Large patch Rhizoctonia solani (known as brown patch in cool season grasses) is a common disease of many turfgrass species. It usually occurs during the cooler months from October through May when temperatures are below 80 degrees Fahrenheit. However, signs and symptoms of large patch and other Rhizoctonia diseases can be observed throughout the summer. Less common Rhizoctonia species that occur during the summer months are Rhizoctoni zeae and Rhizoctonia oryzae. Extended periods of turf wetness from excessive rainfall or overwatering provide ideal conditions for the disease to develop and spread.
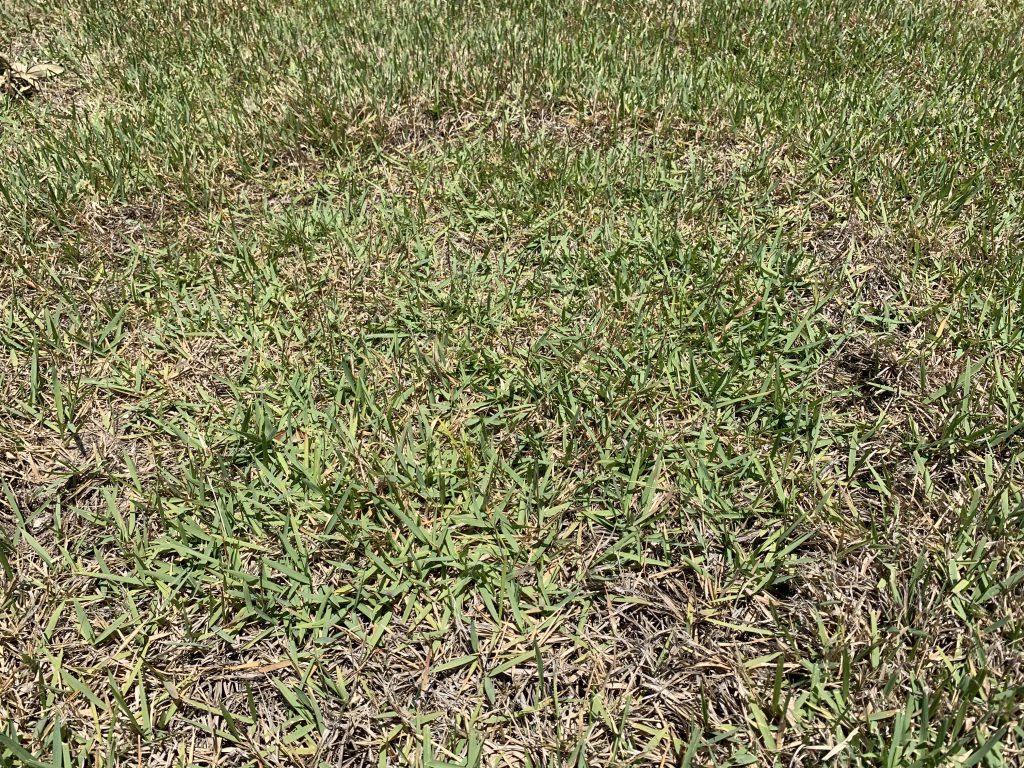

Rhizoctonia in a zoysiagrass lawn. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
This summer in Santa Rosa County, Rhizoctonia has been positively diagnosed in both St. Augustinegrass and zoysiagrass lawns and suspected in a number of centipedegrass lawns. The disease usually starts as small, yellow patches (about a foot in diameter) that turn reddish brown, brown, or straw colored as the leaves start to die. Patches often expand to several feet in diameter. It is common to see rings of yellow or brown turf with otherwise healthy turf in the center. The fungus infects portions of the blades closest to the soil, eventually killing the entire leaf. Grass blades can easily be pulled off their stems, but roots are not affected by the disease.
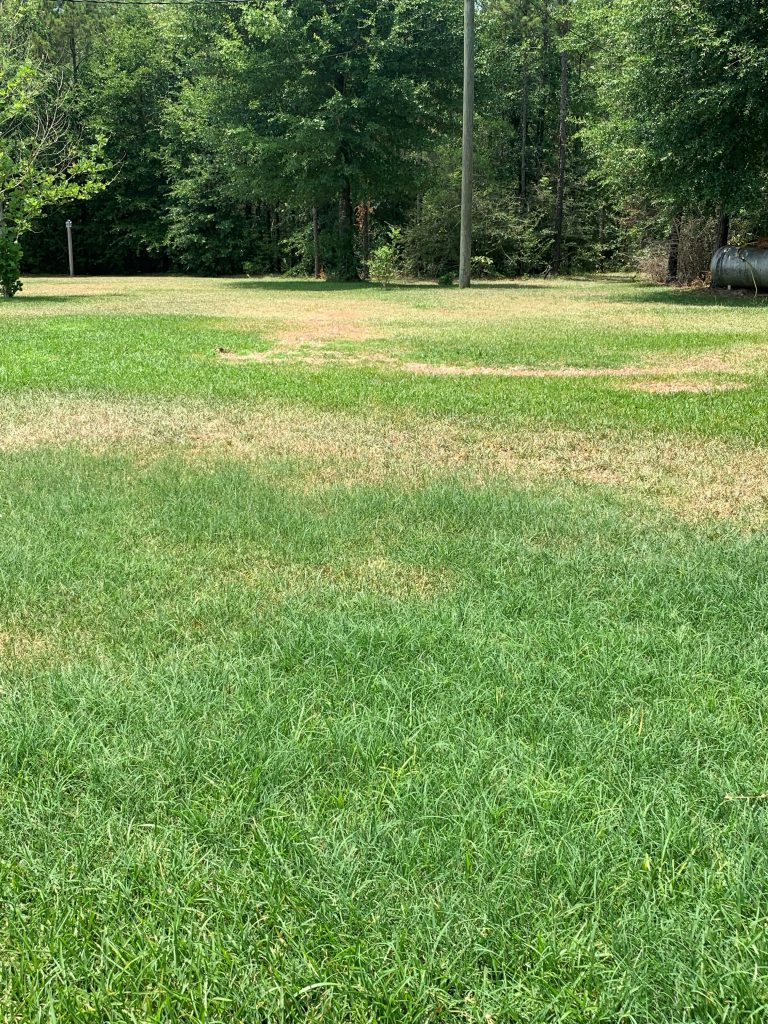

Rhizoctonia in a St. Augustinegrass lawn. Photo Credit: John Atkins, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
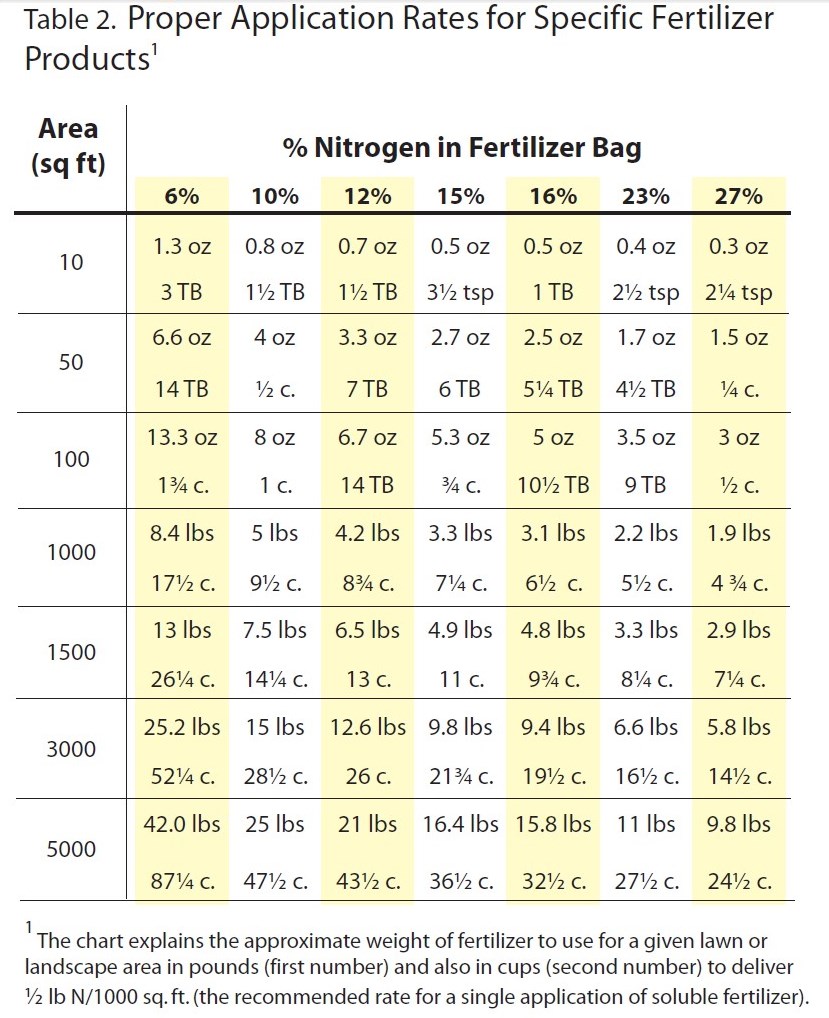
Overwatering and excessive fertilization can both contribute to the development of Rhizoctonia disease. Improper timing of fertilizer application can also promote disease development. In the Florida Panhandle, turfgrass is actively growing from April to October. Slow-release fertilizers are recommended to allow for a more even distribution of nutrients over the course of multiple months. Recommended fertilizer rates are based on turfgrass species, geographical location, and fertilizer analysis. Please refer to the UF/IFAS Publication: “Urban Turf Fertilizer Rule for Home Lawn Fertilization” for rate recommendations.
If large patch or another Rhizoctonia disease is confirmed in your lawn, then chemical controls are necessary to keep the disease from spreading. Fungicide products containing the active ingredients azoxystrobin, chlorothalonil, fludioxonil, flutolanil, iprodione, mancozeb, metconazole, myclobutanil, polyoxin D, propiconazole, thiophanate-methyl, thiram, triadimefon, trifloxystrobin, or triticonazole are viable options for keeping the disease from spreading. For best results, follow the fungicide label for application instructions. It’s important to not only treat the affected areas, but also the healthy turf surrounding these areas in order to keep the diseased spots from growing in size.
Unfortunately, turf diseases are often not noticed until large patches of declining and dead turf are noticed. In these cases when large dead patches exist in the lawn, it is usually necessary to resod these areas. As with most problems that arise in the landscape, good cultural practices are the most proactive way to mitigate the chances with turfgrass diseases. The UF/IFAS Florida Friendly Website provides up-to-date solutions and recommendations for caring for Florida landscapes.
- Crabgrass and Summer Annual Weed Control - February 15, 2024
- Twig Pruners and Girdlers - December 7, 2023
- Screen Trees for Privacy and Noise Reduction - October 13, 2023