
by Suzanne Holloway | Apr 28, 2025
Dietary protein is an important macronutrient for human health, and it can be found in a wide variety of foods. To learn more about the basics of protein, check out this earlier article.
Types of Protein Sources
Before we explore the different types of protein food sources, it is important to think about what else comes with it. When you eat foods that are rich in protein, you are also getting other things like fats, fiber, sodium, and other nutrients. Current evidence suggests that the “protein package,” has a greater impact on our health than the amount of protein eaten.
Traditional Animal-based
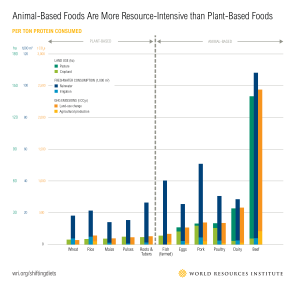
Source: World Resource Institute (Click on the image to see a larger version.)
Traditional sources like beef, pork, lamb, poultry, and seafood usually come from farms or wild sources. These proteins are complete protein sources because they contain all nine essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Additionally, animal-based protein is referred to as “high-quality” protein due to its high concentration of amino acids and digestibility, rather than its impact on human health or the environment. Regardless, it is important to note that not all animal-based proteins are created the same.
Red and Processed Meats
Red meats like beef, pork, and lamb, and processed meats, such as luncheon meats, hot dogs, and jerky, are high in saturated fats; furthermore, processed meats also contain a high amount of sodium. High intake of red meat, especially processed meats, has been linked to increased risk of cardiometabolic diseases, like heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes, and various cancers.
Dairy
Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of calcium, protein, and other important nutrients. But they can also have a lot of saturated fat, so it is better to consider the low-fat options.
Poultry and Eggs
Poultry, like chicken and turkey, is defined as a “high quality” and complete protein source like red meat. However, poultry, unlike red meat, generally has a lower saturated fat content; a notable exception to this generalization is duck. Eggs are also a complete source of protein with healthy fats and other nutrients.
Seafood
Seafood, such as salmon, Pacific oysters, tuna, and whitefish contain important types of omega-3 fatty acids, like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated or “healthy” fat; they play an important role in cellular membrane function and support the function of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. The major concern involved in consuming seafood, specifically fish, is the amount of mercury present; however, these levels vary between species. For advice on eating fish, check out this article from the FDA.
Plant-based
Beans, Peas, Lentils, Grains, and Soy
Beans, peas, and lentils are great plant-based proteins that also give you fiber, vitamins, and minerals. However, typically, a single type of bean, pea, or lentil does not constitute a complete protein by itself. It is advised to mix different types or add other foods to get complete protein, like the classic combination of rice and beans. Soybeans and soy products, like tofu and tempeh, are also a good source of protein, especially for those on a vegan and vegetarian diet. Rice is also a good source of protein, but like other plant-based sources, does not provide a complete protein and should be combined with other foods to ensure adequate intake.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds like almonds, peanuts, chai seeds, and sunflower seeds, are a good source of protein and healthy fats. However, due to their high fat and calorie content be mindful of your portion sizes. Quinoa, which is often classified as a pseudo-cereal but is a seed, is a complete protein.
Microbe-based
Microbial protein comes from microorganisms, mainly fungi (such as yeasts and filamentous fungi), microalgae (like cyanobacteria), and bacteria. The utilization of microbes for protein and food processing is not a new idea and can be observed in the making of bread, yogurt, and cheese, as well as in the direct consumption of yeast and algae. Two of the most well-known types of microbe-based proteins are nutritional yeast and spirulina. Some of the limitations of microbe-based proteins are the cost and product quality. They are not considered a complete protein because microbial protein only has eight out of the nine essential amino acids.
Insect-based
The practice of consuming insects, such as grasshoppers, ants, bees, and caterpillars, has long been established in several cultures throughout South and Central America, Africa, Asia, Oceania, and Europe. Insect-based protein is similar in quality to that from livestock but is more resource-efficient. However, it is important to consider species-specific health concerns, such as potential microbial, allergenic, and toxicological risks.
Cultivated Animal-based
Cultivated or lab-grown meat is an innovative technology that could transform the traditional meat industry. This process involves extracting cells from an animal, without slaughter, and then the cells are grown, harvested, and processed into meat for human consumption. The first lab-grown meat, a beef burger patty that cost $330,000, was developed by a scientist in the Netherlands in 2013. Since then, technological advancements have expanded product offerings to include cell-cultivated versions of pork, chicken, and seafood. The significant challenges facing the cultivated meat industry include scaling up production, reducing the costs of finished products, and replicating the taste and texture of conventional animal products. Still, since it comes from animal cells, it is a complete protein source.
Conclusion
Each protein source comes with its unique set of nutrients, which collectively impact our health more than the protein content alone. Understanding the complexities of each protein source—from traditional animal-based proteins to innovative lab-grown meats—helps us make informed dietary choices that align with our needs and considerations.
Additional Sources
Harvard Health
American Heart Association
World Resources Institute
The Nutrition Source
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Suzanne Holloway | Feb 27, 2025
Defining Proteins
Proteins are important macronutrients, just like carbohydrates and fats. They are large, complex molecules that play numerous roles in the body. For instance, proteins help in building and repairing structures, performing bodily functions, and regulating various processes within the body. You can find proteins essentially everywhere in the body from bones, muscles, enzymes, hormones, skin, and blood.
About Amino Acids
Proteins are composed of smaller parts called amino acids. These amino acids join together to form long, folded chains known as polypeptides. There are 20 different types of amino acids, each with unique properties. Our bodies cannot produce nine specific amino acids, so we need to get them from our food. There are conditionally essential amino acids, which are necessary only during times of sickness and stress. Furthermore, the body can make nonessential amino acids even if they are not present in the foods we eat. Here’s a quick look at these amino acids:
| Name |
Classification |
| Alanine |
Nonessential |
| Arginine |
Conditionally Essential |
| Asparagine |
Nonessential |
| Aspartic acid |
Nonessential |
| Cysteine |
Nonessential |
| Glutamic acid |
Nonessential |
| Glutamine |
Conditionally Essential |
| Glycine |
Conditionally Essential |
| Histidine |
Essential |
| Isoleucine |
Essential |
| Leucine |
Essential |
| Lysine |
Essential |
| Methionine |
Essential |
| Phenylalanine |
Essential |
| Proline |
Conditionally Essential |
| Serine |
Conditionally Essential |
| Threonine |
Essential |
| Tryptophan |
Essential |
| Tyrosine |
Conditionally Essential |
| Valine |
Essential |

Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, beans, and legumes are all good sources of protein. (Adobe Stock photo)
Recommendations
But how much protein do you need? This varies based on several factors such as weight, height, age, sex, and activity level. Generally, 10% to 35% of your daily calories should come from protein. In terms of weight, it’s recommended that a person consumes about 0.36 grams of protein per pound of body weight. It is important to know that one gram of protein provides four calories.
For a 2,000-calorie diet, the daily intake of protein could range from 200 to 700 calories.
For a 200-pound person, the daily intake of protein could be 72 grams.
To determine your recommended protein intake, use one of the following methods:
- Multiply your daily caloric intake by 0.10 – 0.35.
- Multiply your weight by 0.36.
- Use this Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Calculator.
However, if you are pregnant, protein intake should increase. Talk with your doctor about specific protein needs.
When considering your protein source, it is important to consider how it is packaged. You are not just eating the protein found in foods, but the fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients accompanying it. Ideally, you should choose protein sources that are low in saturated and trans fats and processed carbohydrates. We will discuss the pros and cons of the different protein sources in an upcoming post.
An Equal Opportunities Institution.

by Suzanne Holloway | Feb 5, 2025
February is a month to celebrate matters of the heart—both in love and in health. With Valentine’s Day and American Heart Month, February is the perfect time to cherish our loved ones while committing to a heart-healthy lifestyle. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for 1 in 5 deaths in 2022, according to the CDC. By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps, we can build healthier lives, families, and communities.
Heart Disease Defined
© freshidea / Adobe Stock
So, what is heart disease? The term “heart disease” actually refers to several conditions affecting the heart, but the most common is coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD occurs when deposits of Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), “bad” cholesterol, and other substances form plaque in the arteries. Over time, this plaque buildup can narrow the arteries, restricting or blocking blood flow.
Other types of heart diseases include arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), cardiomyopathy (abnormal heart muscle), heart valve disease, and heart failure. Understanding these conditions is essential to recognizing potential and current risk factors and acting.
Knowing Your Risks & Making Changes
When it comes to heart health, some risk factors are beyond our control, such as genetics and age. These elements are woven into the fabric of who we are, making them difficult—or impossible—to change. However, lifestyle choices, such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and even some environmental factors can be changed at the individual level. In the United States, nearly half of the population has at least one of these three key risk factors for heart disease:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- High LDL Cholesterol
- Smoking
Lifestyle changes—such as improving your diet, staying active, and avoiding smoking—can make a significant difference. Taking care of your heart is much like nurturing a great relationship. It begins with small steps and grows stronger with consistent care, dedication, and some compromises. Your daily decisions about food, exercise, and habits like alcohol and tobacco use play a starring role in your heart health. While you can’t change your genetics, the choices you make today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.
Share the Love
Show your loved ones you care by encouraging heart-healthy habits. Plan an active date, such as a scenic nature walk or a fun bike ride, or cook a delicious and nutritious meal together. Celebrate the month of love by taking charge of your heart health and inspiring others to do the same.
Whether it’s making small changes to your routine, learning more about heart disease, or supporting awareness efforts, every step counts toward a healthier, happier future for you and those you love. Let’s make February a heartfelt celebration of love and health.
Additional Sources
CDC American Heart Month Communications Toolkit
About Heart Disease (CDC)
An Equal Opportunity Institution
by Suzanne Holloway | Jan 10, 2025
January is recognized as National Blood Donor Month, but what makes blood and blood donation so important?
What is blood?
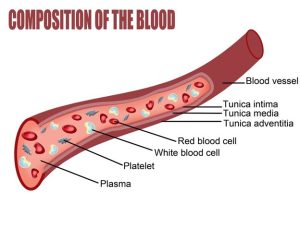
Blood is an essential bodily fluid that constantly flows through your body keeping it working. It has four main components: red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. Each part is designed to specific tasks.
This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-ND
Plasma
The majority of blood—approximately 55%—is composed of plasma. It is yellowish fluid that is a mixture of water, sugar, fats, proteins, and salts. Its main task is to transport blood cells throughout the body, but is also moves products like nutrients, proteins, hormones, and waste.
Red Blood Cells
The second largest component in blood is red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, making up about 40 – 45 percent of its total volume. These cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which helps carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Hemoglobin also gives RBCs, and the rest of the blood, their distinct red color.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells, or leukocytes, make up a much smaller portion than red blood cells about 1% of the blood. Their role is to protect the body from infections.
Platelets
Unlike red and white blood cells, platelets are not actually cells, but rather fragments of cells. They are the small component within blood being less than 1% of the total volume of blood. Platelets manage bleeding by assisting in the blood clotting process (coagulation) to seal damaged blood vessels to prevent a large amount of blood loss.
What are the blood types?
Blood also contains antigens, and a protein called the Rh factor, which serve as markers that determine a person’s blood type. Based on antigens alone, there are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and O. However, the Rh factor further classifies blood as either positive (+) or negative (-), resulting in a total of eight common blood types: A positive (A+), A negative (A-), B positive (B+), B negative (B-), AB positive (AB+), AB negative (AB-), O positive (O+), and O negative (O-). The most common blood type, in the United States, is O positive (O+); the least common, in the United States, is AB negative (AB-).
| Blood Type |
Approximate U.S. Population Percentage |
| A positive |
33% |
| A negative |
6% |
| B positive |
9% |
| B negative |
< 2% |
| AB positive |
< 4% |
| AB negative |
< 1% |
| O positive |
38% |
| O negative |
7% |
Understanding blood types enables healthcare providers to safely perform blood transfusions and organ transplants by ensuring compatibility between the donor and the recipient. Additionally, those with AB positive (AB+) blood are known as universal recipients; those with O negative (O-) blood are universal donors.
What’s the importance of blood donors?
According to the American Red Cross, someone in the United States needs blood and/or platelets every two seconds. That is about 29,000 units of red blood cells, 5,000 units of platelets, and 6,500 units of plasma needed daily. Nonetheless, there is no substitute or manufactured version for blood, which means it has to be generously donated by volunteers. It is important for surgeries, cancer treatment, childbirth, chronic illnesses (e.g., sickle cell disease), and traumatic injuries (e.g., car accidents). For more information on the donation process and how to prepare for a donation check out this website from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
To the almost 7 million people in the United States who donate their time and blood, thank you. Your single donation has saved multiple lives, and your generosity is worth celebrating.
Sources
American Society of Hematology
Cleveland Clinic
American Red Cross

by Suzanne Holloway | Nov 15, 2024
Thanksgiving, like other holidays, promises gratitude and togetherness, but it can also bring stress, awkward moments, and even indigestion. As family members gather – from near and far – to share a meal, navigating conflicting personalities, differing opinion, and the drive for perfection can make hosting feel daunting. To help ensure a peaceful (and maybe even enjoyable) holiday, here are a few Thanksgiving dos and don’ts.
DOs
- Set Realistic Expectations. While many dream of a picture-perfect Thanksgiving, real life is rarely like a cheesy holiday movie. Accept that things might not go as planned, and those imperfections are perfectly fine. Instead of pursuing perfection, aim for a day where everyone has moments of enjoyment, even if brief.
- Plan Ahead. Hosting Thanksgiving can be overwhelming—you’re the cook, cleaner, and event planner all in one. Schedule tasks into manageable chunks over the course of a few days, prepping dishes in advance, and delegating responsibilities. Ask your guests to bring sides – this lightens your load and involves them in the holiday prep.
- Choose Your Seat Wisely. Sit near family members you get along with. If you’re arranging seating, separate personalities likely to clash to keep the atmosphere peaceful.
- Take Care of Yourself. Schedule time for yourself before, during, and after Thanksgiving. It can be a short walk, meditating, or a quick and quiet escape to play a video game or watch a movie. If you are unable to leave a stressful situation, calm yourself with five slow, deep breaths.
- Learn to Let Things Go. Family quirks and annoyances are part of the package. Practice patience and remember, it’s just for a short time.
- Remember the Reason for the Season. Reflect on or share what you are thankful for—whether it’s a good meal, health, a roof over your head, or time with loved ones. Focusing on gratitude can be a great tool to shift the mood toward positivity.
DON’Ts
- Dominate the Conversation. Thanksgiving is for catching up with friends and family, not just talking about yourself. Be mindful, and make space for others to share, especially if it’s been a while since you have seen them.
- Try to Fix Problems. Now is not the time for unsolicited advice or life coaching. One conversation over what is supposed to be a happy meal won’t mend a marriage, convince someone to start a family, make someone a better parent, or get them to hit the gym.
- Discuss Sensitive Topics. Subjects like politics, religion, or lifestyle choices are best left off the dinner table. Even well-meaning questions like “When are you getting married?” or “When can I expect grandchildren?” may seem innocent but can make people uncomfortable. Stick to lighter topics that bring people together, such as favorite family traditions, upcoming plans, or funny memories from past Thanksgivings, this helps create a positive, welcoming environment for everyone.
- Drink Excessively. Some people become argumentative or aggressive when drinking, which can escalate tensions. Avoid these individuals if they get rowdy, and prevent them from driving. If this is an issue for you, consider mocktails or non-alcoholic drinks.
Thanksgiving does not have to be a stressful situation. By prioritizing your well-being and keeping gratitude at the forefront of the celebration, you can make Thanksgiving a meaningful, enjoyable day—flaws and all.
Additional Sources








