
by Amy Mullins, PhD, RDN | Aug 1, 2025

Good nutrition is important to cognitive function. (Adobe Stock Image)
The Connection Between Nutrition and Memory: How Food Affects Cognitive Function
Memory is a complex and multifaceted cognitive function that plays a vital role in our daily lives. From remembering important events and appointments to recalling learned skills and knowledge, memory is essential for our overall well-being and success. While genetics and lifestyle factors can influence memory, a growing body of research suggests that nutrition also plays a significant role in cognitive function and memory.
The Importance of Nutrition for Memory
A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, provides the necessary nutrients and building blocks for optimal brain function. The brain is a hungry organ, accounting for approximately 20% of the body’s total energy expenditure. Adequate nutrition is essential for maintaining healthy brain cells, facilitating communication between neurons, and supporting the growth and development of new neural connections.
Key Nutrients for Memory
Several nutrients have been identified as essential for supporting memory and cognitive function. These include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats, particularly EPA and DHA, are found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Omega-3s support brain cell membrane structure and function, promoting healthy communication between neurons.
- Vitamin D: This essential vitamin is obtained through sun exposure, dietary sources, and supplements. Vitamin D receptors are found in brain cells, and research suggests that vitamin D plays a role in regulating neurotransmitter function and protecting against age-related cognitive decline.
- B Vitamins: B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for synthesizing neurotransmitters and maintaining healthy brain cells. Foods rich in B vitamins include leafy greens, legumes, whole grains, and lean meats.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, and polyphenols found in fruits, vegetables, and tea, help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, which can damage memory and cognitive function.
- Magnesium: This essential mineral supports neuronal function and synaptic plasticity, facilitating learning and memory. Foods rich in magnesium include dark leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains.
Dietary Patterns Associated with Better Memory
Research has identified several dietary patterns that are associated with improved memory and cognitive function. These include:
- Mediterranean diet: Characterized by high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet has been shown to support cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
- DASH diet: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, developed to reduce blood pressure, emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
- Plant-based diet: A diet rich in plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, has been associated with improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline.
Tips for Supporting Memory through Nutrition
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining cognitive function and supporting memory.
- Limit processed and sugary foods: These foods can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells and impair memory.
- Consider supplements: If you’re concerned about getting enough nutrients through diet alone, consider consulting with a healthcare professional about supplementing with omega-3s, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients.
Conclusion
While genetics and lifestyle factors can influence memory, nutrition plays a critical role in supporting cognitive function and memory. By incorporating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, essential nutrients, and healthy fats, you can support optimal brain function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
References:
During the preparation of this work the author used the AI tool, NaviGator. After using this tool/service, the author reviewed and edited the content as needed and takes full responsibility for the content of the publication. Image source: Adobe Stock
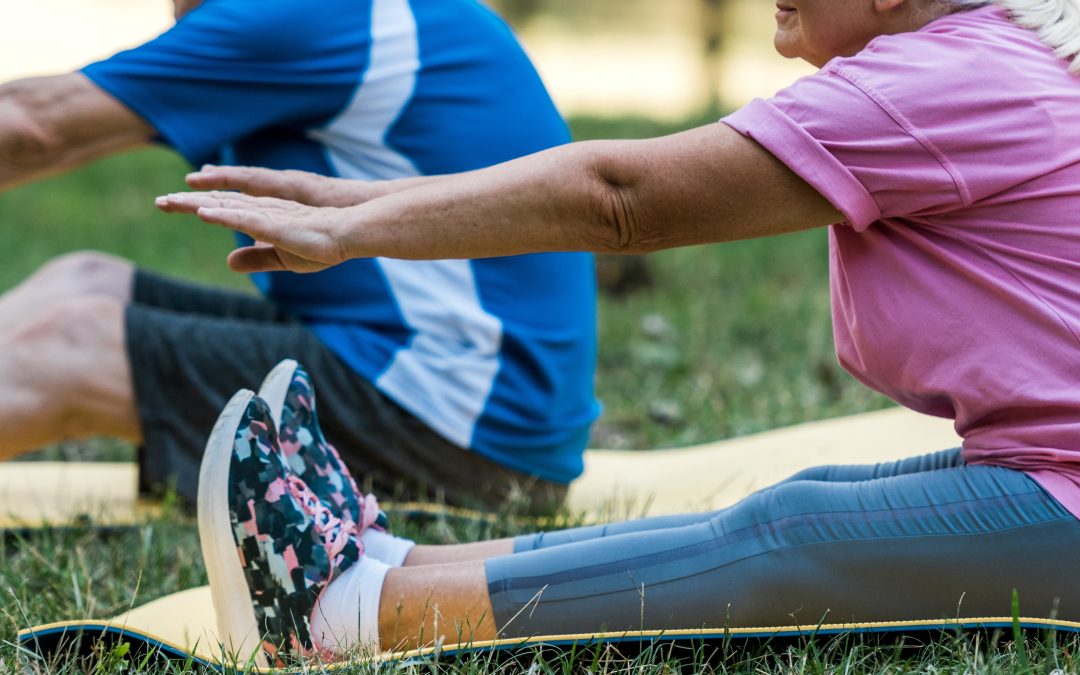

by Amy Mullins, PhD, RDN | Jul 1, 2025

Exercise boosts brain power. (Adobe Stock image)
As we age, our memory and cognitive abilities can decline, making everyday tasks more challenging. While genetics and lifestyle play a significant role in determining our cognitive health, research has shown that regular exercise can have a profound impact on memory and overall cognitive function.
- Increased Blood Flow: Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. This increased blood flow can help to promote the growth of new brain cells and improve communication between neurons.
- Neurotrophic Factors: Exercise stimulates the production of neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which play a key role in promoting the growth and survival of brain cells.
- Reduced Inflammation: Exercise has anti-inflammatory effects, which can help to reduce inflammation in the brain and promote cognitive health.
- Improved Neuroplasticity: Exercise promotes neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and change in response to new experiences. This can help to improve memory and learning.
- Improved Memory: Exercise has been shown to improve memory in both young and old adults, and to reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
- Enhanced Learning: Exercise has been shown to improve learning and memory in both children and adults, and to reduce the risk of cognitive impairment.
- Reduced Risk of Dementia: Regular exercise has been shown to reduce the risk of dementia and other age-related cognitive disorders.
- Improved Mood: Exercise has been shown to improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
According to the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, adults need 150 minutes of aerobic type moderate-intensity, plus 2 or more days of muscle-strengthening exercise per week. Here are some types of exercise that have the greatest impact on cognitive function:
- Aerobic Exercise: Aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, or swimming, has been shown to improve memory and cognitive function.
- Resistance Training: Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, has been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT, which involves short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by periods of rest, has been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce inflammation.
- Mind-Body Exercise: Mind-body exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, have been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce stress.
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can be easier than you think! Here are some tips to get you started:
- Start Small: Begin with short, manageable exercise sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity as you become more comfortable.
- Find an Exercise You Enjoy: Engage in physical activities that bring you joy, whether it’s running, swimming, or dancing.
- Schedule Exercise into Your Day: Treat exercise as a non-negotiable part of your daily routine, just like brushing your teeth or taking a shower.
- Make it Social: Exercise with a friend or family member to make it more enjoyable and to provide accountability.
Exercise is a powerful tool for improving memory and cognitive function. When we exercise, our brain undergoes changes that can have a lasting impact on our cognitive abilities. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline, improve memory and learning, and enhance overall cognitive health. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting out, there’s never been a better time to get moving and improve your brain health.
References:
During the preparation of this work, the author used the AI tool, NaviGator. After using this tool/service, the author reviewed and edited the content as needed and takes full responsibility for the content of the publication.

by Samantha Kennedy | Jun 30, 2025
As hurricane season approaches, families in coastal and low-lying areas are bracing themselves for the possibility of devastating storms. While many people may think they are prepared, the reality is that many families are not equipped with a plan to deal with the chaos and destruction that comes with a hurricane. In this article, we will explore the importance of developing a family emergency plan and provide tips on how to create a comprehensive plan that will keep your loved ones safe.
A Plan is Not a Guess
Developing a family emergency plan should not be a guessing game. It is a proactive step that can mean the difference between life and death. A plan outlines what to do in case of an emergency, including evacuation routes, safe meeting points, and communication protocols. Without a plan, families are left to fend for themselves, which can lead to confusion, panic, and tragedy.

Now is the time to prepare your family’s emergency supply kit. Be sure to include items such as nutritious snacks, canned goods, important documents, first aid kit, and other essential items. (Adobe Stock photo)
Key Components of a Family Emergency Plan
A comprehensive family emergency plan should include the following key components:
Safe Meeting Point: Designate a safe meeting point outside the home in case you get separated. This could be a neighbor’s house, a landmark, or a specific location in your neighborhood.
Communication Plan: Establish a communication plan that includes how you will stay in touch with each other, including phone numbers, email addresses, and social media accounts.
Evacuation Routes: Identify evacuation routes and emergency shelters in your area. Make sure everyone knows the routes and shelters.
Emergency Contact Information: Make sure everyone knows important phone numbers, such as your insurance company, emergency services, and utility companies.
Important Documents: Keep important documents, such as insurance policies, identification, and medical records, in a safe and easily accessible location.
Tips for Creating a Family Emergency Plan
Involve Everyone: Make sure everyone in the household is involved in the planning process. This will ensure that everyone knows what to do in case of an emergency.
Practice Drills: Practice your emergency plan with regular drills to ensure everyone knows what to do.
Stay Informed: Stay informed about weather updates and emergency alerts from local authorities.
Review and Update: Review and update your emergency plan regularly to ensure it is current and effective.
Don’t Wait Until It’s Too Late
Do not wait until the last minute to develop a family emergency plan. The consequences of not having a plan can be dire. By creating a comprehensive plan, you will be better equipped to handle the challenges of hurricane season. Remember, a plan is not a guarantee of safety, but it can significantly reduce the risk of injury or death.
Safety Tips
- Stay away from windows and doors during a hurricane.
- Avoid traveling during a hurricane.
- Keep a first aid kit and emergency supplies with you at all times.
- Stay informed about the latest weather updates and forecasts.
- Follow evacuation orders from local authorities.
Developing a family emergency plan is a crucial step in ensuring the safety and well-being of your loved ones during hurricane season. By creating a comprehensive plan, you will be better equipped to handle the challenges of storms and reduce the risk of injury or death. Do not wait until it is too late – take action now and create a plan that will keep your family safe.
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Judy Corbus | Apr 28, 2025
Spring has sprung and you may feel the urge to give your home a deep cleaning. The American Cleaning Institute finds that 80% of us are doing some type of deep cleaning this spring so you are not alone. Deep cleaning your home after winter gives a fresh restart and boosts your spirits.

Make your own household cleaners to save money and reduce container clutter. Photo credit: Judy Corbus
When choosing cleaning products, keep in mind that you can make your own from ingredients you already may have on hand. You will save money and reduce container clutter with products that can clean multiple surfaces. Here is a list of basic cleaning ingredients:
- Vinegar
- Rubbing alcohol
- Washing soda (can be found near the laundry detergent in most stores)
- Borax (also near the laundry section)
- Mild dish detergent
- Liquid bleach
- Baking soda
- Ammonia
- Water
Here are a few recipes to get you started:
Everyday Household Cleaner
- 2 tablespoons of liquid detergent/soap
- 2 tablespoons of ammonia
- 1 quart of water
Use for all general cleaning jobs.
Window Cleaner
- 1/4 cup rubbing alcohol
- 1/4 cup white vinegar
- 1 tablespoon cornstarch
- 2 cups warm water
Combine all ingredients together in an empty spray bottle and shake well. You will need to shake it a little with each use if you see cornstarch accumulating at the bottom of the bottle. Use crumpled-up newspaper to shine the windows.
Ceramic Tile Floor Cleaner
- 1/4 cup of white vinegar (or more depending on how dirty)
- 1 gallon of water
Typically requires little-to-no scrubbing to remove most dirt and doesn’t leave a film like soap sometimes does when using hard water.
With all cleaning products, remember:
- It is best to mix just what you need and use it all.
- Be sure the container has a label. If you make your own cleaner, always label it.
- Never put cleaners in food containers.
- Store cleaning solutions out of children’s reach.
Note: Use caution when making homemade cleaners! Mixing bleach with ammonia or vinegar will create toxic fumes that are very dangerous to your lungs and breathing!
For additional cleaner recipes, check out:
Reference: Homemade Household Cleaners
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Suzanne Holloway | Apr 28, 2025
Dietary protein is an important macronutrient for human health, and it can be found in a wide variety of foods. To learn more about the basics of protein, check out this earlier article.
Types of Protein Sources
Before we explore the different types of protein food sources, it is important to think about what else comes with it. When you eat foods that are rich in protein, you are also getting other things like fats, fiber, sodium, and other nutrients. Current evidence suggests that the “protein package,” has a greater impact on our health than the amount of protein eaten.
Traditional Animal-based
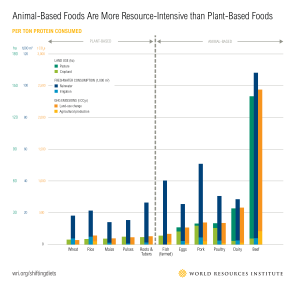
Source: World Resource Institute (Click on the image to see a larger version.)
Traditional sources like beef, pork, lamb, poultry, and seafood usually come from farms or wild sources. These proteins are complete protein sources because they contain all nine essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Additionally, animal-based protein is referred to as “high-quality” protein due to its high concentration of amino acids and digestibility, rather than its impact on human health or the environment. Regardless, it is important to note that not all animal-based proteins are created the same.
Red and Processed Meats
Red meats like beef, pork, and lamb, and processed meats, such as luncheon meats, hot dogs, and jerky, are high in saturated fats; furthermore, processed meats also contain a high amount of sodium. High intake of red meat, especially processed meats, has been linked to increased risk of cardiometabolic diseases, like heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes, and various cancers.
Dairy
Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of calcium, protein, and other important nutrients. But they can also have a lot of saturated fat, so it is better to consider the low-fat options.
Poultry and Eggs
Poultry, like chicken and turkey, is defined as a “high quality” and complete protein source like red meat. However, poultry, unlike red meat, generally has a lower saturated fat content; a notable exception to this generalization is duck. Eggs are also a complete source of protein with healthy fats and other nutrients.
Seafood
Seafood, such as salmon, Pacific oysters, tuna, and whitefish contain important types of omega-3 fatty acids, like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated or “healthy” fat; they play an important role in cellular membrane function and support the function of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. The major concern involved in consuming seafood, specifically fish, is the amount of mercury present; however, these levels vary between species. For advice on eating fish, check out this article from the FDA.
Plant-based
Beans, Peas, Lentils, Grains, and Soy
Beans, peas, and lentils are great plant-based proteins that also give you fiber, vitamins, and minerals. However, typically, a single type of bean, pea, or lentil does not constitute a complete protein by itself. It is advised to mix different types or add other foods to get complete protein, like the classic combination of rice and beans. Soybeans and soy products, like tofu and tempeh, are also a good source of protein, especially for those on a vegan and vegetarian diet. Rice is also a good source of protein, but like other plant-based sources, does not provide a complete protein and should be combined with other foods to ensure adequate intake.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds like almonds, peanuts, chai seeds, and sunflower seeds, are a good source of protein and healthy fats. However, due to their high fat and calorie content be mindful of your portion sizes. Quinoa, which is often classified as a pseudo-cereal but is a seed, is a complete protein.
Microbe-based
Microbial protein comes from microorganisms, mainly fungi (such as yeasts and filamentous fungi), microalgae (like cyanobacteria), and bacteria. The utilization of microbes for protein and food processing is not a new idea and can be observed in the making of bread, yogurt, and cheese, as well as in the direct consumption of yeast and algae. Two of the most well-known types of microbe-based proteins are nutritional yeast and spirulina. Some of the limitations of microbe-based proteins are the cost and product quality. They are not considered a complete protein because microbial protein only has eight out of the nine essential amino acids.
Insect-based
The practice of consuming insects, such as grasshoppers, ants, bees, and caterpillars, has long been established in several cultures throughout South and Central America, Africa, Asia, Oceania, and Europe. Insect-based protein is similar in quality to that from livestock but is more resource-efficient. However, it is important to consider species-specific health concerns, such as potential microbial, allergenic, and toxicological risks.
Cultivated Animal-based
Cultivated or lab-grown meat is an innovative technology that could transform the traditional meat industry. This process involves extracting cells from an animal, without slaughter, and then the cells are grown, harvested, and processed into meat for human consumption. The first lab-grown meat, a beef burger patty that cost $330,000, was developed by a scientist in the Netherlands in 2013. Since then, technological advancements have expanded product offerings to include cell-cultivated versions of pork, chicken, and seafood. The significant challenges facing the cultivated meat industry include scaling up production, reducing the costs of finished products, and replicating the taste and texture of conventional animal products. Still, since it comes from animal cells, it is a complete protein source.
Conclusion
Each protein source comes with its unique set of nutrients, which collectively impact our health more than the protein content alone. Understanding the complexities of each protein source—from traditional animal-based proteins to innovative lab-grown meats—helps us make informed dietary choices that align with our needs and considerations.
Additional Sources
Harvard Health
American Heart Association
World Resources Institute
The Nutrition Source
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Amy Mullins, PhD, RDN | Apr 2, 2025
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system, designed to protect us from infection and injury. However, chronic inflammation is a complex condition characterized by a persistent and low-grade inflammatory response that can lead to various diseases including arthritis, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.

Diet contributes to chronic inflammation in the body.
Chronic inflammation can be caused by various factors, including:
- Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic mutations can affect the body’s inflammatory response, making it more prone to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollutants, stress, and other environmental stressors can trigger chronic inflammation.
- Lifestyle factors: Sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and poor diet can contribute to chronic inflammation.
While genetics, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to chronic inflammation, diet is a controllable risk factor that plays a significant role in its development and exacerbation. There are many common foods in the American diet that are responsible for promoting inflammation in the body.
Some of the most common pro-inflammatory foods include:
- Processed and Packaged Meats: hot dogs, processed deli meats, bacon, and sausage. This includes meat that has been smoked, cured, salted, dried, or canned.
- Refined Carbohydrates: white bread, bakery foods (such as cookies, cakes, and pastries), processed cereals, white rice and pasta.
- Fried Foods: French fries, fried chicken, fried fish, fried vegetables, and fried sweets such as doughnuts.
- Processed and High-Sugar Foods & Beverages: candy, chocolate, soda, energy drinks, and fruit drinks.
- Foods High in Saturated and Trans Fats: red meat (such as beef and pork), processed meats, whole milk, cheese, ice cream, butter, coconut oil, and partially hydrogenated oils (such as margarine and processed snack foods).
- Vegetable & Seed Oils High in Omega-6 Fatty Acids: canola oil, corn oil, soybean oil, peanut oil, safflower, and sunflower oils are often used in frying and production of ultra-processed or convenience foods. Also high in omega-6 fatty acids are mayonnaise and most salad dressings. Although omega-6 fatty acids are essential in the diet, excess intake of omega-6 oils can promote inflammation in the body when not balanced with enough omega-3 fatty acids.
Why do these foods contribute to chronic inflammation?
- High sugar and refined carbohydrate content: Consuming high amounts of sugar and refined carbohydrates can contribute to insulin resistance, a precursor to chronic inflammation.
- Saturated and trans fats: These fats can promote inflammation by altering the body’s fatty acid composition and disrupting the balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Presence of AGEs: Foods cooked at high temperatures, such as charred meats and fried foods, contain advanced glycation end products (AGE), which can cause oxidative stress and stimulate inflammation by binding to specific receptors on immune cells.
- Processed and high-sodium content: Processed foods often contain high amounts of sodium, which can lead to inflammation and cardiovascular disease.
- Lack of essential nutrients: Many pro-inflammatory foods are low in essential nutrients, leading to nutrient deficiencies that can contribute to inflammation.
To reduce chronic inflammation, focus on limiting or avoiding pro-inflammatory foods and incorporating more anti-inflammatory foods and nutrients into the diet.
Nutrients That Can Help Reduce Inflammation
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These essential fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased inflammation.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for reducing inflammation.
Foods that Reduce Inflammation
- Leafy Greens: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in antioxidants and flavonoids, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Berries: Berries like blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are rich in antioxidants and flavonoids, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds like walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Ginger: Ginger has anti-inflammatory compounds called gingerols and shogaols, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Green Tea: Green tea is rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Olive Oil: Olive oil is rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help reduce inflammation.
What can you do to improve your diet? Here are some strategies to help you get started:
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods: Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated with water: Replace sugary drinks with water. Adequate hydration can help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Cook at home: Prepare meals using fresh ingredients to control the amount of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats in your diet.
- Read labels: Be aware of the ingredients and nutritional content of packaged foods, and choose options that are lower in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
- Gradually transition to a balanced diet: Replace pro-inflammatory foods with anti-inflammatory ones and gradually adjust your diet over time.
By making informed choices about the foods we eat and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into our diet, we can reduce our risk of chronic inflammation and promote overall health and well-being.
References:
During the preparation of this work the author used the AI tool, NaviGator. After using this tool/service, the author reviewed and edited the content as needed and takes full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Photo source: https://stock.adobe.com/1277005967 and /532657650












