
by Matt Lollar | Apr 14, 2016

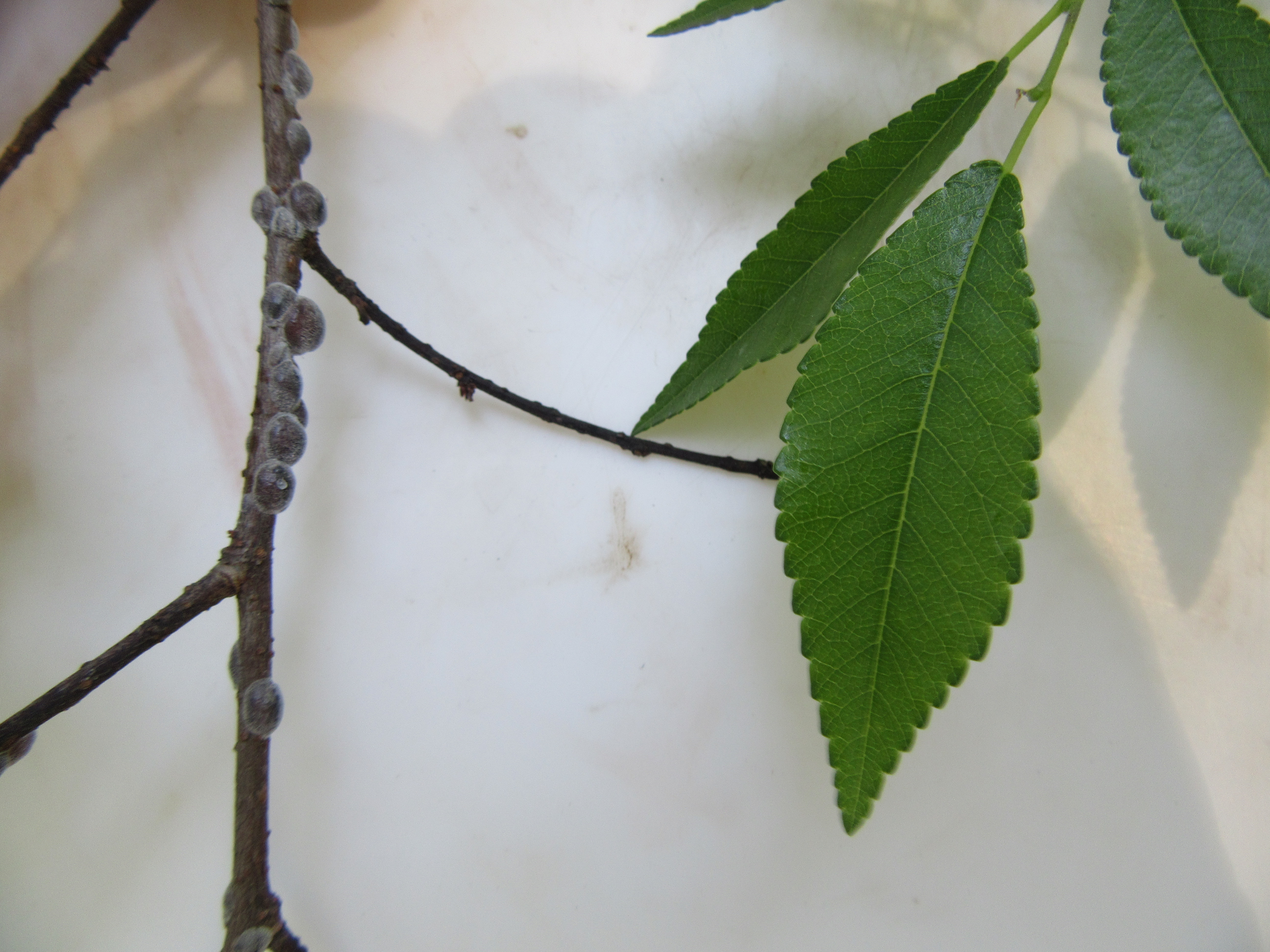
Scales on a Chinese Elm.

Scales on a Chinese Elm.
Last week as I was basking in the shade of the Chinese Elms (Ulmus parvifolia) in my yard, I noticed some strange lumps on the twigs. Upon further investigation, I realized the “lumps” were scales. Scale insects are serious pests of a number of ornamental plants. Here in Florida there are 13 different families of scales with the most common being armored scales, soft scales, and mealybugs. Scales have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Heavy infestations cause extensive leaf yellowing, premature leaf drop, branch dieback, and eventually plant death.
Scale Biology
The life cycle of a scale begins with eggs being laid beneath wax coverings or beneath the adult female. Eggs typically hatch in 1 to 3 weeks. The newly hatched nymphs, called crawlers, move around a plant until they find a spot to feed. Once a feeding site is located, their piercing sucking mouthparts are inserted into the plant and the crawlers begin to feed and grow. The males of many scale species develop wings as adults and fly to other plants to reproduce.

The magnolia white scale. Credits: University of Florida
Armored Scales
Armored scales get their armor by secreting a waxy covering over their bodies that is not attached. The scale lives under this covering and uses it as a protection to feed under. Armored scales can be almost any color or shape and range anywhere from 1/16 to 1/8 inch in diameter. For females, these shapes range from circular to oval to long and slender. The males typically have coverings that are more elongate and smaller than the females. As adults, the males are tiny, winged, gnat-like insects and are rarely seen.

Hemispherical scale on coontie. Credits: Lyle Buss, University of Florida
Soft Scales
Similar to armored scales, soft scales secrete a waxy covering, but it is attached to their bodies. Soft scales can be a number of colors, shapes, and sizes and range anywhere from 1/8 to 1/2 inch in diameter. Their shapes vary from spherical to nearly flat.

Mealybugs. Credits: James Castner, University of Florida
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects that possess a covering of flocculent, white, waxy filaments. They are about 1/8 inch in length and usually pinkish or yellowish in color. Mealybugs have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Mealybug damage produces discolored, wilted, and deformed leaves.
Scale and Mealybug Management
- Cultural Control – Plant inspection prior to purchase or installation is the first line of defense against a scale or mealybug population. Make sure to inspect the undersides of leaves and plant stems. Infested sections of plants can be pruned and plant material should be cleaned from the planting area and discarded. Also, you can increase air flow and decrease humidity by proper installation and pruning. Over-fertilizing can also increase pest populations.

Larva of a brown lacewing. Credits: Lyle Buss, University of Florida.
- Biological Control – Predators, such as ladybugs and green lacewings, are usually present in large enough numbers to suppress scales and mealybugs to a desirable threshold. However, broad-spectrum insecticides and bad weather can reduce predator numbers. Look for signs of predation by inspecting dead scales for jagged holes in their waxy coatings. If predation signs are present, use more selective chemical controls and oils as opposed to broad-spectrum products.
- Chemical Control – Timing is everything when it comes to managing scale and mealybug insects. Crawler activity is more pronounced with the flush of new plant growth in the spring. Before application, prune infested plant parts off first to promote greater penetration of insecticides into the foliage. Contact products (acephate, bifenthrin, carbaryl, etc.) must be applied to inhibit the crawler stages of these insects and systemic products (acetamiprid, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, etc.) can be used on the sessile growth stage. Plants should be sprayed thoroughly to the point of drip or “run off” from leaves, twigs, and stems. Repeated applications may still be necessary even if the timing is right, as crawler populations are often large and crawlers like to hide under old waxy scales. Systemic drenches are also a viable option. With good spray coverage, horticultural oils can kill scales at all stages of growth. Refer to the product label for phytotoxicity and temperature guidelines. Even after successful treatment, the outer coatings of the scales may remain on the plant material for weeks, which can be unsightly. The best way to determine if scales are dead is to squeeze them. They will be dry when squeezed if they are dead and they will ooze liquids if they are living (they were at least alive to the point of being squashed).
For insect identification and additional information on scale control, please see:
A Guide to Scale Insect Identification
UF/IFAS Featured Creatures
Your County Extension Office

by Matthew Orwat | Apr 7, 2016
This spring, most garden plants are putting on lots of tender new growth. The lush foliage is like a free lunch to aphids, whiteflies, mealybugs and thrips. Before broad spectrum insecticides are used to control these pests, consider the impact on beneficial insects. Insecticides that don’t measurably harm predatory beneficial insects include insecticidal soaps and all season horticultural oils, which kill soft-bodied insect pests at application. Here are several common beneficial predatory and parasitic insects that help keep the pests at bay.
Assassin Bug Zelus longipes
Assassin bugs are predators of several leaf feeding and sap sucking insects including the fall army worm and the Asian citrus psyllid. They trap their prey by holding onto it with their forelegs and secreting enzymes into the prey to dissolve the interior tissue. Then they ingest the dissolved tissue.
Lady Bug or Lady Beetle
These insects most commonly feed on aphids, most insect eggs, whiteflies, small caterpillars, scale and mealybugs. They provide a measurable benefit to gardens since they are such generalized feeders. The Lady Beetle larva look substantially different from the adult stage.

Third instar larvae of Hippodamia convergens. Photograph by Luis F. Aristizábal, University of Florida

Newly emerged adult Hippodamia convergens showing typical body markings. Photograph by Luis F. Aristizábal, University of Florida.
Soldier Bug
A different but closely related species of the stink bug, this predator uses its piercing / sucking mouthparts to feed on larval beetles and caterpillars.

Dorsal view of an adult spined soldier bug, Podisus maculiventris (Say), feeding on a mating pair of sumac flea beetles, Blepharida rhois (Forster) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
Lacewings
The green and brown lacewing is often found around aphid infestations. The larva is the major predator, they make the biggest dent on aphid populations. In addition to aphids, lacewings also feed on scale, mealybugs and several species of insect eggs.

Adult brown lacewing (Neuroptera: Hemerobiidae). Photograph by University of Florida.

Larva of a brown lacewing (Neuroptera: Hemerobiidae) preparing to attack and feed on an aphid. The black-colored aphid to the right was probably parasitized by a wasp. Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
Predatory Gall Midges
This aphid predator is easily overlooked because it is so small, and resembles the flower fly. They also feed on scale, thrips and mites.

Adult of the predatory gall-midge, Feltiella acarisuga (Vallot). Photograph by David R. Gillespie, Agassiz.

Larva of the predatory gall-midge, Feltiella acarisuga (Vallot). Photograph by Lance S. Osborne, University of Florida.
Flower Flies (Hover Flies)
Flower Flies actually resemble honeybees or bumblebees. People often run from them! The adult is an important pollinator for many crop species and feeds on nectar and aphid honeydew. This time it’s the larva which is predatory and is a voracious feeder of aphids. Large concentrations of larvae substantially reduce aphid populations in aphid infested gardens and fields.

Larva of Allograpta obliqua (Say), a hover fly. Photograph by James F. Price, University of Florida.

An adult male hover fly, Allograpta obliqua (Say). Graphic by Division of Plant Industry.
Parasitic Flies
There are many types of parasitic flies which parasitize a variety of insect pest species. They may inject their eggs into the host, or lay the egg on the surface of their host. Usually they are very small and not noticeable.
Parasitic Wasps
Most parasitic wasp species are tiny, fast and hard to notice. The average gardener is not aware of their rather plentiful existence. They are a common killer of grubs, caterpillars, whiteflies and aphids. They either insert their eggs into the organism or lay eggs on the surface of their host.

A group of adult Cotesia congregata (Say) wasps feeding on honey solution placed on the underside of a tomato leaf. Photograph by Justin Bredlau, Virginia Commonwealth University.
Big Eyed Bugs and Minute Pirate Bugs
While big eyed bugs and minute pirate bugs are not related, they perform similar functions in gardens and agricultural systems by feeding on chinch bug nymphs, psocids, leafhoppers, aphids, thrips, and mites. They are found in variety of ecosystems and do their job anonymously.

Adult bigeyed bug, Geocoris sp., feeding on a whitefly nymph. Photograph by Jack Dykinga, USDA

The minute pirate bugs are black with white markings. They prey on many small insects and eggs, including thrips. About 70 species exist in North America. Photograph by James Castner, University of Florida
References:

by Carrie Stevenson | Mar 29, 2016
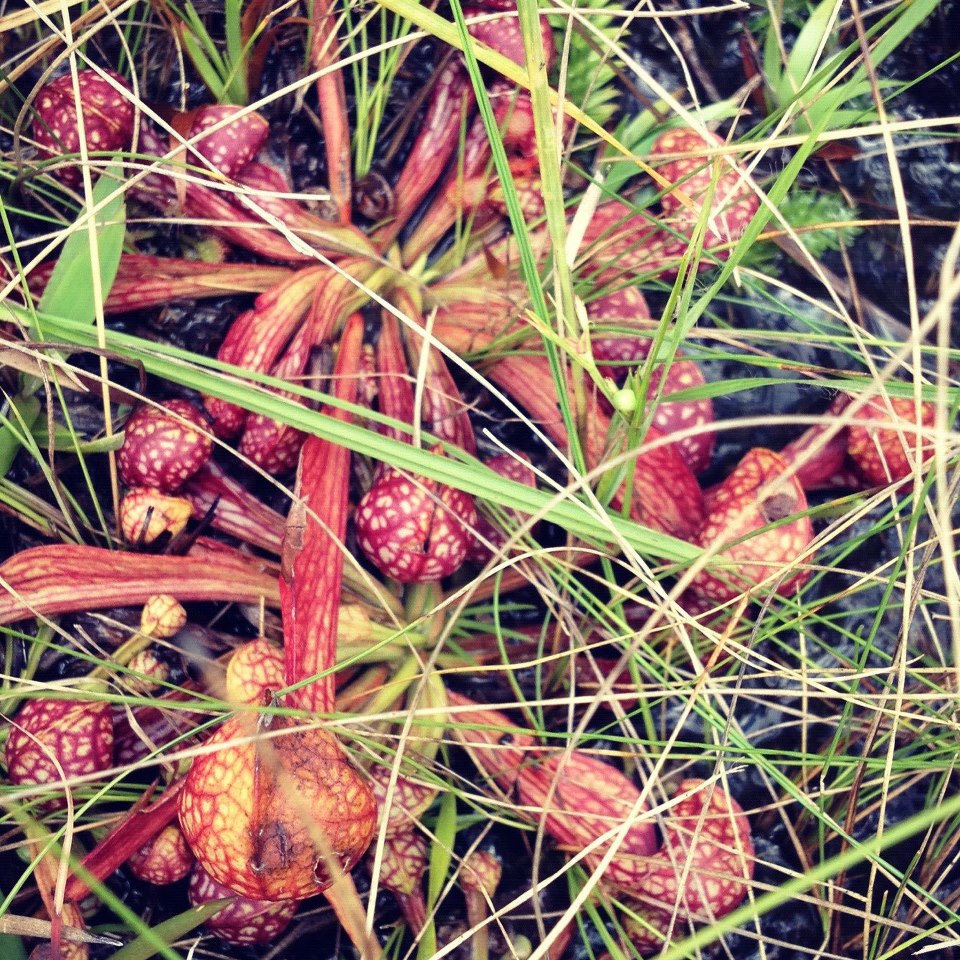
Among the most fascinating natural phenomena in our area are the presence of dozens of species of carnivorous, or meat-eating, plants. Found in bogs, meadows, and seepage slopes with mucky, acidic soils and low levels of nutrients, these plants have adapted to their difficult conditions by developing ways to digest insects.These carnivores are best known by their common names; sundew, butterwort, bladderwort, and pitcher plants.
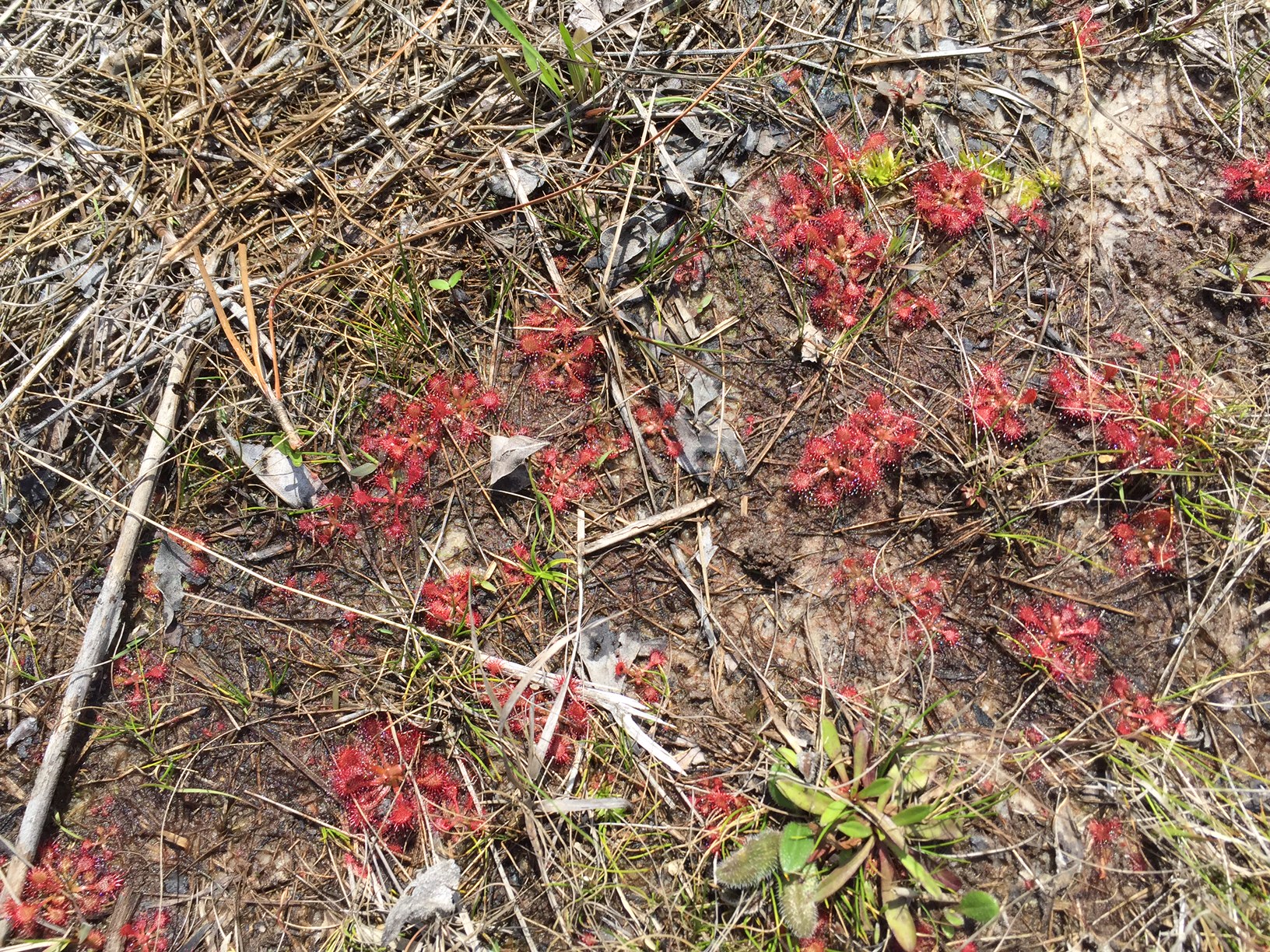

Sundew plants ready to feast

A meadow of white-topped pitcher plants in full spring bloom.
While there are six species of pitcher plants found in the panhandle and throughout the Gulf Coastal Plain, the “world’s largest concentration” can be found at Escambia County’s Tarkiln Bayou Preserve State Park. The “pitcher” part of the plant is actually a modified leaf, which is rounded into a hollow tube open at the top and partially covered by a hood. This hood is colorfully patterned, attracting insects also drawn to nectar inside the tubes. As insects crawl in, downward-facing hairs prevent them from escaping. They drown in the collected water within the tubes, then decompose via acids and enyzymes secreted by the plant into a “liquid fertilizer.” A handful of commensal animals, including flies, spiders, and small frogs, take advantage of the pitcher plants’ insect-trapping expertise and manage to avoid capture.
A guide to identifying all six of these pitcher plant species–white-top, parrot, trumpet-leaf, hooded, sweet, and yellow–can be found at the Florida Department of Environmental Protection’s wetland plant site. Now is the perfect time to see pitcher plants beginning to blossom.
While many people are familiar with pitcher plants, fewer notice the low-growing sundew. These plants may be smaller than a dime in circumference, and grow flat along very mucky soil in full sun. If shaded out even by relatively short grasses, sundew disappear. Their characteristic pinwheel-like appearance and deep red coloring help draw the eye if you look very closely. Sundews also excrete a sticky nectar, on which small insects get stuck and digested to provide nutrients to the plants.The leaves of butterwort plants work very similarly to sundews; they are typically bright green and succulent with sticky hairs that attract nutrients.
Bladderworts, also found in similar environments, use a different mechanism to trap insects. They actually have a bladder-like formation within their root system that opens and closes, siphoning water and unlucky insects in and out.
Regardless of their location, appearance, or method of trapping, carnivorous plants remain one of the most unusual, and interesting groups within the plant kingdom. Be sure to take the opportunity this spring to seek out a park or natural area populated with carnivorous plants–such as Tarkiln, Blackwater River State Park, or the public areas of Eglin Air Force Base and see them for yourself!

by Beth Bolles | Mar 28, 2016
The mining bees or adrenids are often seen in areas of landscapes that have little ground vegetation and loose soil. After mating, the female bee will excavate a very small tunnel in the ground that has several small cells attached to it.

Beneficial solitary bee mounds in the ground. Photo by Beth Bolles
The bee collects pollen and nectar to add to the cell and then lays a single egg in each cell. The emerging larvae feed on the nectar and pollen until it changes to an adult bee in the fall. There is only one generation a year. Although these solitary bees individually produce small nests, sometimes many will nest in close proximity to each other.

Solitary bee entering ground. Photo by Beth Bolles
Solitary bees are not aggressive and stings are quite mild. Most solitary bees can be closely observed and will elicit no defensive behaviors. Perhaps the most common stings that occur are when the sweat bee, which is attracted to moisture, stings when swatted. Males of some solitary bees, which can not sting, will sometimes make aggressive-looking bluffing flights when defending a territory.
Like the most famous honey bee, solitary bees play a beneficial role in the pollination of plants. Their activity in the spring is short-lived and no management is necessary.
by Beth Bolles | Mar 2, 2016
A common question about insects when cold temperatures arrive is whether or not the cold will kill many pests. Although temperatures will occasionally drop below freezing in north Florida, it is normally not cold enough to significantly impact insect populations for the upcoming year.

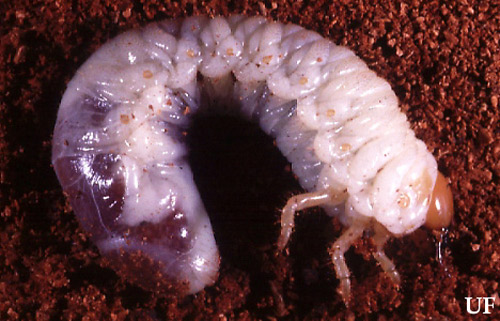
Typical white grub of the genus Phyllophaga. Photograph by John L. Capinera, UF
Even when we do receive a significant amount of cold weather, insects have many methods to survive weather changes. Some insects survive by moving to micro-habitats that are more resistant to temperature fluctuations. Beetle larvae may move deep in the soil or into logs and trees for protection. The grubs can continue feeding on decomposing material throughout winter months. Beneficial insects such as dragonflies and damselflies stay protected in their nymph forms in the mud of ponds and lakes.
One of the most famous insect survival strategies is migration. We are all familiar with the late summer and fall flights of the monarch butterfly to warmer regions of Mexico and southern California. Those butterflies and moths that do not migrate have their own survival techniques. They will overwinter in protective pupal cases to emerge as adults in the spring. Moth cocoons are spun of silk and may be composed of multiple layers, making them a good protection for the transforming insect.
Insects are adapted for survival and can live through far colder winters than we experience. Even though our cold weather will not drastically change insect populations, periods of cold will at least slow down their activity enough for us to enjoy a break from many pest worries.
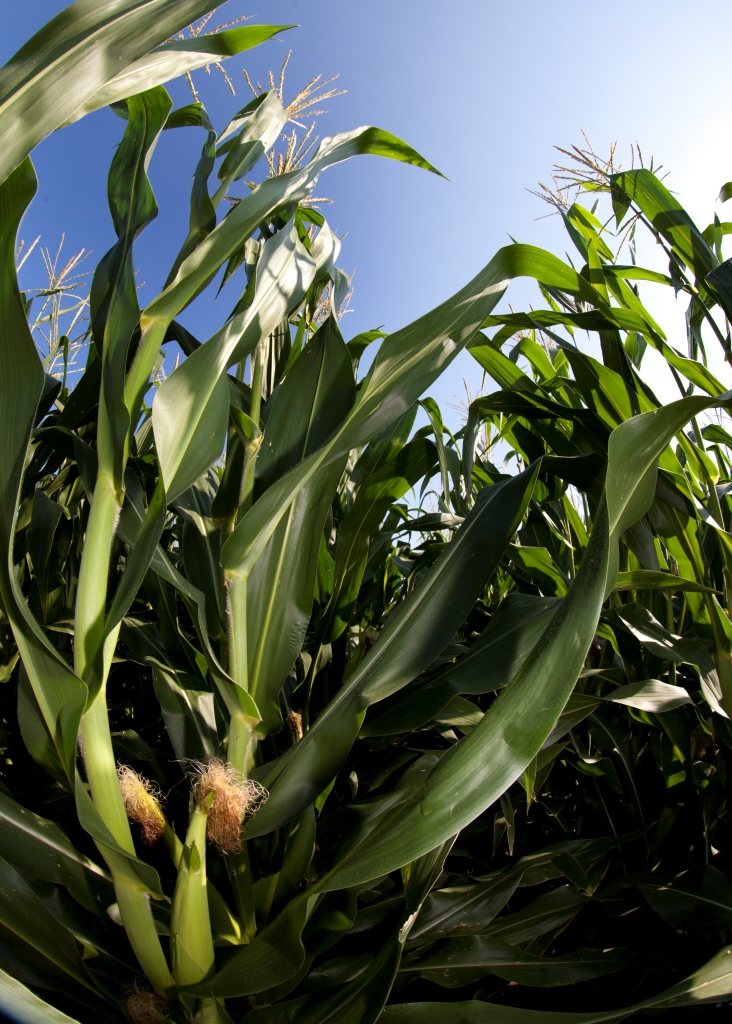

by Judy Biss | Feb 3, 2016

Corn tassels at the top provide the pollen needed to produce the perfect ear of corn on the stalk below. UF/IFAS Photo by Tyler Jones.
It won’t be long until row crops and vegetable gardens are planted and thriving once again next spring. A sometimes taken for granted, yet critical element of any prosperous crop is successful pollination. Most of us know what “text book” pollination means, but did you know in cucurbit plants, (squash, melon, pumpkin) at least 1,000 grains of pollen must be evenly deposited in each bloom to produce a uniform marketable fruit? Or, to grow our favorite summer delight, each watermelon flower must be visited by a honeybee a minimum of 8 times? And how about the fact that each silk in a corn flower is connected to one kernel on the ear of corn, and for the kernel to develop properly pollen must travel down the silk through a pollen tube to the waiting kernel? Add to these facts the dizzying variety of pollen and flowers, bloom times, pollination dynamics, weather conditions, plant growth, and availability of pollinator insects, then one can begin to see how amazing pollination is, and how critical it is to our food supply.
What are the basics of pollination?
The first step of fruit or vegetable reproduction takes place when flowers emerge. Plant flowers can be male, female, or perfect flowers. The male flowers produce pollen. The female flowers have ovaries which, when fertilized, become the fruit or vegetable. “Perfect” flowers have both male and female parts within a single flower. Most garden vegetables such as beans, peppers, and tomatoes have perfect flowers, whereas cucurbits like squash, pumpkins and watermelon, have separate male and female flowers on the same vine. For successful pollination to occur, the male pollen must reach the female ovaries in order for the fruit or vegetable to be produced.
Methods of Pollinating
Transfer of pollen to the plant ovaries for fruit and vegetable production, whether in the same “perfect” flower, or in another separate female flower, occurs in several ways. Some plants, like corn, depend on wind to transfer pollen to the silk, and ultimately ovaries, of the female flower. Other plants, like squash depend on the help of pollinators like insects to deliver the pollen to the ovaries. Plants that produce perfect flowers can self-pollinate, but still benefit from contact with pollinators. In small backyard gardens, many crops in the cucurbit family (squash, melons, etc.) or those that have separate male and female flowers, can be pollinated by the gardener by hand. In the absence of insect pollinators in dooryard gardens, hand pollination will increase yields.
The Importance of Bees
Obviously, in production agriculture, hand pollination of crops is not feasible, and although some crops are wind pollinated, most crops need insect or animal pollinators to accomplish the job. As we know, bees are one of the most important pollinating insects, and it is well documented that yields of many fruit and vegetable crops increase in both quality and quantity when pollinated by honey bees. According to the UF/IFAS publication Minimizing Honey Bee Exposure to Pesticides:
The Business of Pollination
Because they are so critical to increased quality and quantity yields, managed honey bee colonies are used across the country in a thriving contractual pollination industry. According to the UF/IFAS publication Sample Pollination agreement,
The business of pollination is crucial to the agricultural industry in the United States. In Florida, the major need for pollination is in fruit and vegetable production.
And according to the UF/IFAS publication Minimizing Honey Bee Exposure to Pesticides,
Rental of honey bee colonies for pollination purposes is a highly demanded service and a viable component of commercial beekeeping and agriculture. Bee colonies are moved extensively across the country for use in multiple crops every year. There are also over 3,000 registered beekeepers in Florida, managing a total of more than 400,000 honey bee colonies and producing between 10–20 million pounds of honey annually.
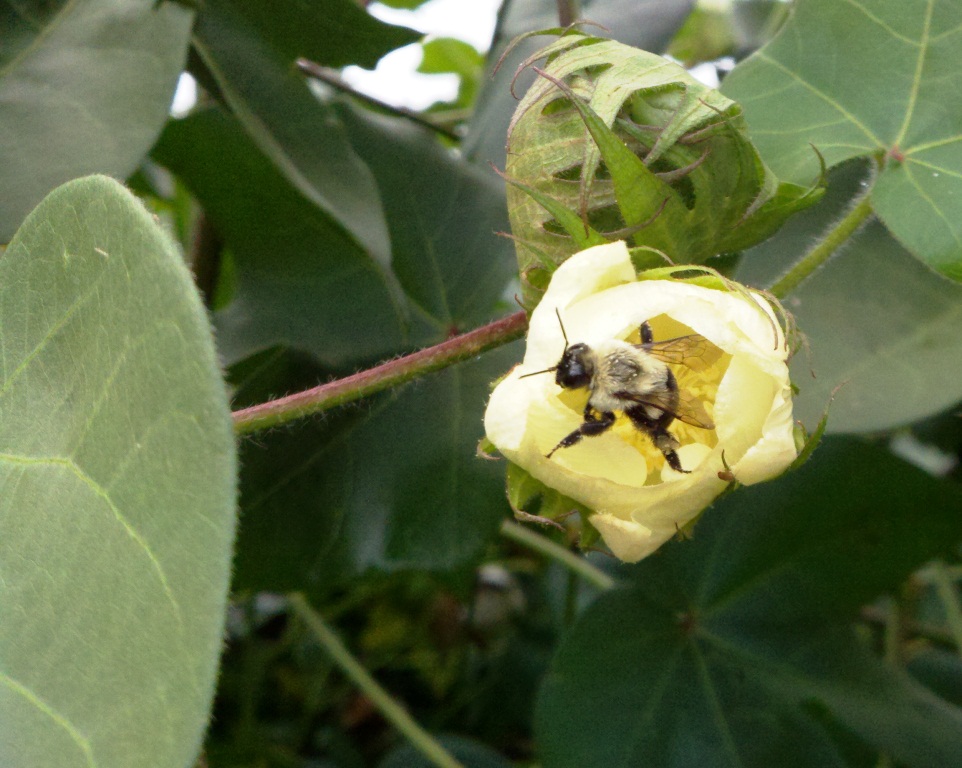

Cotton is largely self-pollinating, but attractive to bees. In some cotton varieties, pollination by bees can increase seed set per boll. Source: University of Georgia Pollination: Crop Pollination Requirements. Photo by Judy Biss
Crop Pollination Requirements
The dynamic of pollination is a fascinating and critical component of both dooryard and production agriculture. Research on plant health, varieties, growth, and potential, as well as research on honey bee colony health and management, all play a role in producing sustainable food yields. The University of Georgia has summarized pertinent literature related to common fruit and vegetable crop pollination requirements (Apple, Blueberry, Cantaloupe, Cucumber, Squash, Watermelon, Other Crops). This comprehensive resource provides the recommended number of beehives per acre for each crop, plus additional information on plant variety characteristics, and other useful information related to maximizing pollination and yield. Check it out: Pollination: Crop Pollination Requirements
So whether you have a dooryard garden or a large farm, it will benefit you to learn all there is to know about your crop’s pollination requirements to maximize yield and quality potential.
For more information on this topic, please see the following publications used as resources for this article:




























