Be Careful of Residual Herbicides: Buying and Selling Hay/Straw for Garden Mulch and Compost
This article was written by Kacey Aukema, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Walton County.
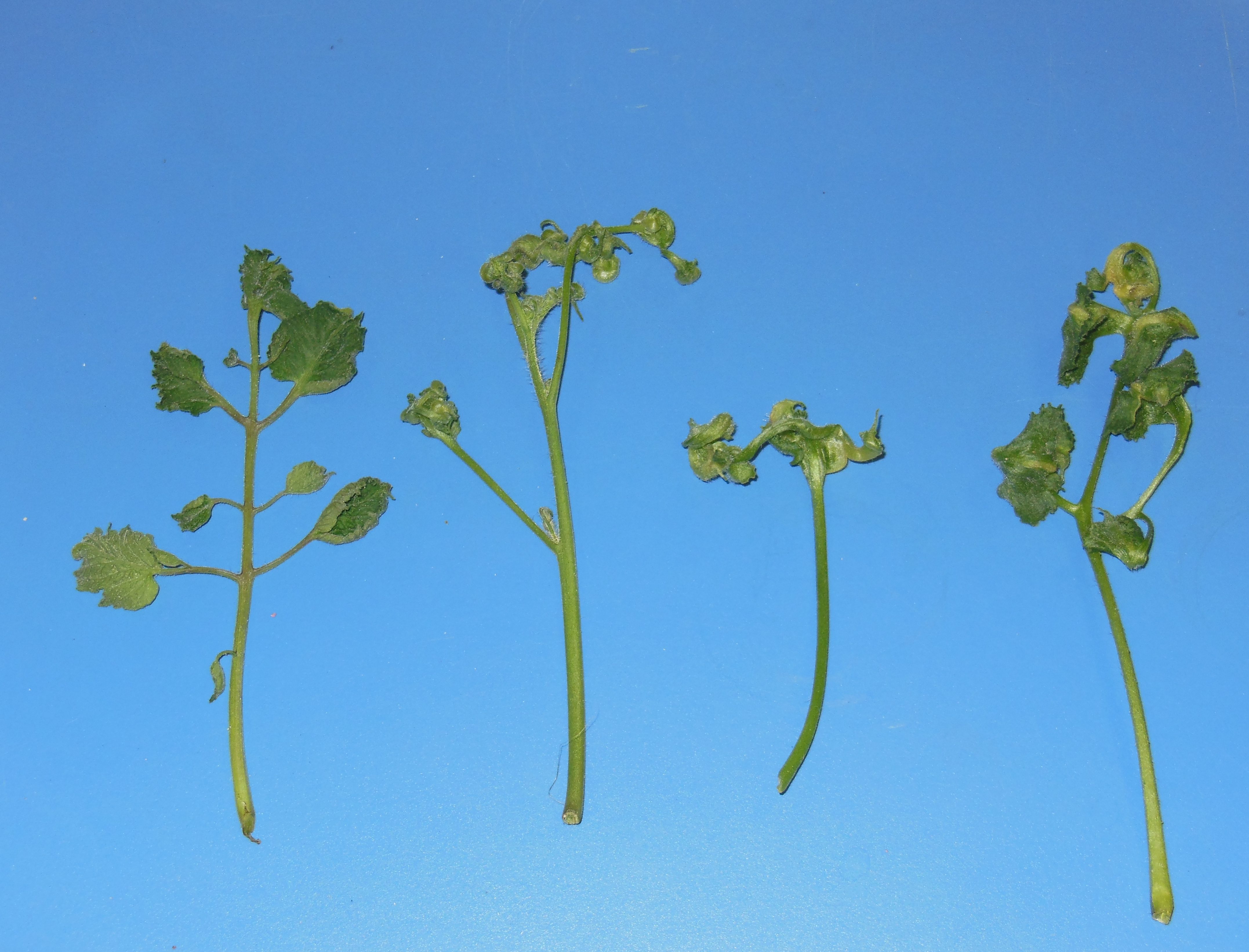
I recently met with a home gardener who brought in tomato plants showing strange symptoms on the leaves. Together we puzzled over the odd leaf-curling symptoms that were affecting their tomato beds, but not other areas of the garden. Upon further investigation it was revealed that hay, used as mulch, had recently been spread around the tomatoes, but not in other areas of the garden. It quickly became apparent that the symptoms were likely related to herbicide residual on the hay that was used. The herbicide aminopyralid was the potential culprit. In this case the residual herbicide was not enough to outright kill the growing tomato plants. However, it was interfering with their growth and development and is a cautionary tale reminding us how important careful sourcing of hay used in mulch or compost can be.
What is aminopyralid and how does residual herbicide affect non-target plants through mulch, compost, etc.?
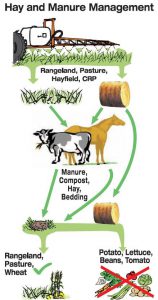
Aminopyralid is a herbicide active ingredient found in several popular pasture products such as GrazonNext™, Milestone™, Chapparral™ and similar products. This and other similar chemicals have residual activity and can be retained in plant tissues, animal manure, and soil, which makes them a very useful for controlling certain troublesome broadleaf weeds in grass pastures for an extended period of time. Unfortunately, this residual activity increases the potential for causing trouble in vegetables or other crops when hay or animal manure from aminopyralid treated pastures is mistakenly used for mulch, compost, etc. In Florida, aminopyralid containing pasture herbicides are often used as the “go to” for control of hard to control weeds like horsenettle and tropical soda apple which are potentially toxic to livestock. Tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplant are in the same genus (Solanum) as those weeds and are therefore very susceptible to this herbicide as are many other vegetable and other broadleaf crops.

Residual aminopyralid damage on a tomato plant. Photo Credit: Kacey Aukema, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Walton County
How can I know if hay is safe to be used for mulch or compost?
Before acquiring hay to be used as mulch or to compost for vegetable beds, be sure to ask if the hay is free of herbicides with residual activity. Find out what was sprayed on the field in the last two seasons before the hay was harvested. Given that hay destined to be used as mulch or compost is usually old and spoiled, management history of a particular hay bale is likely to be hard to pin down. Do not trust hay to be used for mulch or compost in vegetable beds if prior spray management details are unknown. Also consider that well-stored hay may retain residual herbicide better and for a longer period of time than weathered hay, as the active ingredient is less subject to weathering and biological breakdown.
Those who use broadleaf herbicide products with residual activity such as those containing aminopyralid are subject to follow herbicide label guidelines. For instance, supplemental labeling of GrazonNext HL™ (including FL, AL, and GA) indicates that hay/straw from fields sprayed in the past 18 months should not be used for compost, mulch, or mushroom spawn. When in doubt refer to the label of the particular herbicide product used on hay you purchase for any restrictions and/or reach out to your local county extension agent if you have questions about a specific herbicide product. Relevant use restrictions and considerations like in this example should be conveyed between hay producer and buyer.
Perhaps you already have some hay for mulch/compost with an unclear management history, or you would like to double-check and be sure that it is safe. How could one test it to see if it was safe to use? There is a test called a “bioassay”, conducted by growing susceptible plant seedlings like tomatoes or beans in small pots with the hay/compost/mulch in question incorporated into the potting soil. Then, the test plants can be observed to see if any herbicide symptoms develop to know whether the material is safe to use, before using the hay over a larger area or garden where there would be more risk. For more information on how to conduct a bioassay see: Herbicide Residues, in Manure, Compost, or Hay. Similar in-field bioassays are also recommended when rotating areas out of pasture and into other crops when pasture herbicides with residual activity were used. If susceptible crops like peanuts are grown in areas where such herbicides were used in the recent past they can be damaged, as in this case in an older Panhandle Agriculture Newsletter post.
When used according to label instructions, herbicides with residual activity are very useful for control of broad-leafed weeds in pasture and hay fields and may reduce the spread weeds through seed coming in on purchased hay. However, problems can emerge when hay from fields treated with these products change hands without the use restrictions and considerations being adequately explained. Therefore, caution should be taken by both producer and buyer to avoid damaging sensitive crops when hay or livestock manure are used for mulch or compost.