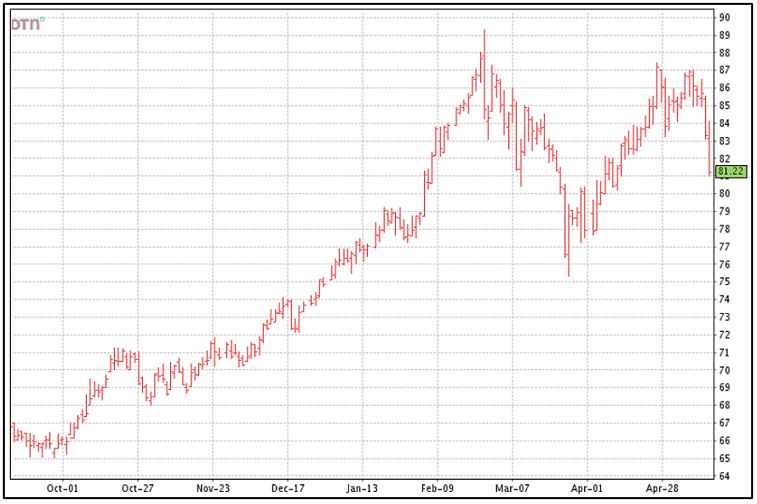
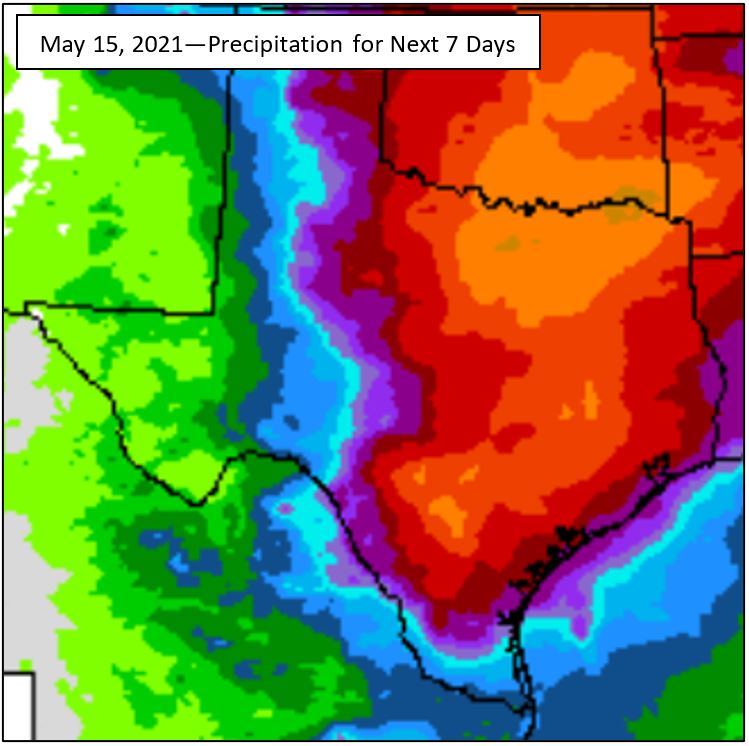
New crop December futures had a miserable week. Texas got rain and that’s good, but the market took a toll on the grower because of it.
December futures lost 567 points for the week—closing at 81.22 cents—the lowest in a month. This wipes out about half of the nice rally since the low in the 77 cent area back in late March.
The market was down 4 of 5 trading days this week with big blows of down 237 points yesterday and another 208 points today.
=
Let’s look briefly at 3 contributors to price action this week:
–
Weather
Texas got rain this week and is expected to get additional rain next week. Some areas of the High Plains and Rolling Plains regions received ¼ to ½ inch or more. All of Texas is expected to continue to get rain over the next 7 days with some areas of the High Plains and Rolling Plains expected to get up to an inch or more.
USDA May Numbers
USDA’s crop production and supply/demand report released on Wednesday contained revisions for the 2020 crop, and the first projections looking ahead at the 2021 crop. The numbers were mixed but mostly bullish. December closed up slightly on Wednesday before it all came crashing down yesterday and today.
The 2020 US crop was raised slightly. Harvested acres was decreased 420,000 acres, but the average yield was raised 36 lbs/acre. As expected it would be now or sometime, exports were increased ½ million bales from 15.75 to 16.25 million. US remaining stocks heading into the 2021 crop year on August 1 were dropped 600,000 bales.
World Use for the 2020 crop year was revised down 440,000 bales. China’s production was raised ½ million bales, and their imports increased ¼ million bales. Imports for Bangladesh and Vietnam were also raised.
Looking ahead to the 2021 crop year, World production is expected to increase, Use increase by 3½%, and stocks decline by a little over 2 million bales. China’s production is forecast to decline 2 million bales, imports declined by 1 ½ million, and Use up slightly.
The 2021 US crop is forecast at 17 million bales—up 16% from last year. Exports are forecast at 14.7 million bales—down 1.55 million bales. US ending stocks are expected to shrink another 200,000 bales.
This is not a particularly encouraging combination for 2021. World Use is expected to continue to rebound, the US crop is expected to increase, but US exports are expected to decline. This could, however, simply be a forecast based partially off the smaller available US supply (larger 2021 crop, but much smaller carry-in compared to 2020) and expected very tight US ending stocks.
–
Weekly Exports
This week’s export report released yesterday (for the previous week ending May 6) showed lower sales and shipments. Net sales were 59,900 bales. Sales have been slow in recent weeks, but this amount is down 35% from the average for the prior 3 weeks. Shipments have been good in recent weeks, but in this week’s report, shipments were 305,400 bales—down 38% from the previous week. Largest destinations were Vietnam, China, and Pakistan.
USDA increasing the 2020 crop year export projection is a positive for the market, but this will continue to be validated by the pace of weekly exports and the market will react accordingly. Exports to date (reported as of May 6) are 12.525 million bales. With a little over 12 reporting weeks remaining, shipments need to average roughly 310,400 bales per week to reach the USDA estimate of 16.25 million bales.
The first estimate of 2021 actual acres planted will be out on June 30. This is a highly unknown and much anticipated number. Weather and crop conditions will continue to be factors. Rainfall in Texas this week and next doesn’t mean much longer term. The first survey-based USDA crop estimates will not be released until August.
While this week’s price action is concerning, both remaining 2020 and 2021 crop outlook are highly uncertain. We certainly want prices to remain in the 80’s. To accomplish that, we first and foremost need continued rebound in demand. Period. Beyond that, strong demand needs to be supported by tight supply.
–