
by pmdavis | Sep 14, 2023

First meeting is Sept 26th at 5:30 EST
I am so thrilled to let you know about a new endeavor with Florida 4-H. We are trying a virtual Food Challenge cooking club this year. This is so exciting for me because some of my fondest memories are cooking with my grandmother and Mom. I got to learn how to prepare foods and be creative as I was growing up pulling on their apron strings. I also enjoyed teaching and sharing these skills with my own children. What makes this even better is now I get to share and learn with all of you who join our program.

Paula and Madelyn Cooking together
By joining the new Virtual 4-H Food Challenge Club, you will embark on a fun, yet challenging, food-focused adventure right from the comfort of your kitchen! The club adventure will provide a fun atmosphere for you and your children to have a family time experience building lasting memories together. With the help from Florida 4-H Youth Development Faculty, you will get to unleash your culinary creativity and try delicious recipes while learning kitchen skills from safety, nutrition, and other food related life skills. Families will learn about competitive events related to foods like the Florida Food Challenge Competition. Families will also have the opportunity to make friends with fellow 4-H members across the state.
The virtual club is open to youth members ages 8-18 and will meet once a month starting in September. The club will meet via ZOOM on the following Tuesdays: September 26th, October 24th, November 28th, December 19th, and January 23rd from 5:30 – 6:30 PM ET. We request that adult supervision is present with the youth during the meeting and home practice sessions. The participants will be asked to gather a list of supplies for each monthly meeting as we focus on a new skill for each meeting.

Paula’s family working with herbs to prepare a dish.
During this course we will help families enjoy preparing food, provide you with opportunities to problem solve together and work as a family team as practice preparation for the Florida 4-H Food Challenge! If you join us, your family will learn how to prepare and create yummy dishes with a predetermined set of ingredients. By the end of the program, your family should have some new recipes for your cooking toolbox, learned essential cooking skills and created wonderful memories from your time together. Do not miss this flavorful opportunity – sign up now via Florida 4-H Online and get cooking with 4-H! If you are not a member of a current 4-H Club there is a $20 membership fee associated with this club. If you are unable to join our virtual club, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office to see if there is an active Food Challenge group that you can join. If not, work with your 4-H or FCS Agent(s) to identify two caring adults who could fill this role.
Enroll, Grab your ingredients, and get ready to join us via Zoom on September 26th@ 5:30 EST
by Marcus Boston Jr. | Apr 26, 2023
Youth shows and fairs provide a valuable opportunity for young people to develop a wide range of life skills. From responsibility and communication to planning and organization, these events offer a unique learning experience that can help young people build important skills for success in all areas of life.
Can a youth’s participation in County fairs and Shows help to develop them into responsible adult? The answer is yes! The Florida 4-H Program seeks to be inclusive to all youth by using a variety of vehicles to teach youth life skills in traditional and non-traditional settings. A recent article in The Journal of Extension by Oregon State professionals found that “having fun” “spending time with friends” and “teamwork” were the highest-rated motivators for youth that participated in fairs.
The study also revealed that participation in fairs through 4-H had a significant positive effect on participants’ levels of caring, contribution, and character. These characteristics are also part of the Essential Elements of 4-H that youth experience by being in an active 4-H program throughout the year. Those elements are Belonging, Independence, Generosity, and Mastery.
One of the most important skills that youth learn through participation in youth shows and fairs is responsibility. Whether they are caring for animals, plants, or other projects, youth must take on the responsibility of ensuring that their projects are healthy, well-cared for, and ready to be presented to judges and visitors.
 Communication is another key skill that youth develop through participation in youth shows and fairs. Through active participation youth learn the ability to articulate complex ideas, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully to questions and feedback.
Communication is another key skill that youth develop through participation in youth shows and fairs. Through active participation youth learn the ability to articulate complex ideas, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully to questions and feedback.
In addition to these skills, youth shows, and fairs also emphasize important values such as sportsmanship and fair play. Participants are encouraged to respect their competitors, accept both victories and defeats graciously, and uphold the highest standards of ethical behavior. This helps young people develop important social skills, including the ability to work collaboratively with others and build positive relationships.
Finally, participation in youth shows and fairs can help young people develop resilience and perseverance in the face of challenges and setbacks. These events can be competitive and stressful, but they also offer opportunities for young people to learn from failures, bounce back from disappointments, and remain motivated to achieve their goals.
A few of the Florida 4-H Shows and Fairs are as follows:
-
- State 4-H Dairy Show Okeechobee March
- 4-H Chick Chain Show Chipley April
- Area North Horse Show Green Cove Springs May
- North Florida Fair Tallahassee November
*For additional opportunities to participate in 4-H Shows and fairs please contact your local 4-H office.
In conclusion, participation in youth shows and fairs can offer a unique and valuable learning experience for young people. By developing important skills such as responsibility, communication, planning, and organization, as well as important values such as sportsmanship and fair play, youth can build the foundation for success in all areas of life.
References:
More information on this study can be obtained by visiting the Journal of Extension at www.joe.org and viewing volume 45, number 6.(Arnold, Meinhold, Skubinna, and Asthton)
by Heather Kent | Feb 10, 2023
 One of the things I love about 4-H is that it offers so many different opportunities for youth to learn leadership skills while pursuing and exploring their sparks. And leadership roles are not confined to the club level- there are opportunities for youth to serve at the district, state, and even national levels. Youth leaders are grown, not born. And just like any living thing, they must be nurtured over time in an intentional way to develop strong leadership skills. This article will describe what a strong youth leadership team looks like and provide some resources to help grow your team. Over the years, I have had the privilege of working with some amazing youth leadership teams at all levels of the 4-H organization. But it was something that we had to cultivate over time- we didn’t start out as a high-functioning team. A strong youth leadership team can be identified by the following five characteristics (download this graphic):
One of the things I love about 4-H is that it offers so many different opportunities for youth to learn leadership skills while pursuing and exploring their sparks. And leadership roles are not confined to the club level- there are opportunities for youth to serve at the district, state, and even national levels. Youth leaders are grown, not born. And just like any living thing, they must be nurtured over time in an intentional way to develop strong leadership skills. This article will describe what a strong youth leadership team looks like and provide some resources to help grow your team. Over the years, I have had the privilege of working with some amazing youth leadership teams at all levels of the 4-H organization. But it was something that we had to cultivate over time- we didn’t start out as a high-functioning team. A strong youth leadership team can be identified by the following five characteristics (download this graphic):
- Clarity

- Cohesiveness
- Communication
- Confidence
- Collaboration
Clarifying the roles of each team member
It’s essential that everyone in the group understands their role and that they have something valuable to contribute to the team. Youth are usually pretty quick to understand their role- often it involves planning an event or solving a community issue through service learning. But the roles of the adults are much vaguer. Some adults view the role as advisory the same way they would a dictator. They want to tell the youth what they should do when they should show up, and how to do everything. But as advisors, our role is to empower youth- make sure they understand their role, and that they are cohesive, or have ground rules for how the group will function.
Establishing a sense of cohesiveness
Once everyone is clear about their roles on the team, the group needs to establish ground rules, or group norms to create a sense of cohesiveness. If the adult mentor sees the group wandering away from the group norms, then it is their job to call the youth out on it and bring them back to a more cohesive state. Not too long ago, I was working with a group of teens to plan a retreat. We had a new member who was constantly putting down other youth’s suggestions. The group got quiet except for the outspoken youth. It was my job to remind everyone that one of our group norms is that each person gets an opportunity to speak, and we don’t put down others’ ideas. Holding the group accountable for these group norms keeps the group cohesive and focused, which is essential for building the next characteristic, communication.
Communication
Leadership teams are a great place for youth to practice communication skills- particularly if they are nervous about speaking in front of large groups. Typically the youth leading the team is responsible for making sure everyone is recognized and heard. However, some youth might need encouragement to speak up- that’s when the adult advisor can help! It is also important to discuss how the team wants to communicate outside of meeting times- reminders about meetings, or any other issues that might come up in-between meetings. As the advisor, make sure everyone comes to a consensus on how and how often the team wants to communicate within meetings (and outside of meetings). As youth become more comfortable with communicating, their confidence will grow.
Confidence
When the members of your youth leadership team are clear about their roles, are cohesive in their approach to leadership, and communicate well with each other, they will be empowered to lead. Teams that are empowered understand that every person on the team has something to contribute. As adults, it’s often easier to just “do it ourselves,” but instead we need to empower youth to take responsibility for a different part of the program the youth are leading. However, we do need to make sure they have the information and tools they need to be empowered. For example, if they want to do an activity they have little experience with, such as sewing dog toys for a pet shelter, connect them with people who have experience and expertise with that type of activity.
Collaboration
The ultimate characteristic of a strong leadership team is collaboration. It is the combined effect of the other four characteristics working together in unison. The collaboration stage is also when youth become role models- not only for other youth but for adults as well. And that is when organizations begin to grow. People will be curious about why and how your youth are working so well together.
Additional Resources:
The UF IFAS publications listed below are free downloads that include hands-on, experiential activities you can do with your youth to help build a strong leadership team:
The best-selling book 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teens written by Stephen Covey is a must-read for any 4-H faculty, staff, or volunteer working with teen leaders.
- Covey, S. (1998). The 7 habits of highly effective teens: the ultimate teenage success guide. New York Simon & Schuster.
by Heather Kent | Aug 29, 2022
 We are excited to announce registration for our 2023 Northwest Florida 4-H Volunteer Forum will open on October 15th! This post contains all the details about our event- who, what, when, where, and how. We hope you will plan to join us for an inspirational Friday night and Saturday as we connect with each other, learn together, and share our successes. Our theme is “Navigating the World of 4-H.” Together, we will learn about empowering youth, inspiring hope, and helping young people reach their full potential.
We are excited to announce registration for our 2023 Northwest Florida 4-H Volunteer Forum will open on October 15th! This post contains all the details about our event- who, what, when, where, and how. We hope you will plan to join us for an inspirational Friday night and Saturday as we connect with each other, learn together, and share our successes. Our theme is “Navigating the World of 4-H.” Together, we will learn about empowering youth, inspiring hope, and helping young people reach their full potential.
WHO
|
Our volunteer forum is for teen and adult volunteers leading and supporting 4-H clubs, groups, or programs in the northwest Extension district. |
WHAT
|
A weekend (Friday night and Saturday) event full of inspirational speakers, hands-on workshops, and opportunities to connect with and support other volunteers! Topics were identified based on last year’s forum participants’ feedback. Feel free to download the agenda and informational flyer. This post highlights some of the activities you won’t want to miss:
Friday night kicks off with our “Make and Take” Fair. Try out a wide variety of fun and exciting 4-H activities you can use with the clubs or groups you work with. Each time you visit a station, you can get your “passport” stamped! There will be selections to support all three 4-H pillar project areas- Healthy Living, STEM (science), and Citizenship/Leadership. During the Make and Take Fair, heavy hors d’oeuvres will be served and you will have the opportunity to test out the activities and take home samples and instructions to share with your youth, parents, and other volunteers.
After the make-and-take fair, we will have a fun icebreaker, and Dr. Stacey Ellison, our 4-H Program Leader, will speak and give a “state of 4-H” update and share strategies for inclusion and diversity. Volunteers are encouraged to network and mingle after her address.
Saturday morning will inspire! Gulf County 4-H Alumnus and best-selling author, Cedric Lennox, will share how his Florida 4-H experiences taught him about youth empowerment and how we can all be “Dealers of Hope.”
Following the keynote address, volunteers will be able to select from a variety of workshops:
- Road Map to Parliamentary Procedure
- Charting a Successful Sports Fishing Project
- Culinary Adventures with the 4-H Food Challenge
- Trek through Teambuilding
- Tour of 4-H Gardening Project
- Smooth Sailing with Cloverbuds
During lunch, connect with other volunteers who have similar interests as you to start building a community of practice for your 4-H clubs and groups! Dr. Jenny Jordan will share expert tips for Experiential Learning (or learn-by-doing).
After lunch, there will be more workshop selections for volunteers to choose from:
- Guide to 4-H Awards, Recognition, & Portfolios
- Voyage through the 4-H Clothing & Textiles Project
- Hike through the “Big Book of Cloverbuds”
- Survey of Service Learning
- Expeditions in Entomology
- A Mindfulness Pilgrimage
We will close our forum by sharing some exciting new resources- including a fundraising toolkit for 4-H volunteers (and more door prizes!). |
WHEN
|
January 20-21st. |
WHERE
|
Embassy Suites in Destin, Florida. No need to make a reservation- your registration is your hotel reservation confirmation! |
HOW
|
Registration opens in 4Holine on October 15th. The deadline to register is Friday, January 6th. Check with your local UF/IFAS Extension office to inquire about carpooling to and from the event. Dress for the weekend is casual (and comfortable)- we will be at the beach! |
HOW MUCH
|
Thanks to donations from the Florida 4-H Foundation and other partners, the registration fee for individuals sharing a suite with another volunteer is $100. The registration fee for a private suite is $150. The registration fee includes the room fee, a conference welcome bag, magnetic name tag, heavy hors d’oeuvres Friday night, breakfast and lunch on Saturday, plus workshop and make-and-take supplies. Many counties are offering scholarships, so please check with your local UF/IFAS 4-H Extension Agent about additional funding. |
by Niki Crawson | Aug 26, 2022
 Joining a new group of individuals can be nerve-wracking for some that may be shy or intimidated by large groups. Incorporating team-building activities into your 4-H clubs and activities is a great way for 4-H members, new and returning, to form a connection with each other and will help set the tone for that particular group setting and/or event. In this post, we’ll provide tips to bring engaging team-building activities into your 4-H clubs and events. In addition, we will share some of the most popular team-building activities for various age groups that you can use to support your work with 4-H youth.
Joining a new group of individuals can be nerve-wracking for some that may be shy or intimidated by large groups. Incorporating team-building activities into your 4-H clubs and activities is a great way for 4-H members, new and returning, to form a connection with each other and will help set the tone for that particular group setting and/or event. In this post, we’ll provide tips to bring engaging team-building activities into your 4-H clubs and events. In addition, we will share some of the most popular team-building activities for various age groups that you can use to support your work with 4-H youth.
Together Everyone Achieves More
Teambuilding has been proven to have many benefits. Two of the most powerful benefits of team building are increased group morale and individual confidence. Having a new group of individuals learn to work collectively as a team builds rapport and trust. Teambuilding allows individuals to contribute their strengths to the team and also gain additional skills learned from others within the group. This allows for personal growth and development… However, teambuilding does not happen on its own- teams are formed over time with good leadership.
Bruce Tuckman’s Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing model (1965) is arguably the most recognized model for team development, and includes four stages of team development: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning:
- Forming: The leader shares goals, but there is no commitment yet; individual roles and responsibilities are unclear. Very leader driven at this point. This stage is essential to help reduce anxiety new members might feel joining a 4-H club or group and will help foster a sense of belonging.
- Storming: Trust hasn’t been established and decisions are difficult to make. Team members try to establish credibility with the group toward the end of this stage.
- Norming: The group is establishing trust—agreement is easier to reach, commitment to goals is evident, and decisions are being made.
- Performing: The group could function on its own without the leader because of the trust, commitment to goals, clarity, and ease of making decisions.
- Adjourning: Recognition and sensitivity to the break-up of the group is important as the team dissolves and members move on to other tasks.
Five Team Building Tips for 4-H Clubs or Groups
Below are five helpful tips for incorporating hands-on activities into your 4-H clubs and events in order to have successful teambuilding interaction:
- The teambuilding process can be longer for some groups than others- it really depends on the needs of the group and how often they meet or interact. If your group meets once a month, it might take longer than if your group is in the same cabin all week at camp.
- Select activities that will address the current needs of your group- if the group is already formed, move on to activities that promote storming.
- If you see a club or activity struggling with a group activity or plan of action, have them take a break and let them participate in a fun
 teambuilding exercise like “Helium Stick“
teambuilding exercise like “Helium Stick“
- Check out our Northwest 4-H Volunteer Google Site for more team-building activities and resources.
- Team building isn’t just for the youth! Consider planning a teambuilding workshop or a night of minute-to-win-it games with your youth vs volunteers or even a 4-H Family night with youth, parents/guardians, and volunteers. This will become a request for an annual event guaranteed!
Five Team Building Activities for “Forming”
The new 4-H year kicks off in just a few days, which means that most 4-H clubs or groups are in the “forming” stage. To help, below are five fun and easy activities you can do with your team to promote “forming.” For more activities and ideas to support all five stages of team building, download our free 4-H Team Building Handbook for a quick reference tool!
- Start your meeting with an easy get-to-know-you icebreaker like “The Superlative Game” in which youth line up based on their birthday, height or age without talking.
- Who’s in the Bag? Ask each person to select an object that represents something about themselves. You can have a variety of objects available for them to select from, or they can bring an item with them. Have each person place their item in the bag, then let each person take turns explaining why the object represents something about themselves.
- Common & Unique- Ask everyone to form a circle. Tell them that you will ask a series of questions, and if the question applies to them, they are to stand inside the circle. Ask questions like “I am the oldest child in my family,” or “I play a sport,” or “I have lived in another state.” This helps members of the group get to know things about other members that they can’t see with their eyes.
- Introductions- Pretend you are hosting a party where no one knows anyone else. Have everyone standing in no particular order. In a party spirit, walk up to one of your “guests” and introduce yourself by name. For example:
- “Hi, I’m Karly. What’s your name? Gabrielle? Hi, Gabrielle, glad to meet you. Come on, there’s someone I want you to meet.” You then take Gabrielle to meet another “guest.”
- “Hi, what’s your name? Paul? Hi, Paul; this is Gabrielle. Gabrielle, this is Paul.” Gabrielle and Paul play it up. They smile, shake hands and say “Glad to meet you.”
- Try to “introduce” everyone in three minutes.
- If you need to meet virtually, don’t skip the team-building activity. Try this activity, “Where Am I?”
By incorporating teambuilding activities into your 4-H delivery, you will be delivering enhanced educational experiential learning in order for our youth to engage in mentally, physically, and socially, fostering the development of essential life skills. To learn more about joining 4-H as a member or volunteer, please contact your local UF IFAS County Extension Office, or visit http://florida4h.org.
SOURCES:
Building A Team Within A 4-H Club. Ohio State University. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.230.6481&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Team Building Activity: Helium Stick. Guide, Inc. 2021. https://guideinc.org/2017/08/21/team-building-activity-helium-stick/
The Superlative Game. North Dakota 4-H Recreation Games & Activities. Page 11. https://www.ndsu.edu/fileadmin/4h/ClubMaterials/FJ825_Games___Activities.pdf
Tuckman, B. W. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384–399.
Why Icebreakers? (2:17) – 4-H Military Partnerships Website – University of Florida/Florida 4-H. https://youtu.be/zWIkGgdEekM
by Heather Kent | Aug 4, 2022

4H youth participate in archery at 4H Camp Cherry Lake. Photo taken 06-08-19.
4-H volunteers and professionals often find themselves teaching a wide variety of audiences with different needs for learning. Keeping youth of different ages and abilities engaged in project learning can be a challenge, so we are offering six specific strategies that will make this much easier- especially with practice! Last week’s post covered spacing, interleaving, and retrieval practice. This week, we will talk about elaboration, concrete examples, and dual coding. This post will also include examples of using these techniques in your work with youth.
Isn’t the 4-H Curriculum “Good Enough?”
Yes! ……And no. Some 4-H curricula have teaching strategies embedded within them. Some just have activities structured to help youth learn content. Sometimes the curriculum was not written for the age group you are working with- in that case, check out our series on applying “ages and stages” to adapt activities for youth. Learning and applying a few of these teaching strategies will make your teaching more interesting and engaging to a wider range of 4-H members. These strategies are not hard, and require a little forethought- but the return on investment can be huge. Engagement + interest = more fun for everyone!
Elaboration

Experiential learning cards are quick reference tools when using elaboration
Elaboration is simply taking the time to ask and explore how and why things work the way they do. In the 4-H world, this is part of the “reflect and apply” part of our learn-by-doing model. To be included in the 4-H Curriculum Clearinghouse (a list of approved curricula for Florida 4-H), the curricula must include opportunities for elaboration. Taking the time to dig deeper into the content this way helps youth connect the information to everyday life, and this helps the information anchor in your memory.
Before rushing to the next activity on the agenda, ask youth to reflect on what they have learned and how they might apply it to another situation. Below are some examples of questions you might ask to help youth elaborate. Another tool that is handy is the 4-H Experiential Learning Flash Cards- each card has sample questions you can use when teaching or facilitating an activity to help youth elaborate. You can order a set from the UF/IFAS Book Store or contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office.
-
- What did you learn about (life skill or activity subject matter) through this activity?
- What did you learn about yourself by doing this activity? How did others help you?
- How did you make your decisions? What steps did you take?
- What problems came up over and over? How did you handle them?
- What key points have you learned?
- Have you had similar experiences related to this project/activity?
- Where have you faced similar challenges in your life?
- How does what you learned relate to other parts of your life?
- How can you use what you learned?
- How can you apply (the life skill you practiced) in the future?
Concrete Examples
Providing specific examples can also help anchor ideas and concepts in a person’s memory. This works particularly well for younger members (juniors and intermediates) who are just starting to understand more abstract ideas. Providing more than one example helps the learner apply the information, not just remember the concept.
For example, the idea of computer coding can be an abstract concept for youth (and even some adults). One concrete example is to compare computer coding with the language we speak. You have to understand the language before you can communicate. Another example is to play “Simon Says.” In this familiar game, the players can only do exactly what “Simon” says to do otherwise they are out of the game. The same is true for computer coding. The computer will only do exactly what the programmer says to do.
Dual Coding
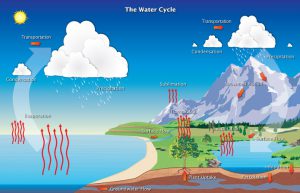
Image credit: The water cycle by NOAA National Weather Service
Dual coding is a fancy term for using words and visuals together. Research has shown that words and visuals help learners learn better than words alone or visuals alone. Some 4-H curricula do a great job including visuals- other times, you may need to search the internet or YouTube to find good visuals for more complex ideas.
For example, when teaching youth about the water cycle, a diagram of the water cycle is very helpful. Alternatively, you could show youth how to make a water cycle bracelet, where each bead represents a different part of the cycle. That way, they have a visual they can wear and refer to when exploring the water cycle.
One of the best things about 4-H is it is learner-centered. That means that youth can choose what they want to do and learn in 4-H. Your local 4-H Extension Office can help you find the best curriculum to support your youths’ learning needs, but the curriculum is only part of learning. 4-H supports learning (usually referred to as a project) through a variety of competitive and non-competitive events. The three strategies described in this post can help volunteers and 4-H professionals link learning between projects and activities. I hope this series has been helpful as you prepare to work with 4-H youth this year to “make the best better!”
References:
- Potter, S. (2021). Educational Design and Delivery – Utilization of Multiple Teaching Strategies. 4-H VKRC Fact Sheets.
- Weinstein, Y., Madan, C. R., & Sumeracki, M. A. (2018). Teaching the science of learning. Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, 3, 2. https://cognitiveresearchjournal.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s41235-017-0087-y
- Weinstein, Y, Sumeracki, M & Caviglioli, O (2019) Understanding how we learn: A visual guide. Routledge, Abingdon, Oxon, UK.















