
by Alex Bolques | Jul 28, 2015
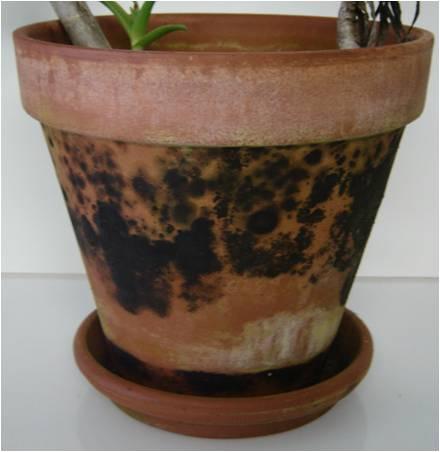
Most likely, we all have them-garden pots. These typically are made of plastic, clay or wood. Garden pots should be sanitized if they were previously used or if they exhibit signs of mold or fungal growth. Whether they are used as garden boxes, planters, or hanging baskets, the surfaces of garden pots can harbor disease organisms, along with unsightly stains and mineral salts deposits. Salts from hard water and fertilizers can leach though clay pots leaving a white film on the pot’s outer surface. Salts accumulation can become flaky and encrusted around the rim and drainage holes of plastic and clay containers.

Mold or fungal growth on an unglazed terra-cotta (clay) pot Photo Credits: Alex Bolques, FAMU Research
To clean clay or plastic containers, use a brush or fine steel wool to remove dirt and debris and wash with a liquid soap detergent. If stains persist, consider using a 50:50 solution of water and vinegar. To sterilize clay or plastic pots, soak them in a mild solution of bleach, 1:10 bleach to water, for about 30 minutes. Then, immerse them in clean water and allow them to dry completely. Containers made of wood are different. If the timber that they are made of is not treated properly, they tend to rot and can harbor disease spores or bacteria. It is best to replace these as they show signs of wear or deterioration. Sanitizing your garden pots will help you avoid unwanted disease problems and unsightly garden container pots.

by Alex Bolques | Jun 17, 2014
Homeowner accounts of white fluffy woolly masses on woody ornamentals have been on the rise. They can appear on the ends of a wide variety of woody ornamental branches in the landscape. A closer inspection of these white woolly masses can provide the curious observer with a startling surprise. “It’s Alive!” It moves and seems to jump at you, most likely jumping away from you. Once you have recovered from the mildly frightful encounter, you ask yourself, “What was that?”

Adult citrus flatid planthopper, Metcalfa pruinosa
(Say). Credits: Photograph by: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida
They are planthoppers (Metcalfa pruinosa), an insect in the order Hemiptera. The common name for this woolly looking planthopper is the citrus flatid planthopper (CFP). As the name implies, they occur on citrus but can also be found on many woody ornamentals and fruit trees. The adult planthopper wing arrangement is tent-like, meaning that the forewings are held over the insect abdomen in a tent configuration.

Nymph of the citrus flatid planthopper, Metcalfa
pruinosa (Say). Credits: Photograph by: Lyle J. Buss,
University of Florida
The nymph, young immature insect, produces the white woolly material that is characteristic of CFP. At first sight, they can be mistaken for mealy bugs, which may look similar since they are covered with cottony white filaments. They can also be mistaken for cottony cushion scale.

Mealybugs. Credits: James Castner, University
of Florida

Cottony cushion scales, Icerya purchasi, on twig.
Credits: James Castner, University of Florida
In both of these cases of mistaken identities, the insect will not jump or hop around. No chemical control is necessary although sooty mold can occur on heavily populated plants. In that case, a soapy water treatment can be applied.
Follow these links to more information on the citrus flatid planthopper, mealy bugs, and cottony-cushion scale.
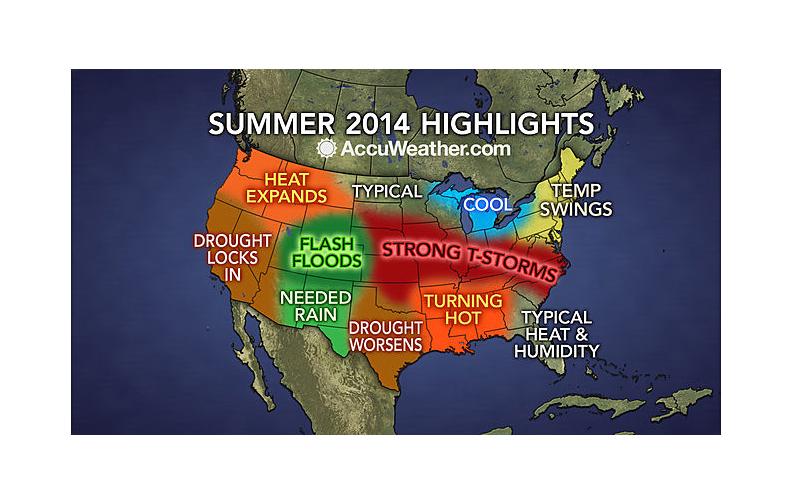
by Alex Bolques | May 13, 2014

Expect typical heat and humidity east of the Apalachicola River with hotter temperatures west.
http://www.accuweather.com/en/weather-video/video-summer-2014-forecast-highlights-drought-severe-weather-increase/3520160310001
As we begin to approach our North Florida hot summer months, Gary Wade with the University of Georgia College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension reminds us that, “temperatures in the high 90s and several weeks without rain can lead to serious, sometimes fatal, conditions for landscape (and garden) plants“. Most likely, we will also experience extreme temperatures in June and July. Under these conditions, heat stress is a great concern for both plants and people in the landscape or garden. Remaining hydrated is key to preventing heat stress.
For plants, mulching is an effective means to conserve moisture in the soil. It also cools the plant root zone, and helps to control weeds. Removing weeds that are growing around desirable plants will also help reduce soil moisture losses.
Consider watering your garden or landscape early in the morning. This method takes advantage of cooler morning temperatures, which can extend soil moisture conditions thus making soil moisture available during the hottest times of the day. Early morning watering will also discourage disease problems on plants susceptible to fungal growth such as lawns, roses, and cucurbits.
The best time to work in the garden or landscape is during the morning hours. To beat the heat, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Heat stress disorders develop when the body cannot shed excess heat. Heat stress, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke are illnesses that can overcome you when your body is unable to cool itself. For more information and resources on how to “Beat the Heat”, visit the UF IFAS Solutions page.
Ref: Wade, G. 2013. Heat, Drought Take Toll on Landscape Plants. University of Georgia College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension.

by Alex Bolques | Mar 25, 2014

Black Titi in bloom. Flower clusters upright at tips of branches. An excellent source of nectar and pollen for honey production. Image: Alex Bolques
Black Titi (also known as Spring Titi or Buckwheat Tree (Cliftonia monophylla (Lam.) Britton ex Sarg. is a native shrub or tree that can be found growing along streams and boggy areas of the Florida Panhandle. It can tolerate acidic wetland soils and once established can also tolerate dry soils in the landscape. Black Titi can reach 15 – 30 feet in height with 3 – 4 inches of trunk diameter. Its bloom period lasts February through March.

Bee visits a Black Titi flower. Image credit: Alex Bolques
Beekeepers love it because it is a wonderful source of nectar and pollen for honey production. Beginning beekeepers may confuse Black Titi with White Titi (also known as Summer Titi or Swamp Titi (Cyrilla racemiflora L.). It should not be grown as a honeybee pollinator plant. The nectar and/or pollen of White Titi can promote a condition known as “Purple brood”, which can be detrimental to honeybee immature stages.The flower of the spring flowering Black Titi is a raceme, a cluster of flowers along a central stem, that appears as an upright cluster on the tip of branches. The flower of the summer flowering White Titi is also a raceme, not as upright, more elongated. Visit the USDA Natural Resource Conservation Service plant database website and click on the image tab to see Black Titi (Buckwheat Tree) or White Titi (Swamp Titi) to view differences in flower morphology.

by Alex Bolques | Feb 4, 2014

Robert H. Mohlenbrock @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA SCS. 1991. Southern wetland flora: Field office guide to plant species. South National Technical Center, Fort Worth.
Found throughout the North Florida Panhandle, the American snowbell, Styrax americanus, is a native small flowering tree. In his book, The Trees of Florida, Gil Nelson describes the blossoms as charming with “the thin, reflexed (flower) petals curve back over the flower base, leaving an attractive mass of yellowish stamens protruding from the star-shaped corolla”. It has dark green deciduous foliage, with the tree reaching up to 16 feet in height. The attractive blooms appear April – July.
Considered as an understory tree, American snowbell grows best in wet partially shaded areas and is somewhat tolerant of full sun. It prefers wet places such as swamps, wet woods, edges of cypress ponds and moist to wet, cool, acid sandy to sandy loam soils. Wet areas of the home landscape where water puddles occur provide adequate growing conditions for the American snowbell.
Wildlife benefits include nectar for bees and butterflies and edible fruit for birds. To try American snowbell in the landscape, check with local native plant nursery or search online. Note: other Styrax species can be found online that are non-native.
Other source: The Native Plant Database












