
by Mark Tancig | Aug 31, 2020
As a compost fanatic, one of my favorite Florida-Friendly Landscaping principles is Recycle Yard Waste – Principle #7. Since the practice of gardening typically leads to various debris, including herbaceous weeds, lawn clippings, woody stems after pruning, and just the leaves that fall from your trees, gardeners must somehow manage all of this material.
Rather than tossing it to the curb, where it goes to the landfill and very slowly breaks down in anoxic conditions (lacking oxygen) leading to increased methane emission, a more sustainable approach is to utilize these materials on site. On-site recycling of garden debris can be done through, my favorite, composting, especially when dealing with herbaceous material.
Grass clippings are best left on the grass, as long as not in excessive clumps. Woody debris can be piled in not-too-conspicuous areas to create brushpiles that will provide wildlife with cover. While many think of snakes and other creepy crawlies in piles of brush, many birds, lizards, mammals, insects, and fungi will call a brushpile home. Fallen leaves can be raked into garden beds to act as mulch, another Florida-Friendly Landscaping principle! Besides not using the energy required and creating the extra methane (a stronger greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide) produced by sending materials to the landfill, recycling materials on-site returns the nutrients in that debris to your soil for future plants to take up.
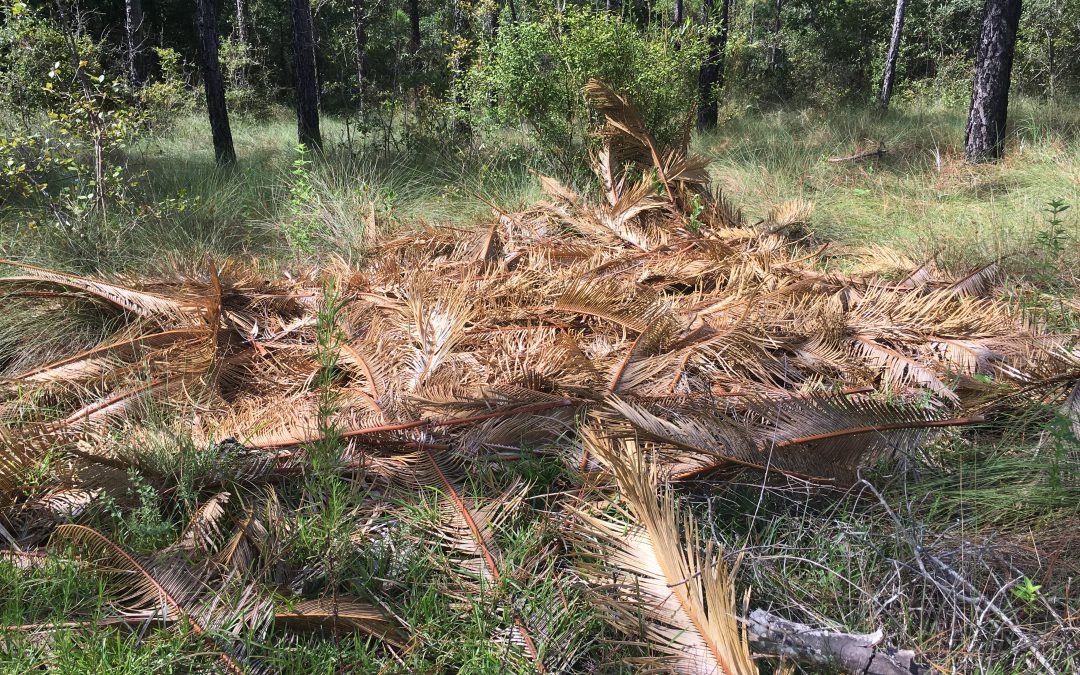
However, there is a fate of yard debris that is even worse than sending to the landfill (cue scary music) – illegally dumping the materials in a natural area!!

Landscape debris dumped in a natural area can spread invasive plants, insects, and disease. Credit: Mark Tancig.
You may have seen this in a local natural area you visit or heard of folks that try to skip paying solid waste fees by dumping it elsewhere. Unscrupulous landscape companies and homeowners have been known to do this, especially when the work site is near a large natural area, such as a state or national forest. The main problem with this, besides that it is illegal, is that invasive species can be spread with debris directly into a native forest. Invasive plants are documented to be spread in this manner, especially those that are easily rooted from stems. Additionally, illegal dumping of plant material can spread non-native fungi, insects, and animals into these areas and disrupt natural ecosystem functions and the organisms that rely on them.

Not only is illegal dumping bad for our natural areas, but it’s illegal! Credit: Mark Tancig.
Homeowners can make sure they don’t contribute to this problem by recycling as much on-site or properly following local guidelines to dispose of landscape debris. Many municipalities have separate bulk collections or drop-off sites for landscape materials. If hiring a landscape contractor, ask where they take the collected material and/or request that it stay on the property. For large jobs, such as tree removal, the estimate should reflect dump fees. If you notice materials dumped in a local natural area, report it to the land manager so they can investigate and/or clean it up and dispose of properly.

by Mark Tancig | Jul 9, 2020
North Florida vegetable gardeners have made it to summer and now the plants and gardeners are starting to give in to the heat and humidity. The squash has likely succumbed to squash vine borers, many of the tomato varieties are having trouble setting fruit, stink bugs are all over, and gardeners easily wilt by noon. This is a good time to use our oppressive heat to your advantage in the vegetable garden by solarizing the soil.
We have reached the peak of heat. Use it to your advantage in the garden. Source: National Weather Service.
Soil solarization is a method of pest control that creates a greenhouse to heat up the soil in an effort to drive away pests. Pests that can be reduced with soil solarization include weeds, various soil-borne fungal pathogens, and nematodes. Weed seeds can actually be killed by the increased temperatures, sometimes as high as 140 degrees Fahrenheit, while fungi and nematodes are merely driven deeper into the soil layer as they try to escape the heat. Although they are not killed, this can help vegetable gardeners as it may take these organisms 3-4 months to repopulate in high enough numbers to cause damage. Soil solarization can be considered another tool in your integrated pest management (IPM) toolbox, along with other cultural, physical, and chemical means of pest control.

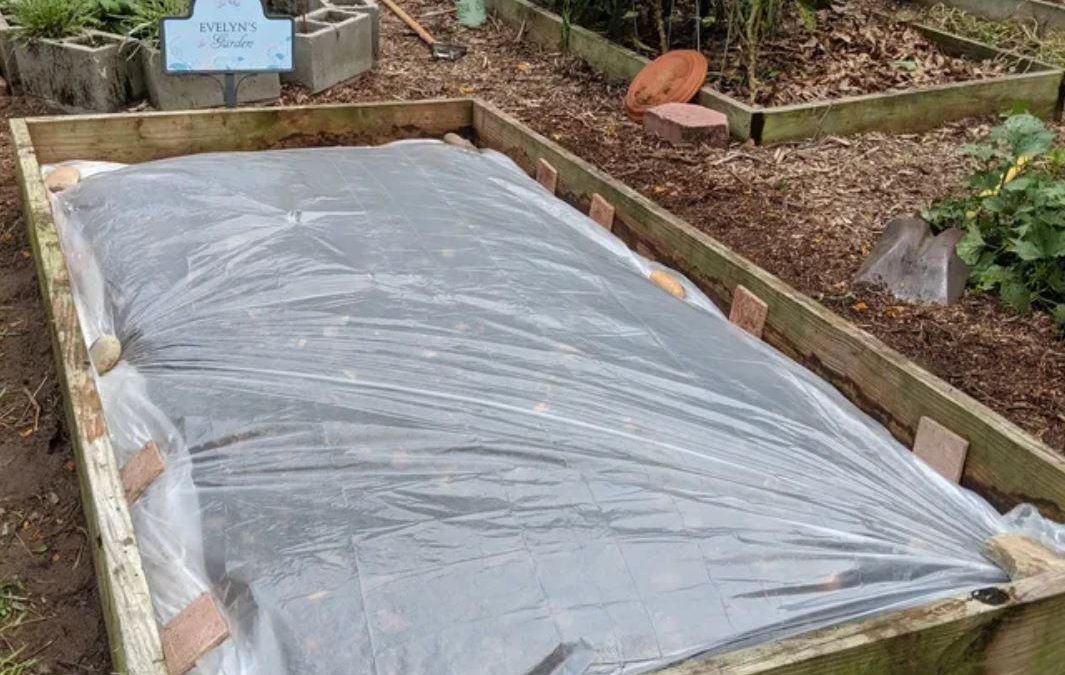
A raised bed being solarized over the summer. Source: Evelyn Gonzalez, UF/IFAS Master Gardener Volunteer.
To properly execute soil solarization, the site should be in full sun and the existing vegetation removed, either by hand or with a tiller or other implement. Tilling can help loosen the soil surface and allow heat to penetrate deeper in the soil horizon. Before being covered with plastic, the area should receive rainfall or be irrigated, as the water will help conduct heat to greater depths. The next step is to cover the area with plastic. Note that this can also be done over raised beds! Clear plastic is best for maximum solar radiation penetration. Black plastic will heat up mostly on the surface and opaque plastic sheeting may not let enough light in to get temperatures high enough. The plastic should be slightly larger than the area covered, as the edges will need to be buried to create an air-tight seal. It’s recommended to leave the plastic in place for at least six to eight weeks, just in time to begin fall gardening preparations.
It’s important to monitor the site while it’s “cooking” to look for any holes that might appear. Small holes can be repaired with duct tape, while large holes or rips in the plastic may require starting over. Overlapping strips of plastic is not recommended since too much heat will be lost.
You may be wondering what happens to all of the good soil microbes. Well, unfortunately, they are also either killed or suppressed. Fortunately, researchers have found that they are able to repopulate quicker than the pest organisms, especially in soils with a good amount of organic matter.
Much more information on soil solarization can be found in these two documents:
Introduction to Soil Solarization – https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/IN/IN85600.pdf
Solarization for Pest Management in Florida – http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/IN/IN82400.pdf
Also, please contact your local county extension office for more gardening tips.

by Mark Tancig | Apr 30, 2020

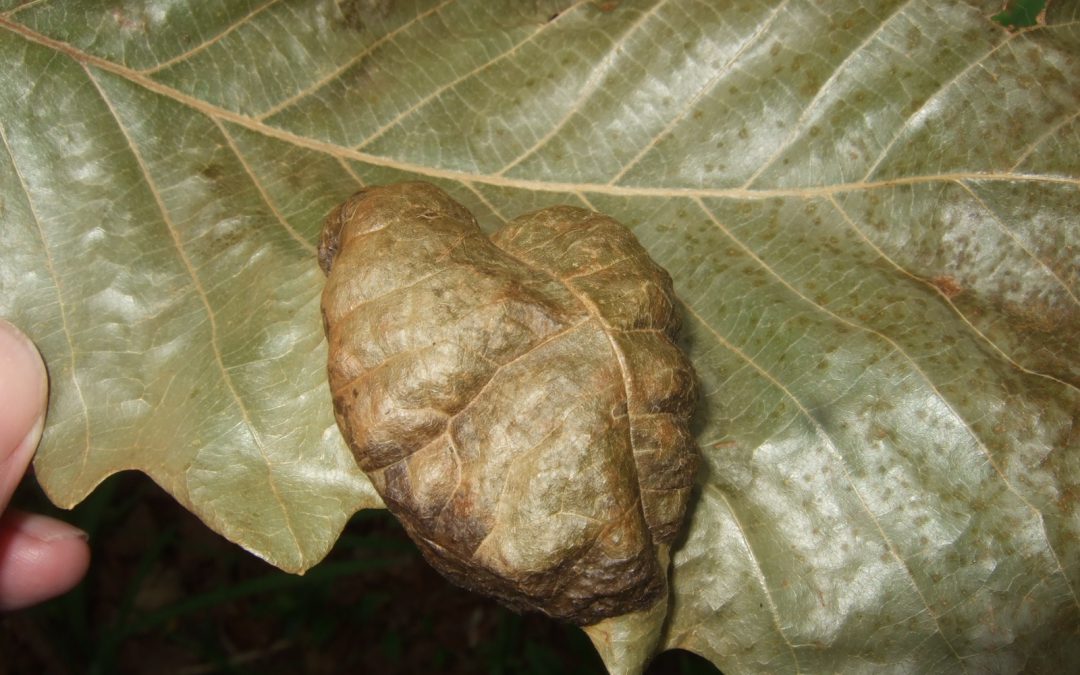
Symptoms of oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
Even during global pandemics, it’s a joy to be outside during the great north Florida spring we’ve been experiencing lately. As cold fronts come through with their rain bands, some packing a punch, they leave behind the most pleasant mornings, clear blue daytime skies, and crisp evenings. Unfortunately, we’re not the only organism that also enjoys those cool days. Many species of fungi are quite active this type of year as the rains, followed by warmer, yet not too hot temperatures, create the perfect conditions for fungal growth. Some of these fungi grow right on or in the plants we’d like to be enjoying for ourselves, stealing nutrients and causing plant decline or merely causing aesthetic damage. As this is an active time for certain species of fungi, local extension offices are getting more calls and questions regarding lawn and landscape damage due to fungal pathogens. A recent call was a new one for me and an example of a native fungi-plant interaction that looks bad but requires no intervention from us. It also highlights how correctly identifying a disease leads to the best action and can often save time and money and prevent unnecessary pesticides (in this case a fungicide) from entering the environment.

Close up of oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
The fungi and plant involved here was the oak leaf blister (Taphrina caerulescens) on a swamp chestnut oak (Quercus michauxii). It forms, you guessed it, blisters on the leaves of any of the oaks, though live oak (Quercus virginiana), laurel oak (Quercus laurifolia), and water oak (Quercus nigra) seem to be preferred hosts. The spores of the fungi, dormant since the previous summer/fall and which happen to get lodged in bud scales through wind and rain, germinate in cool, wet weather. The fungus then infects young leaves as they flush and its growth causes a disruption in the leaves’ development. This leads to the blistered look of the leaf tissue and, during extended periods of cool, wet weather, the entire leaf sort of shrivels, browns, and eventually falls off. Spores are eventually released from the fallen leaves to start the process over the next spring.

Severe oak leaf blister on swamp chestnut oak. Credit: Gordon Magill.
Though the leaves look pretty terrible, this fungal disease rarely causes plant health issues and the tree recovers just fine. Specimen trees that experience it year to year may be treated with a fungicide, but most homeowners can just let it go. Raking up and disposing of the leaves may help prevent further infections by reducing the number of spores released in the area.
As you enjoy another cool morning after an evening rainstorm, remember that the fungi all around you are also having a great day. You may want to look at your landscape plants and see if there’s anything abnormal going on. If so, take a photo and send it to your local extension office for help with identification and best methods of control, or, like in this case, just leaving it alone.
p.s. As I said this was a new one for me and I want to thank Stan Rosenthal, Extension Agent emeritus, for assisting with identification.

by Mark Tancig | Jan 13, 2020
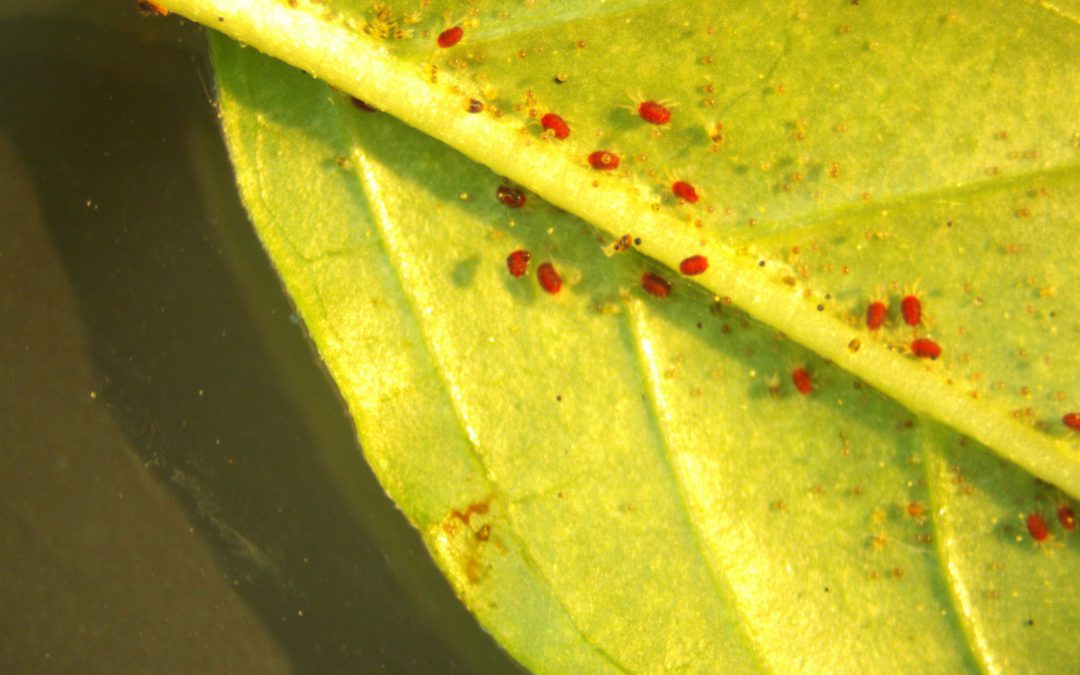
I was recently asked what kind of fungus was affecting a plant brought into the UF/IFAS Leon County Extension Office. Upon close inspection, it was not a fungus at all, but turned out to be damage from spider mites and the little critters were right there on the plant.

Spider mites along the bottom of the leaf. Credit: Mark Tancig, UF/IFAS.
Spider mites, as the name implies, are eight-legged creatures that are kin to spiders and in the mite and tick group of arachnids. They can cause damage to ornamental, fruit, and vegetable plants, especially in hot, dry weather or when grown in greenhouses or indoors. The plants that came into the office had been growing in a greenhouse.
Spider mites are a piercing, sucking pest that pierce their mouthparts into the leaf tissue to suck out nutritious plant saps. High densities of spider mites can pull enough plant tissues out to cause a light colored, grayish look to the leaves, somewhat resembling downy mildew damage. Upon close inspection, small brown to red dots on the bottom of the leaf and/or spider web-like webbing along the stem and petioles may be observed, confirming the identification of spider mites.

Webbing caused by high numbers of spider mites. Credit: UF/IFAS.
Plants grown outdoors don’t usually experience spider mite damage, as natural predators such as lady beetles, minute pirate bugs, thrips, and lacewings provide biological control. For spider mite infestations on houseplants or in greenhouse operations, control can be achieved through physical and chemical control. As part of an integrated pest management plan, regular monitoring of these plants can help identify problems before they get too bad. Sprays of water and rubbing undersides of leaves can remove many spider mites and provide control of small populations. If that doesn’t take care of them or they are at infestation level, insecticidal soaps and horticultural oils can provide adequate control.
Remember that correct identification is key to properly controlling a pest. If the damage was treated as a fungus and a fungicide sprayed, the pest would not be controlled, and time, money, and product would be wasted. If you have questions regarding what is ailing your plants, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office.

by Mark Tancig | Dec 10, 2019
The diversity of life is impressive. As gardeners, we focus on plant life, which has so much diversity that you could probably study plants all your life and still feel like there is so much more to know and discover.
Botanists attempt to classify all living plants (and extinct ones, too!) according to binomial nomenclature and have created a long list of terms to describe the myriad plant structures, shapes, textures, etc. present in the plant world. One of the many interesting structures that you may notice upon close inspection are extra-floral nectaries.

The small bumos on this passionflower leaf are extra floral nectaries. Source: UF/IFAS.
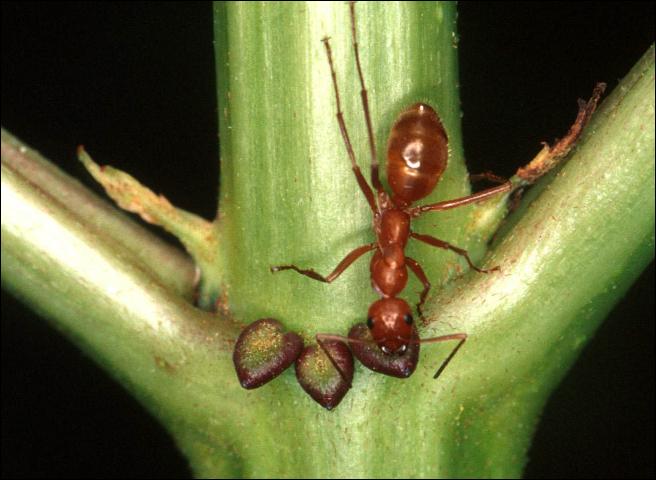
Extra-floral nectaries are nectar-producing structures that are found outside of the flower (extra-floral means out of flower like extra-terrestrial means out of earth). Most of us are familiar with nectar being produced in the flowers as part of pollination. The plant’s sweet, nutritious nectar entices pollinators to visit, sip some nectar, bump against the anthers and get pollen stuck on themselves, visit the next flower for more nectar, and transfer that pollen to another plant’s stigma. So, what would be the benefit of producing nectar in areas outside the flower? Turns out, that while the diversity of life is impressive, the relationships formed between various species are fascinating and the presence of extra-floral nectaries in certain plant species highlight such inter-relationships.
Scientists have long been interested in these structures and have found that many of the plants that form extra-floral nectaries do so to entice insects for protection from other insects. Ants are usually associated with plants that produce extra-floral nectaries and have been shown to protect the plant from herbivores that may want to munch on the plant. Some ants have been recorded spraying formic acid (the compound that causes the burn of a fire ant sting) on potential plant pests. The ants benefit by having a regular source of carbohydrate-rich nectar. Carnivorous plants, including our locally famous pitcher plants (Sarracenia spp.), use extra-floral nectaries to entice insect prey and to create a slick surface that causes its prey to fall in the pitcher. The plant-ant relationship is an example a mutualistic symbiosis (both organisms benefit) whereas the pitcher plant-insect relationship is an example of predation.

An ant visiting the extra floral nectaries on an elderberry shrub. Source: UF/IFAS.
Many familiar plants produce extra-floral nectaries, including cotton, hibiscus, passionflower, and peach. These nectar producing glands usually look like small bumps and are found along the petiole (leaf stalk), the base of leaves, at the stipules (small leaf-like structures where petiole meets stem), and sometimes near the bracts found just outside of the flower.

Peach trees are a common tree that contain extra floral nectaries at the base of the leaf. Source: UF/IFAS.
Next time you notice a strange bump on a leaf, a line of ants along the stem, or an insect regularly visiting leaves instead of flowers, take a closer look and you may be observing one of the many amazing examples of diversity and inter-relationships of species. To learn more about extra-floral nectaries, please see the EDIS publication Many Plants Have Extrafloral Nectaries Helpful to Beneficials. For a thorough glossary of botanical terms, visit the Missouri Botanic Garden glossary page.

















