by Taylor Vandiver | Jan 22, 2015
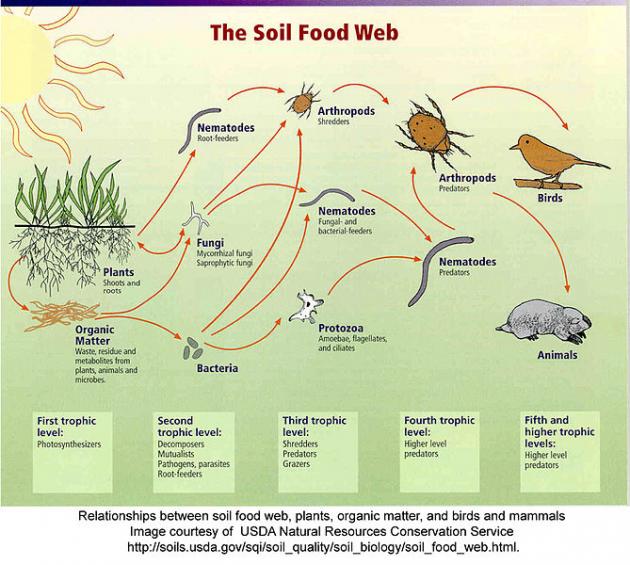
You’re digging up a ridiculously stubborn patch of Florida betony when an earthworm crawls across your path. As you break apart the soil in your hands a world of active organisms is being sifted through your fingers. Fertile soil is teeming with beneficial microbes. It is estimated that there can be billions of microbes in a single gram of soil.
Bacteria, fungi, and protozoa are major players in soil microbial processes. They perform a variety of functions beneficial to soil and the plants growing in that soil. Other soil organisms of importance are nematodes, arthropods, and earthworms.

Soil Food Web. Photo courtesy USDA-NRCS.
Rather than being an inert material, soil houses a dynamic living ecosystem. Most soil organisms are too small to be seen, however they are still performing a great service to gardeners in many ways. These organisms are vitally important to improving the health of our soils. They also play a key role in making nutrients available to plants.
Soil organisms are naturally active during certain times of the year. Most are active during late spring and early summer when the soil is warm and moist. If the soil dries out during the summer months, soil organism activity will decline. During fall months, if there is rain or snow that moistens the soil while it is still warm, soil organisms may resume partial activity. As the soil cools in the fall, many organisms go dormant. It is important for gardeners to note that soil organisms help breakdown certain fertilizers and during the cool, dry months these fertilizers, if applied, will be less available for plants to take up.
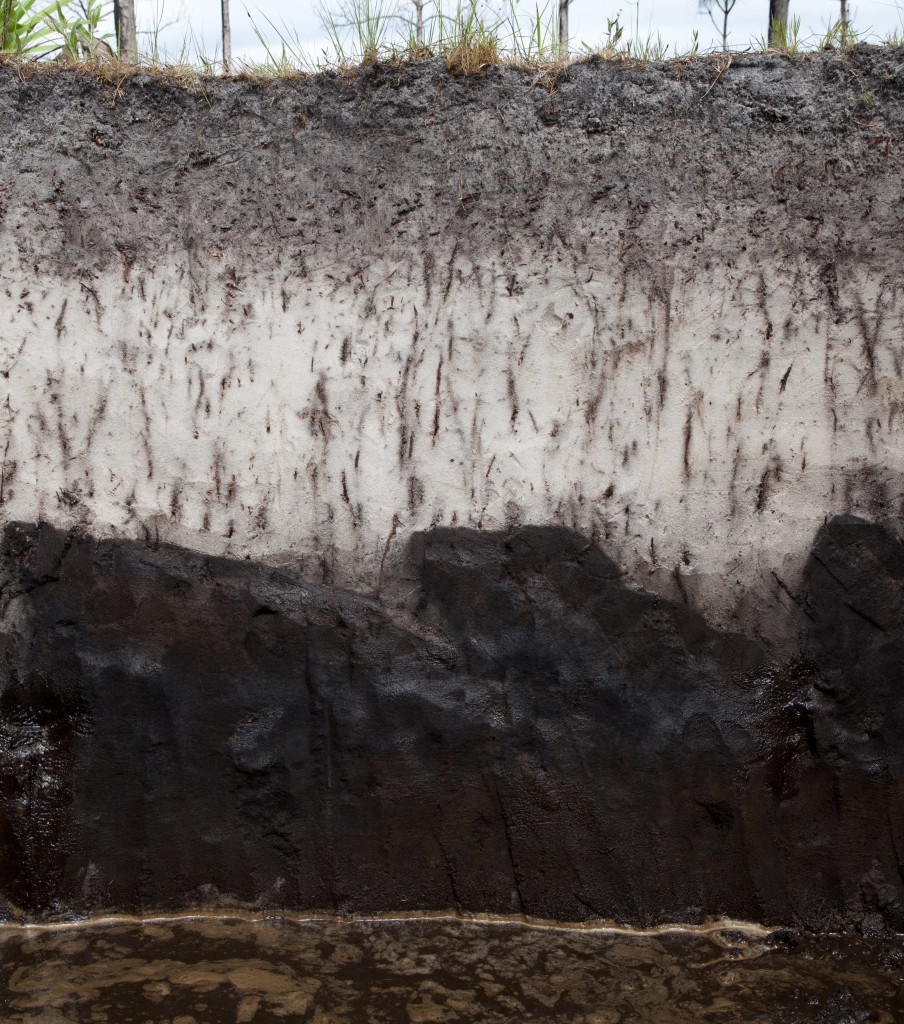

Soil profile. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
Soil organisms are generally placed within three categories: organisms that are beneficial to plants, organisms that play a neutral role in plant growth, and organisms that are harmful to plants. Creating a favorable environment for beneficial soil organisms can improve plant growth and reduce garden maintenance. Encouraging their efforts is key to building a healthy fertile soil. Here are some ways you can encourage beneficial organisms in your soil:
- Add organic matter to the soil. Soil organisms require a food source from soil amendments (compost, crop residues) and/or mulch.
- Water effectively. Soil organisms are happiest in an environment that is damp, but not soggy. (Avoid over-irrigation because waterlogged soils will be harmful to beneficial soil organisms)
- Avoid unnecessary tilling, as it can destroy the mycorrhizae and soil structure. Instead of tilling, mulch for weed control.
- Avoid pesticide applications that aren’t necessary. Some fungicides, insecticides and herbicides are harmful to various types of soil organisms.

by Taylor Vandiver | Dec 16, 2014
Now that we’ve all been stuffed like a Thanksgiving turkey, it’s time to transition into the final and, arguably, most ornate holidays of the year. Right now you can hear your mantles and door frames crying out to be adorned. Your windows are begging for wreaths and giant red bows. And there may be a certain corner in your house that has been waiting all year for an evergreen, or two.
As we delve into the winter holidays our homes are being dressed to impress. There is nothing better than fresh foliage placed along a mantle or maybe a little mistletoe hanging from a previously unadorned beam. The scent of pine is in the air and I don’t know about you, but I’m ready to get decorating.
Here is a list of a few evergreen plants that make wonderful decorations for the season. You may even find some in your own backyard! Just make sure when you are removing foliage and fruit that you do it gently, so as not to harm the plant. Make all cuts at a 45 degree angle so that water will not pool on branch tips and rot. Also, if you forcefully remove foliage from a plant you could expose the susceptible cambium layer.

Wreaths and a decorated door frame add a bit of holiday cheer to this snowy scene. Photo courtesy Taylor Vandiver.
Traditional
Magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora) – This southern staple provides foliage that will liven up any banister or door frame. After being cut from the tree it can withstand the dryer temperatures indoors for days on end.
Hollies (Ilex spp.) – Hollies not only provide glossy green foliage, but bright red fruit that will beautifully adorn holiday arrangements and centerpieces.
Pine/Pinecones (Pinus spp.) – Pine trees offer a wispy presence to many decorations and their cones can give structure to wreaths and mantle pieces.
Boxwood (Buxus spp.) – Boxwoods are great for a touch of green.

Yaupon holly fruit and foliage. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
New Ideas
Abelia (Abelia x grandiflora) (evergreen to semi-evergreen) – Abelia are not commonly thought of when making holiday arrangements, but the texture of their foliage and the myriad of colors can spice up traditional decorations.
Aucuba (Aucuba japonica) – Aucuba offer a coarse texture that would pair well with the wispier pine foliage. Also, the gold dust variety will add a little more color to the mix.
Aspidistra (Aspidistra elatior) – Aspidistra foliage tends to feel more tropical. If you want to try a non-traditional arrangement these would work well and they can last for days provided a small amount of water.

Aspidistra foliage that could easily be worked into a stunning arrangement.
Remember that a few well placed planters can liven up even the smallest spaces. Try using a small evergreen tree or shrub such as a magnolia, cypress / false cypress or arborvitae and surround them with poinsettia or pansies. You can try a smaller planter and add in pine cones, poinsettia, grasses, etc. Also if you are celebrating this holiday season with a live Christmas tree, then don’t be afraid to ask the grower/retail center for discarded branches. These can easily be formed into a wreath or used throughout the house. And since this is Florida there’s always the option of decorating your palm tree!

by Taylor Vandiver | Nov 11, 2014
As winter approaches, short days and cool temperatures cause many plants to slow down and enter a suspended growth phase known as dormancy. Dormancy in plants is similar to the way bears hibernate during the winter. You may be asking yourself what is dormancy? And how can I get in on that? Well, to be honest, there isn’t an all-encompassing answer. It seems that plants (and bears) are keeping that secret all to themselves.

Fall foliage of Florida maple. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
Now that winter is indeed coming, deciduous plants start to breakdown proteins and other chemicals in their leaves and store them in the buds, bark and wood for growth next spring. Many deciduous plants lose their leaves as they become dormant, such as maples and dogwoods. Evergreen plants such as pine trees and camellias keep their leaves all winter.
There are actually two types of dormancy during the winter. One is called endo-dormancy. In endo-dormancy, the plant refuses to grow even under hospitable conditions. In endo-dormancy, something inside the plants is inhibiting growth. The other form is eco-dormancy and occurs when the plant is ready to grow, but the environmental conditions are not favorable (usually too cold). Short days and freezing temperatures in the fall induce endo-dormancy in the plant, which occurs first.

Shumard oak showing off its fall colors. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
As the plant enters endo-dormancy, it tracks chilling hours to chart the passage of the winter. Chilling hours are the time when temperatures drop below 45 degrees Fahrenheit. The number of hours required for chilling varies for different plants. Many people think the plant is tracking hours below freezing. However, hours below freezing have no effect on chilling, but will increase cold hardiness. If warm weather occurs before the plant completes its chilling requirement, no growth occurs. Chilling and endo-dormancy normally prevent plants from beginning growth during warm spells in the middle of the winter. Not all hours above freezing are equal. Temperatures between 35 and 45 degrees Fahrenheit seem to be most effective. Temperatures just above freezing and above 50 F are less effective and temperatures above 60 F often have a negative effect on chilling.
After a plant has checked off its chilling hours it is no longer in a state of endo-dormancy. It is now in eco-dormancy. The plants are dormant only because of cold temperatures. Warmer weather will cause plants to yawn, make that final stretch, and begin to grow. Growth first becomes apparent when buds swell and then green tissue emerges from the bud. However, plants actually begin growing before we notice their swelling buds. So this winter when your plants start to shed their leaves don’t be frightened, they may just be taking a much deserved rest in preparation for a brilliant show come spring.
Please contact your local extension office for more information.
by Taylor Vandiver | Oct 7, 2014
I think it’s safe to say fall is officially here. Shouts can be heard from local football stadiums, occasionally a crisp fall breeze will send us looking for a light jacket, and coffee shops are pushing all things pumpkin. Now that we can officially appreciate the cooler fall weather, it may be time to stretch our legs and marvel at the spectacular show of color our landscapes are putting on. Here are a few plants that are showing off this time of year.
Firebush (Hamelia patens) – This charming Florida native will delight everyone with beautiful orange-red flowers throughout most of the year. Hummingbirds and butterflies enjoy the nectar in the flowers. Firebush can reach a height and width of 8 to 12 feet. It is a fast growing plant that will grow well in part to full sun environments.

Bright orange-red blooms on a firebush. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
Salvia (Salvia spp.) – Salvias are great plants for bringing butterflies and hummingbirds to your garden and as a bonus, they have no serious pests. With hundreds of annual and perennial species coming in an array of colors and sizes, you can easily find one or more to complement your landscape. Salvias perform best in full sun environments and are considered drought tolerant.

Deep purple blooms on a salvia in the landscape. Photo courtesy Taylor Vandiver.
Turk’s Cap (Malvaviscus arboreus) – Turk’s cap can add a cheerful pop of color at a time when little else is blooming. This old-fashioned Florida-Friendly shrub like perennial is related to the hibiscus. It’s known for its bright red flowers that always seem ready to open, but never do. Turk’s cap starts blooming in summer and keeps going until through winter, unless hit by a hard frost. It can grow in full sun and reach up to ten feet tall and ten feet wide, so give it room to grow. This easy-care native perennial requires little maintenance once it’s established.

Turk’s cap showing off its unique blooms. Photo courtesy Taylor Vandiver
Coleus (Solenostemon scutellarioides) – When imagining fall color we often don’t consider coleus. However, the vibrant foliage can add interest to any landscape throughout the fall. Coleus is prized for its colorful foliage, which comes in shades of green, yellow, pink, red, and maroon. Coleus varieties can range from one to several feet in height. They can be used in hanging baskets, containers on patios, or in landscape beds. Coleus prefers partial shade and you can pinch the growing stems of young plants frequently to encourage dense foliage. Keep an eye out for mealybugs on coleus and use insecticidal soap if problems develop

Burnt orange foliage standing out amongst the neutral green of the landscape. Photo courtesy Taylor Vandiver.
Fore more information contact your local extension agent. Also you can visit us at gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu or edis.ifas.ufl.edu.

by Taylor Vandiver | Sep 9, 2014
What’s eating my lawn? Does your grass look ragged in areas, as if someone randomly used a weed-eater here and there? Are you noticing brown patches that have a closely clipped appearance compared to other areas of your lawn? Your turf may be playing host to Tropical Sod Webworm.

Sod webworm damage in a home lawn. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
Sod webworm damage is subtle at first. You have to look closely to notice larval feeding damage. However, an easy indication of their presence is the light tan/brown colored moths, which are the adult stage of the pest. You may see them fly up as you walk through your lawn or if you disturb a nearby bush. The moths do not cause any damage to the turf, but they are depositing eggs, which will result in their offspring, the caterpillars, who do all the chewing damage.
The larvae are gray-green and have spots on each segment. The mature larvae can be up to 1 inch in length. Larvae will curl up in the soil during the day and feed at night. So if you happen to notice caterpillars feeding during the day, it’s probably not sod webworm. You will notice chewed notches along the leaf blade, holes in the leaf and even leaf blade skeletonizing. The older the larvae are, the more they will eat. Damage may start out as a ragged appearance in your turf, which can be hard to diagnose. However, if left unchecked, sod webworm can cause considerable injury to your lawn.

Sod webworm larvae. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
If you are uncertain of their presence you can always use a soap drench to flush out larvae. Mix 2 tablespoons of dish soap with 2 gallons of water and pour it over a damaged area (about 3 square ft.). The soap mixture will irritate the pest and bring them to the surface so you can easily identify them. If nothing appears in the area tested move to another damaged site and try again. Here is a link to a video that will give more information on identifying Tropical Sod Webworm.
Tropical Sod Webworm is considered a pest of all warm-season turfgrasses. However, St. Augustinegrass is most commonly affected. The best way to prevent a pest infestation is to use proper cultural maintenance practices for your lawn type. However, if the pest does appear, chemical control should be targeting the larvae stage of the pest. There are multiple products marketed to control lawn caterpillars. However, you may want to consider using B.t. (Bacillus thurengiensis), which is a bacterium that will only harm caterpillars and not bother beneficial insects that may be in your lawn. For more information you can contact your local extension office.














