by Laura Tiu | Aug 9, 2019
During a recent fishing trip, as we jigged for bait and got repeated stuck by the tiny hooks, talk turned to the recent reports of a death and infections in the Florida Panhandle from the saltwater-dwelling bacterium, Vibrio vulnificus. Many reports used the term “flesh-eating bacteria” to refer to Vibrio. This description is false and misleading and causes unnecessary fear and panic. Most healthy individuals are not at risk for V. vulnificus infection, however, to ensure that your time on the water is safe and enjoyable, be aware of your risk and take steps to minimize becoming infected.
The name Vibrio refers to a large and diverse group of marine bacteria. Most members are harmless, however, some strains produce harmful toxins and are capable of causing a disease known as “vibriosis.” Because of Florida’s warm climate, Vibrio are present in brackish waters year-round. They are most abundant from April to November when the water is the warmest. For infection to occur, pathogenic Vibrio strains must enter the body of a susceptible individual who either eats raw and contaminated seafood or exposes an open wound for a prolonged period in water containing these bacteria.
Symptoms of vibriosis may arise within 1–3 days, but usually occur a few hours after exposure. Infections typically begin with swelling and redness of skin, followed by severe pain, blistering, and discharge at the site of the wound. If you suspect infection, seek medical treatment immediately.
Anglers can reduce their risk by following a few safety tips. Because fish, including live bait, carry Vibrio on their bodies, avoid or minimize handling whenever possible. The proper use of landing gear and release tools can help to minimize handling. If you cannot avoid handling the fish, use a wet towel or gloves to protect yourself. Be aware of areas that can cause injury like spines, barbs, and teeth.
Always wash your hands thoroughly after fishing, especially before handling food. Be sure to clean your gear after each use, taking special care with sharp objects like hooks and knives.
Adapted from: Abeels, H., G. Barbarite, A. Wright, and P. McCarthy. 2016. Frequently Asked Questions about Vibrio in Florida. SGEF-231. https://eos.ucs.uri.edu/EOS_Linked_Documents/flsgp/SGEF_231_fact-sheet_2016.pdf
“An Equal Opportunity Institution”

A happy angler with a Trigger fish near Destin, Florida (Photo credit: L. Tiu).

by Scott Jackson | Jul 2, 2016

Recent news reports have Panhandle Beaches trending on social media. Beaches are open and ready for the holiday weekend. Here’s information to help make sure you are ready too. Photo by Florida Sea Grant.
The threat of bacteria in coastal waters can be scary and a challenge to understand. Here is information that helps clarify the threat to beach visitors and recreational users of marine waters. This is a good opportunity to think about bacteria exposure risks related to the coastal environment that we can control. It is important to remember the probability of severe illness in a normal healthy individual is very low.
There are two different un-related groups of bacteria species that often are cited in the news. One general group is fecal coliform and the other group are marine specific known as Vibrio.
Fecal coliform including Enterococci bacteria are used by public health managers as indicators of water quality. High levels of these bacteria can indicate an elevated health risk for beach visitors. For some individuals contact in impacted waters can result in gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, stomachache, diarrhea, headache or fever. Other symptoms might include rashes, sore throat, ear ache, and other cold-like or upper respiratory symptoms.
When “no-swimming” advisories are posted you can avoid these concerns by following warning and guidance information. Many times advisories are for specific locations due to storm run-off and water circulation patterns. If an area has a warning or is closed, usually there are better choices for swimming activities nearby. The Florida Department of Health has an established testing of many of Florida’s coastal swimming areas. The latest guidance information can be found at http://www.floridahealth.gov/environmental-health/beach-water-quality
On the other hand, Vibrio exposure that results in illness is potentially more severe. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention now estimate 80,000 Vibrio illnesses and 100 deaths occur annually in the United States. In perspective, The Clean Beaches Coalition estimates 180 million Americans annually make 2 billion visits to ocean, gulf and inland beaches.
According Georgia Sea Grant’s SafeOysters.org website and research, many Vibrio infections are not reported and usually do not cause serious or life-threatening illness in healthy people, although they may cause gastroenteritis (nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea) or cellulitis (skin infection). For a Vibrio infection to occur there must be an entry point into the body. This usually is either through water entering an open wound or eating raw or undercooked seafood.
Symptoms of infection due to consumption of raw or undercooked seafood often develop in 12 to 48 hours and may include:
-
Fever/chills
-
Nausea/stomach pain/vomiting
-
Diarrhea
Individuals with weakened immune systems, chronic diseases or conditions, or undergoing certain medical treatments (see list below) are more susceptible to Vibrio vulnificus infections and are also more likely to become seriously ill or die from them. The fatality rate may be as high as 61% for Vibrio vulnificus infections in people that have been diagnosed with one or more of the following health conditions:
-
Liver disease (from cirrhosis, hepatitis, or cancer)

No need to feel left out! Fully cooked oyster dishes like Oysters Rockefeller are a coastal classic that’s safe and tastes great! Photo by Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services.
-
Diabetes
-
Alcoholism
-
Kidney disease or failure
-
Cancer (includes lymphoma, leukemia, and Hodgkin’s disease)
-
HIV/AIDS
-
Stomach disorders including surgery, taking acid reflux medication or antacids
-
Hemochromatosis (iron overload disease)
* If you are unsure of your risk, consult your doctor. You can always indulge in great oyster recipes that are fully cooked like Oyster Rockefeller or oyster chowder.
Perhaps one of the most common group of listed individuals are those taking acid reflux or heartburn medications. This would also include antacids and prescription medications for acid reflux and other common digestive conditions. Many of these medications work by reducing acid which can potentially increase pH in the digestive system. This lowers the natural defense barrier to several foodborne bacteria including Vibrio. If you take these medications do not eat raw or under cooked seafood. If you have any question about your risk, consult your doctor.

An oysterman uses his 11 foot long tongs to collect oysters from the bottom of Apalachicola Bay
Photo: Sea Grant
As mentioned earlier, Vibrio can also enter the body through open wounds. Vibrio is sometimes misnamed as “flesh-eating” bacteria. “Flesh-eating” is not a medical term and was likely derived from the fact that tissue death, or necrosis, can occur during advanced, late stages of infection around a wound if it is left untreated, especially in those with weakened immune systems (Oliver 2005). The best advice is to seek medical attention early if you experience any of these symptoms or have suffered cut or puncture injury in coastal waters. (See Vibrio FAQs from UF/IFAS and Florida Sea Grant)
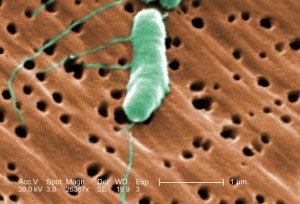
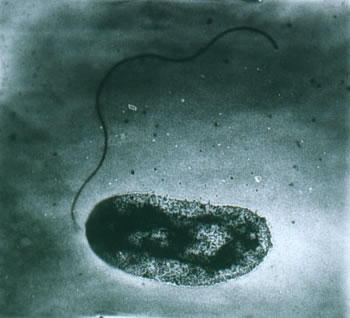
The rod-shaped bacterium known as Vibrio. Courtesy: Florida International University
Wound infection symptoms may develop within 3 to 24 hours and include:
-
Rapid swelling, pain, and reddening of skin around wound (present in 100% of infections)
-
Large blisters, die-off of tissue around wound (30 – 50% of infections)
-
Gangrene (<10%)
If Vibrio vulnificus infections are left untreated in people at risk for serious infection, symptoms may quickly increase in severity and include:
-
Fluid accumulation, especially in legs
-
Blood-filled large blisters, mainly on extremities
-
Septicemia (bacteria enter and spread through blood stream)
-
Shock (rapid drop in blood pressure)
-
Death
For additional information and details please visit SafeOysters.org
Here are some final thoughts and advice:
-
Remember the majority of healthy individuals will not have any problems.
-
If you are recovering from illness know your limits and use the above resources to make informed decisions to protect your health.
-
Plan your beach vacation for safety but then confidently relax and enjoy the experience.
-
For additional beach safety and enjoyment of our natural resources see our other articles on the UF/IFAS Panhandle Outdoors website.

A great blue heron at sunset stalks the shoreline ready for his next meal. Scenes like this await coastal visitors. It’s an experience like nowhere else. Photo by the author.
An Equal Opportunity Institution. UF/IFAS Extension, University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Nick T. Place, dean for UF/IFAS Extension. Single copies of UF/IFAS Extension publications (excluding 4-H and youth publications) are available free to Florida residents from county UF/IFAS Extension offices.

by Rick O'Connor | Jul 10, 2015
After the recent report of a fatality due to the Vibrio bacteria near Tampa many locals have become concerned about their safety when entering the Gulf of Mexico this time of year. So what are the risks and how do you protect yourself?

The rod-shaped bacterium known as Vibrio. Courtesy: Florida International University
What is the Flesh Eating Disease Vibrio?
Vibrio vulnificus is a salt-loving rod-shaped bacteria that is common in brackish waters. As with many bacteria, their numbers increase with increasing temperatures. Though the organism can be found year round they tend peak in July and August and remain elevated until temperature decline.
How do people contract Vibrio?
The most common methods of contact with Vibrio are entrance through open wounds exposed to seawater or marine animals and by consuming raw or undercooked shellfish, primarily oysters. The bacterium can also be contracted by eating food that is either served, and has made contact with, raw or undercooked shellfish or the juice of raw or undercooked shellfish.
What is the risk of serious health problems after contracting Vibrio?
Cases of Vibrio infection are rare and the risk of serious health problems is much higher for humans who are have a suppressed or compromised immune system, liver disease or blood disorders such as iron overload (hemochromatosis). Examples include HIV positive, in the process of cancer treatment, and studies show a particularly high risk for those with a chronic liver disease. The Center for Disease Control indicates that humans who are immunocompromised have an 80 times higher chance of serious health issues from Vibrio than healthy people. He also found that most cases involve males over the age of 40. According to the Center for Disease Control there were about 900 cases reported between 1988 and 2006; averaging around 50 cases each year. The Florida Department of Health reported 32 cases of Vibrio infections within Florida in 2014 with 7 of these begin fatal. Five of the cases were in the Florida panhandle but none were fatal. So far this year in Florida there have been 11 cases statewide, 5 of those fatal. Only 1 case was in the panhandle and it was nonfatal. Though 43 cases and 12 fatalities over the last two years in Florida are reasons for concern, when compared to the number of humans who enter marine and brackish water systems every day across the state, the numbers are quite low.
What are the symptoms of Vibrio infection?
For healthy people who consume Vibrio containing shellfish symptoms could include vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Wounds exposed to seawater that become infected will show redness and swelling. For the at-risk populations described above the bacteria will enter the bloodstream and rapidly cause fever and chills, decreased blood pressure, and blistering skin lesions. For these at-risk population 50% of the cases are fatal and death generally occurs within 48 hours.
It is important that anyone who believes they are at high risk and have the above symptoms that they seek medical attention as quickly as possible.
How can I protect myself from Vibrio infection?
We recommend anyone who has a chronic liver condition, hemochromatosis, or any other immune suppressing medical condition, not consume raw or undercooked filter-feeding shellfish and not enter the water if they have an open wound.
The Center of Disease Control recommends
- If harvesting or purchasing uncooked shellfish do not consume any whose shells are already open
- Keep all shellfish on ice and drain melted ice
- If steaming, do so until the shell opens and then for 9 more minutes
- If frying, do so for 10 minutes at 375°F
- Avoid foods served, and has had contact with, raw or poorly cooked shellfish or that has had contact with raw shellfish juice
- If shucking oysters at a fish house or restaurant, wear protective gloves
It is also important to know that the bacteria does NOT change the appearance or odor of the shellfish product, so you cannot tell by looking at them whether they are good or bad.
For more information on this bacteria visit:
http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/vibrio-infections/vibrio-vulnificus/
http://www.cdc.gov/vibrio/vibriov.html








