
by Matt Lollar | Jan 2, 2025
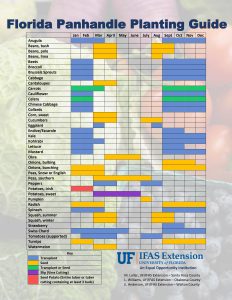
It’s a new year and if you’re still contemplating resolutions, here’s one for you. Stay organized with your vegetable planting schedule. Since it’s January, let’s start with what you can do now. Crops like beets, broccoli, and Brussels are best planted as transplants in January. But carrots and celery can be started from seed and potatoes can be planted as seed potatoes, which are usually pieces of potato tubers containing at least 3 buds (eyes). January is also a good time to start transplants indoors for the spring garden. Tomato and pepper transplants can be planted in the garden as early as February or March depending on the year. If all this planting talk is overwhelming, then at least consider collecting and mailing off a soil sample for nutrient analysis. More information on soil testing can be found on askIFAS. This will give you a head start on adjusting pH with lime and improving soil health with compost and other organic materials. To help plan this “Year of the Vegetable Garden” please click below to enlarge the image of the handy “Florida Panhandle Planting Guide”.

by Matt Lollar | Nov 13, 2024

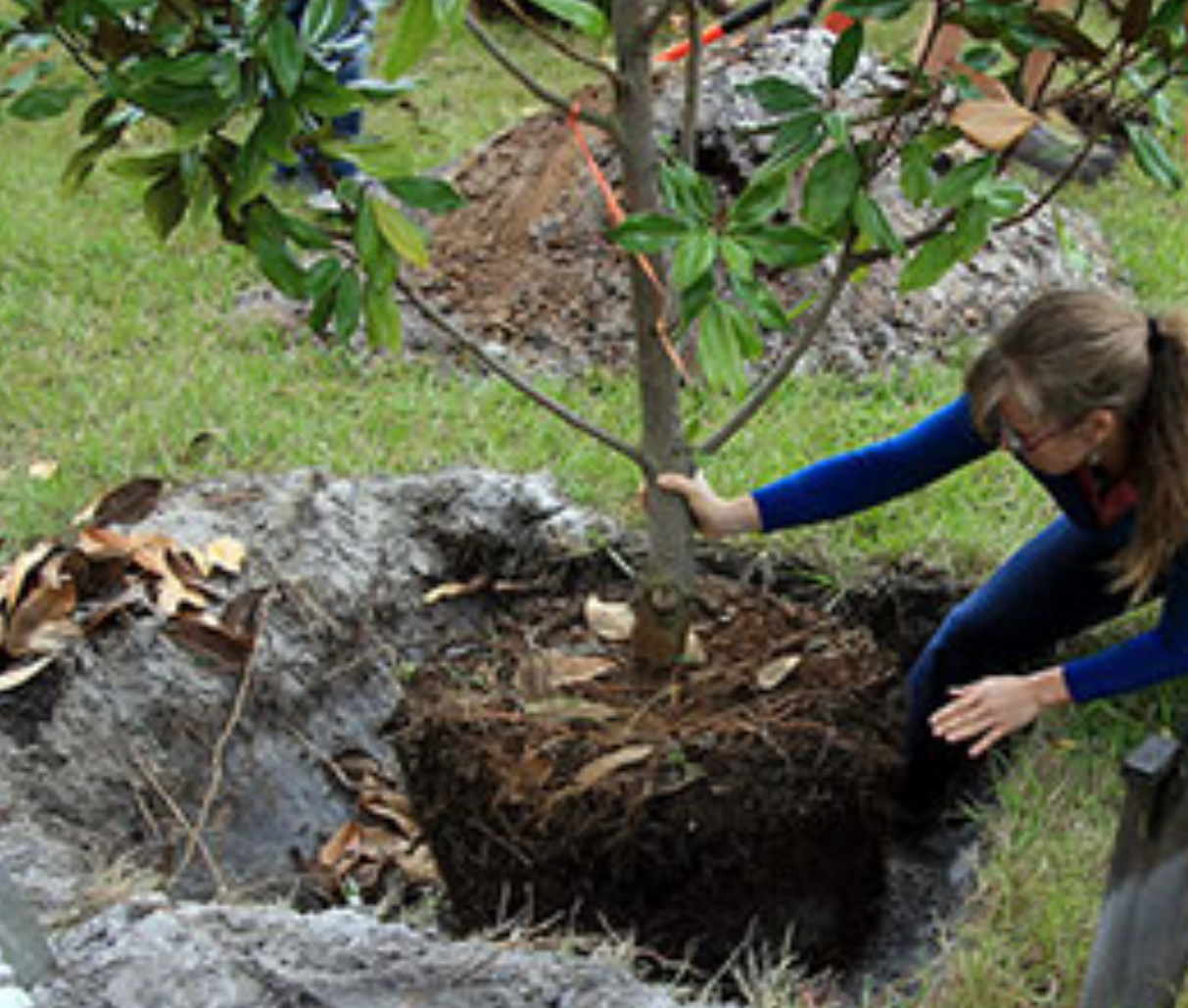
A planted tree with water retention berm. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Extension agents are frequently tasked with evaluation of unhealthy plants in the landscape. They diagnose all sorts of plant problems including those caused by disease infection, insect infiltration, or improper culture.
When evaluating trees, one problem that often comes to the surface is improper tree installation. Although poorly installed trees may survive for 10 or 15 years after planting, they rarely thrive and often experience a slow death.
Fall is an excellent time to plant a tree in Florida. A couple of weeks ago beautiful Nuttall Oak was planted at Bagdad Mill Site Park in Santa Rosa County, FL. Here are 11 easy steps to follow for proper tree installation:
- Look around and up for wire, light poles, and buildings that may interfere with growth;
- Dig a shallow planting hole as wide as possible;
- Find the point where the top-most root emerges from the trunk;
- Slide the tree carefully into the planting hole;
- Position the point where the top-most root emerges from the trunk slightly above the landscape soil surface;
- Straighten the tree in the hole;
- Remove synthetic materials from around trunk and root ball;
- Slice a shovel down in to the back fill;
- Cover the exposed sides of the root ball with mulch and create water retention berm;
- Stake the tree if necessary;
- Come back to remove hardware after establishment.
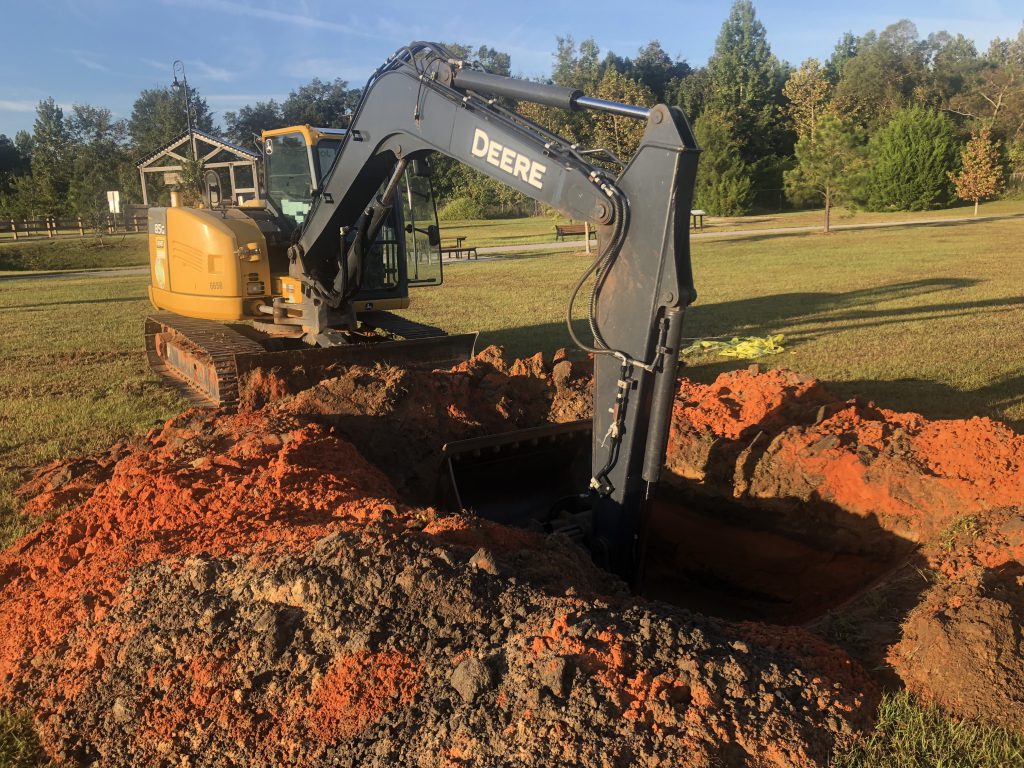

Digging a properly sized hole for planting a tree. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
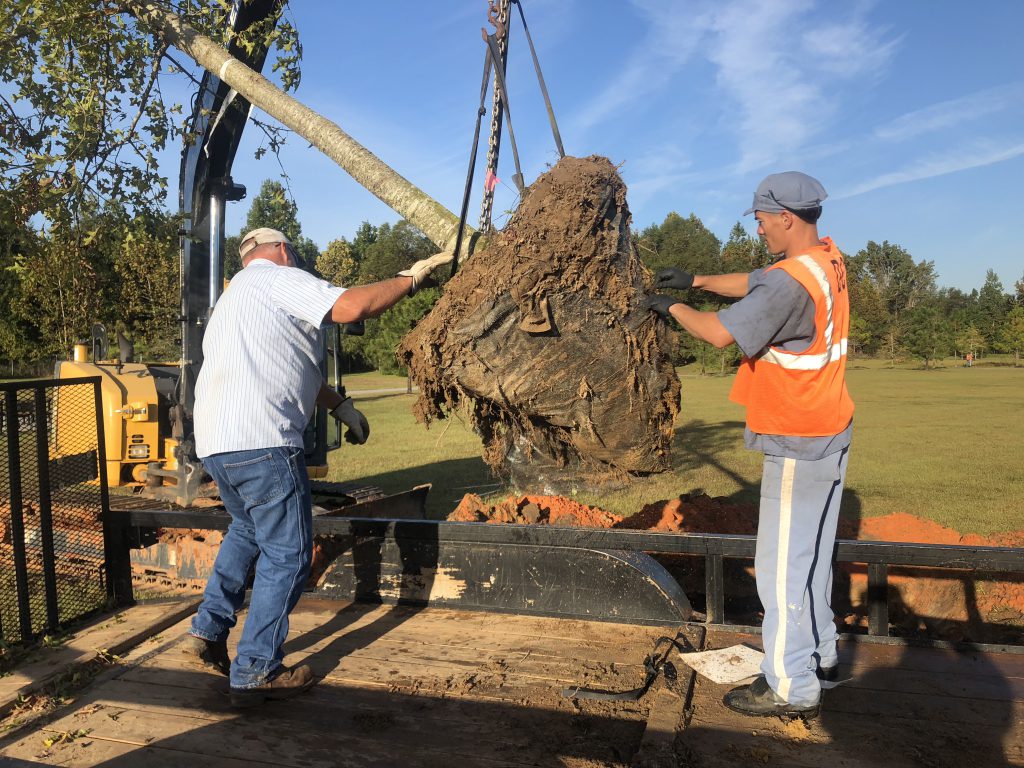

Removing synthetic material from the root ball. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
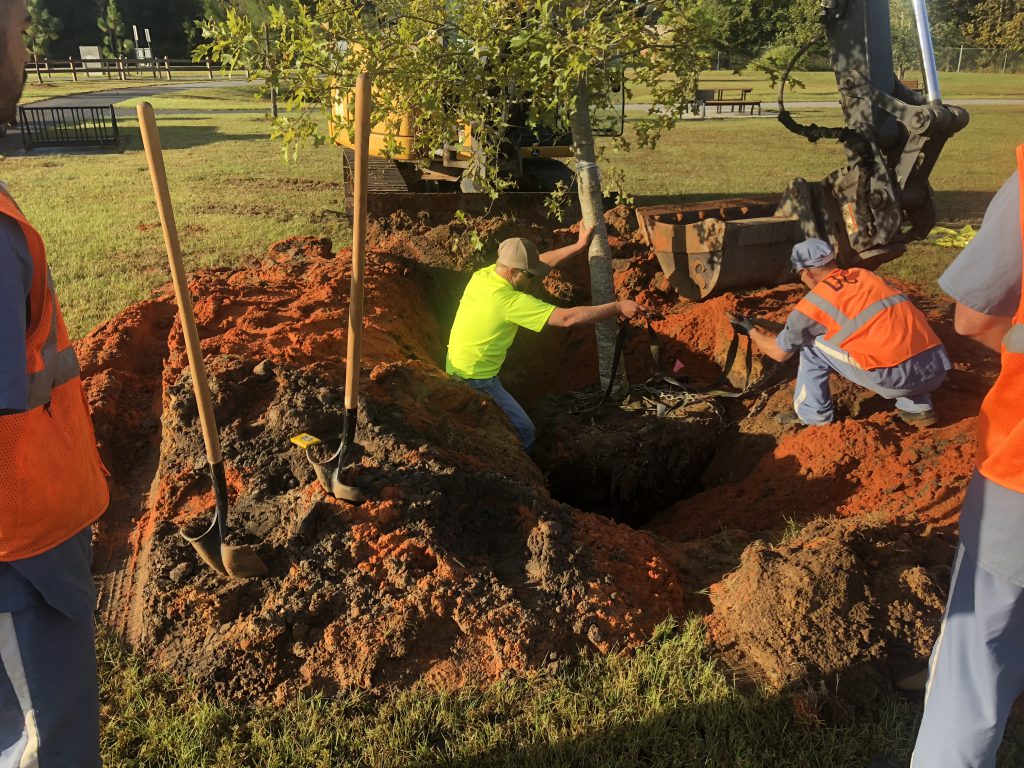

Straightening a tree and adjusting planting height. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida – Santa Rosa County
For more detailed information on planting trees and shrubs visit this UF/IFAS Website – “Steps to Planting a Tree”.
For more information Nuttall Oaks visit this University of Arkansas Website.

by Matt Lollar | Oct 8, 2024
On a recent family walk, I noticed something pretty obvious. One of our neighbors had a broken irrigation head. Luckily this is an easy fix, because a new rotor can just be screwed into place. But seeing the amount of water running into the street got me thinking about some additional ways to save water. Scroll down for some water saving tips based on the 9 Principles for Florida Friendly Landscaping.

Water runoff from a broken irrigation head. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
4 Ways to Save Water
- Pick the right plant for the right place. Turf is an excellent choice for catching runoff in the situation pictured above. However, it’s important to evaluate your yard based on the amount of sunlight received throughout the day. Once you’ve determined if you need sun loving, shade loving, or plants that can handle a little of both, you’ll want to check how well your soil drains. Some plants can handle wet conditions better than others. Use the FFL Plant Guide to help pick the plants for your space.
- Irrigate based on plant requirements. Plants like to be watered thoroughly to the extent of their rootzones. For turf, we recommend irrigating deeply and infrequently early in the morning. This method encourages the roots to grow deep to reach the water needed. Most established trees and shrubs don’t need supplemental irrigation unless we’re going through an extended period of drought. Review the Summary of Turf and Landscape Irrigation Recommendations to help determine the amount of water your yard needs.
- Calibrate the irrigation system. If you have an irrigation system, then you need to make sure it’s calibrated. To do this, you’ll first need to make sure your system doesn’t have any leaks or broken heads and redirect heads to water plants instead of the driveway, sidewalk, or road. Next, you’ll need to determine how long to run your system based on water output. The run time test is detailed on the UF/IFAS Calibrating Your Irrigation System webpage.
- Use mulch around trees and shrubs. Mulch can help hold moisture and conserve water. It’s important to keep mulch to between 2 and 3 inches deep and at least 2 inches away from the base of trees and shrubs. There’s a lot more information on Choosing and Installing Mulches on the Gardening Solutions website.
Following these simple tips will ensure that you’re watering efficiently and effectively. If you have additional questions about irrigation or just about anything plant related, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office.

by Matt Lollar | Jun 20, 2024
It seems like I’m always finding a unique spider in the house. Whether I’ve been summoned to remove it from the premises or by a chance encounter. It is no surprise to me that there are more than 250 species of spiders found in Florida. In fact, I figured there were quite a bit more. Some spiders are aggressive, some have extreme patience, and others aren’t even spiders at all. Continue reading for some interesting facts about a few of the most common spiders in North Florida.

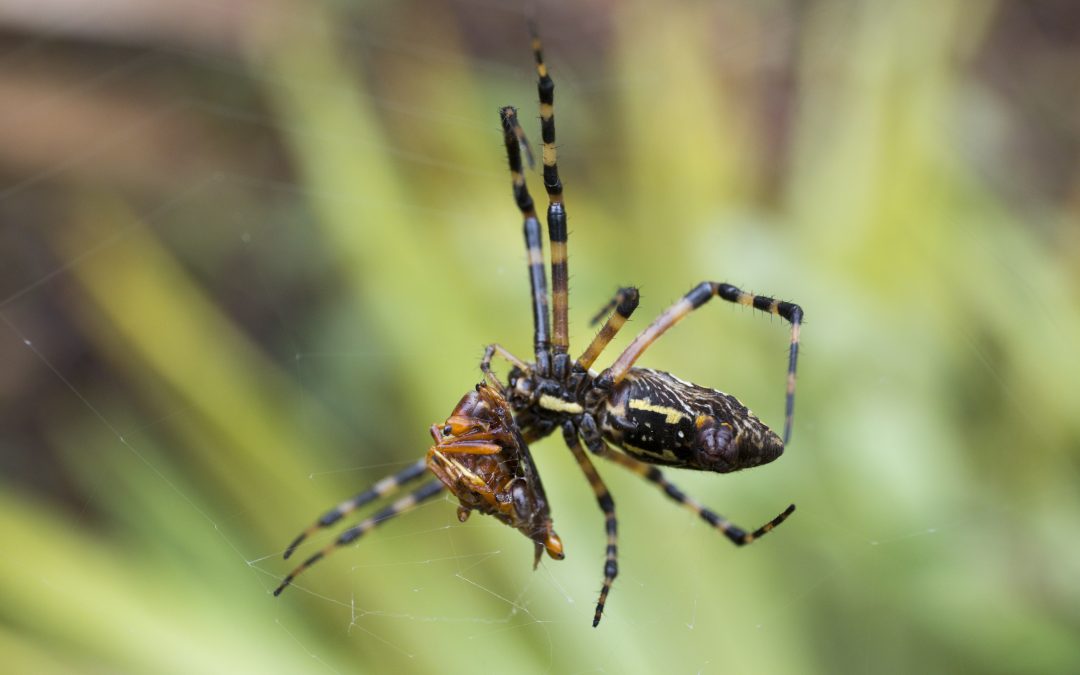
A golden silk orb-weaver spider with captured prey. Photo Credit: Tyler Jones, University of Florida.
Golden Silk Orb Weaver (Trichonephila Clavipes)
I grew referring to orb weavers as banana spiders. I guess I wasn’t the only one, because banana spiders are another one of their common names. Orb weavers are known for making big webs and producing really strong silk. Female spiders usually have other, smaller spiders occupying their webs. Male orb weavers are roughly a quarter the size of their female counterparts. In addition to the orb weaver couple on the web, small kleptoparasitic dewdrop spiders in the genus Argyrodes can be found eating bits and pieces of prey left behind.
Southern House Spider (Kukulcania hibernalis)
The brown recluse is a spider we can live without. Fortunately, they’re not very common in Florida. However, male southern house spiders are often mistaken for recluse spiders. If you want to be sure, just count the number of eyes. House spiders have eight eyes, whereas brown recluses only have six. Female southern house spiders don’t look like recluses or male southern house spiders at all. The females are dark brown with thick bodies and males are lanky and light brown. These spiders build thick webs in wall corners and the edges of windows.

Male (a) and female (b) southern house spider (Kukulcania hibernalis) The male is light brown with long pedipalps, while the female is a dark velvety brown with shorter pedipalps.
Photo Credit: Erin C. Powell, FDACS-DPI
Harvestmen (Opiliones Family)
Everyone has seen a “daddy long legs” spider or at least we think we have. We may sometimes refer to harvestmen as “daddy long legs” spider, but they’re not even spiders at all. Harvestmen are classified as arachnids like spiders, scorpions, and mites, but they come from a different family (Opiliones). They only have one body segment, instead of two, they have no venom glands, and they can’t produce silk. And if anyone tells you they are the most venomous spider but can’t bit humans because their mouths are too small – well you know what to tell them. And there is such a thing as a cellar spider (Pholcus spp.) that has long legs, two body segments, and is also referred to as a “daddy long legs”, but what’s the fun in that.
We could go on and on about all the different spiders that can be found in and around your home, or not. If you are interested in other common spiders in Florida, then you should check out the UF/IFAS publication “An Introduction to Some Common and Charismatic Florida Spiders”. Then you’ll know exactly what’s lurking around the corner.

by Matt Lollar | May 2, 2024
They’ve mostly all moved away for now, but every winter and early spring the office gets questions about tiny beetles in homes. These beetles are small with spotty color patterns. The answer is carpet beetles. Carpet may be in their name, but it may not be their favorite spot. Carpet beetles feed on a lot of the same things as clothes moths such as wool, felt, and fur because these materials contain keratin. And their feeding damage is often mistaken for that of clothes moths.

Varied carpet beetle adult. Photo Credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida/IFAS
Adult carpet beetles are between 1/16 to 1/8-inch in length. They are oval-shaped and range in color from black to various patterns of white, brown, yellow, and orange. The majority of samples we see are black and white mottled. The adults are often found on windowsills and window stools in the springtime. The larvae conduct all the damage to fabrics and other materials, while the adults stick to feeding on flower pollen. The evidence of feeding can be seen by threadbare spots and irregular holes. Blankets and clothes in storage and carpeted areas under furniture are preferred because they are undisturbed.
As with most insect pests, prevention is the best control for carpet beetles. In addition to feeding on fabrics and material, larvae feed on dust, lint, and animal hair. Frequent cleaning of floors and vacuuming of rugs and carpets eliminates most of the food supply. Stored blankets, clothes, and rugs should be periodically cleaned, brushed, and or sunned. Moth balls can be used at labeled rates but should not be the sole means of control.
For more information on carpet beetles and more detailed prevention and control tactics, please go the University of Florida/IFAS Publication: “Pests in and around the Souther Lawn – Carpet Beetles”.














