
by Angela Hinkle | Oct 22, 2019
Delicious, nutritious, and super helpful for today’s needs, peanut butter is a great addition to your shopping cart. But it’s more than just a tasty and healthy food that also helps those in need (more on that below). Pound for pound, peanut butter saves.

Nutty for Peanut Butter
Photo Source: Angela Hinkle
Compared to a pound of ground beef, a pound of peanut butter saves:
- Money at the grocery store. A pound of peanut butter currently comes in at around $2.50. A pound of ground beef will run you around $3.82.
- Time. It takes about 2-3 minutes to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. A burger at home will take you anywhere from about 8-15 minutes to prepare.
- Environmental costs. If you make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich for lunch instead of a hamburger, you can save 2.5 pounds of carbon dioxide, 133 gallons of water, and 24 square feet of crop land.
- Saturated fat. That’s the kind that tends to clog up arteries and cause health problems. Eating the PB&J gives you about 3 grams. You consume about 10 grams of saturated fat in a 90% lean quarter pound hamburger.
- Utilities. No gas, coals, or electricity is required to cook or safely store peanut butter.
- Hunger. Families in hardship situations often need help from food pantries. The most requested item from these pantries is – yes, you guessed it – peanut butter. It is shelf stable so you don’t have to worry about keeping it cold or heating it up. People like it. And it is a healthy plant-based food with fiber and oleic acid – a healthier monounsaturated fat.
Maybe you’re like me – you like a really good, juicy all-beef burger. Every once in a while, sure. But pound for pound, peanut butter really can save the day.
Here’s how you can help with the local hunger part:
- Buy peanut butter. Look for BOGOS (Buy One Get One Free Sales). Keep one for yourself. Then…
- Now through November 27, donate unopened jars of peanut butter for the Peanut Butter Challenge. Check with your Florida Panhandle UF/IFAS Extension Office for collection sites.
- All collected peanut butter will be given to local food pantries to assist hungry families in need.
So save, save, save with peanut butter. And help save a family from hunger.
Check out 2019 Peanut Butter Challenge for additional information.
Resources: https://foodtank.com/news/2013/12/why-meat-eats-resources/ and https://www.farmprogress.com/peanut/peanut-s-environmental-footprint-stretches-beyond-farm
by Kendra Hughson | Oct 21, 2019

Most foods freeze well. Pancakes are easy to make ahead and freeze for later use. Photo Credit: Kendra Zamojski
You get home after a busy day and now it’s time to figure out what to make for dinner. You open the pantry and the refrigerator in a search for something to make for dinner. Maybe you can’t find the right ingredients or you don’t feel like cooking, so you pick up the phone to order delivery. A little planning ahead, could help you save money and make healthier choices.
Meals that you can make ahead and freeze are great to have on hand for use on busy days. According to the USDA, most foods can be frozen. Canned foods and shell eggs should not be frozen. This is because liquid expands when frozen and can cause shelled eggs and metal cans or glass jars to crack or break. Instead, remove canned foods from metal cans before freezing. To freeze eggs, beat together yolk and whites for better quality; egg whites can be frozen separately. Some foods don’t freeze well like mayonnaise, cream sauces, and lettuce. These exceptions aside, make ahead meals are easy to freeze and convenient to have on hand.
Cooking ahead doesn’t need to be complicated. Start freezing leftovers for later use or try doubling recipes when you are already cooking. Soups, stews, chili, casseroles, sloppy joes, and taco filling are easy recipes to experiment with batch cooking. Freeze in airtight plastic or glass containers or freezer safe bags or packaging. If you freeze foods in glass or plastic containers, leave 1-2 inches of head space between the food and the lid to allow room for expansion. Use labels to identify the frozen products, including the date and any cooking instructions. Store food in the quantities that you want to use for later. For example, whole casseroles can be reheated for family meals or soups and stews can be stored in single-serving quantities for quick and easy lunches. Freeze quickly for the best quality and to reduce freezer burn.
When it’s time to thaw, plan ahead. Do not thaw foods on the counter. Cook frozen foods immediately after thawing. Use one of the following recommended methods:
- Refrigerator: Small quantities can thaw in the refrigerator overnight. Larger quantities may take a day or two.
- Water method: Place in a sealed, leak-proof plastic bag and submerge in cold water. Change the water every 30 minutes, until thawed.
- Microwave defrosting: Defrosting in the microwave can cause some parts of the food to start cooking. Be sure to cook foods immediately after thawing.
- Cooking from a frozen state: Casseroles and other prepared foods can be cooked from a frozen state. Plan for extra cooking time by adding 15 to 30 minutes to the cooking time. Use a food thermometer to be sure it reaches an internal temperature of 165 degrees. Never place a frozen dish in a hot, pre-heated oven.This could cause the dish to crack or break.
If you enjoy experimenting with batch cooking, there are a lot of great resources for make ahead recipes and weekly meal plans. For more information, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office: http://sfyl.ifas.ufl.edu/find-your-local-office/
Sources:
Freezing and Food Safety: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/wps/wcm/connect/cce745c9-0fc9-4ce6-a50c-84363e5b5a48/Freezing_and_Food_Safety.pdf?MOD=AJPERES
Make Ahead Freezer Meals to the Rescue: https://extension.psu.edu/make-ahead-freezer-meals-to-the-rescue
Freezing Food for Multiple Meals: https://www.ksre.k-state.edu/humannutrition/nutrition-topics/eatingwell-budget/makeaheadmeals.html

by Laurie Osgood | Oct 11, 2019
Meatless Burger Alternatives

If you have been watching television lately, you may have seen commercials for meatless burgers that are making a splash. Many restaurants including Burger King and Red Robin are now offering this alternative meat source on their menus. https://www.bk.com/menu-item/impossible-whopper, https://www.redrobin.com/burgers/impossible-burger.html,
Beyond Beef™ and Impossible Burgers™ are two of the meat alternatives created by The Beyond Meat ™ https://www.beyondmeat.com/products/ and The Impossible Foods https://impossiblefoods.com/ companies. The Beyond Burger™ and Impossible Burger™ are similar in ingredients, color and texture, and they actually taste like…meat!
According to Emily Gelsomin, in the August 19th edition of Harvard Health Publishing, “Plant-based burgers are not a novel concept. But new products designed to taste like meat are now being marketed to vegetarians and meat-eaters alike”. Gelsomin suggests that meatless burgers are a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
But What Are They?
Keep in mind that meatless burgers are created in a lab, not in a pasture. Meatless burgers look, sizzle, and even “bleed” like a regular hamburger. But they contain no animal protein and are a completely plant-based patty. This plant-based protein is a blend of potato and soy proteins. Meatless burger alternatives get their red color and “bleeding” effect from beet juice. Meatless burgers sizzle while being cooked because of sunflower and coconut oils, the meatless burger’s fat sources. To hold everything together, meatless burgers contain methylcellulose, a bulk-forming fiber source.
Are Meatless Burgers Safe?
Yes, meatless burgers are safe to eat, unless you are allergic to soy, coconut or sunflower.
The Good News:
Meatless burgers contain less sodium, cholesterol and fat than traditional beef or ground turkey patties do. Meatless burgers contain 2-3 grams of fiber per serving, whereas traditional hamburger patties contain no fiber.
The Bad News:
Just because they are a plant-based alternative to meat, doesn’t mean that they are healthier for you. The calories found in a meatless burger are similar to a traditional beef patty and meatless burgers are heavily processed and high in saturated fat.
How Do These Meatless Burger Alternatives Compare Nutritionally to Ground Beef and Ground Turkey Patties?
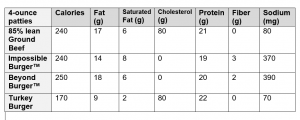
Source: Harvard Health Blog. Impossible and Beyond: How healthy are these meatless burgers? August 15, 2019.
The Bottom Line:
Meatless burgers such as The Impossible Burger™ and Beyond Burger™ are unique alternatives, although nutritionally not that different from a traditional hamburger patty. However, due to its popularity, companies such as Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat have struggled to keep up with the demand.
Contact your local Family & Consumer Sciences Extension Agent to learn more about meatless alternatives.
Sources
https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/impossible-and-beyond-how-healthy-are-these-meatless-burgers-2019081517448
Shopping for Health, Vegetarian Diets https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/FS/FS16700.pdf

by Heidi Copeland | Sep 13, 2019
The American chestnut tree, (Genus: Castanea dentata, Species: C. sativa, Family: Fagaceae) is a large monoecious deciduous tree. This big, beautiful tree provides green shade in the summer, a stunning array of fall foliage and a spinney cupule (bur) that holds and protects the chestnut during its growth and maturation. As its leaves begin to fall, so does the bur whereupon it splits and releases the chestnut. The American chestnut is important for both food and forage. This was of course until the American chestnut tree was devastated by chestnut blight-a fungal disease (Cryphonectria parasitica)) where upon it has been estimated that between 3 and 4 billion American chestnut trees were destroyed in the first half of the 20th century.

American/Chinese Chestnut
Photo Source UF/IFAS
However, through scientific research it has been discovered that the Chinese chestnut tree (Castanea mollissima) is recognized as being highly blight resistant (but not immune). Many places in the United States have replanted the American chestnut tree with the Chinese chestnut and its cultivars. In fact, there are several chestnut orchards.
The chestnut is classified as a nut.

Chestnut Tree
Photo Source: Vern Wilkins, Indiana University, Bugwood.org
However, it differs from most nuts, as it is low in lipid (fat) content – approximately three percent. Nonetheless, the chestnut is nutritious; it contains carbohydrates, proteins and is rich in vitamins and minerals. The mature chestnut (nut pulp) is more than 50 percent water thus special care must be taken to extend its storage so that it does not spoil.
Local, fresh chestnuts are generally only available in the fall. A good chestnut is fairly large, firm to the touch and feels dense. The USDA does not have any standards for grades of chestnuts although sometimes size standards are based on the number of nuts per pound.
According to the American Chestnut Foundation® if fresh chestnuts are to be stored for eating, store them in a paper grocery bag for up to two months. Leaving fresh chestnuts at room temperature for a few days helps their starches convert to sugar. For longer storage, put chestnuts in the freezer and use immediately after thawing or they will become mushy.
Chestnuts can be eaten in a variety of forms –
- Fresh – dry roasted or boiled
- Frozen
- Dried
- Canned
- Pureed
- Ground into flour (obtained by grinding dried and peeled chestnuts)

Three chestnuts inside the open but of the American Chestnut tree.
Photo Source: USDA Forest Service Southern Research Station, Bugwood.org
Cooking methods for chestnuts vary widely too. Customarily though, chestnuts are Dry-Roasted in the oven, over hot embers, on top of the stove in a skillet, or even in the microwave. Once peeled, the chestnut can be pureed, added to soups, stews, stuffing’s, and vegetable dishes or even turned into a decadent dessert.
- Heat a skillet on top of the stove or preheat the oven to 425° F
- Rinse the chestnuts in cold water. (this removes any bird droppings etc….)
- Using a sharp knife, score the flat side of each chestnut nut with “X”. (The chestnut is FULL of moisture, the “X” keeps it from exploding.)
- Using a roasting pan or skillet place the chestnuts in the oven, over an open fire, or on top of the stove.
- Dry roast, stirring every five minutes until the shells begin to split open. (At this point the shells are brittle and have curled back some at the X.)
- Remove from the heat when the insides feel soft. (This will depend on the nut but usually about 15 – 20 minutes.)
- Peel the shells off the chestnuts and enjoy warm or cold.
The internet contains a wealth of chestnut recipes. One I particularly enjoy is Chestnut Hummus. Instead of using your favorite bean, prepare a pound of chestnuts by either boiling or dry roasting.
When cool enough to handle toss all of the traditional hummus ingredients into a food processor and process until smooth. Serve in your favorite bowl drizzled with a bit of extra oil and favorite accoutrements.
Chestnut Hummus
1 pound prepared chestnuts
1 whole lemon, juiced
¼ cup tahini or 1/4 cup sesame oil
1-teaspoon cumin, whole or ground (or your favorite seasoning! – have you tried harissa?)
¼-cup oil
½ cup hot water, more if necessary to make a good spreading consistency
Salt to taste
Serve with your favorite accompaniments. (crackers, fresh sliced vegetables etc.)
Bon Appetite!

by Angela Hinkle | Sep 3, 2019
Hurricane season is June 1 to November 30, with peak season in September and October. And hurricanes are not the only disasters we have to contend with. Living Well in the Panhandle provides the trusted Disaster Resources you need so you know what to do to keep your family and you living well.
Disaster Resources
Below are helpful resources for preparing for and handling the aftermath of a disaster. For more information, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office.
Food Safety
Is My Food Safe to Eat?
Keeping Your Food Safe During Emergencies: Power Outages, Floods, and Fires
USDA – A Consumer’s Guide to Food Safety-Severe Storms and Hurricanes Guide
Well Water Safety
Well Water Testing
Housing
Search for an open emergency shelter near you by texting SHELTER and your zip code to 4FEMA (43362) Example: SHELTER 01234

Lightning storm. Photo Source: UF/IFAS
Cleaning Up After a Hurricane
Safety Comes First!
Get the Right Tree Care Professional
Hiring an Arborist – Spanish
Cleaning Mold After a Flood
Hurricanes and Mosquitoes
Mosquito Control Tips for Homeowners
Money Management/Consumer Issues
Avoiding Fraud and Deception
Six Steps in Making an Insurance Claim
Replacing Lost or Damaged Documents
FEMA – Individual Disaster Assistance
FEMA – Interim Housing Resources
USDA Farm Service Agency Disaster Assistance
Disaster Recovery Loans
Tax Relief After a Disaster
Complaints – If you have a complaint about disaster relief assistance, contact the Department of Homeland Security’s Inspector General’s Office at 1-800-323-8603.
Family Health and Wellness
Call the Disaster Distress Helpline 24/7 for free counseling – 1-800-985-5990 (TTY) 1-800-846-8517
OR text TalkWithUs to 66746
Mental Health for Adults
Mental Health for Kids
Mental Health for Adolescents
Agriculture and Natural Resources
Practices to Minimize Flooding Damage to Commercial Vegetable Production
Florida Panhandle Agriculture
Florida Panhandle Agriculture Facebook

by Stephanie Herzog | Jul 25, 2019

Eating fresh, local produce is a great way to be healthier, save money, and support the local economy. (Photo source: Stephanie Herzog)
Summer Local Eats – Supporting Farmers’ Markets
Summer is a great time of year to eat locally grown fresh produce! There are many options rich in a variety of colors, shapes, sizes, and nutrients. Farmers work hard to provide life-sustaining sustenance for society, and consumers supporting their efforts at the local level has an array of health and economic benefits.
Fresh summer crops in the panhandle abound. Produce that is ready this time of year includes peppers, cucumber, peanuts, okra, squash, corn, and watermelon. Spice up a summer salad with fresh cucumbers or peppers or try tasty yellow meat watermelon for a chill and nutritious summertime snack! Local, fresh produce is a healthy alternative to processed foods or produce found in grocery stores. Produce sold by local farmers is freshly picked and because you know where it comes from, it is both safer to eat and keeps for longer periods of time than grocery store produce, which often has traveled long distances, is seldom inspected, and is kept in storage before finally being put out on the floor for purchase.
Supporting your farmers’ market benefits both you and your community in many ways. Purchasing from local farmers and farmers’ markets is both financially sound for you and is supportive of the community’s economy – the money changes hands locally and creates and maintains jobs. Not only does it benefit the economy, it also fosters a stronger sense of community unity and trusted relationships, which is vital to any successful society and local economy. For example, farmers will sometimes offer a “u-pick” program, depending on the crop, where you go to their farm and pick what produce you want right from the field! You get to keep half, and the farmer keeps half. This is a great cooperative effort that benefits everyone – you get free, fresh produce, and the farmer gets free labor. Who doesn’t love a win-win scenario?
Jackson County farmers’ markets information. Residents in Jackson County have a wonderful farmers’ market in the heart of downtown Marianna, located at Madison Street Park (2881 Madison St.) that goes throughout the summer every Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday morning from 7am-12pm. After September, the market will continue through the fall, winter, and spring each Saturday at the same time. Tuesday and Thursday have farmer vendors only, while Saturday includes a variety of vendors, such as arts and crafts, plants and flowers, jams, jellies, honey, etc. This market also offers a raffle when you purchase items from vendors! For any questions about the market or how to join as a vendor, visit their Facebook page or contact Tony Mayo, the current farmers’ market manager or Terry Johnson, the public relations manager for the market. His number is 850-592-5114. It’s a good idea to bring cash or checks, but some vendors do accept credit and debit cards.
Want to find a farmers’ market near you or learn more about the benefits and best practices shopping at a farmers’ market?
Come experience the buzz and benefits of the farmers’ market!
Sources:
Local farmers at the Marianna City Farmers’ Market
Wang, Q., Evans, E. A., Pikarsky, M., & Olczyk, T. Consuming local vegetables from our local growers. UF IFAS publication HS1251.
















