by Rachel Pienta | May 26, 2023
What does it mean to be a coach? When you hear the word coach, do you picture someone with a whistle on a sports field? Most of us are probably familiar with sports coaching. However, the concept of coaching has grown to include life and professional coaching as well! This expansion of coaching has established that it is a skill that has applications across a broad array of life situations.
If you google professional coaching, you will find a plethora of books available on the topic. Writer Julie Starr has identified several fundamental coaching skills: building rapport, listening, asking good questions, and giving constructive feedback (Starr, 2021). Those skills sound like the characteristics agents hope to find in a 4-H volunteer!
How Is Coaching Different From Mentoring?
How does coaching differ from mentoring? Zust (2017) contrasted coaching versus mentoring in the business setting, explaining that coaching is a partnership between the coach and the person receiving coaching. The coach helps an individual or team reach or grow toward their potential. Just as a sports coach has a season, a coach in the business setting helps the person or team to reach a goal. How does coaching translate to the 4-H setting? In 4-H, youth may want to complete a project or compete in an event. As a volunteer, you can help coach them through a successful experience! In contrast, Zust (2017) characterizes mentoring as a longer term, developmental process that may not be focused on one particular event or project. In an earlier blog post, I addressed types of mentoring and mentoring practices.
As a volunteer, you may recognize that the 4-H agent you work with has been coaching you! As a 4-H club volunteer, you also have the opportunity to coach the youth enrolled in the 4-H program. In this blog post, you will learn about coaching techniques and how to be a more effective coach to the youth in your clubs. What does it mean to be effective as a coach? In the context of youth development, coaching effectiveness can be defined as the integrated application of “professional, interpersonal, and intrapersonal knowledge to improve youth competence, confidence, connection and character” (Vella et al, 2011).

4-H coaches help youth achieve their goals.
Getting in the Zone (of Proximal Development)
To better understand how to effectively implement coaching with youth, we will consider the following learning concepts: the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) and “scaffolding” (Vinson and Parker, 2019). Vygotsky (1978) defined ZPD as the “distance between actual developmental level as determined by independent problem-solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem-solving under adult guidance or in collaboration with more capable peers.” When I read Vygotsky’s definition of ZPD, I immediately think, “That’s 4-H!” Youth are able to develop and improve skills, ultimately achieving more with the support of caring adults. In 4-H, we also encourage youth to apply what they have learned through teaching others. Several coaching behaviors suggested by Vygotsky include “questioning, demonstrating and introducing the beginnings of task solution” (Vinson and Parker, 2019). These behaviors are ways to use scaffolding as a technique in youth development.
How to Incorporate Scaffolding into Your Coaching Toolkit
Scaffolding is a learning process that can be used as a technique in effective coaching. This technique can help youth build on existing knowledge they have previously acquired. The process works similarly for skill-building and “Scaffolding practices provide the opportunity for children to reach higher-level skills by building on and extending their existing skills” (Mincemoyer, 2016). Three examples of scaffolding strategies that can be used to coach 4-H youth include:
- Modeling and demonstrating: Adult volunteers can demonstrate the skill or ask a youth to demonstrate.
- Incorporating reflection into the club meeting: Build in time for youth to explain to you and their peers what they learned during a club activity.
- Using documentation: Illustrated talks and project books are forms of documentation. Youth may document their learning with photographs, written descriptions, and even video. This documentation becomes a foundation to build on moving forward as more skills are developed.
(Adapted from Mincemoyer, 2016).
In closing, you may already be engaging in effective coaching strategies as a 4-H volunteer without knowing that was what you were doing! If coaching is a new concept for you, this blog post should serve as a starting point for further development in your volunteer experience. Your 4-H agent can be an excellent knowledge resource as well as serving in a coaching role for you.
For more information about positive youth development (PYD) strategies or to learn more about becoming a 4-H volunteer, reach out to your local Extension office.

Youth engage in a mock Cooking Challenge with coach support.
Resources for Further Reading
Mincemoyer, C. (2016). “Scaffolding Approaches and Practices.” Penn State Extension. Pennsylvania State University. http://bkc-od-media.vmhost.psu.edu/documents/HO_MIL_GI_Scaffolding.pdf
Starr, J. (2021). The Coaching Manual. 5th edition. Pearson Business.
Vella, Stewart & Oades, Lindsay & Crowe, Trevor. (2011). The Role of the Coach in Facilitating Positive Youth Development: Moving from Theory to Practice. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology. 23. 33-48. 10.1080/10413200.2010.511423.
Vinson, D. and Parker, A. (2019) Vygotsky and Sports Coaching: Non-linear practice in youth and adult settings. Curriculum Studies in Health and Physical Education, 10 (1). pp. 91-106. doi:10.1080/25742981.2018.1555003 ORCID: 0000-0001-6842-3067
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in Society: The development of higher psychological processes. Harvard: Harvard University Press.
Zust, C. (2017). “Know the Difference Between Coaching and Mentoring.” Kent State University. https://www.kent.edu/yourtrainingpartner/know-difference-between-coaching-and-mentoring

by Niki Crawson | May 19, 2023

We know that younger youth look up to older youth and like to model their behaviors. We see it in siblings all the time, absorbing behaviors of their older brothers or sisters like sponges. Often times, younger youth find the attention and encouragement of older youth more relatable due to the closeness in age. Peer teaching fosters a more engaging and even symbiotic learning experience as this gives teens the opportunity to share and reinforce their own knowledge. In addition, by pairing the two age groups together in a learning environment, a sense of comradery can develop, creating a greater sense of belonging within the 4-H community. In this post, we will define peer teaching, share a few examples of how to utilize your teens as teachers and provide tips for getting peer teaching started in your clubs and other 4-H events and activities successfully.

WHAT IS PEER TEACHING?
What do we mean by peer teaching exactly? It is the process of youth learning together and from each other through engaging, hands-on activities. In 4-H, we have the wonderful ability to utilize teens as volunteers and positive role models for our younger youth in our positive youth development programs. Empowering our teens as teachers for our younger members allows life skills to develop among our youth being instructed and also the instructors. The teen instructors are teaching specific topics to their peers at the same time they are strengthening their own leadership, communication, and social skills.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF PEER TEACHING?
As stated previously, one of the greatest outcomes is that the teacher and the student both gain knowledge and skills. It creates a mutually beneficial environment in which all youth can achieve personal growth and development if implemented and managed correctly. In addition, there are many other benefits of peer teaching such as:
- Peers being taught may form a quicker and better connection with teens due to communication, technology and other trends.
- An increase in peer confidence as they may feel more comfortable in asking questions, discussing topics with others closer to their age.
- Greater creativity as teens may have more innovative or modern ideas to bring to the activities.
- An increase in volunteers as teens have the ability to recruit more teens easier than typical adult volunteers.
- An increase in retention of youth as peers stay in the program and become the next generation of teen volunteers/teachers.
WHAT DOES PEER TEACHING LOOK LIKE IN 4-H?
Below are just a few programs for teens to practice the method of peer teaching in their 4-H county:
- New Members – When new youth join 4-H, it can be overwhelming at times to learn some of the 4-H activities, customs, and such. This would be a great opportunity for
 peer teaching. Have teens assigned to new members that join in order to teach them the 4-H pledge, motto, club expectations, member names, etc. This creates a greater sense of belonging and fosters a supportive environment within the club for new members to engage more quickly and successfully.
peer teaching. Have teens assigned to new members that join in order to teach them the 4-H pledge, motto, club expectations, member names, etc. This creates a greater sense of belonging and fosters a supportive environment within the club for new members to engage more quickly and successfully.
- Cloverbud Club Meetings – Utilizing your teen members in club meetings involving Cloverbuds (members ages 5-7) is a great way to incorporate peer teaching in your 4-H program. Younger members thrive off of creativity and enthusiasm which teens often portray easily. Teens can funnel this energy into teaching lessons to Cloverbuds that are engaging and interactive in a simplistic way.
- Summer Day Camps – 4-H programs often times need additional volunteers during the summer to assist with the volume of programming and youth participants. Therefore, summer is a great time to recruit teens to become peer teachers. Having teens as peer teachers helps with supervision and instruction while at the same time, allows them to stay involved in 4-H, continue to apply their life skills learned, and help the program teach life skills to other youth in the community.
TIPS TO GET PEER TEACHING STARTED IN YOUR 4-H COUNTY
What does it take to get peer teaching started in your 4-H county? Time and patience to start with. Teaching with teens is an ongoing task and will take a little effort on your part. Below are a few tips to get you started on having teens peer teach in your county:
- Identify programming that would benefit by peer teaching.
- Recruit quality teen teachers.
- Train and support teens as peer teachers.
- Assign teens appropriate roles in the peer teacher process.
- Model appropriate teaching methods in 4-H programs.
- Shadow teens in the role as peer teachers to provide support and guidance.
- Evaluate, provide feedback, and continue professional development for continued success.
Remember, peer teaching is a great way to utilize teen members in your 4-H programs. Younger youth need as many positive role models as possible in their lives. By having teen teachers take the lead in instruction in your 4-H programs, you are fostering an environment of learning, inclusivity, empowerment, and leadership.
To learn more about 4-H opportunities where teens can take the lead as teachers for their peers, please contact your local UF IFAS County Extension Office, or visit http://florida4h.org.
ADDITIONAL SOURCES:
Burse, G., Crocker, E. T., Jordan, J., McKinney, M., & Murphy, L. (2021). Teens as Teachers 4-H Project: Curriculum and Resources. UF/IFAS Extension, University of Florida. Retrieved May 1, 2023, from https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/4H432
Eckhoff, A., & Swistock, B. (2011). Staffing with Teenagers and Teens as Cross-Age Teachers. Rutgers Cooperative Extension.

by Rachel Pienta | May 8, 2023
4-H functions most effectively as a youth-adult partnership that fosters positive youth development. Youth-adult partnerships can take several forms. One form is a mentoring relationship between a caring adult volunteer and a 4-H youth.
Mentoring is a relationship-based process that occurs over time. The mentoring process can be formal or informal. This blog post will explore what it means to be a mentor and the importance of mentoring roles in youth development. The person being mentored may be referred to as a protégé or as a mentee. Mentoring is not a one-way relationship. The relationship can fulfill professional and socioemotional needs for both mentor and protégé (Inzer & Crawford, 2005).
Formal mentoring tends to occur within an organizational structure. A senior member of an organization or an adult may be assigned to serve in a mentoring role to a new member or to a youth. Informal mentoring relationships are voluntarily formed between two people who choose each other (Inzer & Crawford, 2005). A third, hybrid approach known as youth-initiated mentoring (YIM) is also an option as a model and may be optimal for building mentor relationships in 4-H programs (van Dam L. B., 2021).

Mentors play one or more of these five roles for mentees.
5 Roles of the Mentor
The following mentoring roles can be accomplished within a formal or informal mentor relationship:
- Goal Setter: Help identify and prioritize the goals of the person you are mentoring.
- Adviser: Provide advice and guidance, often based on life experience and organizational knowledge.
- Cheerleader: Encourage positive actions and celebrate success.
- Growth Cultivator: Suggest activities that will help the person grow.
- Role Model: Serve as a model of potential success and provide real-life examples of how to surmount obstacles.
Goal Setter: The mentor as goal setter helps the youth to identify potential goals to set. Mentors can also play an important role in teaching youth how to balance and prioritize goals. For example, Susy may want to win a blue ribbon at the livestock show. At the same time, Susy is also trying to maintain a 4.0-grade average and work part-time. Susy’s mentor can help her to set realistic goals that help her to develop time management skills.
Adviser: It can be helpful for youth to learn from the experiences of others. For example, Michael wants to become state 4-H president. He has connected with adult volunteer Cory, who was state president when he was a 4-H youth. Cory serves as a sounding board and often shares how he learned from mistakes and was able to build on his successes to achieve his leadership goal.
Cheerleader: The cheerleader role may seem simple but also the most important. Celebrating youth successes – whether large or small – can make a big difference in a child’s life. Marking success with recognition and encouragement helps to reinforce positive behavior and helps to build a foundation for continued achievement. For example, Anna has been working on her aim during archer
y club practice. She wants to compete in an upcoming match. You observe her stance and coach her to adjust her posture. Anna is now able to hit the center target three out of four times. You praise her improvement and celebrate the achievement with her, sharing an exuberant high five.
Growth Cultivator: 4-H professionals and volunteers often refer to growing leaders and “making the best better” – the growth cultivator does these things. As a growth cultivator, a mentor helps to point youth in the direction of the next and most appropriate challenge that will help foster positive development. For example, Nathan has prepared a strong project board display for the county fair. You suggest he use that project board to develop an illustrated talk for district showcase.
Role Model: Serving as a role model for youth may seem like a full-time job! However, the key part of being a role model is honesty. Role models do not have to be perfect, but modeling honesty and how to be accountable when mistakes are made are critical elements of being a good role model. For example, you are usually early to club activities, greeting everyone with a smile and a personal acknowledgment when they come through the door. On the way to a district council meeting, you encounter heavy traffic and run late. When you arrive, your club youth members are already there and a 4-H agent has started the meeting. At the break, you shrug off your poor mood and tell your youth, “I didn’t leave early enough to allow for rush hour traffic. That is on me. I appreciate how you were all here on time and were able to participate in the meeting before I arrived.”
3 Key Elements of Effective Mentoring
A robust, growing body of research on youth mentoring suggests that a hybrid model of targeted mentoring and relational bond mentoring may produce the best outcomes for youth development (Christensen, 2020). Targeted mentoring involves a relationship focusing on a specific outcome or behavior – such as academic or career mentoring. Relational bond mentoring focuses on developing rapport and may present a more holistic approach. 4-H is built on a developmental model that uses this hybrid approach. Youth-adult relationships may initially form to reach specific goals – such as completing a project. Over time, as the youth becomes more involved with the program, relational bonds may develop. Research by Raposa et al (2019) suggests that effective youth mentoring involves an “interconnected set of three processes (i.e., social-emotional, cognitive, and identity formation processes) through which the establishment of close, caring relationships with non-parental adults are expected to promote positive developmental trajectories” (Raposa, 2019). Effective youth mentoring is likely to incorporate all three of these elements: social-emotional, cognitive, and identity formation processes.
How Does Youth-Initiated Mentoring (YIM) Work?
4-H can have an important role in providing a structured, safe environment where youth choose and develop mentoring relationships. One way to establish these type of mentoring relationships is youth-initiated mentoring (YIM). YIM is a hybrid approach in which youths and their families are helped to identify and recruit caring adult mentors from within their existing social networks (van Dam L. R., 2021).
The 4-H youth-adult partnership model provides a structure for helping youth to identify, recruit, and maintain connections with caring adults (van Dam L. B., 2021). The key elements in YIM are youth agency and choice in establishing and maintaining relationships.

Club leader teaches poultry anatomy to youth.
Which Type of Mentor Role Fits?
The mentor role that best fits you and your mentee may incorporate one or more of the five mentor roles. It is likely that at some point during a long-term mentoring relationship a mentor will have played all of the five roles in supporting their mentor.
Become a Mentor with 4-H!
As a 4-H volunteer, you will opportunities to serve as a mentor to youth looking to form relationships with caring adults. To learn more about how to get involved, reach out to your local UF/IFAS County Extension office.
References:
- Christensen, K. H. (2020). Non-Specific versus Targeted Approaches to Youth Mentoring: A Follow-up Meta-analysis. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 959–972.
- Inzer, L., & Crawford, C. (2005). A Review of Formal and Informal Mentoring: Processes, Problems, and Design. Journal of Leadership Education, 33-50.
- Raposa, E. R. (2019). The Effects of Youth Mentoring Programs: A Meta-analysis of Outcome Studies. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 423–443.
- van Dam, L. B. (2021). Youth Initiated Mentoring: A Meta-analytic Study of a Hybrid Approach to Youth Mentoring. J Youth Adolescence, 219–230.
- van Dam, L. R. (2021). Youth-Initiated Mentoring as a Scalable Approach to Addressing Mental Health Problems During the COVID-19 Crisis. JAMA Psychiatry, 818.
by Marcus Boston Jr. | Apr 26, 2023
Youth shows and fairs provide a valuable opportunity for young people to develop a wide range of life skills. From responsibility and communication to planning and organization, these events offer a unique learning experience that can help young people build important skills for success in all areas of life.
Can a youth’s participation in County fairs and Shows help to develop them into responsible adult? The answer is yes! The Florida 4-H Program seeks to be inclusive to all youth by using a variety of vehicles to teach youth life skills in traditional and non-traditional settings. A recent article in The Journal of Extension by Oregon State professionals found that “having fun” “spending time with friends” and “teamwork” were the highest-rated motivators for youth that participated in fairs.
The study also revealed that participation in fairs through 4-H had a significant positive effect on participants’ levels of caring, contribution, and character. These characteristics are also part of the Essential Elements of 4-H that youth experience by being in an active 4-H program throughout the year. Those elements are Belonging, Independence, Generosity, and Mastery.
One of the most important skills that youth learn through participation in youth shows and fairs is responsibility. Whether they are caring for animals, plants, or other projects, youth must take on the responsibility of ensuring that their projects are healthy, well-cared for, and ready to be presented to judges and visitors.
 Communication is another key skill that youth develop through participation in youth shows and fairs. Through active participation youth learn the ability to articulate complex ideas, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully to questions and feedback.
Communication is another key skill that youth develop through participation in youth shows and fairs. Through active participation youth learn the ability to articulate complex ideas, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully to questions and feedback.
In addition to these skills, youth shows, and fairs also emphasize important values such as sportsmanship and fair play. Participants are encouraged to respect their competitors, accept both victories and defeats graciously, and uphold the highest standards of ethical behavior. This helps young people develop important social skills, including the ability to work collaboratively with others and build positive relationships.
Finally, participation in youth shows and fairs can help young people develop resilience and perseverance in the face of challenges and setbacks. These events can be competitive and stressful, but they also offer opportunities for young people to learn from failures, bounce back from disappointments, and remain motivated to achieve their goals.
A few of the Florida 4-H Shows and Fairs are as follows:
-
- State 4-H Dairy Show Okeechobee March
- 4-H Chick Chain Show Chipley April
- Area North Horse Show Green Cove Springs May
- North Florida Fair Tallahassee November
*For additional opportunities to participate in 4-H Shows and fairs please contact your local 4-H office.
In conclusion, participation in youth shows and fairs can offer a unique and valuable learning experience for young people. By developing important skills such as responsibility, communication, planning, and organization, as well as important values such as sportsmanship and fair play, youth can build the foundation for success in all areas of life.
References:
More information on this study can be obtained by visiting the Journal of Extension at www.joe.org and viewing volume 45, number 6.(Arnold, Meinhold, Skubinna, and Asthton)
by Niki Crawson | Apr 6, 2023
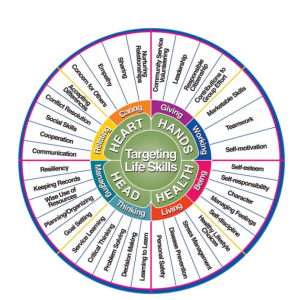
Figure 1. Hendricks, P. (1998) “Developing Youth Curriculum Using the Targeting Life Skills Model”
During the summertime, 4-H typically offers more opportunities for our teen audience since school is not in session as their schedules are more flexible. Because of this, we want to ensure that we are targeting skills that are specific to our teens’ immediate and future wellbeing and success.
In this article, I will discuss why life skills are so important, what 4-H programs already established target, which life skills are most beneficial for our teens and what, when, and how teens can get involved.
WHY DO WE CARE SO MUCH ABOUT LIFE SKILLS?
We know that life skills are abilities learned that help individuals reach their full potential in life. They assist in helping folks successfully handle day-to-day life experiences. We believe they are developed through hands-on learning, activities, and practice.
Life skills are the foundation of 4-H. Utilizing the Targeting Life Skills Wheel (Hendricks, 1998), we connect life skills through 4-H projects, programs, and events to real life experiences based on our Head, Heart, Hands and Health model. By helping youth achieve these life skills, 4-H professionals and volunteers are providing the framework for future academic and employment success, as well as youth thriving and community outreach.

Five essential life skills from the Targeting Life Skills Model commonly developed by participating in 4-H are:
- Communication
- Problem-solving
- Teamwork
- Responsibility
- Interpersonal Relationships
PROJECTS & EVENTS RELATED TO LIFE SKILLS FOR TEENS
Below are just a few 4-H projects and events in Florida 4-H for teens to get involved in to develop and strengthen essential life skills:
- 4-H Tailgating Contest – This program teaches healthy living and the science of grilling seafood, pork, poultry and beef safely outdoors. This program teaches decision making, healthy lifestyle choices, and communication life skills, among others.
- Gator Pit – The Gator Pit is a program open to all teens ages 14-18 in Florida. Youth are taught how to develop entrepreneurial skills through mentorship, competition, and networking to the business community.
- 4-H Legislative – Florida 4-H Legislature provides an opportunity for teens ages 14-18 to experience state government procedures and prepare them for potential leadership in the American democratic process. Youth learn, practice, and defend public policy.
- 4-H University – Florida 4-H University is an opportunity for teens to participate in educational workshops lead by UF faculty, explore potential careers, strengthen interpersonal relationships with peers, and develop critical life skills that will help them become leaders and engaged citizens in their communities.
The Florida 4-H Curriculum Clearinghouse is a list of 4-H resources available, including project curriculum, record books, club resources and other educational publications that meet the standards of Florida 4-H. In this site you can view resources for specific projects. To learn more about 4-H opportunities for teens, please contact your local UF IFAS County Extension Office, or visit http://florida4h.org.
ADDITIONAL SOURCES:
Hendricks, P.A. (1998). Developing Youth Curriculum Using the Targeting Life Skills Model: Incorporating Developmentally Appropriate Learning Opportunities to Assess Impact of Life Skill Development. Iowa State Extension Publication. https://extension.purdue.edu/4-H/about/impact-targeting-life-skills.
Irvine, K. (2019). What are Life Skills? https://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/nassauco/2019/02/04/what-are-life-skills/
by Heather Kent | Feb 10, 2023
 One of the things I love about 4-H is that it offers so many different opportunities for youth to learn leadership skills while pursuing and exploring their sparks. And leadership roles are not confined to the club level- there are opportunities for youth to serve at the district, state, and even national levels. Youth leaders are grown, not born. And just like any living thing, they must be nurtured over time in an intentional way to develop strong leadership skills. This article will describe what a strong youth leadership team looks like and provide some resources to help grow your team. Over the years, I have had the privilege of working with some amazing youth leadership teams at all levels of the 4-H organization. But it was something that we had to cultivate over time- we didn’t start out as a high-functioning team. A strong youth leadership team can be identified by the following five characteristics (download this graphic):
One of the things I love about 4-H is that it offers so many different opportunities for youth to learn leadership skills while pursuing and exploring their sparks. And leadership roles are not confined to the club level- there are opportunities for youth to serve at the district, state, and even national levels. Youth leaders are grown, not born. And just like any living thing, they must be nurtured over time in an intentional way to develop strong leadership skills. This article will describe what a strong youth leadership team looks like and provide some resources to help grow your team. Over the years, I have had the privilege of working with some amazing youth leadership teams at all levels of the 4-H organization. But it was something that we had to cultivate over time- we didn’t start out as a high-functioning team. A strong youth leadership team can be identified by the following five characteristics (download this graphic):
- Clarity

- Cohesiveness
- Communication
- Confidence
- Collaboration
Clarifying the roles of each team member
It’s essential that everyone in the group understands their role and that they have something valuable to contribute to the team. Youth are usually pretty quick to understand their role- often it involves planning an event or solving a community issue through service learning. But the roles of the adults are much vaguer. Some adults view the role as advisory the same way they would a dictator. They want to tell the youth what they should do when they should show up, and how to do everything. But as advisors, our role is to empower youth- make sure they understand their role, and that they are cohesive, or have ground rules for how the group will function.
Establishing a sense of cohesiveness
Once everyone is clear about their roles on the team, the group needs to establish ground rules, or group norms to create a sense of cohesiveness. If the adult mentor sees the group wandering away from the group norms, then it is their job to call the youth out on it and bring them back to a more cohesive state. Not too long ago, I was working with a group of teens to plan a retreat. We had a new member who was constantly putting down other youth’s suggestions. The group got quiet except for the outspoken youth. It was my job to remind everyone that one of our group norms is that each person gets an opportunity to speak, and we don’t put down others’ ideas. Holding the group accountable for these group norms keeps the group cohesive and focused, which is essential for building the next characteristic, communication.
Communication
Leadership teams are a great place for youth to practice communication skills- particularly if they are nervous about speaking in front of large groups. Typically the youth leading the team is responsible for making sure everyone is recognized and heard. However, some youth might need encouragement to speak up- that’s when the adult advisor can help! It is also important to discuss how the team wants to communicate outside of meeting times- reminders about meetings, or any other issues that might come up in-between meetings. As the advisor, make sure everyone comes to a consensus on how and how often the team wants to communicate within meetings (and outside of meetings). As youth become more comfortable with communicating, their confidence will grow.
Confidence
When the members of your youth leadership team are clear about their roles, are cohesive in their approach to leadership, and communicate well with each other, they will be empowered to lead. Teams that are empowered understand that every person on the team has something to contribute. As adults, it’s often easier to just “do it ourselves,” but instead we need to empower youth to take responsibility for a different part of the program the youth are leading. However, we do need to make sure they have the information and tools they need to be empowered. For example, if they want to do an activity they have little experience with, such as sewing dog toys for a pet shelter, connect them with people who have experience and expertise with that type of activity.
Collaboration
The ultimate characteristic of a strong leadership team is collaboration. It is the combined effect of the other four characteristics working together in unison. The collaboration stage is also when youth become role models- not only for other youth but for adults as well. And that is when organizations begin to grow. People will be curious about why and how your youth are working so well together.
Additional Resources:
The UF IFAS publications listed below are free downloads that include hands-on, experiential activities you can do with your youth to help build a strong leadership team:
The best-selling book 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teens written by Stephen Covey is a must-read for any 4-H faculty, staff, or volunteer working with teen leaders.
- Covey, S. (1998). The 7 habits of highly effective teens: the ultimate teenage success guide. New York Simon & Schuster.
















