
by Scott Jackson | Jun 21, 2019
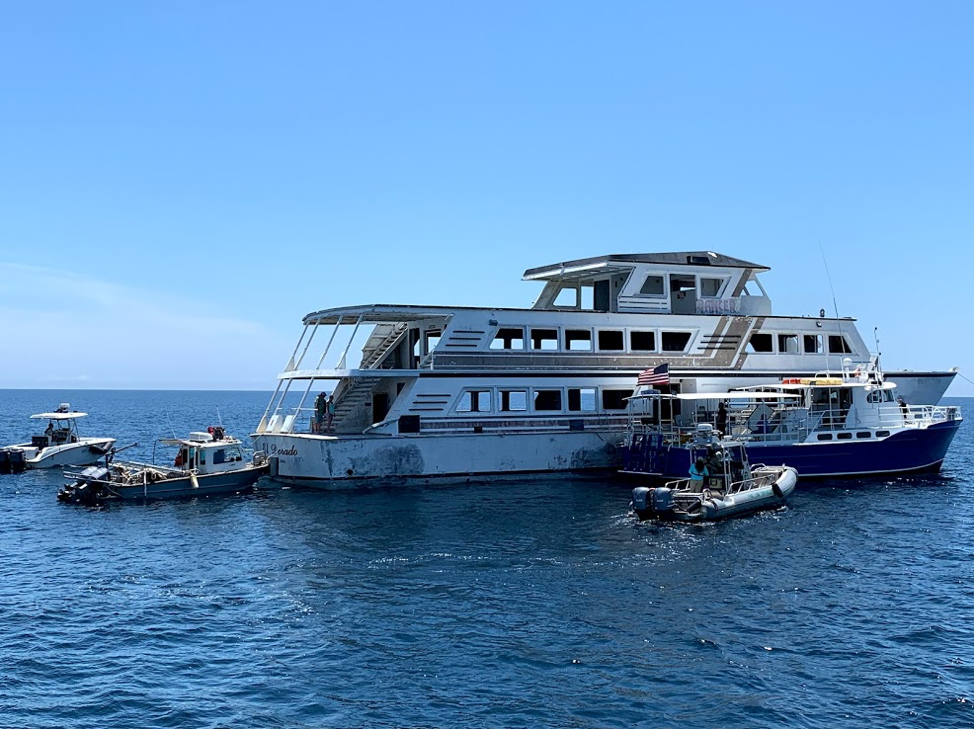

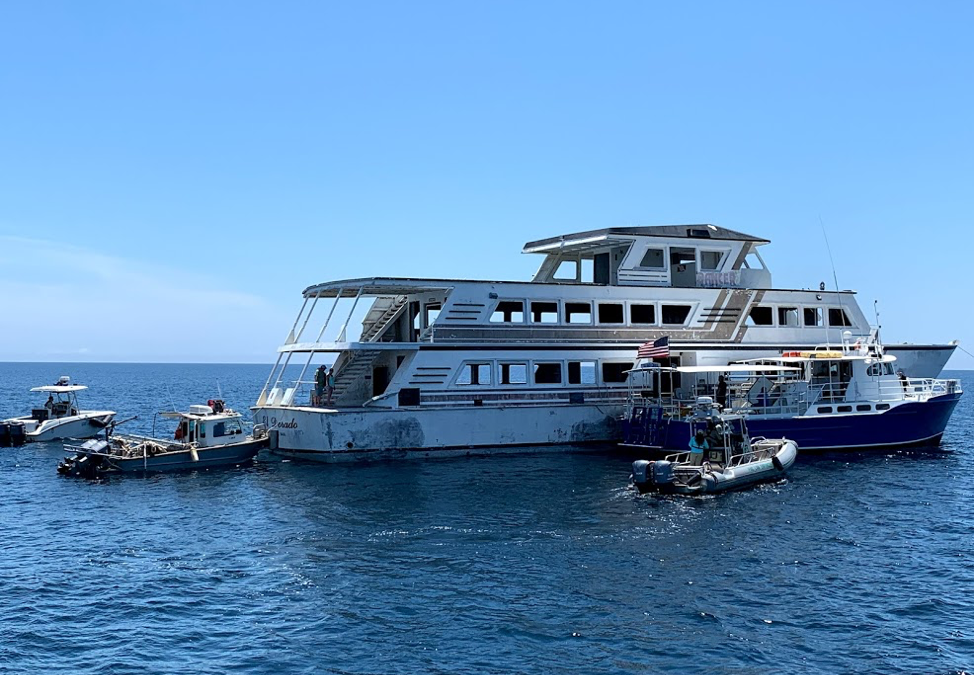
Panama City Dive Center’s Island Diver pulls alongside of the El Dorado supporting the vessel deployment by Hondo Enterprises. Florida Fish and Wildlife crews also are pictured and assisted with the project from recovery through deployment. The 144 foot El Dorado reef is located 12 nautical miles south of St Andrew Pass at 29° 58.568 N, 85° 50.487 W. Photo by L. Scott Jackson.
In the past month, Bay County worked with fishing and diving groups as well as numerous volunteers to deploy two artificial reef projects; the El Dorado and the first of the Natural Resources Damage Assessment (NRDA) reefs.
These sites are in Florida waters but additional opportunities for red snapper fishing are available this year to anglers that book for hire charters with captains holding federal licenses. Federal licensed Gulf of Mexico charters started Red Snapper season June 1st and continue through August 1st. Recreational Red Snapper fishing for other vessels in State and Federal waters is June 11th – July 12th. So booking a federally licensed charter can add a few extra fish to your catch this year.
The conversion of the El Dorado from a storm impacted vessel to prized artificial reef is compelling. Hurricane Michael left the vessel aground in shallow waters. This was in a highly visible location close to Carl Grey Park and the Hathaway Bridge. The Bay County Board of County Commissioners (BOCC) acquired the El Dorado, January 14, 2019 through negotiations with vessel owner and agencies responsible for recovery of storm impacted vessels post Hurricane Michael.
The El Dorado was righted and stabilized, then transported to Panama City’s St Andrews Marina by Global Diving with support from the Coast Guard and Florida Fish and Wildlife. Hondo Enterprises, was awarded a contract to complete the preparation and deployment of the vessel for use as an artificial reef.
Reefing the El Dorado provides new recreational opportunities for our residents and tourists. The new reef delivers support for Bay County’s fishing and diving charters continuing to recover after Hurricane Michael. Several local dive charter captains assisted in the towing and sinking of the El Dorado.
The El Dorado was deployed approximately 12 nm south of St. Andrew Bay near the DuPont Bridge Spans May 2, 2019. Ocean depth in this area is 102 feet, meaning the deployed vessel is accessible to divers at 60 feet below the surface.
The Bay County Board of County Commissioners continues to invest in the county’s artificial reef program just as before Hurricane Michael. Additional reef projects are planned for 2019 – 2020 utilizing Natural Resources Damage Assessment (NRDA) and Resources and Ecosystems Sustainability, Tourist Opportunities, and Revived Economies of the Gulf Coast States Act (RESTORE Act) funds. These additional projects total over 1.3 million dollars utilizing fines as a result of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Deployments will occur in state waters in sites located to both the east and west of St. Andrew Bay Pass.
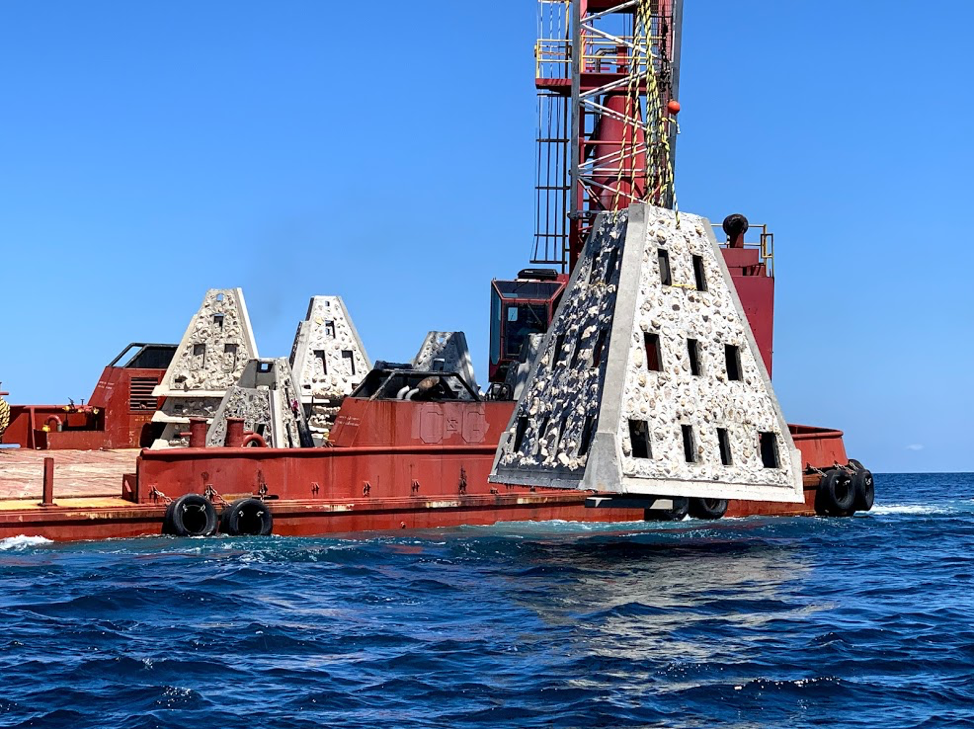

Walter Marine deploys one of nine super reefs deployed in Bay County’s NRDA Phase I project located approximately 12 nautical miles southeast of the St. Andrew Pass. Each massive super reef weighs over 36,000 lbs and is 15 ft tall. Multiple modules deployed in tandem provides equivalent tonnage and structure similar to a medium to large sized scuttled vessel. Photo by Bob Cox, Mexico Beach Artificial Reef Association.
The first of these NRDA deployments for Bay County BOCC was completed May 21, 2019 in partnership with Mexico Beach Artificial Reef Association, Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, and Florida Department of Environmental Protection using a $120,000 portion of the total funding. The deployment site in the Sherman Artificial Reef Permit Area is approximately 12 nm south east of St Andrew Bay Pass at a depth of 78 – 80ft.
| Patch Reef # |
Latitude |
Longitude |
| BC2018 Set 1
(6 Super Reefs and 4 Florida Specials) |
29° 55.384 N |
85° 40.202 W |
| BC2018 Set 2
(1 Super Reef and 4 Florida Specials) |
29° 55.384 N |
85° 39.739 W |
| BC2018 Set 3
(1 Super Reef and 4 Florida Specials) |
29° 55.384 N |
85° 39.273 W |
| BC2018 Set 4
(1 Super Reef and 4 Florida Specials) |
29° 55.384 N |
85° 38,787 W |
In 2014, Dr. Bill Huth from the University of West Florida, estimated in Bay County the total artificial reef related fishing and diving economic impact was 1,936 jobs, $131.98 million in economic output and provided $49.02 million in income. Bay County ranked #8 statewide in artificial reef jobs from fishing and diving. Bay County ranked #3 in scuba diving economy and scuba diving was 48.4 % of the total jobs related to artificial reefs. Dr. Huth also determine that large vessels were the preferred type of artificial reef for fishing and diving, with bridge spans and material the next most popular. Scuba diving and fishing on artificial reefs contributes significantly to the county’s economic health.
For more information and assistance, contact UF/IFAS Extension Bay County at 850-784-6105 or Bay@ifas.ufl.edu. Follow us on Facebook at http://faceboook.com/bayifas .
An Equal Opportunity Institution. UF/IFAS Extension, University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Nick T. Place, Dean for UF/IFAS Extension. Single copies of UF/IFAS Extension publications (excluding 4-H and youth publications) are available free to Florida residents from county UF/IFAS Extension offices.
This article is also available through the the Panama City New Herald

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 14, 2017

The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill was one of the worst natural disasters in our country’s history.
Photo: Gulf Sea Grant
We are pleased to announce the release of a pair of new bulletins outlining how the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill impacted the popular marine animals dolphins and sea turtles. To read these and other oil spill science publications, go to http://gulfseagrant.org/oilspilloutreach/publications/.
The Deepwater Horizon’s impact on bottlenose dolphins – In 2010, scientists documented a markedly increased number of stranded dolphins in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Was oil exposure to blame? Could other factors have been in play? Read the answers to these questions here: http://masgc.org/oilscience/oil-spill-science-dolphins.pdf.
Sea turtles and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill – This publication reviews the estimated damage oil exposure caused to sea turtles and discusses continued research and monitoring efforts for these already endangered and threatened species. Click here to read this bulletin: http://masgc.org/oilscience/oil-spill-science-sea-turtles.pdf.
Also –
“Sea turtles and oil spills” presentations – On March 23 in Brownsville, Texas, more than 100 participants gathered in person and online to listen to scientists, responders, and sea turtle specialists explain what we know about how these creatures fared in 2010 and detail ongoing conservation programs. Watch videos of the presentations here: http://gulfseagrant.org/sea-turtles-oil-spills/.
Our oil spill science outreach team hopes you will find these resources useful! J

by Laura Tiu | Jul 22, 2016

Dr. Monica Wilson, University of Florida Sea Grant, shares an update on the research that has occurred in the past five years since the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Presented in the Rodeo Room at the Destin History and Fishing Museum. Photo credit: Laura Tiu
The Deepwater Horizon (DWH) oil spill occurred about 50 miles offshore of Louisiana in April 2010. Approximately 172 million gallons of oil entered the Gulf of Mexico. Five years after the incident, locals and tourists still have questions. The Okaloosa County UF/IFAS Extension Office invited a Gulf of Mexico Oil Spill Scientist, Dr. Monica Wilson, to help answer the five most common questions about the oil spill and to increase the use of oil spill science by people whose livelihoods depend on a healthy Gulf.
The event was held at the Destin History and Fishing Museum on Monday evening, July 11, 2016. Executive Director, Kathy Marler Blue partnered with the University of Florida to host the event. “The Destin History and Fishing Museum has a vision that includes expanding its programs to include a lecture series,” said Blue. Over 20 interested individuals attended the lecture and the question and answer session was lively. This was the first in what hopes to be an ongoing lecture series, bringing more scientific information to our county.
Dr. Wilson is based in St. Petersburg, Florida with the Florida Sea Grant College Program. Monica uses her physical oceanography background to model circulation and flushing of coastal systems in the region and the impacts of tropical storms on these systems. She focuses on the distribution, dispersion and dilution of petroleum under the action of physical ocean processes and storms. For this lecture, she covered topics such as: the safety of eating Gulf seafood, impacts to wildlife, what cleanup techniques were used, how they were implemented, where the oil went, where is it now, and do dispersants make it unsafe to swim in the water?
The oil spill science outreach program also allows Sea Grant specialists to find out what types of information target audiences want and develop tailor-made products for those audiences. The outreach specialists produce a variety of materials, such as fact sheets and bulletins, focused on meeting stakeholder information needs. The specialists also gather input from target audiences through workshops and work with researchers to share oil spill research results at science seminars that are facilitated by the specialists.
The Destin History and Fishing Museum is a nonprofit organization whose members are dedicated to preserving, documenting, and sharing the complete history of Destin. Please subscribe to their Facebook page for information on upcoming events. The UF IFAS Extension Okaloosa County office also hosts a Facebook page with announcement of upcoming programs.
For additional information and publications related to the oil spill please visit: https://gulfseagrant.wordpress.com/oilspilloutreach/

by Laura Tiu | Apr 22, 2016
The Deepwater Horizon (DWH) oil spill occurred about 50 miles offshore of Louisiana in April 2010. Approximately 172 million gallons of oil entered the Gulf of Mexico. Five years after the incident, locals and tourists still have questions. This article addresses the five most common questions.
QUESTION #1: Is Gulf seafood safe to eat?
Ongoing monitoring has shown that Gulf seafood harvested from waters that are open to fishing is safe to eat. Over 22,000 seafood samples have been tested and not a single sample came back with levels above the level of concern. Testing continues today.
QUESTION #2: What are the impacts to wildlife?
This question is difficult to answer as the Gulf of Mexico is a complex ecosystem with many different species — from bacteria, fish, oysters, to whales, turtles, and birds. While oil affected individuals of some fish in the lab, scientists have not found that the spill impacted whole fish populations or communities in the wild. Some fish species populations declined, but eventually rebounded. The oil spill did affect at least one non-fish population, resulting in a mass die-off of bottlenose dolphins. Scientists continue to study fish populations to determine the long term impact of the spill.
Question #3: What cleanup techniques were used, and how were they implemented?
Several different methods were used to remove the oil. Offshore, oil was removed using skimmers, devices used for removing oil from the sea’s surface before it reaches the coastline. Controlled burns were also used, where surface oil was removed by surrounding it with fireproof booms and burning it. Chemical dispersants were used to break up the oil at the surface and below the surface. Shoreline cleanup on beaches involved sifting sand and removing tarballs and mats by hand.
QUESTION #4: Where did the oil go and where is it now?
The oil spill covered 29,000 square miles, approximately 4.7% of the Gulf of Mexico’s surface. During and after the spill, oil mixed with Gulf of Mexico waters and made its way into some coastal and deep-sea sediments. Oil moved with the ocean currents along the coast of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. Recent studies show that about 3-5% of the unaccounted oil has made its way onto the seafloor.
QUESTION #5: Do dispersants make it unsafe to swim in the water?
The dispersant used on the spill was a product called Corexit, with doctyl sodium sulfosuccinate (DOSS) as a primary ingredient. Corexit is a concern as exposure to high levels can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation. To evaluate the risk, scientists collected water from more than 26 sites. The highest level of DOSS detected was 425 times lower than the levels of DOSS known to cause harm to humans.
For additional information and publications related to the oil spill please visit: https://gulfseagrant.wordpress.com/oilspilloutreach/
Adapted From:
Maung-Douglass, E., Wilson, M., Graham, L., Hale, C., Sempier, S., and Swann, L. (2015). Oil Spill Science: Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions about the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. GOMSG-G-15-002.
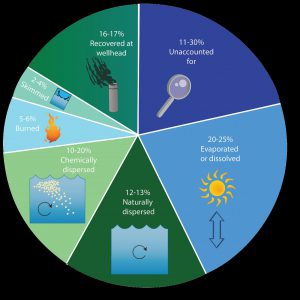
An estimate of what happened to approximately 200 million gallons oil from the DWH oil spill. Data from Lehr, 2014. (Florida Sea Grant/Anna Hinkeldey)
The Foundation for the Gator Nation, An Equal Opportunity Institution.








