
by Samantha Kennedy | Dec 6, 2024
In the middle of the daily jungle of stressors, there lies a powerful antidote: nature. Research has shown time and again that spending time in green spaces can significantly reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. And here in Wakulla County, we are blessed with a variety of beautiful places where we can get close to nature.
Here are five ways in which nature works its magic on our minds and bodies:

Spending time with loved ones in nature has been shown to reduce feelings of stress, depression, and anxiety. (Adobe Stock photo)
Step into a forest and be greeted by a symphony of birdsong, rustling leaves, and babbling brooks. These natural sounds have a remarkable ability to soothe frayed nerves and calm anxious minds. Studies have found that exposure to nature sounds can lower levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, and promote relaxation. Additionally, the fragrances emitted by plants and trees, such as pine and lavender, have been shown to have therapeutic effects, reducing stress and anxiety.
The sight of lush greenery and expansive landscapes can have a huge impact on our mental well-being. Whether it is a sprawling meadow, a tranquil lake, or a majestic mountain range, natural scenery provides a visual feast that helps alleviate stress and elevate mood. Even a brief glimpse of nature through a window or a walk in the park during lunch breaks can rejuvenate the mind and enhance cognitive function.
Spending time outdoors exposes us to fresh air and sunlight, both of which are essential for our physical and mental health. Sunlight triggers the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and promotes feelings of happiness and relaxation. Additionally, exposure to natural light helps to regulate our circadian rhythms, leading to better sleep quality and overall well-being. Meanwhile, fresh air rich in oxygen boosts brain function and invigorates the body, providing a natural energy boost.
Engaging in physical activities such as hiking, gardening, or even just taking a leisurely stroll in the park allows us to reap the dual benefits of exercise and nature. Exercise is known to be a potent stress reliever, releasing endorphins that act as natural mood lifters. When combined with the calming effects of nature, physical activity becomes even more effective at reducing stress and improving mental health. Furthermore, outdoor exercise encourages mindfulness and promotes a sense of connection with the natural world, fostering feelings of peace and contentment.
Interacting with wildlife, whether it is watching birds soar overhead or spotting deer in the woods, fosters a sense of connection with the natural world. Studies have shown that spending time in nature and observing wildlife can evoke feelings of awe and wonder, which in turn reduces stress and increases feelings of happiness and well-being. Additionally, caring for pets or spending time with animals has been found to have therapeutic effects such as lowering blood pressure and reducing anxiety.
In conclusion, the healing power of nature is undeniable. By immersing ourselves in green spaces and reconnecting with the natural world, we can effectively manage stress, improve mental health, and enhance overall quality of life. So, the next time feelings of stress seem overwhelmed, consider taking a stroll in the park or escaping to the great outdoors.
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Suzanne Holloway | Aug 28, 2024
There always appears to be one person in every group that mosquitoes seem to flock. If you are that person, you know the frustration. While scientists do not fully understand why some people are mosquito magnets, increased knowledge of their preferences can help prevent bites and the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.

UF/IFAS Photo by Camila Guillen
Despite their tiny size, mosquitoes are the deadliest animal on Earth, claiming more lives than any other creature. They transmit diseases like dengue, yellow fever, Zika, malaria, and West Nile virus (WNV). West Nile virus is the most common mosquito-borne illness in the United States, with an average of 2,400 reported cases annually. Globally, malaria remains the leading cause of preventable death, with nearly 250 million cases and over 600,000 fatalities reported in 2022. Approximately 40% of the world’s population is at risk.
So what attracts mosquitos to certain individuals?
Several factors influence mosquito attraction. One study found that mosquitoes prefer the O blood type, but they do not avoid or dislike other blood types. Beyond blood type, characteristics such as odor, skin composition, body heat, and carbon dioxide play significant roles. Mosquitos are highly sensitive and drawn to specific chemicals in sweat – lactic acid, ammonia, and uric acid – which are influenced by diet, hygiene, health, and genetics. High levels of carboxylic acid, a fatty acid found in the skin, are also associated with attractiveness.
Those who exhale more carbon dioxide – namely, larger individuals – are more likely to be targeted by mosquitoes. They love the carbon dioxide aroma and can detect it from nearly half a football field away. Additionally, mosquitoes use thermoreceptors, heat-sensing organs, to detect changes in temperatures; they are attracted to higher temperatures, often targeting the extremities, head, and neck. Pregnant people are particularly attractive to mosquitoes due to their slightly elevated body temperature and hormone-related chemical changes in body odor. Furthermore, mosquitoes tend to prefer dark colors like black and navy – something to consider when getting ready during the hot summer months.
Understanding these factors can help individuals take steps to reduce their attractiveness to mosquitoes and protect themselves from serious diseases. Click for more information about mosquito repellents.
Sources:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
National Institutes of Health
Hartford HealthCare
Our Blood Institute
An Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Julie McMillian | Jan 13, 2022

Trees help to clean the air and provide a relaxing setting to reduce stress.
Photo credit: Anitra Mayhann
Do you know how vital trees really are? Trees conserve soil and water and clean the air. Research has shown that there are both mental and physical health benefits from forests. Trees provide us with oxygen through photosynthesis. Not to mention, think of the beauty they add to an area. Florida has celebrated Arbor Day for many years, since 1886 to be exact. It is the third Friday in January, whereas the National Arbor Day is the last Friday in April.
We can improve our health just by spending time outside in nature. Forests and trees can boost our immune system, reduce stress, increase our ability to sleep as well as boost energy levels while improving mood and helping us to focus. Studies in health care show a link between nature and health. Plants put off airborne chemicals called phytoncides to repel insects. The antifungal and antibacterial qualities that are put off in this process help us as we breathe them in by increasing our white blood cell count.
It is important that we remove ourselves occasionally from our office or home to explore green spaces to take a mental break. That might mean a walk in the forest, gardening, exercising, or resting and meditating to unplug from our fast-paced busy life. Many doctors encourage and incorporate this type of therapy for wellness for their patients and for children diagnosed with attention deficit disorder.
There are many ways to celebrate trees. They are a great gift for birthdays, holidays, or anniversaries. You might also consider planting a tree in honor of a family member who has passed on or to remember a beloved pet. This year, give a gift that gives back as well as be encouraged to celebrate Florida’s Arbor Day on January 21st, 2022.
Many holidays celebrate something we remember, but Arbor Day is a way to celebrate hope for the future by planting a tree to support a healthy community. I encourage you to check with your local government offices, Forrester, or Extension office to see if there are any special celebrations planned that you could join or plan your own activity to honor trees as a resource and how they impact your environment.
For more information, visit Arbor Day Foundation or Florida Urban and Community Forestry.

by Samantha Kennedy | May 13, 2021
I would like to continue on the theme of reducing food waste by talking more specifically about ways to use food scraps effectively to prevent them from ending up in the landfill.
As I was thinking about this topic, I was reminded of a funny scene from the 1982 film Night Shift, where Michael Keaton’s character, Billy Blaze, says into his tape recorder, “Idea to eliminate garbage: edible paper. You see, you eat it, it’s gone. Eat it, it’s out of there. No garbage.” Think about how much less waste would go into our landfills if we could just eat paper!
It is the same concept for food waste. As much as 40% of food grown, processed, and transported in the United States will never be eaten, destined to end up in the landfill. That is literally thousands of tons of food wasted each year. But what if we could help reduce that amount?

Got leftover veggie scraps? Instead of throwing them away, save them for a delicious veggie soup.
(Photo source: UF/IFAS)
Here are two great ideas for using leftover food scraps instead of throwing them away.
Cook with them. Leftover vegetables are great ingredients for a simple and delicious soup. Simply take the leftovers, combine them with an aromatic base of onions, garlic, and celery, add a liquid such as stock or broth (or water and white wine), throw in a generous helping of herbs, and cook for about 25-30 minutes. Then use an immersion blender or food processor (or stand-up blender) to blend into a creamy soup. Any type of vegetable works for this type of soup, from greens and cauliflower to parsnips and sweet potatoes, which makes it an ideal way to use up those scraps.
Another great way to use vegetable scraps is to make homemade stock. Vegetable parts such as carrot ends and peels, celery ends and greens, corn cobs, pea pods, and all the other bits trimmed off during food preparation can be used to make stock. Not in the mood to make stock right away? No problem! Veggie scraps can be saved in a zippered bag and kept frozen for up to six months.
When the time comes, simply dump the scraps into a large stock pot (that is why it is called a stock pot!) or Dutch oven, fill the pot 3/4 of the way with water, bring to a boil and simmer for at least 30 minutes. (The longer it simmers, the richer the flavor.) Strain it all through a sieve. The remaining liquid is the stock. Fresh stock can be stored 3-5 days in the refrigerator or frozen up to three months. Here is a simple resource from Cornell University Extension on how to make vegetable stock from kitchen scraps. (Here is another one from Tasty.co.)
Hold on! There are still scraps left over. What about those? Well, that brings me to the second great way to use kitchen scraps.

Food waste such as vegetable scraps can be added to compost to create a nutrient-rich fertilizer for home gardens.
(Photo source: Tyler Jones, UF/IFAS)
Compost them. Creating compost at home takes a little work and perseverance, but it can certainly pay off in the home garden. Nutrient-rich compost can add oomph to flower beds and vegetable patches and turn any garden into a showcase.
Vegetable scraps are perfect additions to any compost pile. Any vegetable scraps can be added to compost. Just remember to remove the little stickers, as those are not compostable.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), there are many benefits to compost. It enriches soil, helping retain moisture and suppress plant diseases and pests. It reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. And it encourages the production of beneficial bacteria and fungi that break down organic matter to create humus, a rich nutrient-filled material. These fact sheets (this one and this one) from UF/IFAS Extension are a wealth of information about home composting.
The reduction of unnecessary food waste begins with us, the consumers. By learning how to use those scraps in useful ways, such as cooking and composting, we can help eliminate the excess food waste filling our landfills.
UF/IFAS is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Heidi Copeland | Apr 7, 2021

Carrots
Photo source: Heidi Copeland
According to industry standards, some of these carrots could not be sold because of “Serious damage” or any defect which seriously affects the general appearance of the
carrots in the container.
Waste less, save money is a great creed to live by. Really, it is that simple. One excellent example of this is food. Research indicates that 40% of all food in America is wasted yet, one in eight Americans does not have enough access to affordable, nutritious food. In other words, they are “food insecure.”
Wasted food is a MASSIVE problem at the commercial, institutional and residential levels. In fact, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates there is more food than any other single material in our everyday trash and that approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption worldwide is lost or wasted. In fact, in 2015, the USDA joined with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to set a goal to cut our nation’s food waste by 50 percent by the year 2030.
The sad fact is, most people do not realize how much impact food and food waste has on the earth and its issues of sustainability. Food waste occurs at every level of involvement. Examples of food waste include growing, processing (by-products too), transporting, point of sale, plate waste and uneaten prepared foods, and kitchen trimmings and their eventual disposal. Preventing food waste at all these levels can make a difference in addressing this issue.
However, preventing food waste it is not as easy as it seems. Many consumer factors also contribute to the problem.
- Food date labels confuse people. Use by/sell by dates are not always about food safety but about peak quality. Many foods are still safe to eat after their dates. Inspect “expired” foods closely via sight and smell before consuming – find ways to use up food past its prime.
- Households overbuy – do you really need super sizes? Buying in bulk is not always less expensive if much of it is discarded. Only purchase what you know you will use and do not get lured in by the “more for less” deals.
- Massive portions are often served – share or learn to love leftovers. Split enormous portions into multiple meals.
- Grocery stores overstock their shelves to maintain an image of abundance.
- People demand “perfect” produce. Farmers have a hard time selling less than stellar items. “Ugly” fruits and vegetables are just as delicious and nutritious as their more photogenic counterparts. Places such as farmers’ markets and community gardens are good places to find imperfect produce that would otherwise go to waste.
This Earth Day, (an event first celebrated on April 22, 1970 in the United States and is now a globally coordinated event in more than 193 countries) commit yourself to taking an action. As the late Neil Armstrong famously quoted as he stepped on to the moon… “This is one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind!” If each of us considered and implemented our own practical or creative approaches to preventing food from going to waste what would our collective actions mean for mankind?

Fresh Carrots
Photo Source: Heidi Copeland
The best way to reduce food loss at home is not to create it in the first place. Not only would we individually save money, our collective efforts could conserve resources for future generations. The best method is the one you use.
- Reduce wasted food – shop smart, plan what you purchase, and use it, ALL of it!
- Maximize the efficiency of your refrigerator based on science. Read your refrigerator manual to learn where the coldest spots in the refrigerator are and what foods benefit from refrigerator location.
- Maximize the efficacy of canned products… use the FIFO (first in first out) method of rotation to use the oldest product before the newest on the shelf.
- Donate what you cannot use to others.
- Divert food scraps to animal food (chickens anyone?)
- Compost
- Landfill as the last resort.
Common causes of personal food waste include overbuying, over preparing and spoilage. The basic tenets of sustainability – reduce, reuse, recycle and refuse, work to reduce food waste too! Pay attention to purchases, eat what is prepared, store food properly, and refuse to waste. We can all do our part! Let’s start today.
https://savethefood.com/recipes/

by Andrea Albertin | Oct 11, 2020
During and after floods or heavy rains, the soil in your septic system drainfield can become waterlogged. For your septic system to treat wastewater, water needs to drain freely in the drainfield. Special care needs to be taken with your septic system under flood conditions.
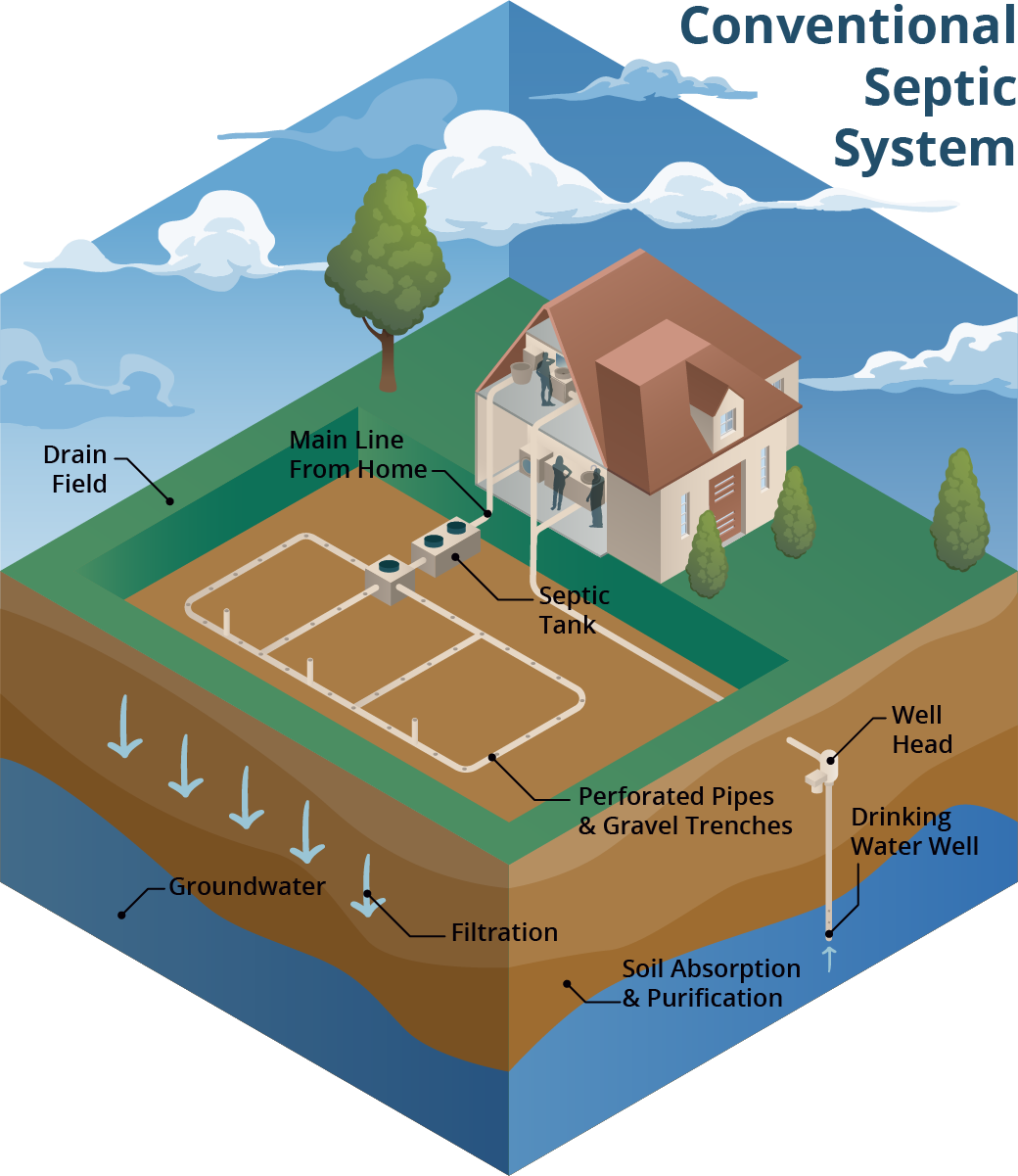
A conventional septic system is made up of a septic tank (a watertight container buried in the gound) and a drainfield. Image: Soil and Water Science Lab UF/IFAS GREC.
A conventional septic system is made up of a septic tank and a drainfield or leach field. Wastewater flows from the septic tank into the drainfield, which is typically made up of a distribution box (to ensure the wastewater is distributed evenly) and a series of trenches or a single bed with perforated PVC pipes. Wastewater seeps from these pipes into the surrounding soil. Most wastewater treatment occurs in the drainfield soil. When working properly, many contaminants, like harmful bacteria, are removed through die-off, filtering and interaction with soil surfaces.
What should you do if flooding occurs?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers these guidelines:
- Relieve pressure on the septic system by using it less or not at all until floodwaters recede and the soil has drained. Under flooded conditions, wastewater can’t drain in the drainfield and can back up in your septic system and household drains. Clean up floodwater in the house without dumping it into the sinks or toilet. This adds additional water that an already saturated drainfield won’t be able to process. Remember that in most homes all water sent down the pipes goes into the septic system.
- Avoid digging around the septic tank and drainfield while the soil is waterlogged. Don’t drive vehicles or equipment over the drainfield. Saturated soil is very susceptible to compaction. By working on your septic system while the soil is still wet, you can compact the soil in your drainfield, and water won’t be able to drain properly. This reduces the drainfield’s ability to treat wastewater and leads to system failure.
- Don’t open or pump the septic tank if the soil is waterlogged. Silt and mud can get into the tank if it is opened and can end up in the drainfield, reducing its drainage capability. Pumping under these conditions can cause a tank to float or ‘pop out’ of the ground, and can damage inlet and outlet pipes.
- If you suspect your system has been damaged, have the tank inspected and serviced by a professional. How can you tell if your system is damaged? Signs include: settling, wastewater backs up into household drains, the soil in the drainfield remains soggy and never fully drains, a foul odor persists around the tank and drainfield.
- Keep rainwater drainage systems away from the septic drainfield. As a preventive measure, make sure that water from roof gutters doesn’t drain towards or into your septic drainfield. This adds an additional source of water that the drainfield has to process.
- Have your private well water tested if your septic system or well were flooded or damaged in any way. Your well water may not be safe to drink or use for household purposes (making ice, cooking, brushing teeth or bathing). You need to have it tested by the Health Department or other certified laboratory for total coliform bacteria and coli to ensure it is safe to use.
For more information on septic system maintenance after flooding, go to:
More information on having your well water tested can be found at:
More Information on conventional and advanced treatment septic systems can be found on the UF/IFAS Septic System website














