Plant-parasitic nematodes are a major yield-limiting pest in potato production in Florida. Nematicide application is one of the main management strategies available to growers in potato production. (Harvesting potatoes in Hastings, Florida. UF/IFAS)
Plant-parasitic nematodes are a major yield-limiting pest in potato production in Florida. Nematicide application is one of the main management strategies available to growers in potato production. In recent years, new nematicide chemistries have been developed and these products are becoming available to growers. This article summarizes results of work with new and old nematicides over the past 3 years at the Hastings Agricultural Extension Center. Work in 2016 and 2017 was conducted by Dr. Joe Noling, UF/IFAS professor emeritus and Dr. Noling collaborated on work in 2018.
Trial Layout
In 2016, 2017, and 2018, a trial comparing Nimitz (active ingredient fluensulfone), a non-fumigant registered for use in potato this year, at various rates with the commercial standard Telone II (1,3-dichloropropene) and an untreated control, was conducted.
| Table 1. Nematicide treatments for trial conducted in 2016, 2017, and 2018 | ||
| Treatment Number | Product | Rate |
| 1 | Nimitz | 2.5 pints /acre |
| 2 | Nimitz | 3.5 pints /acre |
| 3 | Nimitz | 5.0 pints /acre |
| 4 | Nimitz | 7.0 pints /acre |
| 5 | Telone II | 6.5 gal/acre |
| 6 | Untreated Control | —— |
In 2018, a trial was also conducted to compare a range of nematicides available on the market (Table 2).
| Table 2. Nematicide treatments for trial conducted in 2018 only. | ||
| Treatment Number | Product | Rate |
| 1 | Nimitz | 5.0 pt/ acre |
| 2 | Mocap EC | 1.5 gal/acre |
| 3 | Velum Prime | 6.8 oz/acre |
| 4 | Telone ll | 6.5 gal/acre |
| 5 | Vydate C-LV | 2 gal/acre |
| 6 | Untreated Control | — |
Nimitz, MoCap EC (ethoprop), and Velum Prime (fluopyram) are liquid products that were applied with a boom 3 weeks before planting and incorporated with rotary tillage. Telone fumigant was inject in-row 3 weeks before planting. Vydate C-LV (oxamyl) was sprayed in a band in the seed furrow followed by 3 foliar sprays. Treatments were applied to 100’ plots with 4 rows at 40” row spacing. There were 6 replicates in each trial. Soil abundances of plant-parasitic nematodes were counted before planting and at harvest, and tuber yield was measured. Sting nematode was the primary plant-parasitic nematode present in the trial.
Results of Nimitz rate trial 2016-2018
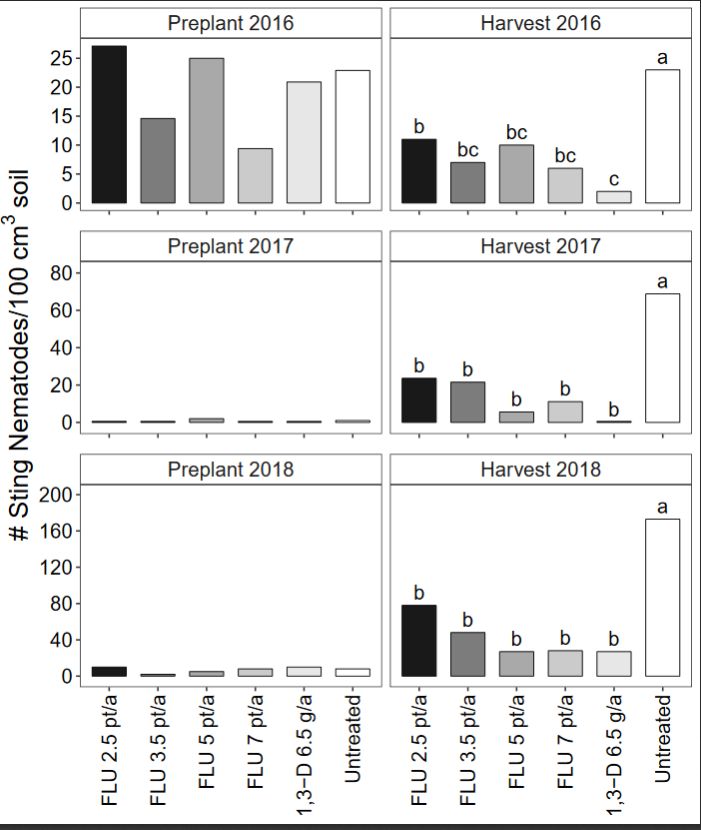
In all 3 years of the Nimitz rate trial, all rates of Nimitz and Telone significantly reduced sting nematode abundances at harvest relative to untreated control (Fig. 1). Nematode management was better with Telone than Nimitz at 2.5 pt/a in 2016, but Nimitz and Telone performed similarly in all other cases.
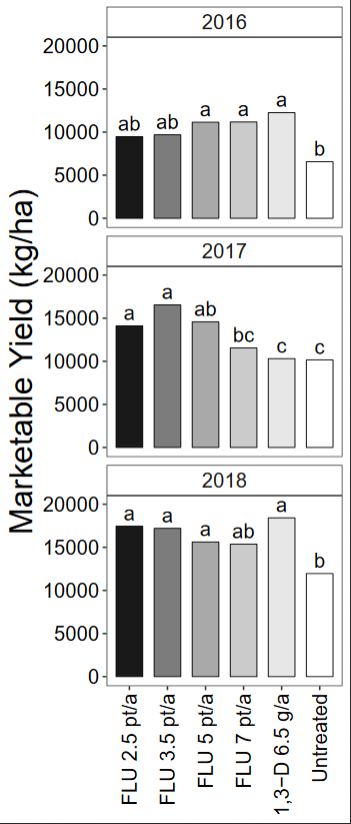
The influence of nematicide treatments on potato yields varied somewhat from year to year (Fig. 2). In 2016, higher rates of Nimitz (5 or 7 pt/a) and Telone increased marketable yield compared with untreated control. In 2017, lower Nimitz rates (2.5, 3.5, or 5 pt/a) increased potato yield, but high rates of Nimitz (7 pt/a) and Telone had yields similar to untreated. Phytotoxicity is a potential explanation for reduced yields with Nimitz at 7 pt/a and Telone, although no specific symptoms were observed. In 2018, all Nimitz and Telone treatments increased tuber yield except Nimitz 7 pt/a, which was similar to untreated.
Results of 2018 commercial nematicides trial
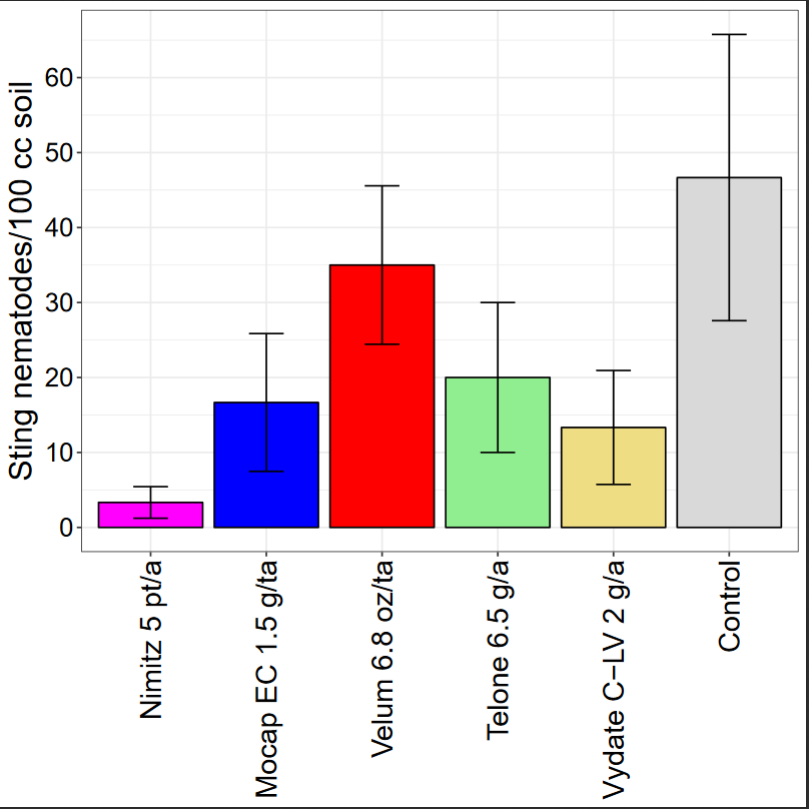
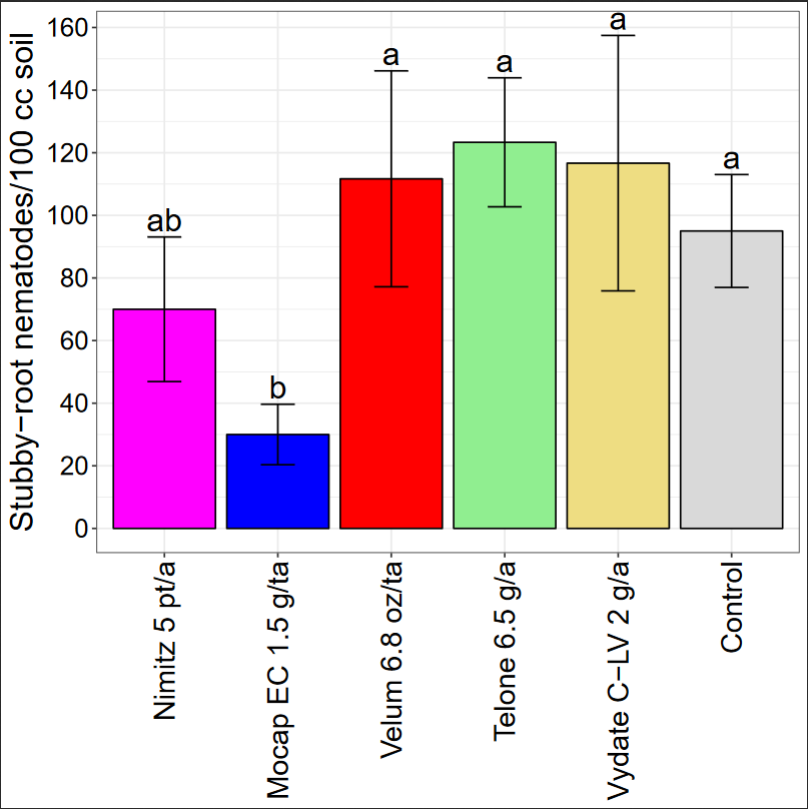
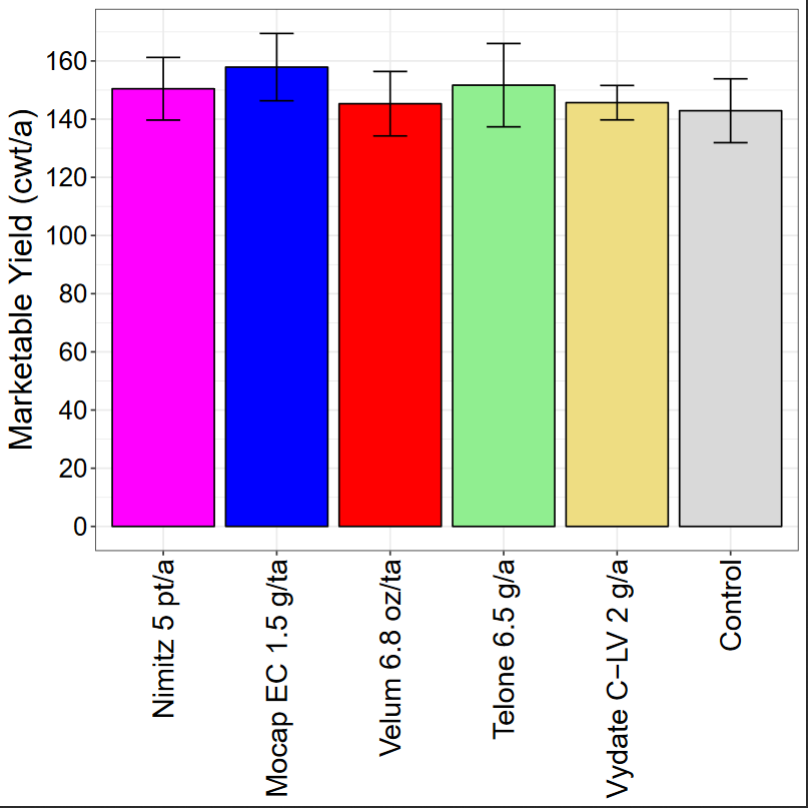
In the 2018 trial testing various nematicides, none of the products significantly reduced final sting nematode abundances compared with untreated control although strong numerical trends occurred (Fig. 3). Only Mocap significantly reduced stubby-root nematode abundances relative to untreated control (Fig. 4). Nematicide treatments did not affect marketable potato yield (Fig. 5). This suggests that nematode pressure was too low to affect yield in this trial.
Summary and action items
In summary, Nimitz shows promise for effectively managing sting nematodes and increasing potato yields when used at the optimum rate. Telone also continues to be an effective option. Due to relatively low nematode pressure in the 2018 trial, further testing is needed to determine the efficacy of other relatively new (Velum Prime) or returning (Vydate) products.
Action items: 1. Determine nematode pressure by taking soil samples, preferable while a prior crop is still growing, when considering nematode management, including nematicide application. 2. Consider UF/IFAS research results when choosing a pesticide. 3. Integrate multiple forms of management into your nematode management plan including nematicide application, crop rotation, and weed management.
For more information on nematode management in Irish potato see the UF/IFAS publication, Nematode Management in Potatoes
- Salibro: A Recently-Registered Conventional Nematicide for Select Horticulture Crops - March 7, 2025
- What Cotton Cultivars have Resistance or Tolerance to Southern Root-knot and Reniform Nematode? - February 28, 2025
- How Well Do Root-Knot Nematode Resistant Peanut Cultivars Perform in Florida? - February 14, 2025