
by Claire Davis | Nov 21, 2025
A few years ago, I found myself juggling too much, including: work, family, school, health, and everything in between. I was constantly exhausted, mentally foggy, and emotionally drained. I didn’t realize it at the time, but I was neglecting more than just my physical health. It wasn’t until I began exploring the idea of wellness in a broader sense that I started to feel whole again. I learned that wellness is about far more than eating right or exercising; it’s about nurturing every part of your life.
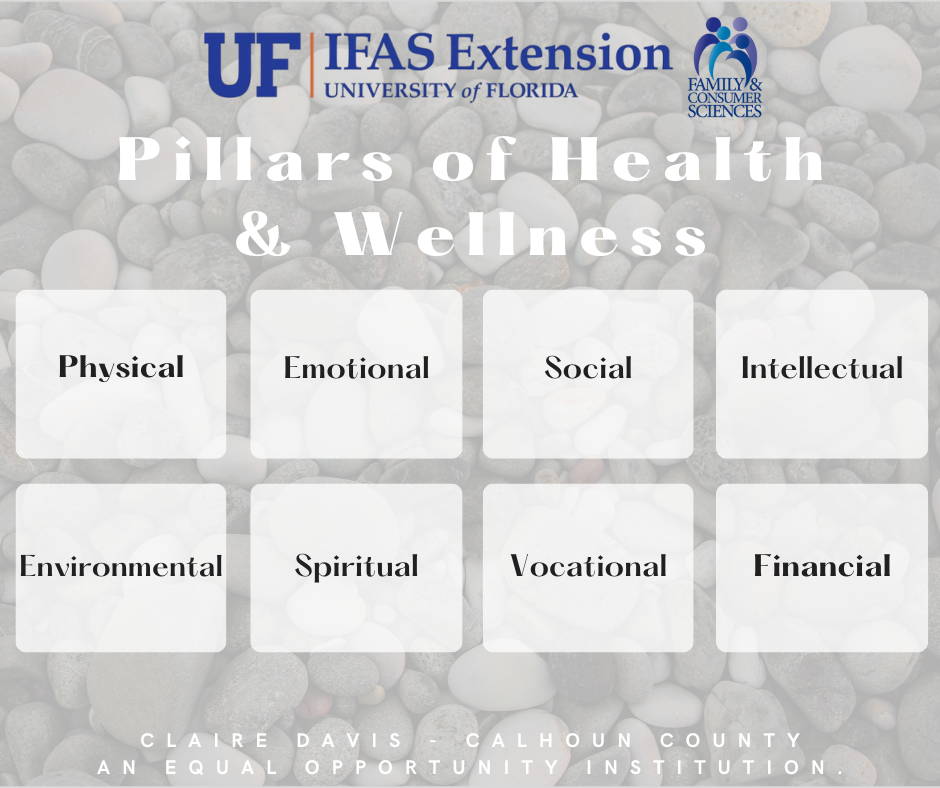
The most difficult thing for me to grasp was that wellness is not a destination, it’s an ongoing process and a lifelong journey. It’s about making intentional choices every day that contribute to your overall well-being, no matter where you are starting from. At its core, wellness is more than just physical health. It is the balance and integration of multiple interconnected dimensions that together form a strong foundation for a thriving life.
When we take a holistic approach to our health, we acknowledge that all aspects of our lives—mental, emotional, physical, social, and more—are connected. Focusing on the eight dimensions of wellness can not only improve your quality of life, but also contribute to longer life expectancy, better management of health conditions, and support in recovering from illness, injury, or addiction. It can even help prevent burnout, reduce stress, and increase life satisfaction.
The 8 Dimensions of Wellness
Each of the eight dimensions plays a vital role in your overall health and happiness, otherwise known as holistic health. When nurtured, they work together to create a more balanced and meaningful life. Here’s a look at what they are and how you can start integrating them into your life:
- Physical Wellness: Physical wellness involves taking care of your body through regular exercise, proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and preventive healthcare. Staying physically well boosts your energy, enhances your mood, and helps prevent chronic illness. To improve physical wellness, try this: Take a daily walk, drink more water, or schedule that overdue check-up. Start with one healthy habit and build from there.
- Emotional Wellness: Emotional wellness is the ability to understand, express, and manage your emotions in a healthy way. This includes recognizing stress, building resilience, and seeking support when needed. To improve emotional wellness, try this: Practice mindfulness, journal your feelings, or talk to a trusted friend or therapist when you’re feeling overwhelmed.
- Social Wellness: Social wellness is about creating and maintaining meaningful relationships and a strong support network. Connecting with others fosters a sense of belonging and can improve both mental and emotional health. To improve social wellness, try this: Reach out to a friend you haven’t spoken to in a while, join a community group, or attend a local event.
- Intellectual Wellness: Intellectual wellness encourages lifelong learning, critical thinking, and the pursuit of knowledge. Challenging your mind and staying curious can boost your confidence and creativity. To improve intellectual wellness, try this: Read a book, take an online class, learn a new hobby, or engage in thoughtful discussions.
- Environmental Wellness: Environmental wellness involves creating and sustaining a safe, healthy, and supportive space around you. This includes caring for your physical surroundings and being mindful of your impact on the planet. To improve environmental wellness, try this: Declutter your living space, spend time in nature, or reduce waste by recycling or using reusable products.
- Spiritual Wellness: Spiritual wellness is about finding purpose, meaning, and connection in life. Whether through religion, meditation, nature, or personal reflection, spiritual practices can offer clarity and inner peace. To improve spiritual wellness, try this: Start your day with a moment of gratitude, reflect in a journal, or explore practices that align with your values and beliefs.
- Vocational Wellness: Vocational wellness means pursuing work or academic paths that are fulfilling, align with your values, and make use of your strengths. It also involves finding a balance between work, school, and home life. To improve vocational wellness, try this: Reflect on your strengths and passions, set goals that align with your values, or find ways to bring more purpose into your daily tasks.
- Financial Wellness: Financial wellness involves understanding and managing your financial resources. It includes budgeting, saving, and planning for the future. Planning skills will help reduce stress and build long-term stability. To improve financial wellness, try this: Set a monthly budget, start a savings plan, or seek out resources to improve your financial literacy.

Take time to reflect on the different areas of wellness in your life.
Wellness Is for Everyone
Wellness is not reserved for a select few or those with perfect routines. It’s for everyone, no matter your age, background, or current circumstances. The beauty of wellness is that it’s highly personal, flexible, and does not have to be perfect. You don’t have to overhaul your entire life to make progress. You don’t have to address all eight areas at once. Even small, meaningful actions in one area can spark positive change in others. This can create a ripple effect across your entire holistic well-being.
Focus on progress, not perfection. Take time to reflect on what wellness means to you. Seek support when needed. And most importantly, be kind to yourself as you grow. Growth doesn’t happen overnight, but with intention and self-compassion, you can build a life of balance, vitality, and purpose.

by Melanie Southerland | Oct 24, 2025
Osteoporosis is a chronic condition that weakens bones. Weak bones are more likely to break. Osteoporosis is often called the “silent disease” because it can progress without symptoms until a fracture occurs, typically in the hip, spine, or wrist.
What Is Osteoporosis?

Strength training exercises help maintain bone density.
Image Source: Adobe Stock.
Osteoporosis occurs when bone density and quality are reduced. Bones become porous and brittle due to an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption. While bone is a living tissue that constantly renews itself, this process slows with age, especially after 30, leading to gradual bone loss.
Who Is at Risk?
Osteoporosis affects over 50 million people in the U.S., with women—especially postmenopausal—being at higher risk. However, men are also vulnerable, particularly after age 70. Key risk factors include:
- Age: Risk increases after 50.
- Sex: Women are four times more likely to develop osteoporosis.
- Race: White and Asian individuals are at higher risk.
- Family history: Genetics play a significant role.
- Body size: Smaller, thinner individuals have less bone mass to lose.
- Hormonal changes: Low estrogen or testosterone levels accelerate bone loss.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol, poor diet, and inactivity contribute to risk.
- Medical conditions and medications: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, and long-term use of corticosteroids or cancer treatments can increase susceptibility.
Symptoms and Signs
Osteoporosis often goes unnoticed until a fracture occurs. However, some signs may include:
- Loss of height
- Stooped posture
- Back pain from collapsed vertebrae
- Fractures from minor falls or stresses like coughing
Diagnosis
The primary diagnostic tool is a bone density test (DEXA scan), which measures bone mineral content. It’s recommended for:
- Women aged 65+
- Men aged 70+
- Postmenopausal women and men over 50 with risk factors
Prevention Strategies
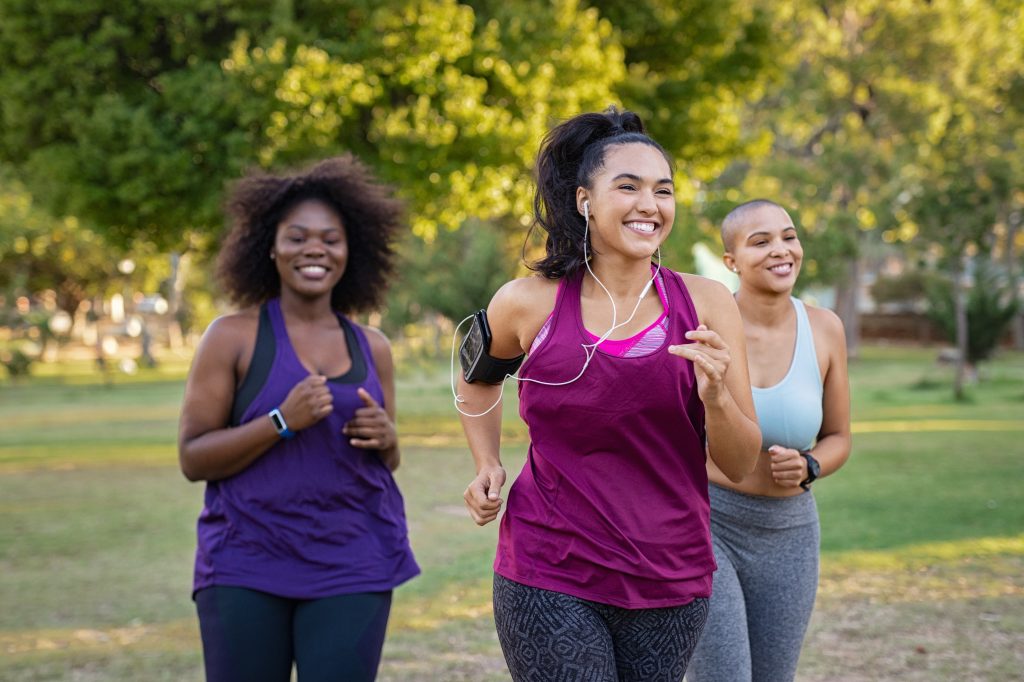

Weight-bearing exercises like walking or running can help to keep bones strong.
Photo Source: Adobe Stock Images.
Preventing osteoporosis involves lifestyle and dietary changes:
- Nutrition: Adequate intake of calcium (1,000–1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (600–800 IU/day) is essential.
- Exercise: Weight-bearing and resistance exercises like walking, dancing, and strength training help maintain bone density.
- Avoid harmful habits: Limit alcohol, quit smoking, and reduce caffeine and sodium intake.
- Fall prevention: Keep living spaces safe and use assistive devices if needed.
Treatment Options
Treatment aims to prevent fractures and slow bone loss. Options include:
- Medications: Talk with your healthcare provider for more information on medications for bone health.
- Supplements: Calcium and vitamin D are often prescribed to support bone health.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Continued exercise, balanced diet, and regular monitoring.
Living with Osteoporosis
Managing osteoporosis is a lifelong commitment. Regular checkups, bone density monitoring, and adherence to treatment plans are crucial. With proper care, individuals can maintain mobility, reduce fracture risk, and improve quality of life.
During the preparation of this work, the author used the AI tool, CoPilot
References
[1] Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment – Cleveland Clinic
[2] Osteoporosis – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
[3] Osteoporosis Causes, Risk Factors, & Symptoms | NIAMS
[4] Osteoporosis – Johns Hopkins Medicine

by Melanie Southerland | Oct 1, 2025
The Power of Positive Thinking: How It Shapes Mental Health
In a world filled with daily stressors and uncertainties, the way we think can significantly influence how we feel. Positive thinking—more than just a feel-good phrase—has been shown to have profound effects on mental health, emotional resilience, and overall well-being.

Photo Source: Adobe Stock Images
What Is Positive Thinking?
Positive thinking doesn’t mean ignoring life’s challenges or pretending everything is perfect. Instead, it’s about approaching difficulties with a constructive mindset, focusing on solutions, and maintaining hope. It often begins with positive self-talk, the internal dialogue that shapes how we interpret and respond to events.
Mental Health Benefits of Positive Thinking
Research shows that cultivating a positive mindset can lead to:
- Reduced stress and anxiety: Optimists tend to view challenges as manageable, which lowers the body’s stress response.
- Lower risk of depression: Positive thinkers are less likely to ruminate on negative thoughts, a key factor in depression.
- Improved emotional resilience: A hopeful outlook helps people bounce back from setbacks more quickly.
- Better coping skills: Optimism encourages proactive problem-solving and seeking support when needed.
- Enhanced psychological well-being: Positive emotions like gratitude and joy contribute to a more balanced mental state[1][3].
The Science Behind It
Positive thinking influences the brain’s chemistry. It boosts the release of dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins—neurotransmitters that enhance mood and reduce pain. It also reduces levels of cortisol, the stress hormone linked to anxiety and inflammation. Over time, these changes can rewire the brain through neuroplasticity, making optimism a more natural response[4].
Physical Health Connection
Mental and physical health are deeply connected. Positive thinking has been linked to:
- Stronger immune function
- Lower blood pressure
- Better cardiovascular health
- Faster recovery from illness or surgery
- Longer life expectancy[1][4]
️ How to Cultivate Positive Thinking
Building a positive mindset takes practice. Here are some proven strategies:
- Practice gratitude: Keep a journal of things you’re thankful for.
- Reframe negative thoughts: Challenge pessimistic beliefs and replace them with more balanced ones.
- Surround yourself with positivity: Spend time with supportive, uplifting people.
- Set realistic goals: Achieving small wins builds confidence and optimism.
- Engage in mindfulness or meditation: These practices help you become aware of negative thought patterns and shift your focus[3].
Final Thoughts
Positive thinking isn’t about ignoring reality—it’s about choosing a mindset that supports mental strength, emotional balance, and healthier living. Whether you’re facing everyday stress or managing a mental health condition, cultivating optimism can be a powerful tool for healing and growth.
References
[1] Positive thinking: Reduce stress by eliminating negative self-talk …
[2] Positive Thinking: Benefits and How To Practice
[3] The Power of Positive Thinking and Mental Health | EmpathyHQ
[4] The Power of Positive Thinking on Health – sciencenewstoday.org

by Samantha Kennedy | Sep 26, 2025
Today’s world can offer up a lot of stressors and as a result, many individuals face mounting pressures and mental health challenges. Recent studies reveal that pet ownership provides a unique sense of comfort and stability that can alleviate stress and anxiety. By inviting a pet into one’s home, people often experience immediate emotional support and a renewed sense of purpose. The presence of a loving animal can transform a lonely day into one filled with hope and connection.
Experts in psychology and human behavior have long noted the therapeutic benefits of caring for pets. Regular interactions with animals not only reduce cortisol levels but also increase oxytocin production, a hormone associated with happiness and bonding. Dog walks, playful cat moments, and even the calm companionship of a fish tank routine give structure to daily life. These activities encourage mindfulness, improve mood, and help many cope with depression.

Holding a pet can reduce stress and increase production of “feel-good” chemicals in the brain that can improve mood. (Photo source: Adobe Stock)
One of the biggest benefits of pet ownership is that pets offer unconditional emotional support without judgment. Caring for a pet refocuses negative thought patterns by providing individuals with a sense of responsibility. Additionally, the daily routines associated with pet care foster discipline and regularity, which are essential for maintaining mental balance. Patients who engage actively with their pets frequently report feeling less isolated and more optimistic about their futures.
Community connections can also blossom through pet ownership. Local pet events and dog parks bring together individuals from varied backgrounds, creating networks of support that extend beyond the pet’s company. Such encounters not only foster social interaction but also build trust and empathy among neighbors. In many cases, these casual relationships evolve into meaningful friendships that serve as additional layers of safety and emotional reassurance. Community events centered around pets underscore the social benefits that extend from personal well-being to societal harmony.
As mental health continues to be a focal point in discussions on overall wellness, owning a pet emerges as a natural remedy for many of modern society’s stressors. While pets require time, effort, and dedication, their rewards often surpass the challenges. A pet not only enhances an individual’s health by providing physical activity through daily routines but also nurtures mental and emotional strengths. In moments of grief or stress, the steady presence of a pet can remind owners that life’s simplest pleasures are often the most profound.
For those struggling with isolation or depression, the embrace of a pet might provide a much-needed bridge to a happier, healthier future. Amid the hustle of everyday life, the soft purr of a cat, the wag of a dog’s tail, or even the quiet flutter of a bird’s wings offers solace and hope. People who have adopted pets express an enriched sense of belonging and community, experiences that are increasingly recognized as integral to mental health. Research continues to delve deeper into the intricate link between animal companionship and psychological resilience. In the meantime, pet ownership can serve as a valuable complement to traditional mental health treatments such as therapy and medication.
For more information about this and other mental health topics, please call your local Family & Consumer Sciences (FCS) agent. You can find your nearest Florida FCS agent here.
An Equal Opportunity Institution
by Marie Arick | Sep 5, 2025

photo credit: Marie Arick
In these unusual times, embracing World Heart Day this September 29th could be more important than ever! The World Heart Federation uses this date to educate the world regarding cardiovascular diseases and the actions people can take to prevent or delay the onset of cardiovascular diseases including heart disease and stroke. The following is a simple three step action plan that one could implement in celebration of World Heart Day.
Action one, self-assessment. Waist circumference is a simple way to determine if you are at risk for health infirmities including cardiovascular diseases. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a waist circumference of 35 inches or more for women and a waist circumference of 40 inches or more for men places an individual at higher risk for heart disease. The NIH also notes that the higher the number, the higher the risk.
Action two, get moving. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) note just over half of the adults in the United States get enough aerobic exercise. Walking is one of the easiest aerobic exercises to perform; no special equipment required. Walking can improve your health by aiding with managing or preventing heart disease. Walking is a simple way to promote weight loss or maintain a healthy weight. Walking also aids with lowering risks and/or aids in the management of diabetes which is a risk factor for heart disease. Additionally, the National Institutes for Health (NIH) endorses walking for exercise as it aids in reducing anxiety and depression leading to improved cognitive function and self-esteem. Yet another benefit that can help during these trying times. Give it a try. Not one to exercise regularly? Start slowly. Begin with a small goal of 10 minutes daily and gradually increase the time and distance. Concerned that you have underlying health conditions? Speak with your physician to determine a walking plan or exercise regimen that is appropriate for you.
Action three, journaling or accountability. Using phone applications or a daily calendar can truly aid in accountability. Just noting time spent exercising or obstacles that occurred can aid with confirming the commitment to exercise. This is a form of personal accountability and tends to aid with the process of personal acknowledgement and commitment leading to a higher rate of follow through. Another option is to have an accountability partner. Accountability partners are great when you need someone to remind you of why you started the journey. No matter if you go it alone or include others, the commitment must be there.
Although our society is adjusting to our ‘new normal’ while navigating the Coronavirus, we can still embrace World Heart Day. Take the opportunity to assess our own personal health, get moving by incorporate walking into your daily regimen to not only combat cardiovascular disease, record your journey to aid with accountability and finally take charge of the course of our personal health.

by Suzanne Holloway | Aug 1, 2025
The term “freshman 15” describes the widespread belief that college students gain fifteen pounds during their first year. This concept originated in the mid-to-late 1980s, with a 1985 peer-reviewed article reporting an average weight gain of 8.8 pounds in women. Later, in 1989, Seventeen magazine popularized the phrase by chronicling a student’s struggle with first-year weight gain. Despite its popularity, the evidence behind the “freshman 15” experience is limited. Furthermore, studies have been somewhat inconsistent, with some observing weight gain, others showing weight loss, and/or no change in weight. For example, a 2008 study found weight changes ranging from -5 to +20 pounds with an average of roughly +3 pounds.
For most students, the “freshman 15” is more accurately a “freshman 5.” Both numbers, though, are broad generalizations, and real experiences vary. Starting college marks a major life transition: the independence, new routines, and unique pressures involved can all influence well-being. As a result, some students may gain weight, others might lose weight, and some may see no change at all. Nonetheless, it is important to note that weight and body mass index (BMI) should not be used as sole indicators for health since they do not factor in lifestyle behaviors and body composition.
College Wellness Tips
Looking to build healthy habits in college? Here are some wellness tips and resources to help incoming and current college students.
Eating Habits
With limited access to kitchens, many freshmen rely on dining halls, restaurants, and convenience stores for food. The abundance of choices, particularly at dining halls, including many tempting comfort foods, can easily lead to mindless eating, especially during times of stress or homesickness. Just because your parents aren’t there to remind you doesn’t mean you should stop eating fruits and vegetables; they remain an essential part of a healthy diet and lifestyle. Practicing mindful eating by paying attention to hunger cues, savoring your food, and choosing a balanced meal can make it easier to nourish your body, avoid overeating, and feel your best.

© ActionGP / Adobe Stock
Sleeping Habits
Poor or inconsistent sleep can undermine both physical and mental health, impairing cognitive function and even increasing appetite (which can contribute to overeating and weight gain). Good sleep hygiene is vital—try to keep a regular bedtime, limit caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol late in the day, avoid screens before sleep, and wind down with relaxing activities like reading or meditation.
Stress Management
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, sometimes called the “stress hormone.” When stress is chronic (long-term), cortisol remains high and disrupts the body, slowing metabolism, increasing fat storage (especially in the abdomen), raising blood sugar, and fueling cravings for calorie-dense comforting foods. This can explain why people often “eat their feelings” and reach for familiar or sugary snacks during tough times. Chronic stress is also linked to conditions like depression, high blood pressure, metabolic disorders (e.g., obesity), and fatigue. Healthy ways to cope with stress include seeking social support, building a consistent sleep routine, practicing mindful eating, and staying physically active.
University Student Wellness Resources
If you’re struggling with your physical or mental health, don’t hesitate to reach out. Most universities offer support services for students, such as Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University, Florida State University, and the University of Florida.
Additional Sources
University of Georgia
University of Utah













