
by Laurie Osgood | Oct 11, 2019
Meatless Burger Alternatives

If you have been watching television lately, you may have seen commercials for meatless burgers that are making a splash. Many restaurants including Burger King and Red Robin are now offering this alternative meat source on their menus. https://www.bk.com/menu-item/impossible-whopper, https://www.redrobin.com/burgers/impossible-burger.html,
Beyond Beef™ and Impossible Burgers™ are two of the meat alternatives created by The Beyond Meat ™ https://www.beyondmeat.com/products/ and The Impossible Foods https://impossiblefoods.com/ companies. The Beyond Burger™ and Impossible Burger™ are similar in ingredients, color and texture, and they actually taste like…meat!
According to Emily Gelsomin, in the August 19th edition of Harvard Health Publishing, “Plant-based burgers are not a novel concept. But new products designed to taste like meat are now being marketed to vegetarians and meat-eaters alike”. Gelsomin suggests that meatless burgers are a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
But What Are They?
Keep in mind that meatless burgers are created in a lab, not in a pasture. Meatless burgers look, sizzle, and even “bleed” like a regular hamburger. But they contain no animal protein and are a completely plant-based patty. This plant-based protein is a blend of potato and soy proteins. Meatless burger alternatives get their red color and “bleeding” effect from beet juice. Meatless burgers sizzle while being cooked because of sunflower and coconut oils, the meatless burger’s fat sources. To hold everything together, meatless burgers contain methylcellulose, a bulk-forming fiber source.
Are Meatless Burgers Safe?
Yes, meatless burgers are safe to eat, unless you are allergic to soy, coconut or sunflower.
The Good News:
Meatless burgers contain less sodium, cholesterol and fat than traditional beef or ground turkey patties do. Meatless burgers contain 2-3 grams of fiber per serving, whereas traditional hamburger patties contain no fiber.
The Bad News:
Just because they are a plant-based alternative to meat, doesn’t mean that they are healthier for you. The calories found in a meatless burger are similar to a traditional beef patty and meatless burgers are heavily processed and high in saturated fat.
How Do These Meatless Burger Alternatives Compare Nutritionally to Ground Beef and Ground Turkey Patties?
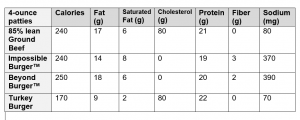
Source: Harvard Health Blog. Impossible and Beyond: How healthy are these meatless burgers? August 15, 2019.
The Bottom Line:
Meatless burgers such as The Impossible Burger™ and Beyond Burger™ are unique alternatives, although nutritionally not that different from a traditional hamburger patty. However, due to its popularity, companies such as Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat have struggled to keep up with the demand.
Contact your local Family & Consumer Sciences Extension Agent to learn more about meatless alternatives.
Sources
https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/impossible-and-beyond-how-healthy-are-these-meatless-burgers-2019081517448
Shopping for Health, Vegetarian Diets https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/FS/FS16700.pdf

by Stephanie Herzog | Oct 11, 2019
Have you ever been bullied or know someone who has been bullied? I know I have. October is National Bullying Prevention Month. Each October since 2006, there has been a national effort to raise awareness about bullying and provide education and resources to try to prevent it. According to data from 2017, about 20% of youth ages 12-18 experienced bullying at school and nearly 30% reported cyberbullying during their lifetime. That is a lot of our country’s youth!
What Exactly is Bullying?
Bullying is unwanted aggressive behavior. Bullying must have a real or perceived power imbalance between the bully and the victim, where the bully uses their power to control or hurt their victim. The bullying behavior needs to be repeated over time, or at least have the potential to repeat over time.
There are three categories of bullying:
- Verbal bullying includes teasing, taunting, threats, or name-calling
- Social or relational bullying includes ignoring someone on purpose, ostracizing, spreading rumors, or embarrassing someone
- Physical bullying includes damaging belongings or harming another’s body such as spitting, hitting, pushing, rude gestures, or tripping

The constant and easy access of cell phones, social media, and the internet has increased the real dangers of cyberbullying. (Photo source: UF/IFAS)
Cyberbullying
Technology has changed the ways of bullying. Bullying is no longer only ‘picking on’ someone, making fun of them, calling them names, or ignoring them at school. The constant and easy access of cell phones, social media, and the internet has truly expanded bullying to an unthinkable, unending scale. There are many ways to bully someone online, including:
- Verbal attacks, mean messages, or rumors on social media accounts, online games such as Fortnite, or through email or text
- Releasing embarrassing or inappropriate pictures, GIFs, or videos online or through text (e.g. sexting)
- Creating fake profiles or hacking into someone’s account online in order to hurt that person
Perhaps one of the most dangerous things about cyberbullying is once something is posted online and is circulated, it’s very hard to permanently remove. This oftentimes makes escape from the bullying unusually difficult or even seemingly impossible. It’s so important to keep up with ways technology is advancing in order to protect ourselves from things like cyberbullying.
Effects of Bullying
The negative psychological effects of bullying are very real – for the bully, the victim, and those who may witness it.
For the bully, they have a greater risk of using substances, engaging in risky or violent behavior, being abusive in future relationships, committing crimes, and developing other external behavior problems.
Effects of bullying include low self-esteem, fear, loneliness, heartache, and potential physical illness. These effects put a widespread toll on the mental, physical, and social health of the victims and also those who witness bullying. The increased risk of using addictive and illegal substances, anxiety, depression, eating disorders or even becoming suicidal are to be taken seriously and should be treated appropriately. Seek out mental health professionals or physicians and consult with them on the best combination of treatment. These effects can last days, months, years, or even lifetimes depending on the person and the circumstance.
The Story of Amanda Todd
The story of Amanda Todd is an unfortunate real example of cyberbullying and how unforgiving and never-ending it can be. Amanda ultimately committed suicide to get away from it; she was only 15 years old. Her YouTube video, published in 2012 a month before she committed suicide, has 13.5 million views to date. To better understand the reality of bullying, please consider watching it or sharing it. However, viewer discretion is advised.
Bullying, harassment, discrimination, or any other type of negative, cruel, or harmful behavior is never okay or acceptable in any way. If you have been a witness of bullying or a bully, stand up to stop it! If you have been bullied or know someone who has, please seek help from caring professionals, family, or friends. Go-to resources are found below.
Additional Resources
Stop Bullying Now Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- Available 24/7, managed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 1-800-273-8255
- Available 24/7, there is an online chat option available here
The Trevor Project: 1-866-488-7386
- Available 24/7, suicide prevention help specifically for the LGBTQ+ community
- Texting and chat options are available here
National Eating Disorders Association: 1-800-931-2237
- Mon-Thu 9am-9pm, Fri 9am-5pm
The Cybersmile Foundation
STOMP Out Bullying
Stopbullying.gov
Sources
National Center for Educational Statistics, Indicators of School Crime and Safety Indicator 10: Bullying at School and Electronic Bullying, April 2019.
Cyberbullying Research Center
The Amanda Todd Legacy

by Dorothy C. Lee | Jul 21, 2019
Eating healthy is not something that just happens by going on a particular diet. In fact, the best kind of diet is where the right choices are made, and it becomes a way of life. Sometimes we need to know some ways to change the bad habits we have developed. There is no ‘quick fix’.

Tune Up Your Lifestyle
Photo Source: UF/IFAS
With today’s fast-paced lifestyles sometimes we feel we don’t have the time to do the things we know we should. For instance, to get more exercise, do things like park a distance from the store when you go shopping, walk up and down the stairs instead of taking the elevator, walk to lunch, or even turn up the speed on regular activities you perform around the house.
When grocery shopping choose foods from the basic food groups (fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and reduced-fat dairy products) to round out a healthy meal plan.
Convenience foods are a part of today’s lifestyle, but they often lack nutritional quality, texture, and flavor. Preparing foods at home can be healthy and economical. You can boost nutrition and flavor by adding fresh herbs, spices, and aromatic vegetables to the meal menu.
Foods and beverages high in sugar add empty calories to the diet and contribute no nutritional value. Read labels to determine the amount of added sugar in food products. Choose lower calorie beverages.
Experiment with new food items. Try adding different fruits, vegetables, or grains to your diet. For example, try tropical fruits such as mango, guava, papaya, or grains as quinoa, barley, or millet, to add vitamins, minerals and fiber to the diet.
Before you go out to eat, don’t starve yourself. Drink water before the meal to avoid overeating or eat a snack before dinner and you won’t be tempted to overeat.
When socializing don’t meet at eating places. When you do dine out, cut out fried main dishes or ones with heavy sauces and gravies. Eat smaller portions and don’t go back for seconds. Order low-fat foods when possible. However, keep in mind that you too need to allow for indulgence along the way.
Be active! Physical activity has health benefits. Being physically active not only burns calories, it aids in physical strength, and cardiovascular health. U.S. Dietary Guidelines recommend being physically active at least 150 minutes a week for adults. (https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/).
Chances are, along with a healthy diet and regular physical activity, your tune up will result in living a healthy lifestyle.
https://www.freshfromflorida.com/Consumer-Resources/Buy-Fresh-From-Florida/Tropical-Fruit
https://www.tropicalfruitgrowers.com/
For further information, contact:
Dorothy C. Lee, C.F.C.S.
UF/IFAS Extension Escambia County
3740 Stefani Road
Cantonment, FL 32533-7792
(850) 475-5230
dclee@ufl.edu

by Angela Hinkle | Jul 18, 2019
Cold and refreshing on a hot summer day. Official by presidential proclamation. It practically saved my life once. Behold – The Power of Ice Cream.
HISTORY
Some say the Chinese invented ice cream in the first century. Roman emperors are also credited with flavoring ice gathered from mountain tops. Still others say ice cream found its start in the areas of Iran or Ancient Greece. Regardless of its origins, ice cream was often only available to royalty who could afford the resources to make it. Once refrigeration/freezing became affordable, the popularity and availability of ice cream rose considerably. So now, most of us – royalty or not – can enjoy the Power of Ice Cream all year long.
THE 411
- Ice Cream is made with greater than 10% milkfat.
- Gelato is generally made up of 7%-8% fat.
- Soft serve has more air mixed in.
- Frozen Yogurt is usually lower in fat and is often available soft-serve style.
- Sherbet freezes a combination of fruit juice with milk, cream, egg white, or gelatin.
THE 911
Picture it. Moving day. One of the hottest, most humid days of the year. The kind of day that you feel like you’re walking around in really warm soup. Though I’m staying hydrated, after about four hours in, it hits me. I go into a fog and literally start to go down to the ground. Luckily, my dad is pretty quick on his feet for a big Sicilian man. He puts me in the shade and says, “Don’t move!’ To this day, I don’t know how he did it so fast, but within two minutes, he got me the best cold ice cream dessert ever. The world was quickly righted as was I. Though this is NOT normal emergency protocol, it’s my miracle ice cream story and I’m sticking to it.
COOL TIDBITS

A cool and refreshing sweet treat
Photo Source: Angela Hinkle
- The United States leads the way in ice cream consumption, eating or licking or drinking about 48 pints or 23 pounds a year.
- President Ronald Reagan declared July National Ice Cream Month. The third Sunday in July, this year July 21st, is National Ice Cream Day.
- Though boasting 31 flavors, Baskin Robbins’ most popular flavor is vanilla.
- Because acquiring vanilla was so difficult before the mid-1800s, vanilla ice cream was considered quite an exotic treat.
- Sometimes, because nerve endings on the roof of your mouth suddenly get cold from eating ice cream, your brain tells the blood vessels, “Contract!” When they go back to their normal size, blood rushes back in. And ooh, “ice cream headache.” One recommendation to prevent this “brain freeze” is to eat slowly. And a recommendation to stop it is to put your tongue up to the roof of your mouth. Nothing guaranteed – so good luck.
- 15%-20% of Americans say they eat ice cream in bed. For more interesting ice cream trivia, visit foodreference.com
BENEFITS
Though not a particularly nutrient dense food, ice cream does have some health benefits. The area of your brain called the orbitofrontal cortex – or pleasure center – is activated when people are happy. Eating ice cream has been identified with having an immediate “happy” effect on the brain. There is also calcium in ice cream, which is good for building strong bones and teeth. Question – should all your daily calcium come from ice cream? Answer – Um, No. Try to choose more calcium-rich foods that are lower in fat and sugar.
So, in moderation of course, enjoy the Power of Ice Cream!

Cold, Delicious, and so many flavors! Photo source: Lyndsey B.
See Below for two healthier ice cream options. Yum!
MyPlate Sundae
This recipe includes all five food groups.
Layer in a clear glass bowl, mug, or cup so you can see all the colorful layers.
- Dairy – Gelato or frozen yogurt – your choice of flavor
- Vegetable – Frozen sweetened rhubarb or cooked, mashed, and cooled sweet potato
- Fruit – Most any berry works great
- Grain – granola
- Protein – Sprinkle on your favorite nuts
Cool and Creamy Calcium Dreamy
Serves 3
Items needed
1 – gallon heavy-duty ziptop bag
1 – quart heavy-duty ziptop bag
rock salt
ice
Procedure – In the 1 quart bag add the following:
¼ cup pasteurized liquid eggs
1 cup fat-free milk
1 cup fat-free half and half
½ cup sugar
1 teaspoon vanilla flavoring
Zip the top closed. Put the 1-quart bag inside the gallon bag. Pack the gallon bag with ice and ¾ cup of rock salt. Close the top. Work the bag back and forth – rolling over and over or tossing back and forth for 15 minutes. It may help to have potholders or a dish towel to hold the bag, as it will get very cold. Drain the water off and stir your cool and creamy calcium dreamy. Repack the gallon bag with ice and rock salt and roll or toss for five more minutes.
Serve immediately with fresh local fruits and nuts. Enjoy!
For more about the dairy food group see https://www.choosemyplate.gov/dairy

by Ginny Hinton | Jul 5, 2019
Summer has hit the Florida Panhandle with a vengeance this year! If you’re out in the heat it’s especially important to make sure to keep your body well-hydrated. After all, water is the single largest component of our body, and it’s essential for life.
Recommendations for how much to drink vary depending on several factors including your age, how active you are, how hot it is outside, what you’re wearing, and if you have certain medical conditions. A pretty good “ballpark” from the Institute of Medicine Food & Nutrition Board (IOMB) is to drink around 3 quarts of water a day for women and around 4 quarts for men. It’s important to start hydrating even before your feet hit the floor in the morning, because your body has been losing fluid while you slept. And if you can go more than 4 hours during the day without taking a bathroom break, you’re probably already dehydrated.

Water: Drink Up!
Photo Source: Ginny Hinton
Why worry about dehydration? In addition to making you more at risk of overheating, dehydration can affect a host of different organs and functions in your body. For example:
- Dehydration makes it harder for kidneys to flush toxins (poison) from your system, creating an infection-friendly environment.
- When you’re dehydrated, your blood becomes thicker and your heart has to pump harder to move it through your veins. This can lead to higher blood pressure.
- Dehydrated skin loses its elasticity and looks dry and flaky. Your sweat becomes more concentrated, making it harder for you to sweat as much as you need.
- Dehydrated joints are more brittle and more likely to become inflamed or damaged.
- When your body is low on water, it pulls too much liquid from the stool to use for other functions. That can cause constipation, in addition to inflammation throughout your body.
- Moist mucus membranes in the nose protect you from airborne allergens. Dehydration can dry them out and make you more vulnerable to irritating allergies.
- Dehydration makes you have less energy, and it also affects your mood and concentration. There’s a documented link between stress and dehydration.
The good news is that it’s easier to stay hydrated than you think. Water is a great way to hydrate, but it’s far from the only option. Watch the sugar and caffeine content when choosing other beverages, but milk, fruit juice, coffee and tea can all help you stay hydrated. The current guidelines to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks of caffeine intake are to drink no more than 1/3 to 4 cups of coffee per day (depending on the caffeine content) and 1 to 8 cups a day for tea. You can cut the sugar content but still have a tasty beverage by mixing half sweet tea with half unsweet, by mixing fruit juice with water, and by drinking flavored carbonated water with a splash of fruit juice to substitute for soda. Even food can help you stay hydrated! Watermelon, for example, is 90% water. Citrus fruits have a high water content as well, and vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers and lettuce pack a powerful hydration punch.
As you get out and enjoy Florida’s sunny summer weather, just be sure to keep hydration in mind. Your body will thank you for it!

by Judy Corbus | Jul 5, 2019

Visit places close to home for a vacation that won’t break the budget. (Photo source: UF/IFAS)
“Summer” and “vacation” seem to go hand-in-hand, as school is out and schedules are a little more laid back. Now that summer is here, you may be making plans for a getaway to your favorite spot. Perhaps, you are saving up for that dream trip next summer but you’d still like to take a break and have some fun this year. How can your family and you enjoy yourselves without breaking the bank? The answer might be right in your own backyard!
- Plan a staycation. Rather than traveling out of the area, use your home as base and plan some fun activities – family game time, camping out in the backyard and making s’mores, or running through the sprinklers and having a water balloon fight. Or just relax with a good book and a glass of lemonade or catch a few zzzs under a tree. The key is to turn off the devices, forget about work, and not worry about projects around the house – they will be there after you “return.”
- Plan day trips. These can be a part of your staycation, too. If you live fairly close to the beach, pack the car and head out early to enjoy the surf before temperatures rise. Make a day of it by enjoying the sunset before heading home. State parks also offer hiking and biking trails, boating and canoeing, swimming, playgrounds, picnic areas, and other fun activities. Florida boasts of 175 state parks, trails, and historic sites around the state so your next adventure may be just a short drive away. Check out https://www.floridastateparks.org/ for a park near you.
- Check out local events. Libraries and museums often feature special exhibits for free or a nominal charge. Several years ago, I visited a traveling exhibit about the Titanic at an arts center an easy drive from home. It made for an enjoyable and educational afternoon! Contact your local library or museum for a schedule of summer program offerings.
- Take part in a service project. A number of families are opting to use some of their vacation time to help others in need in their communities – projects include yard work, painting, basic home repairs, assisting with a food pantry/clothes closet, and serving meals to the homeless. These projects may be sponsored by a community service organization or church. During this past spring, local media outlets reported on several groups of college students representing campus ministries, fraternities, and other organizations who volunteered their Spring Break time to assist with Hurricane Michael clean-up and recovery. Participating in a service project as a family can be a meaningful way to give back to the community and make a difference locally. Contact your place of worship or local service organizations for opportunities in your area.
This summer, “recharge” without a super charge to your wallet!
Source: https://www.daveramsey.com/blog/i-need-a-staycation















