardening in Raised Beds: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP472
And there are always questions about weeds
How can I eradicate cogongrass?

Chamber bitter is a troublesome warm season weed in our region. Photo credit: Brantlee Spakes Richter, University of Florida, Bugwood.org
Cogongrass: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/WG202
Is it okay to use cardboard for weed control?
The Cardboard Controversy: https://gardenprofessors.com/the-cardboard-controversy/
What is the best way to control weeds in grass and landscape beds?
Weed Management Guide for Florida Lawns: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP141
Improving Weed Control in Landscape Planting Beds: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/EP/EP52300.pdf
Landscape practices
Can ground water be brackish and stunt plants?
Reclaimed Water Use in the Landscape: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ss545
How can I prevent erosion from rainwater runoff?
Stormwater Runoff Control – NRCS: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/national/water/?cid=nrcs144p2_027171
Rain Gardens: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/design/types-of-gardens/rain-gardens.html
And https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/articles/rain-garden-manual-hillsborough.pdf
What is the best time of the year to propagate flowering trees in zone 8B?
Landscape Plant Propagation Information Page – UF/IFAS Env. Hort: https://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/database/lppi/
Which type of mulch works best on slopes greater than 3 percent?
Landscape Mulches: How Quickly do they Settle?: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/FR052
When should bulbs be fertilized?
Bulbs and More – UI Extension: https://web.extension.illinois.edu/bulbs/planting.cfm
Should I cut the spent blooms of agapanthus?
Agapanthus, extending the bloom time: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/agapanthus.html
http://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/wakullaco/2020/10/07/extending-bloom-time/
Plant questions

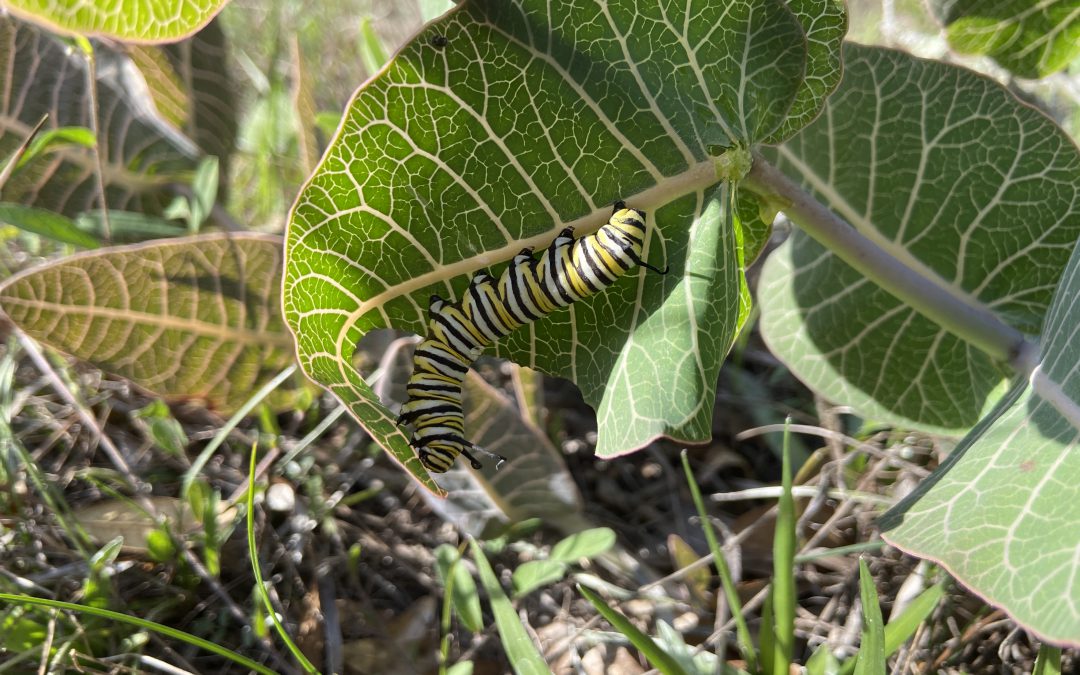
Monarch caterpillar munching on our native sandhill milkweed, Asclepias humistrata. Photo credit: Mary Salinas, UF IFAS Extension.
I planted native milkweed and have many monarch caterpillars. Should I protect them or leave them in nature?
It’s best to leave them in place. Featured Creatures: Monarch Butterfly: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/IN/IN780/IN780-Dxyup8sjiv.pdf
How does Vinca (periwinkle) do in direct sun? Will it make it through one of our panhandle summers? Can I plant in late August?
Periwinkles and No more fail with Cora series: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/periwinkles.html#:~:text=Plant%20your%20periwinkles%20where%20they,rot%20if%20irrigated%20too%20frequently.
Insect and disease pests
What to do if you get termites in your raised bed?
The Facts About Termites and Mulch: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN651
How to combat fungus?
Guidelines for ID and Management of Plant Disease Problems: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/mg442
Are there preventative measures to prevent diseases when the humidity is very high and it is hot?
Fungi in Your Landscape by Maxine Hunter: http://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/marionco/2020/01/16/fungi-in-your-landscape/
If you missed an episode, check out our playlist on YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bp0HfdEkIQw&list=PLhgoAzWbtRXImdFE8Jdt0jsAOd-XldNCd

by Daniel J. Leonard | Apr 22, 2021
With the traditional planting date of Good Friday behind us, the home tomato gardening season in the Panhandle is in full swing. While tomatoes are the most persnickety veggie we grow, there are several practices you can adopt to help you succeed: selecting an adapted variety; regularly scouting for insects and disease; and watering and fertilizing appropriately. However, the most overlooked practice for success gardeners can adopt is proper pruning.

‘Big Beef’ Tomato with lower leaves removed. This is an excellent disease reduction practice. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Correct pruning does a couple of positive things for tomatoes. First, it reduces the incidence of disease by preventing leaf contact with the soil, opening the interior of the plant, and allowing better airflow. This is important as many plant pathogens reside in the soil and only need a splash of water to travel onto plant leaves. Also, densely foliaged plants trap warm, moist air in their canopies, creating a perfect environment for disease to flourish. Letting the plant canopy “breathe” through pruning prevents that negative environment from forming! Second, correct pruning of “suckers” (extra growth points that can develop into shoots) helps tomato plants develop optimum yield and fruit quality. By removing suckers, more water, nutrients, airflow, and light are directed to the main stems, where the majority of tomato fruit production occurs. Failing to remove suckers (especially on indeterminate varieties) can result in reduced yields, increased disease, and generally messy plants!
With the reasons for pruning tomatoes established, the next step is learning exactly what to prune and how to do it in a sanitary matter.
- Get rid of any foliage that could encounter the soil, generally all leaves occurring on the lower 12-16″ of the plant. All kinds of nasty tomato destroying diseases, like Early Blight and Bacterial Leaf Spot, reside in the soil and are just waiting to be splashed onto your plants – don’t let that happen.
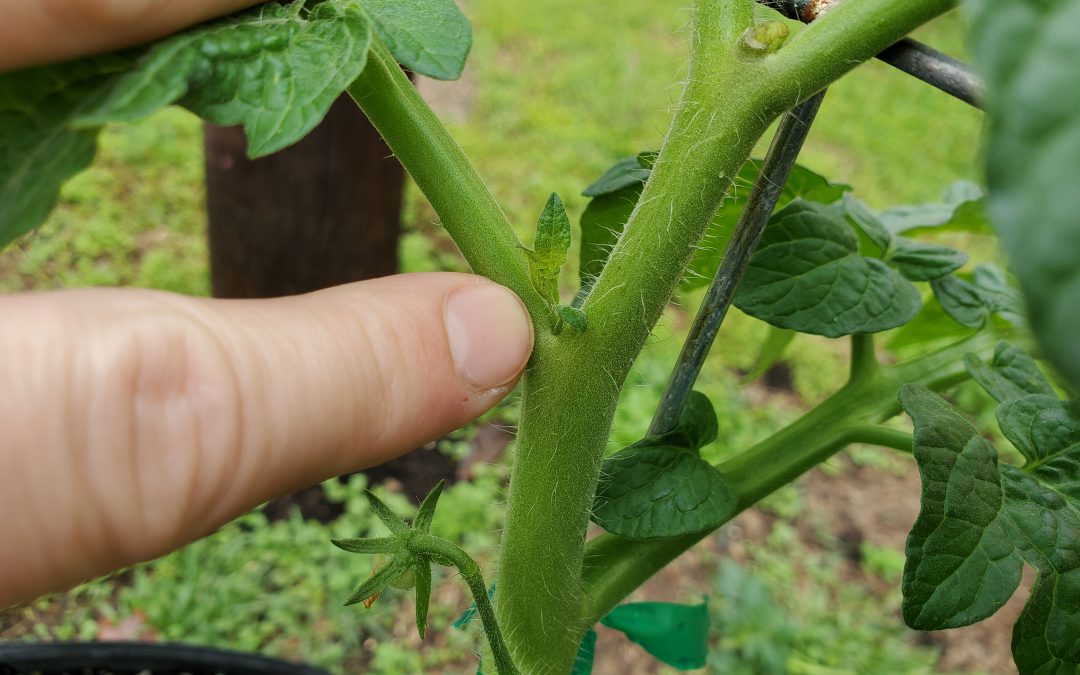
- Determine how many primary shoots you want your plant to have. Leave enough lower suckers to achieve that number (generally just one, two, or three as more than 3 primary stems gets hard to manage), and prune or pinch out all the rest. To prevent stress from pruning, be diligent in removing suckers when they are still small, 2” or less.
- Always clean and disinfect your pruners before making a cut on a tomato plant. This is best accomplished by rinsing the blades with warm soapy water, drying, and following with by a quick alcohol spray. A 10% bleach solution will also work, but if not thoroughly rinsed after, bleach can corrode pruner blades and other working parts. If you make cuts on a plant that appears diseased, repeat the sanitizing process before you begin pruning another plant as “dirty” pruners are an easy way to spread pathogens in the garden.

Developing vegetative “sucker” that will need to be removed. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
While tomatoes are indeed a difficult vegetable to grow, learning to prune them correctly will greatly help to make this a successful season. If you just keep leaves off the ground, suckers pinched, and pruners cleaned, you’ll be well on your way to less disease, prettier plants, and more tomatoes to pick. For more information on growing tomatoes and any other horticultural topic, please contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension office. Happy Gardening!

by Carrie Stevenson | Jun 4, 2020

Fig. 1 An adult redbay ambrosia beetle compared to the size of a single penny. Credit: UF/IFAS File Photo.
While most bark beetles are important in forest ecology by recycling fallen dead trees and eliminating sick and damaged trees, some of them may impact healthy trees. A group of bark beetles that has become a major concern to forest managers, nurseries, and homeowners is the ambrosia beetle. Ambrosia beetles are extremely small, 1-2 mm in length, and live and reproduce inside the wood of various species of trees (Fig. 1). Ambrosia beetles differ from other bark beetles in that they do not feed directly on wood, but on a symbiotic fungus that digests wood tissue for them. Every year, non-native species of ambrosia beetles enter the United States through international cargo and we have now nearly forty non-native species of ambrosia beetles confirmed in the United States. Among them, the redbay ambrosia beetle (Xyleborus glabratus), originally from Southeast Asia, is the vector of the fungal pathogen causing laurel wilt, a disease that devastated the Lauracaea population in the southeastern USA, killing millions of redbay, swamp bay, sassafaras and silk bay.

Fig. 2: A mature dooryard avocado tree with large sections of dead and missing leaves, caused by laurel wilt disease. Summer 2009 Impact Magazine image. Credit: UF/IFAS File Photo.
When these beetles attack a laurel tree, the symbiotic fungus is vectored to the tree’s sapwood after the beetle has tunneled deep into the tree’s xylem, actively colonizing the tree’s vascular system. This colonization leads to an occlusion of the xylem, causing wilting of individual branches and in a matter of weeks progresses throughout the entire canopy, eventually leading to tree death (Fig. 2). The laurel wilt disease has spread rapidly after the vector was first detected in Georgia in 2002. The redbay ambrosia beetle was first detected in Florida in 2004, in Duval County, attacking redbay and swamp bay trees. At this point, it is estimated that more than one-third of redbay in the U.S.A., 300 million trees, have succumbed to the disease.
Starting in 2017, we examined the efficacy of verbenone against redbay ambrosia beetle in live laurel trees in a natural forest setting. Verbenone is an anti-aggregation pheromone that has been used since the 1980’s to protect lodgepole pine. Verbenone also has the potential to be used over large areas and is currently being used to protect ponderosa pine plantations from the Mountain Pine Beetle in the western US.
We have found verbenone to be an environmentally friendly and safe tool to prophylactically protect laurel trees against redbay ambrosia beetle. Our protocol consists of the application of four 17 g dollops of a slow-release wax based repellent (SPLAT Verb®, ISCA technology of Riverside, CA) to the trunk of redbay trees at 1 – 1.5 m above ground level (Fig. 3). The wax needs to be reapplied every 4 months during fall and winter and every 3 months during spring and fall when temperature is higher. When compared to the control trees without repellents, we found that trunk applications of verbenone reduced landing of the redbay ambrosia beetle on live redbay trees and increased survivorship of laurel trees compared to untreated trees (Fig. 4). Verbenone should be considered as part of a holistic management system against redbay ambrosia beetle that also includes removal and chipping of contaminated trees.
If you have Redbay or other bay species on your property and are concerned about Laurel Wilt Disease or Redbay Ambrosia Beetle damage, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Agents for help!
This article is courtesy of Dr. Xavier Martini and Mr. Derek Conover of the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC) in Quincy.

Fig. 3: Application of SPLAT Verb on a redbay tree during a field trial
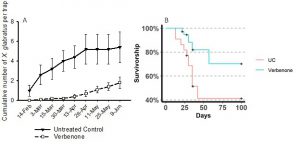
Figure 4: (A): Cumulative capture of redbay ambrosia beetles Xyleborus glabratus following a single application of verbenone vs untreated control (UC). (B) Survivorship of redbay and swamp bay trees treated with verbenone on four different studies conducted in 2017 and 2018.

by Mark Tancig | Apr 30, 2020

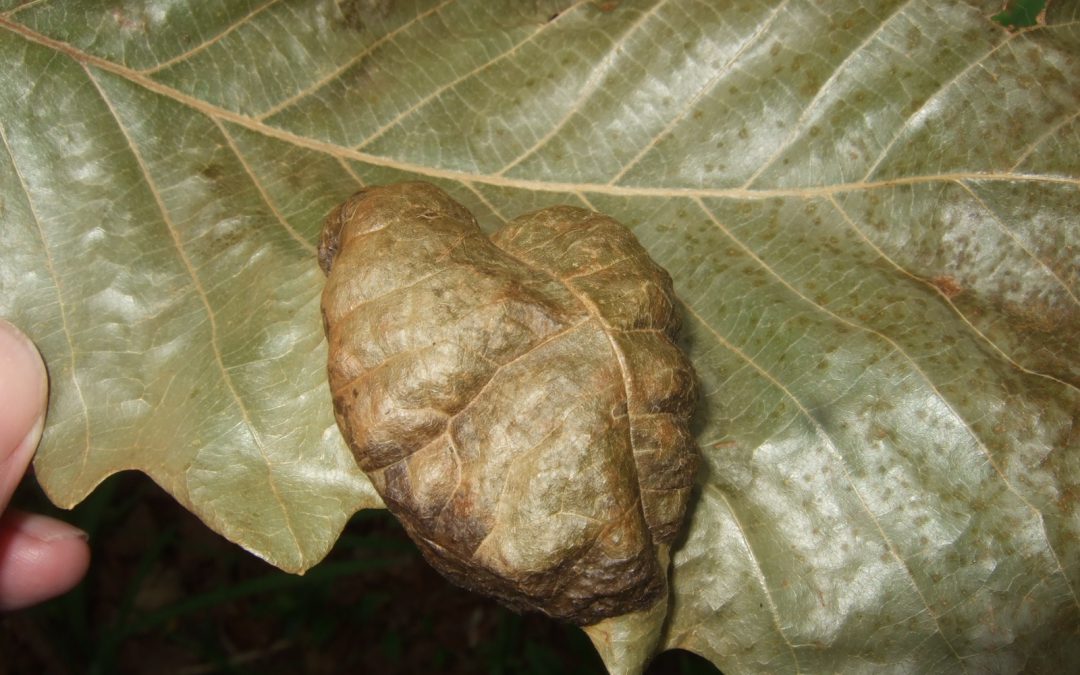
Symptoms of oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
Even during global pandemics, it’s a joy to be outside during the great north Florida spring we’ve been experiencing lately. As cold fronts come through with their rain bands, some packing a punch, they leave behind the most pleasant mornings, clear blue daytime skies, and crisp evenings. Unfortunately, we’re not the only organism that also enjoys those cool days. Many species of fungi are quite active this type of year as the rains, followed by warmer, yet not too hot temperatures, create the perfect conditions for fungal growth. Some of these fungi grow right on or in the plants we’d like to be enjoying for ourselves, stealing nutrients and causing plant decline or merely causing aesthetic damage. As this is an active time for certain species of fungi, local extension offices are getting more calls and questions regarding lawn and landscape damage due to fungal pathogens. A recent call was a new one for me and an example of a native fungi-plant interaction that looks bad but requires no intervention from us. It also highlights how correctly identifying a disease leads to the best action and can often save time and money and prevent unnecessary pesticides (in this case a fungicide) from entering the environment.

Close up of oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
The fungi and plant involved here was the oak leaf blister (Taphrina caerulescens) on a swamp chestnut oak (Quercus michauxii). It forms, you guessed it, blisters on the leaves of any of the oaks, though live oak (Quercus virginiana), laurel oak (Quercus laurifolia), and water oak (Quercus nigra) seem to be preferred hosts. The spores of the fungi, dormant since the previous summer/fall and which happen to get lodged in bud scales through wind and rain, germinate in cool, wet weather. The fungus then infects young leaves as they flush and its growth causes a disruption in the leaves’ development. This leads to the blistered look of the leaf tissue and, during extended periods of cool, wet weather, the entire leaf sort of shrivels, browns, and eventually falls off. Spores are eventually released from the fallen leaves to start the process over the next spring.

Severe oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
Though the leaves look pretty terrible, this fungal disease rarely causes plant health issues and the tree recovers just fine. Specimen trees that experience it year to year may be treated with a fungicide, but most homeowners can just let it go. Raking up and disposing of the leaves may help prevent further infections by reducing the number of spores released in the area.
As you enjoy another cool morning after an evening rainstorm, remember that the fungi all around you are also having a great day. You may want to look at your landscape plants and see if there’s anything abnormal going on. If so, take a photo and send it to your local extension office for help with identification and best methods of control, or, like in this case, just leaving it alone.
p.s. As I said this was a new one for me and I want to thank Stan Rosenthal, Extension Agent emeritus, for assisting with identification.

by Les Harrison | Oct 8, 2019

Mushrooms growing on the roots of trees is a bad sign. This indicates the roots are decaying and the tree will soon become (or already is) unsafe.
On the doorstep of autumn, the weather is making its seasonal change in north Florida. It has been a bit cooler in the mornings, but the afternoons still qualify as hot.
What the winds of October will blow in is still anyone’s guess, but last year it was Hurricane Michael. Unfortunately, the storm’s brunt came in causing severe damage to homes, businesses and marine enterprises in several counties.
October is typically the month when tropical cyclone activity lessens in the Atlantic, but accelerates in the Gulf of Mexico. While beastly events like Hurricane Michael are relatively rare, it only takes one such incident to necessitate recovery efforts and expenses for years, if not decades.
The prudent course of action is to prepare for the worst while hoping for the best. One area of preparation where residents can have a distinctly positive effect is readying their trees for the potential assault.
Damage from falling trees and limbs is a major cause of destruction during tropical storms and hurricanes. Removing potential problems before the storm can minimize harm to structures and injury to residents.
Trees in decline are especially hazardous. Their compromised health makes them subject to uprooting and breakage with far less force than would effect a healthy tree.
There are several key indicators for tree health. Any single factor or a combination can mark a tree as unsafe.
Mushrooms growing on or very close to trees is a sign the tree is dying. The fungus is not the cause of decline, but only an indicator of the eventual fate.
Spores of the mushrooms are scattered by wind and water. Landing randomly, most arrive on a site devoid of necessary resources and never sprout.
Those lucky spores which land on decaying wood will likely sprout and take nourishment from the rotting plant material. Their roots accelerate the decomposition of the wood by consuming the available material and exposing more of the tree to colonization by mushrooms.
Sites on trees and plants infected with mushrooms typically are break points when pressure or stress is applied. If the mushrooms are located at the base of the tree, it is likely to be detached from its roots and topple over in heavy winds.
Another indicator of tree health is its crown, or the uppermost branches and leaves. Healthy trees and plants have full, green, and growing crowns.
When the crown turns brown and the leaves drop off, it is a good indicator the tree’s days are numbered. The causes may be disease, lightning, or mechanical interruption of the root system.
Lastly, bifurcation or trunk forking is a sign of a structurally weak tree. This condition may display itself when the tree emerges from the ground or at an elevated place on the mature tree trunk.
When the wind direction stresses the tree with enough force at its angle of vulnerability, a collapse results. Unfortunately, there is no simple way to tell how much wind is required to produce the failure.
Any tree with these problems should be evaluated by a certified arborist and removed when necessary. It may result in an expense now, but can save on expenses, inconvenience and aggravation if a storm randomly removes the tree in the future.
The question must be asked: Is it worth the gamble to wait on the winds of October?
To learn more about the tree health in north Florida, read the UF/IFAS publication HOW TREES GROW IN AN URBAN ENVIRONMENT.


















