
by Carrie Stevenson | Mar 24, 2022
The local Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, and Snow network is seeking interested citizen scientists to participate in the collecting weather data. See the notice below from local coordinator, Larry McDonald, for more information:

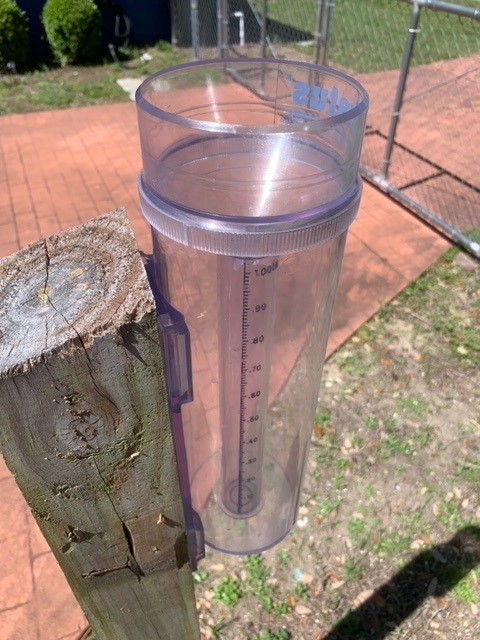
Citizen scientists interested in collecting rain data utilized by organizations all over the country use this type of rain gauge. Photo credit: Larry McDonald, CoCoRAHS
Weather forecasting depends on taking readings and measurements from the atmosphere. And it’s not just professionals, like meteorologists, who measure rainfall, temperatures, and humidity levels. You can, too! The Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, and Snow network (CoCoRaHS) allows everyday citizens to participate in weather data collection by measuring daily precipitation/rainfall totals at their own homes or workplaces. Using a special rain gauge that provides great detail in detecting rain amounts, CoCoRaHS observers submit rain observations online to a national network… along with over 20,000 participants in the U.S., Canada, and the Bahamas. Precipitation amounts are then evaluated for many needs by national, regional, and local weather forecasters, researchers, drought and flood monitoring, and agricultural interests. Rainfall data submitted can also be used in forecasting to predict the possibility of flash flooding for local flood prone areas.
A CoCoRaHS observer simply needs to purchase the approved rain gauge (costing from $30 to $40), mount the gauge in an open area away from roofs, fences, and vegetation, and simply collect rain that falls directly from the sky over a 24-hour period. Once each day, between 5:30 AM and 9:00 AM, the gauge is checked for rain with the amount recorded and submitted to the CoCoRaHS website. Missing a day or more is okay, but the more you report, the better the overall data becomes for your area. New and active CoCoRaHS observers are needed throughout Escambia and Santa Rosa Counties.
Those interested in possibly joining CoCoRaHS as an observer can obtain more information by visiting https://cocorahs.org/. You can also contact the CoCoRaHS local volunteer coordinator for Escambia and Santa Rosa Counties by emailing escambia_fl_cocorahs@icloud.com

by Judy Biss | Feb 2, 2014

Even though adapted to weather extremes, these migratory American goldfinches (Spinus tristis) appreciated the food and cover provided in this backyard. Photo by Judy Ludlow
North Florida experienced a weather delight (or distress depending on your point of view!) this week in the form of freezing rain and snow! The words “Florida” and “snow” are two words most people would not place together in the same sentence, but you may be surprised to learn that snow has been documented a number of times in Florida as revealed by records as early as 1891. In Tallahassee, measurable snow has not fallen since 1989.
The following information is taken from the National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Tallahassee, FL about the history of Snowfall in Tallahassee: Several winters ago, NWS Tallahassee Climate Focal Point, Tim Barry, responded to an inquiry from a reporter concerning snow climatology in Tallahassee. Some of those questions and answers are listed below.
In ten-year intervals, how many times has it snowed in Tallahassee Florida?
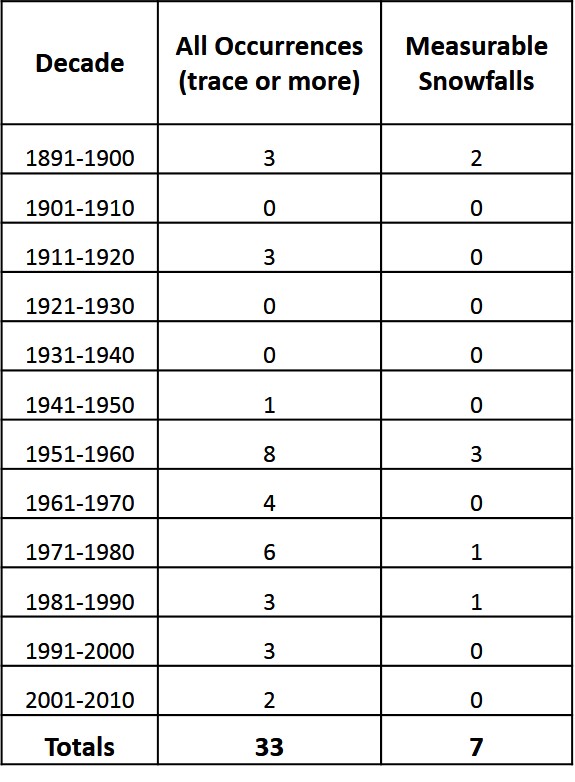 How frequently does Tallahassee see snowfall?
How frequently does Tallahassee see snowfall?
From the information provided in the 1st question, we see that it snowed 32 times in Tallahassee since 1891. Please note that all but 7 of these occurrences were only Trace amounts. If we were to divide the period of record (117 years) by 32 we would get a frequency of once every 3.66 years. But as you can see from above, the more frequent occurrences of snow in the 50’s ,60’s and 70’s have skewed the results. The return period for measurable snow is just once every 17 years. The most snow recorded in a 24-hour period was 2.8″ from February 12th – 13th, 1958.
Any interesting or exciting facts about Tallahassee winters?
There is a significant difference between the climate of north Florida and the southern portions of the peninsula. On average, we experience 35 days with minimum temperatures at or below freezing with most of these occurring from December through March. The coldest temperature ever recorded in Tallahassee was -2 F on February 13th 1899. More recently, we dipped down to 6 degrees F on January 21st, 1985.
Florida’s wildlife, although adapted to Florida’s weather, will thrive given the added boost of backyard habitats planned for their benefit, especially during these winter weather extremes! During the winter, Florida’s native, resident, wildlife species are also joined by species which are here temporarily as they migrate through our state. The hundreds of American goldfinches (Spinus tristis) outside my window are one example.
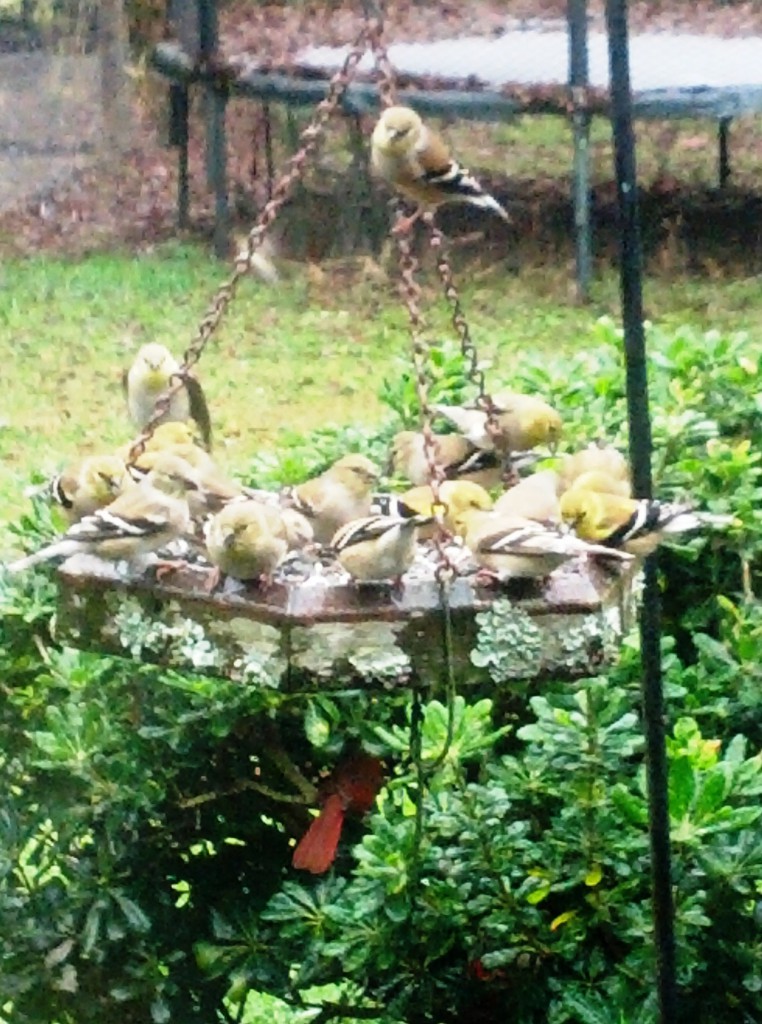

Do you see the red cardinal in the shrub? A variety of cover strategically placed near food sources helps minimize predation and provides protection from weather extremes. Photo by Judy Ludlow
When growing your backyard habitat, think about recreating features which are naturally provided in undisturbed habitats, but only on a smaller scale. To flourish, wildlife need adequate nutritious foods, functional cover, and clean water. Locating food close to cover minimizes the exposure of foraging wildlife to severe weather conditions and to predation; these two factors account for a large percentage of mortality. Cover comes in the form of trees, shrubs, brush piles, etc. of varying heights and sizes.
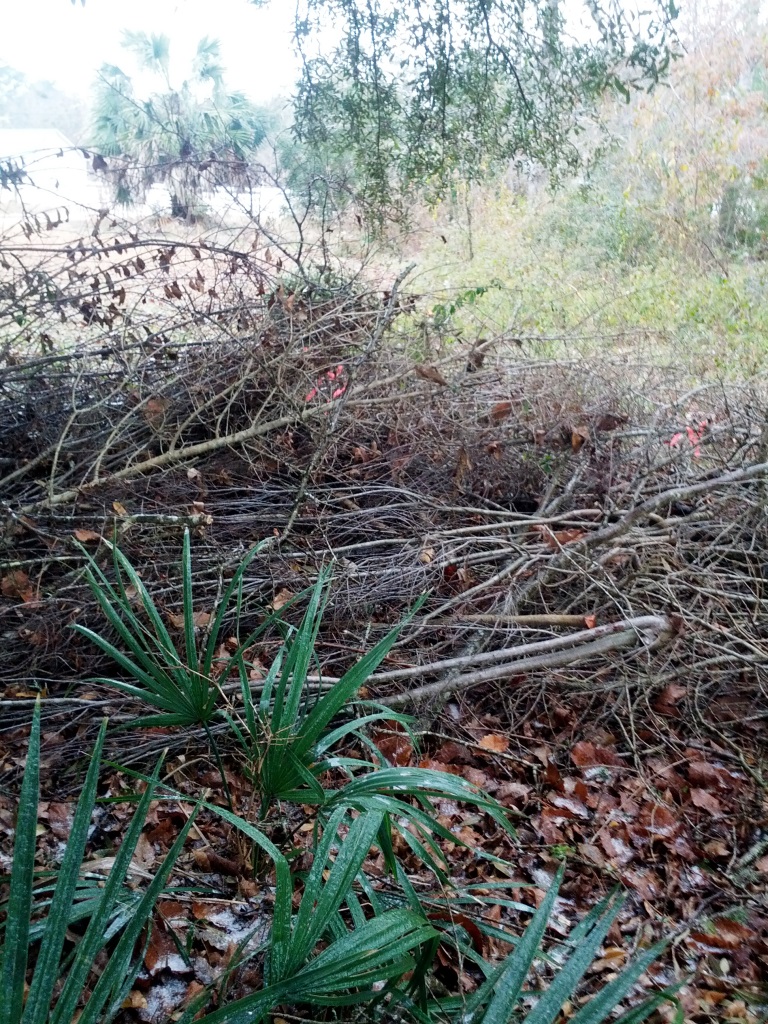

Brush piles such as this one provide valuable wildlife habitat for many species. Photo by Judy Ludlow
The following information is from the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s publication: Planting a Refuge for Wildlife.
Cover: Breeding, nesting, hiding, sleeping, feeding and traveling are just a few of the necessary functions in an animal’s life which require protective cover or shelter. Often plants used for cover double as food sources. Strategic placement of cover is very important in that it reduces exposure to weather extremes and provides escape from predators.
Food: All animals get their energy for survival from plants or other animals. The ideal wildlife management plan uses natural vegetation to supply year-round food – from the earliest summer berries to fruits that persist through winter and spring (such as sweetgum, juniper and holly). You will attract the widest variety of wildlife to your land by using native plants to simulate small areas of nearby habitat types. The “edges” where these habitat types meet will probably be the most visited areas in your neighborhood.
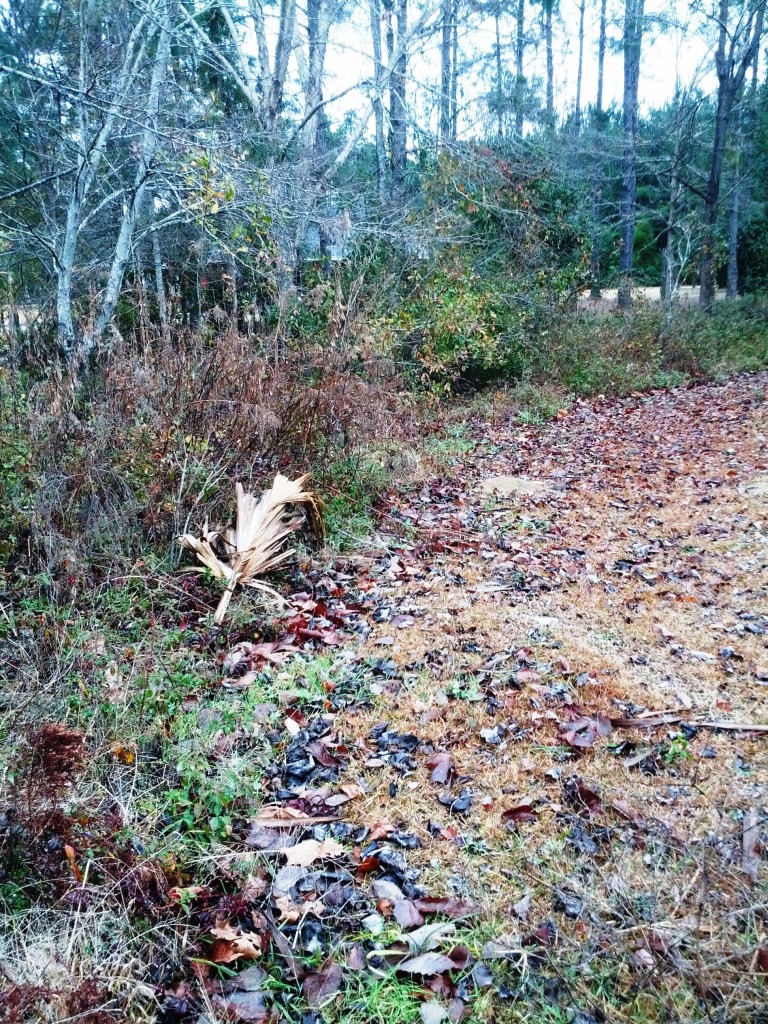

The boundary between two habitats such as between this lawn and small wooded area, creates an “edge effect” which is important to wildlife. Photo by Judy Ludlow
If you are interested in learning more about this topic, please read the following publications and, as always, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Agent if you have any questions.
Planting a Refuge for Wildlife
Landscaping for Wildlife
A Drop to Drink
Eight Ways to Double the Bird Species at Your Feeders
Landscaping for a Song
Making Your Backyard a Way Station for Migrants
On Your Own Turf
Plant Berry Producing Shrubs & Trees
Plant Wax Myrtles
There’s Life in Dead Trees







