
by Sheila Dunning | Jul 16, 2020
Dog Star nights Astro Bob
The “Dog Days” are the hottest, muggiest days of summer. In the northern hemisphere, they usually fall between early July and early September. The actual dates vary greatly from region to region, depending on latitude and climate. Life is so uncertain right now. But, fall is coming.
In ancient times, when the night sky was not obscured by artificial lights, the Romans used the stars to keep track of the seasons. The brightest constellation, Canis Major (Large Dog), includes the “dog star”, Sirius. In the summer, Sirius used to rise and set with the sun, leading the ancient Romans to believe that it added heat to the sun. Although the period between July 3 and August 11 is typically the warmest period of the summer, the heat is not due to the added radiation from a far-away star, regardless of its brightness. The heat of summer is a direct result of the earth’s tilt.
Spending time outdoors this time of year is uncomfortable, potentially dangerous, due to the intense heat. However, the chinch bugs are very active in St. Augustine grass (for more information: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/lh036), and the summer flowers need water. So, take care of those tasks early in the day and then retreat to the air conditioning to plan your fall planting.
Plant tomato plants in August for fruit in October. Varieties such as Phoenix, Florida 91, Solar Set and Heat Wave II are good selections for setting fruit in high temperatures, should summer temperatures continue. Otherwise, try some of the newer UF/IFAS recommended varieties for fall planting in North Florida such as Bella Rosa, Tribute or Finishline. For more information on tomato selection refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in756. For information on other vegetables for fall gardening refer to the Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vh021.
Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all

Hummingbird at Firespike flower
winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg319.
Dependable fall blooming perennials include lion’s ear (Leonotis leonurus), pineapple sage (Salvia elegans), firebush (Hamelia patens), cigar plant (Cuphea micropetala), yellowbells (Tecoma stans) and firespike
(Odontonema strictum). Also, garden mums (Chrysanthemum sp.) and many different Irises will add color again in the spring. To gain information on perennials for Florida refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg035.
Webster’s second definition of “dog days” is a period of stagnation or inactivity. But, even when the heat forces you to slow down on the labor-intensive work, there is plenty of gardening “activity” to do. Stay in the air conditioning and plan that spectacular fall and winter yard.

by Sheila Dunning | Jul 9, 2020

Utility tree trimming truck
With hurricane season upon us, evidence of preparation is all around us. Tree trimmers, contracted by the local electrical utility companies, have been removing trees, branches and other vegetation that is “too close” to power lines. Many homeowners are concerned over the practice.
In order to prevent power outages, the federally approved Vegetation Management Reliability Standard, FAC-033-2, requires utilities to manage vegetation growth along the path of power lines to prevent contact. A minimum clearance of fourteen (14) feet between trees and transmission lines in the right-of-way must be maintained at all times in order to achieve service reliability and public safety.
By Florida Statute 163, an electric utility is granted easement or right-of-way on private property in order to build and maintain electric power lines. Vegetation maintenance allows for the mowing of vegetation within the right-of-way, removal of trees or brush within the right-of-way and selective removal of tree branches that extend within the right-of-way by the electric utility personnel, licensed contractors or International Society of Arboriculture (ISA) Certified Arborists. The choice of how to trim trees and manage vegetation growth near a power line (e.g. pruning, herbicides, or tree removal) is primarily made by the electric utility, subject to state and local requirements and laws, applicable safety codes, and any limitations or obligations specified in right-of-way agreements. An individual may contact the utility company to obtain a copy of the right-of-way agreement for their property.

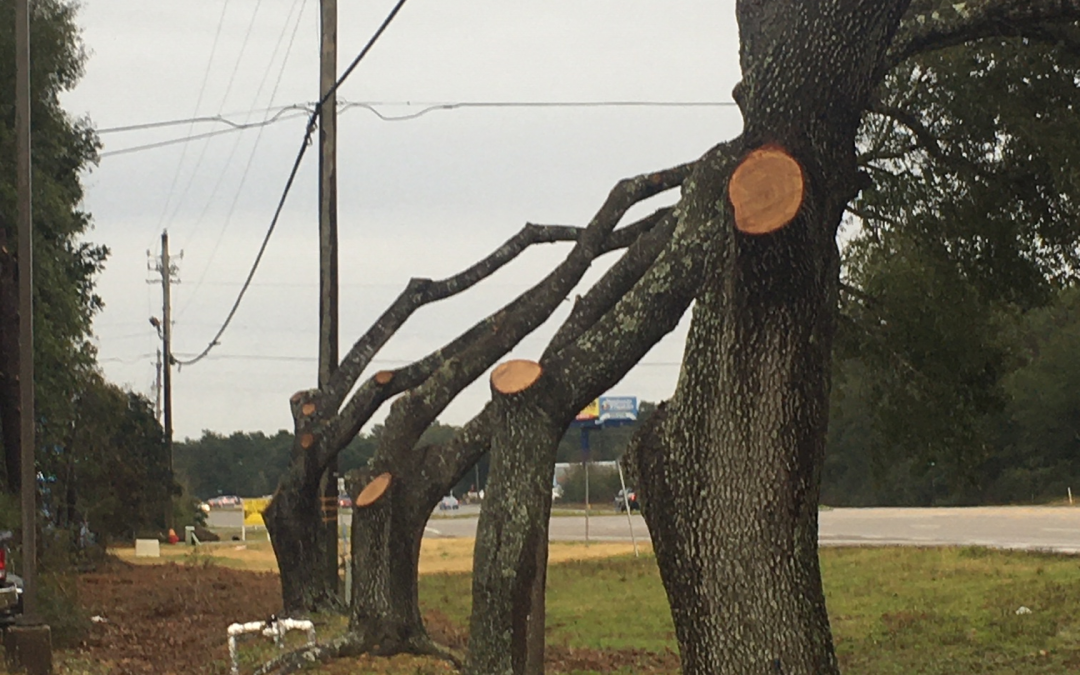
Over-pruned trees along power line
Sometimes, it appears to some that excessive vegetation has been removed. But, remember the utility companies are required to maintain the appropriate clearance “at all times.” For example, in the summer, power lines sag as they expand from rising air temperatures and heavy use. Also, wind and future growth must be taken into account when determining where to prune. Electric utilities usually prune or remove vegetation to a distance greater than the minimum clearances to account for all these factors. However, in many instances, removal of the tree would be more aesthetically pleasing and could avoid leaving a hazardous tree in the landscape. But, that is not part of their contract. That decision must be made by the property owner.
Tree trimming around power lines may seem like a local issue, but vegetation growth also affects interstate transmission lines. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that electric utility service interruptions cost businesses and communities tens of billions of dollars annually. Tree contact with transmission lines was the leading cause of the August 2003 blackout that affected 50 million people in the Northeastern United States and Canada. In fact, that particular blackout prompted Congress to pass the Energy Policy Act of 2005, which lead the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to establish the Vegetation Management Reliability Standard.
Should we have a storm that impacts Northwest Florida, remember that the clearing of trees and branches provides faster access for first responders, line repair crews, and other emergency service personnel. So, as you watch the preparation work being done, think about where you will be planting a tree so that it can reach full maturity without threatening power lines, therefore, not requiring “ugly pruning!”
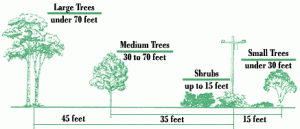
Spacing between trees and power lines
The urban forest is much different from a natural forest. Trees often develop a form that is more susceptible to breakage when grown in developed commercial and residential environments. As a result, trees need preventive pruning to develop strong structure. Research and observation show that well pruned trees can create a more wind resistant urban forest.
Pruning to create stronger tree structure is an ongoing process. To minimize the likelihood of tree damage it is necessary to reduce the length of limbs with a weak attachment to the trunk and to balance the canopy by reducing the length of limbs on the side where weight is concentrated. Do not remove interior branches, as this concentrates foliage at the tips of branches and causes them to break in strong winds.
Limbs that are more than ½ the diameter of the trunk and multiple trunks of similar size must be reduced in order to form strong branch unions and eliminate co-dominant leaders. A reduction cut is pruned back to a smaller lateral branch. Good pruning cuts avoid cutting into the collar. The collar is the swollen area at the base of the branch where it joins the trunk. The tissue is rich in energy reserves and chemicals that hinder the spread of decay.
Preventative pruning only applies to woody tree species. Palms need fronds to protect the bud and provide nutrients for growth. Arborists report that results from previous storms revealed that palms that had been “hurricane pruned” suffered more damage than those that were not pruned. Do not wait until the last minute to prepare your trees for hurricane season. Take action now. For more information on pruning visit: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/woody/pruning.shtml.
If you want professional help evaluating your trees or performing the proper corrective actions, visit: https://www.treesaregood.org/findanarborist to locate a Certified Arborist working in your area.

by Sheila Dunning | May 27, 2020

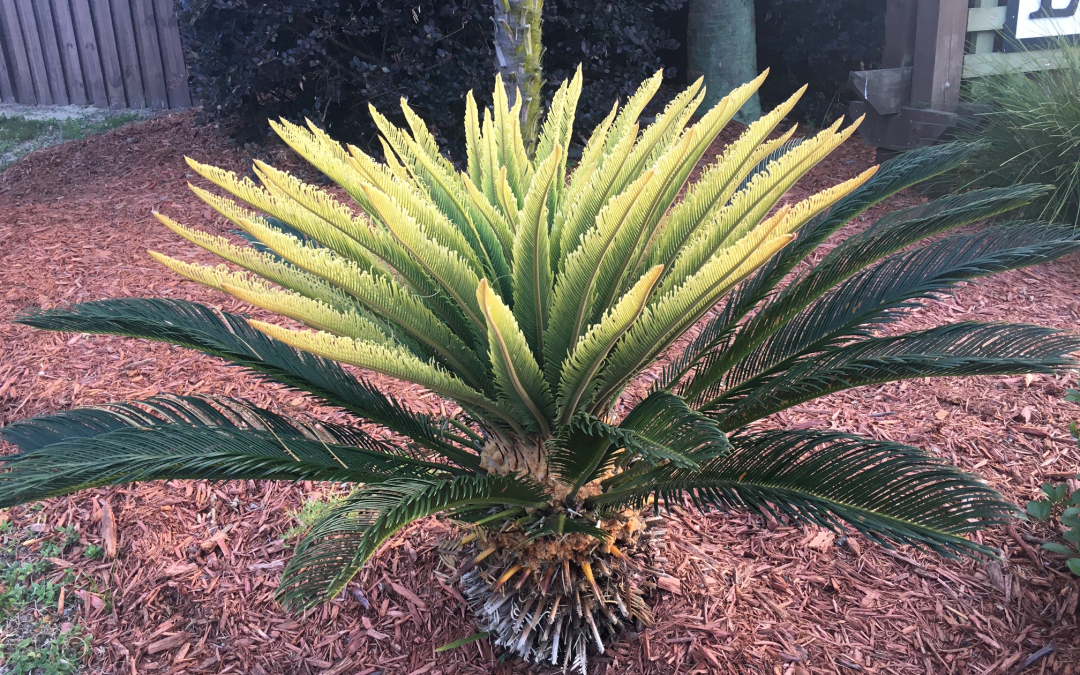
Photo by: Sheila Dunning
The first sign that something is going wrong in a plant is often a loss of the color green. When a sago is forming all new yellow leaves it is a matter of concern. Typically, this a common nutritional deficiency – manganese. Sandy soils of the Panhandle have a hard time retaining nutrients. Manganese and other micronutrient availability is highly influenced by soil pH. Being an essential plant nutrient, manganese is critical to growth. More specifically, it is the base of the metalloenzyme cluster of the oxygen evolving complex (OEC) in photosystem II (PSII). I hope that means more to you than it does me. Basically, manganese is part of the photosynthetic activity and since it isn’t very mobile in the plant, the new growth of sagos turns yellow.
If the nutrient deficiency isn’t corrected, the newly-formed leaves will become deformed and turn brown. In a sago this is referred to as “frizzle-top”. Many people believe the plant has a disease when they see the symptoms and may apply fungicides to no avail. Keep in mind the discoloration of the affected leaves cannot be reversed. However, manganese replacement in the soil will enable the sago to form normal leaves with the next growth phase. Damaged fronds can be removed later to improve the appearance of the sago over time.
Begin this process by determining the soil pH through a soil test. Your local Extension office can help you obtain lab submission forms and explain the collection procedure. Manganese is most available for uptake by sagos when the soil pH is between 5.5 and 6.5. If the pH is above 6.5, larger amounts of manganese will have to be present before the plant can utilize it. When the soil pH is below 5.5 the nutrient is quickly leached out of the soil during rain events.
To correct a manganese deficiency the sago plant will need to receive manganese sulfate. The product is readily available at local nurseries, garden centers and building supply stores. The amount needed for each plant will vary with the size of the sago and the existing soil pH. Sagos growing in sandy, acidic soil will require less manganese sulfate than those in high pH soils. Refer to the package label for application rates.

by Sheila Dunning | Apr 23, 2020
Members of the Phyllophaga genus are found throughout Florida and most of North America. One of them is the May/June beetle. Adults are most active during the rainy season. So in parts of the country where the wetter months are May or June, the common name of this insect makes common sense. But, when an area experiences extra rain earlier in the spring, the May/June beetle may emerge from the ground in March or April. That is what has happened in the western Panhandle this spring. May/June beetles have been leaving the soil and flying to the lights of people’s homes.
The life cycle of these beetles varies from one to four years. Eggs are laid in soil each spring by females. In 3 to 4 weeks, small grubs (larvae) hatch from eggs and develop through three stages (instars), with the first two stages lasting about 3 weeks. The larvae will move closer to the surface and back deeper in the soil as the soil temperature changes. While close to the surface, larvae feed on grass roots about one inch below the soil surface. Damaged grass turns brown and increases in size over time. Heavy infested turf feels spongy and moves when walked upon. The last larval stage remains in the soil from the fall through spring. The cool soil temperatures drive the larvae deeper in the soil where they remain relatively inactive. Typically, on the third year, white grubs pupate 3 to 6 inches deep in the soil and emerge as adults.
 Larvae, called grubs, vary in length from ¾ to 1 ¾ inches depending on the stages. Grubs are white with a C-shaped body with a brown head and three pairs of legs near the head. Adults have ½ to 1 inch long, shiny bodies that are dark yellow to brownish-red in color. Adults do feed on the foliage of several species of ornamental plants, but the damage is typically only aesthetic; not causing long-term harm.
Larvae, called grubs, vary in length from ¾ to 1 ¾ inches depending on the stages. Grubs are white with a C-shaped body with a brown head and three pairs of legs near the head. Adults have ½ to 1 inch long, shiny bodies that are dark yellow to brownish-red in color. Adults do feed on the foliage of several species of ornamental plants, but the damage is typically only aesthetic; not causing long-term harm.
Monitoring of and managing emerging adults can help with deciding on the need for insecticide control for the grubs. To catch and remove adult beetles, place white buckets containing soapy water near plants that have chew marks or areas with lights at night. Leave it overnight. The beetles can easily be disposed of the next day. If there are more than 12 in the bucket be prepared to monitor the lawn for grubs. Extra rain or frequent irrigation during the adult flight time may attract more egg-laying females.
To inspect for grubs, turn over sod to a depth of at least two-inches. If there are an average of three or more per square foot, an insecticide treatment may be needed. To confirm that they are May/June beetles inspect the darkened rear of the grub. Locate the anal slit. It should be Y-shaped with two rows of parallel bristles that point toward each other. This is referred to as the raster pattern. All grub species can be identified using their unique “butt” features.
The most effective time to control this pest is summer or early fall when the larvae are small. Remove as much thatch as possible before applying an insecticide. Spot treat the off-colored area plus the surrounding 10 feet with products containing imidacloprid or halofenozide in early summer. Follow up in the fall with insecticides such as trichlorfon, bifenthrin or carbaryl if grubs persist.

by Sheila Dunning | Mar 20, 2020
Until recently, rainfall has been plentiful. That’s great for the water table and preparing plants to wake up for spring. But, insects are also stirring. Bugs are affected by rain in many ways. When water is plentiful, they can grow faster, reproduce sooner and travel farther. Combine that with the fact that the insects’ homes are being flooded out and their normal food sources are displaced; and where do you think they are headed? Yes, into your house. Four bugs you can anticipate seeing after rain events include cockroaches, sowbugs, ants and centipedes.

American Cockroach
Photo by: J.L. Castner
UF/IFAS
Roaches tend to live in places that flood easily, especially this time of year. To survive the cold nights, cockroaches need to find a warm place to rest. Typically those places would be drains, pipes, sewers, along foundations and in crawl spaces. But, when it rains, these locations are often flooded, forcing cockroaches to scurry for their lives to avoid drowning. A crack in weather stripping or window caulking makes a quick hideaway. Once inside, they may decide to stay. Frequent rainy days create the lingering humidity that makes all kinds of places more livable for roaches.
Sowbugs and his cousin, the pillbug, are very small, pill-shaped pests with multiple legs and a series of shell-like plates. Often referred to as roly-polys, these creatures are actually a form of land

Sowbug
Photo by: J.L. Castner UF/IFAS
crustacean related to lobsters, crabs, and crayfish. The sowbug’s breathing tubes require moisture to function properly, so they must stay near water. Typically this fact restricts the sowbug to living in moist soil or sand. Ending up inside a building is normally a terminal condition for them. However, due to the moisture left in the air after a rain event, sowbugs that seek refuge inside are able to survive for longer periods of time. Given the opportunity, sowbugs will reproduce indoors. If they have decaying organic material to feed on, they may stick around even longer; having time to create a multi-generational infestation.

Carpenter Ant
Photo by: J.L.Castner
UF/IFAS
Ants are never too far away. They usually build their colonies in the soil near convenient sources of food and shelter. Being in the ground puts ant colonies at great risk for flooding out, even with short periods of rainfall. When this happens, ants are forces to find higher, drier ground quickly or risk being washed away. What better place than a house? Once inside, the ants get back to work looking for food and building the colony. Expect to see ants around kitchen sinks, on window sills and working their way into cupboards and pantry areas during and after a heavy rain. Unfortunately, if they find all the elements needed to make their home, the ants will be very reluctant to go back outside.

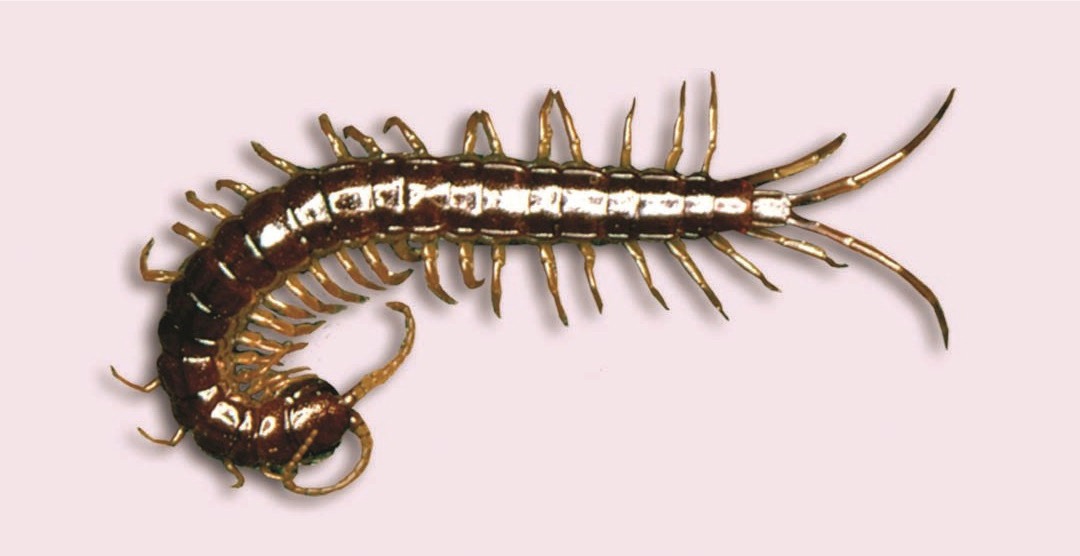
Centipede Photo by: J.L. Castner UF/IFAS
Like the other pests mentioned, centipedes are attracted to humid environments. But, centipedes are active hunting carnivores. They like to feed on roaches, sowbugs and ants. So, they follow them into the house, a well-stocked hunting ground. Centipedes typically only hunt late at night, but in dark areas they can hunt day and night. Finding centipedes if most likely an indication of another pest infestation.
These rain-displaced pests may need some help from a pest control product and/or operator to be discouraged from staying inside. We need the rain. But, keep a close watch for the unwanted visitors.
















