Plant-parasitic nematodes can drastically suppress cotton yield, often without noticeable above-ground symptoms. For this reason, nematode management is an important part of a successful operation. Nematicides, pesticides that target nematodes, can be a useful component of a nematode management program, particularly when nematode pressure is high.
In 2016, my first field season in Florida, I had the opportunity to evaluate nematode populations in 3 nematicide trials set up by Dr. David Wright’s lab. These trials tested a relatively new non-fumigant nematicide (stays as a liquid or solid not a gas), Velum Total (active ingredients fluopyram for nematodes, imidacloprid for insects), that is applied as a liquid spray in-furrow at planting. All three trials were conducted at the North Florida Research and Education Center in Quincy, Florida. There was high pressure from reniform nematode (Rotylenchulus reniformis) in all three studies.
Two trials were industry-sponsored. Trial 1 included combinations of a basic seed treatment (BB in Figure 1), Velum Total in-furrow nematicide (VT), Aeris insecticide/nematicide seed treatment (AE), Admire Pro in-furrow insecticide (AD), and Velum seed treatment (VS). (Admire contains imidacloprid and Aeris contains imidacloprid and thiodicarb.) Deltapine 1538 was also a treatment. Other plots were planted to Stoneville 4747. Nematode counts were taken around harvest for all trials. There were no statistical differences between treatments, but reniform nematode populations tended to be less with Velum Total treatment. Treatments did not significantly affect yield with lint yield ranging from 662 to 835 lb/A.
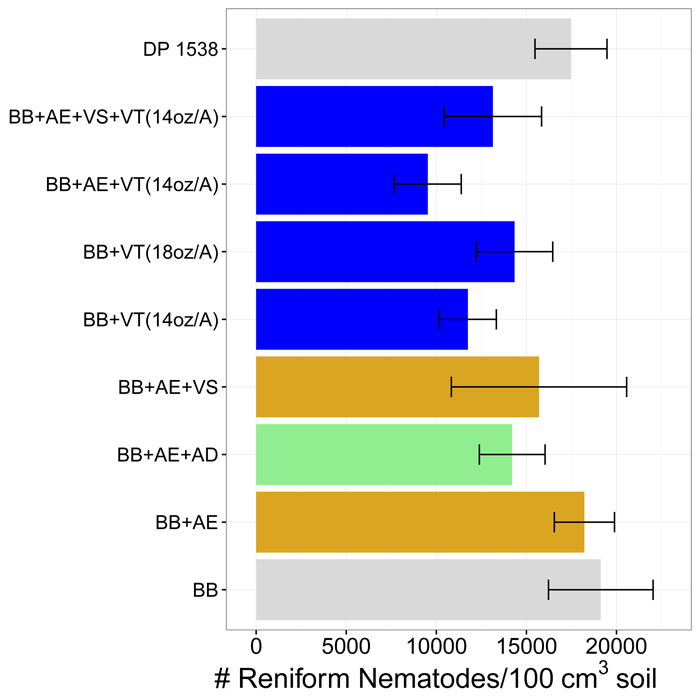
Figure 1. Reniform nematode population densities around harvest in industry Trial 1 as affected by nematicide treatments. VT=Velum Total in-furrow, AE=Aeris seed treatment, AD=Admire Pro in-furrow insecticide, VS=Velum seed treatment, DP 1538=Deltapine 1538
The second industry trial included all the products & varieties from Trial 1 plus a root-knot nematode-resistant variety (DP 1558). There were statistically significant differences in this trial (Figure 2). Treatments with the same letter are not significantly different. Some rates of Velum Total decreased reniform nematode density compared to other treatments, but there was not a consistent trend. Nematicide treatments did not affect yield, which ranged from 736 to 927 lb/A.
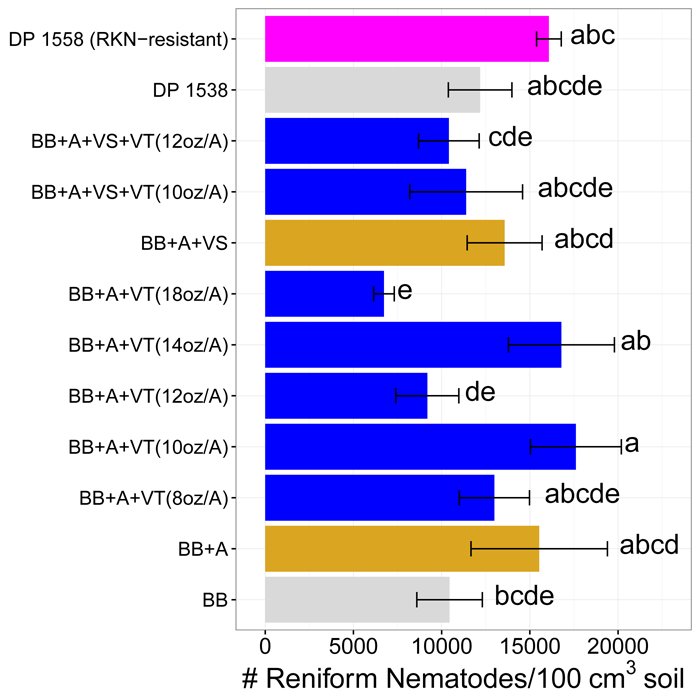
Figure 2. Reniform nematode populations around harvest in industry Trial 2 as affected by nematicide treatments. VT= Velum Total in-furrow nematicide, AE= Aeris seed treatment, AD= Admire Pro in-furrow insecticide, DP 1538= Deltapine nematode susceptible variety, DP 1558= root-knot nematode-resistant variety
The third trial was conducted in the sod-based rotation research plots. In that trial, cotton in a conventional rotation (cotton-cotton-peanut) and sod-based rotation (cotton-peanut-2 years bahiagrass) were compared with and without Velum Total nematicide. Velum Total application did not affect reniform nematode population densities around harvest (Figure 3), regardless of rotation scheme. Similarly, cotton yield was not affected by Velum Total application (1,050 and 1,100 lb lint/A).
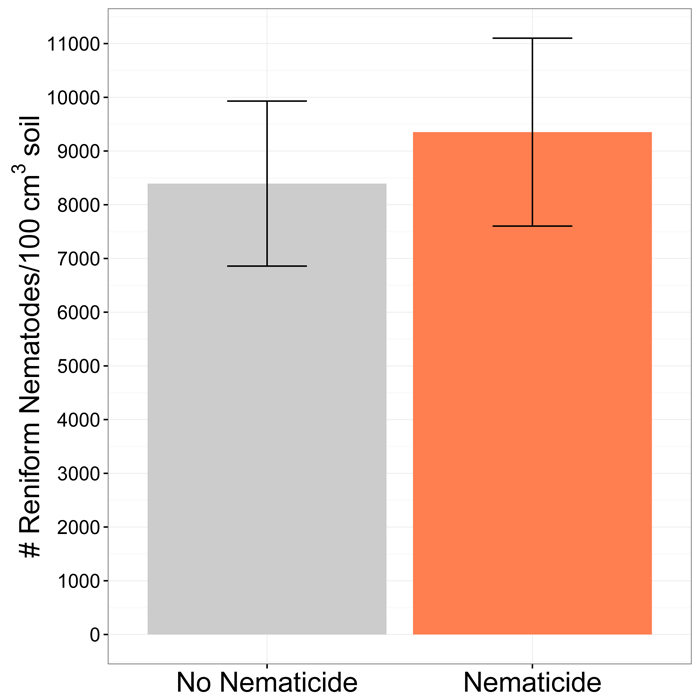
Figure 3. Reniform nematode populations around harvest with and without Velum Total nematicide. Includes cotton in conventional and sod-based rotations.
To summarize, there was some evidence that Velum was helping reduce reniform nematode populations, but there wasn’t any sizeable yield benefit. Further research is needed before any definitive conclusions about Velum benefits in Florida are made though, particularly because these are only results for one year in one location. Further trials testing nematicides in cotton production are planned for the 2017 season, including an on-farm trial in Jackson County comparing the main nematicides available for Florida cotton producers.
There are a few nematicides available for cotton in addition to Velum Total. Among fumigants, pesticides that move through the soil as a gas, 1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone II and other products), metam sodium (Vapam and others), and metam potassium (K-Pam and others) are available. Among non-fumigants, there is a new aldicarb product (the active ingredient in Temik) called AgLogic 15G. AgLogic is federally labelled for cotton, but is not registered for sale or commercial transportation to Florida for the 2017 season. Growers who are able to buy AgLogic in a state where it is registered, such as Georgia, and transport it to Florida themselves are allowed to apply it in Florida cotton in 2017. All of these nematicides are restricted use pesticides, so only certified pesticide applicators can purchase or apply them and all label requirements as well as state-specific requirements must be followed.
For further information about nematodes that attack cotton and how to manage them, use the following link to the UF/IFAS EDIS fact-sheet:
Management of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Florida Cotton Production
- Salibro: A Recently-Registered Conventional Nematicide for Select Horticulture Crops - March 7, 2025
- What Cotton Cultivars have Resistance or Tolerance to Southern Root-knot and Reniform Nematode? - February 28, 2025
- How Well Do Root-Knot Nematode Resistant Peanut Cultivars Perform in Florida? - February 14, 2025
