
Deer grazing test plots at the NFREC in Quincy. Food plots can benefit deer year round, not just during hunting season.
To the chagrin of hunters across the panhandle deer season has drawn to a close. As the days lengthen and temperatures begin to climb, many of the area’s outdoorsmen (and women) shift their focus to a more aquatic nature. However, those sportsmen, who will place a premium on antler size in the fall, should not neglect the nutritional needs of the deer herd during the spring and summer months.
There is a well-documented correlation between deer nutrition and antler growth. Antler growth is suppressed when adequate nutrition is not available. Antler growth requires a large amount of energy and protein. The energy requirements for antler growth can generally be met by the deer’s natural environment. However, some natural environments may not supply enough protein to maximize antler growth. Nutrition is only one of several factors effecting antler growth but it is perhaps the easiest of those factors to alter.
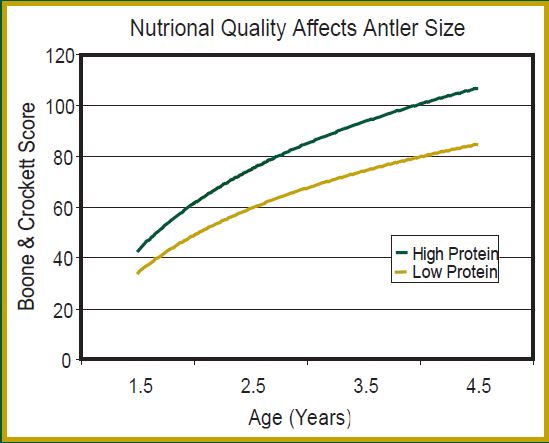
Source: Mississippi State University, Forest & Wildlife Research Center
http://www.fwrc.msstate.edu/pubs/antler.pdf
As with all animals, a deer’s nutritional demands change over time. The suppressing effect of insufficient protein in the diet is most evident in younger bucks. This is because the bodies of immature deer are still growing. The processes of growth and development demand protein. When antler growth is added to the equation the protein demand of a young buck can easily exceed what is provided by it natural environment. Research indicates that young, growing deer during antler development need a diet that is approximately 16% crude protein in order to maximize antler growth. Mature bucks can maximize antler growth with as little as 10% crude protein.
Planting and maintaining warm season food plots is a good way for a deer herd manager to help prevent any nutritional limitations to antler growth. Food plots are often thought of in terms of their ability to attract deer to a specific location during hunting season. However, if properly utilized food plots can have a lasting positive effect on an area’s deer herd and other wildlife. Follow the links for the basics on food plot establishment and soil fertility management.
If your goal is to increase the amount of protein available to the deer herd then legumes are your best bet. Some warm season legumes that do well in the panhandle include Aeschynomene, Alyceclover, Cowpeas, Soybeans, Lablab, and Perennial Peanut. It is important that you select species and varieties that are suited to the conditions (especially soil properties) of the area you intend to use them. It is also recommended that you plant a variety of species in any food plot.
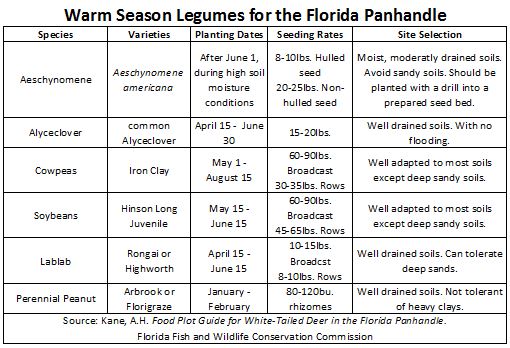
The species listed vary in terms of grazing tolerance and recommended planting technique. Contact your county’s extension office for more details.
Legumes provide high amounts of protein to deer and other wildlife because they contain relatively high amounts of nitrogen. Due to a symbiotic relationship with a specific type bacteria, legumes are able to utilize atmospheric nitrogen. Other plants are dependent solely on soil nitrogen. To ensure that the proper bacteria is available to the legume it is important to inoculate legume seeds prior to planting. Inoculants are available through most seed dealers. Be sure that you get the proper inoculant for the species you are planting. Aeschynomene, Alyceclover, and Cowpeas all require the inoculant for the cowpea group. Soybeans and Lablab each have a species specific inoculant. Perennial Peanut does not require inoculation because it is not planted from seeds. Additional information about inoculants, planting techniques, and fertilization is available from your county’s extension office.
Planting food plots does not guarantee any additional antler growth but it is one way to help alleviate a possible limiting factor. Habitat improvement and additional available nutrition can benefit the entire ecosystem. If you want to get the most out of your property, in terms of deer production, it is important to provide the deer what they need all year long, not just during hunting season.
- Fall is an Excellent Time to Manage Vegetation - October 21, 2025
- Believe It or Not, It’s Time to Start Working on Cool-Season Food Plots - August 4, 2025
- Fall is Here, It’s Time to Spray Cogongrass - October 11, 2024
