
by Rick O'Connor | Aug 3, 2018
Of all the issues facing our local estuaries, high levels of fecal bacteria is the one that hinders commercial and recreational use the most. When bacteria levels increase and health advisories are issued, people become leery of swimming, paddling, or consuming seafood from these waterways.

Closed due to bacteria.
Photo: Rick O’Connor
I have been following the fecal bacteria situation in the Pensacola Bay system for several decades. Cheryl Bunch (Florida Department of Environmental Protection) has done an excellent job monitoring and reporting the bacteria levels, along with other parameters, for years – she has been fantastic.
The organisms used for monitoring have changed, so comparing numbers now and 30 years ago is somewhat difficult – but those changes came with good reason.
Fecal bacteria are organisms found in the large intestine of birds and mammals. They assist with digestion and are not a real threat to our health. Understanding that both birds and mammals in and near our estuaries must defecate, it is understandable that some levels of these bacteria are in the waterways. However, when levels are high there is a concern there are high levels of waste in the water. This waste can carry other organisms that can cause health problems for humans – such as hepatitis and cholera. So fecal bacteria monitoring is used as a proxy for other potential harmful organisms. No one wants to swim in sewage.
E. coli is a classic proxy for this type of monitoring and has been used for years. Recently it was found that saline water could kill some of the fecal bacteria – giving monitors’ low readings in estuarine systems – suggesting that there is little sewage in the water – when in fact there may be high levels of sewage undetected. They have found Enterococcus a better proxy for marine waters, particularly Enterococcus faecalis. Researchers have determined that a single sample of bay water should have more than 35 colonies of Enterococcus (ENT). If they find 35 or more colonies – a second sample is taken. If the counts are again high – a health advisory will be issued.
Over the last 30 years of monitoring FDEP’s reports on the Pensacola Bay area – there have been patterns. Most of the “hot spots” have been bayous and locations where rivers are discharging into an estuary. In addition, the periods of high fecal counts correspond well with periods of high rainfall. Locally, in the Pensacola Bay area, sampling has been reduced due to budget issues and some bodies of water are not sampled as often as others. Today both FDEP and the Florida Department of Health (FDOH) monitor and post their data via the Healthy Beaches Program. In this program, the sample stations are commonly used swimming areas – meaning some other locations are rarely, if ever, sampled. Based on these data, 30-40% of the samples from local bayous annually require a health advisory to be issued.
Health advisories can reduce interest in human related recreation activities, such as wakeboarding, paddling, or even fishing – and certainly impacts interest in swimming. Decades ago, swimming and skiing were very popular in local bayous. Today it is rare to see anyone doing so – most are motoring through heading to open bodies of water to spend their day. It may also be effecting property purchases. I have been contacted more than once with the question “would you buy on a house on XXX Bayou?”
Several local waterways are listed as impaired, and one is a BMAP area, due to high levels of bacteria. A BMAP (Basin Management Action Plan – read more at the link below) is a state designated body of water that is impaired (for some reason) and is required to make annual improvements to reduce the problem.
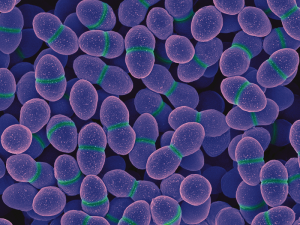
The spherical cells of the “coccus” bacteria Enterococcus.
Photo: National Institute of Health
So What Can We Do to Reduce This Problem?
In the Pensacola area, both the city and county have made efforts to modify and improve stormwater problems. Baffle boxes in east Pensacola have helped to reduce the amount of runoff entering the bayous and bays, thus reducing the frequency health advisories are being issued. That said, during heavy events the counts still increase – and rainfall seems to be increasing in the area in recent years. We will continue to monitor the frequency of advisories and post these on Sea Grant Notes through the Escambia County extension office each week.
From our side of the story (you and me) – anything you can do to reduce runoff will certainly help. Florida Friendly Landscaping techniques are a good start (see article on FFL posted below). Clean up after your pet, both in your yard and after walks – most people do… but not all. Septic systems have been a point of concern. If you have a septic system, maintain it (see article below on how). If the opportunity presents itself, you can move from septic to a sewer system. At many public places along the waterfront have signs asking everyone not to feed the birds. Congregating birds equals congregating bird feces and this can be a health issue.
Local and state governments are working to reduce the stormwater impacts on our local estuaries – which trigger other problems as well as high bacteria counts. Local residents and businesses can do the same.
References
Lewis, M.J., J.T. Kirschenfeld, T. Goodhart. 2016. Environmental Quality of the Pensacola Bay System: Retrospective Review for Future Resource Management and Rehabilitation. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Gulf Breeze FL. EPA/600/R-16/169.
BMAP
https://floridadep.gov/dear/water-quality-restoration/content/basin-management-action-plans-bmaps.
Florida Friendly Landscaping
Restoring the Health of Pensacola Bay, What You Can Do to Help? – Florida Friendly Landscaping
http://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/escambiaco/2018/06/08/restoring-the-health-of-pensacola-bay-what-can-you-do-to-help-a-florida-friendly-yard/.
Septic Systems
Maintain Your Septic Tank System to Save Money and Reduce Water Pollution
https://nwdistrict.ifas.ufl.edu/nat/2017/04/29/maintain-your-septic-system-to-save-money-and-reduce-water-pollution/.
Septic Tanks: What You Should Do When a Flood Occurs
https://nwdistrict.ifas.ufl.edu/nat/2018/05/04/septic-systems-what-should-you-do-when-a-flood-occurs/.

by Rick O'Connor | Jun 8, 2018
We have been posting articles discussing some of the issues our estuaries are facing; this post will focus on one of the things you can do to help reduce the problem – a Florida Friendly Yard.

Florida Friendly Landscaping saves money and reduces our impact on the estuarine environment.
Photo: UF IFAS
The University of Florida IFAS developed the Florida Friendly Landscaping Program. It was developed to be included in the Florida Yards & Neighborhoods (FYN) program, HomeOwner and FYN Builder and Developer programs, and the Florida-Friendly Best Management Practices for Protection of Water Resources by the Green Industries (GI-BMP) Program in 2008.
A Florida Friendly Yard is based on nine principals that can both reduce your impact on local water quality but also save you money. Those nine principals are:
- Right Plant, Right Place – We recommend that you use native plants in the right location whenever possible. Native plants require little fertilizer, water, or pesticides to maintain them. This not only reduces the chance of these chemicals entering our waterways but also saves you money. The first step in this process is to have your soil tested at your local extension office. Once your soil chemistry is known, extension agents can do a better job recommending native plants for you.
- Water Efficiently – Many homeowners in the Florida panhandle have irrigation systems on timers. This makes sense from a management point of view but can lead to unnecessary runoff and higher water bills. We have all seen sprinkler systems operating during rain events – watering at that time certainly is not needed. FFY recommends you water only when your plants show signs of wilting, water during the cooler times of day to reduce evaporation of your resource, and check system for leaks periodically. Again, this helps our estuaries and saves you money.
- Fertilize Appropriately – No doubt, plants need fertilizer. Water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide produce the needed energy for plants to grow, but it does not provide all of the nutrients needed to create new cells – fertilizers provide needed those nutrients. However, plants – like all creatures – can only consume so much before the remainder is waste. This is the case with fertilizers. Fertilizer that is not taken up by the plant will wash away and eventually end up in a local waterway where it can contribute to eutrophication, hypoxia, and possible fish kills. Apply fertilizers according to UF/IFAS recommendations. Never fertilize before a heavy rain.
- Mulch – In a natural setting, leaf litter remains on the forest floor. The environment and microbes, recycling needed nutrients within the system, break down these leaves. They also reduce the evaporation of needed moisture in the soil. FFY recommends a 2-3” layer of mulch in your landscape.
- Attract Wildlife – Native plants provide habitat for a variety of local wildlife. Birds, butterflies, and other creatures benefit from a Florida Friendly Yard. Choose plants with fruits and berries to attract birds and pollinators. This not only helps maintain their populations but you will find enjoyment watching them in your yard.
- Manage Yard Pests Responsibly – This is a toughie. Once you have invested in your yard, you do not want insect, or fungal, pests to consume it. There is a program called the Integrated Pest Management Program (IPM) that is recommended to help protect your lawn. The flow of the program basically begins with the least toxic form of pest management and moves down the line. Hopefully, there will not be a need for strong toxic chemicals. Your local county extension office can assist you with implementing an IPM program.
- Recycle – Return valuable nutrients to the soil and reduce waste that can enter our waterways by composting your turfgrass clippings, raked leaves, and pruned plants.
- Reduce Stormwater Runoff – ‘All drains lead to the sea’ – this line from Finding Nemo is, for the most part, true. Any water leaving your property will most likely end in a local waterway, and eventually the estuary. Rain barrels can be connected to rain gutters to collect rainwater. This water can be used for irrigating your landscape. I know of one family who used it to wash their clothes. Rain barrels must be maintained properly to not produce swarms of mosquitos, and your local extension office can provide you tips on how to do this. More costly and labor intensive, but can actually enhance your yard, are rain gardens. Modifying your landscape so that the rainwater flows into low areas where water tolerant plants grow not only reduces runoff but also provides a chance to grow beautiful plants and enhance some local wildlife.
- Protect the Waterfront – For those who live on a waterway, a living shoreline is a great way to reduce your impact on poor water quality. Living shorelines reduce erosion, remove pollutants, and enhance fisheries – all good. A living shoreline is basically restoring your shoreline to a natural vegetative state. You can design this so that you still have water access but at the same time help reduce storm water runoff issues. Planting below the mean high tide line will require a permit from the Florida Department of Environmental Protection, since the state owns that land, and it could require a breakwater just offshore to help protect those plants while they are becoming established. If you have questions about what type of living shoreline you need, and how to navigate the permit process, contact your local county extension office.

Santa Rosa Sound
Photo: Dr. Matt Deitch
These nine principals of a Florida Friendly Yard, if used, will go a long way in reducing our communities’ impact on the water and soil quality in our local waterways. Read more at http://fyn.ifas.ufl.edu/about.htm.






