
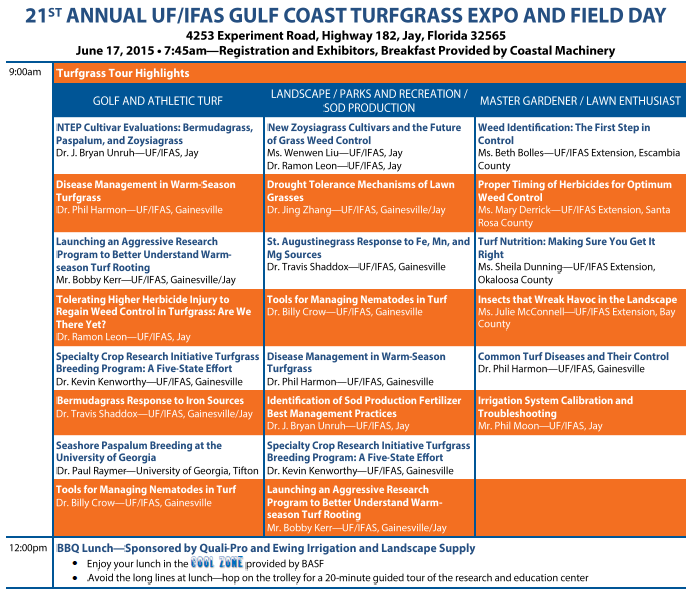
21st Annual Gulf Coast Turfgrass Expo & Field Day
21st Annual Gulf Coast Turfgrass Expo & Field Day





Many people treat their lawn with an insecticide when they see mole crickets in the spring or at the first sign of a brown area in their lawn. What they don’t understand is the biology of this pest.
Mole crickets spend the winter as adults in the soil. As temperatures warm in late February and March, adult mole crickets emerge and begin to mate. Male mole crickets construct a chamber in the soil and chirp to attract female crickets. Attracted females fly to the males. After mating, males die and females fly to a suitable area for egg laying. Mated females begin tunneling and laying eggs in the tunnels. They lay about four clutches of eggs in different areas, averaging 35 eggs per clutch. Female crickets die shortly after laying their eggs.
Use of insecticides during early spring is not recommended because:
The best time to treat for mole crickets is during mid-June through July. This will be when eggs have hatched but before the nymphs (immature mole crickets) are large enough to do much damage. Proper timing of the insecticide application is very important to achieve control.
If you are not sure if mole crickets are present, you can find out with a soap solution. Mix 1½ fluid ounces of a lemon scented liquid dishwashing soap in two gallons of water in a sprinkling can or bucket. Pour the soapy water over an area approximately four square feet and count the number of mole crickets that emerge. If they are present, it only takes several minutes for mole crickets to crawl to the surface after the soap treatment. Repeat the process around the yard where you suspect mole cricket problems. If you flush an average of two to four crickets per site, treat the lawn with an insecticide. Follow up with spot treatments if any crickets escape the first insecticide treatment. But don’t treat at all if there is no evidence of mole cricket activity.
There are a number of products for mole cricket control in home lawns. Look for insecticides that contain the following active ingredients: bifenthrin, carbaryl, cyfluthrin, deltamethrin, imidacloprid , lambda-cyhalothrin or permethrin.
Before using any product for mole cricket control first identify the problem as mole cricket damage by using the soap flush technique. Then choose an insecticide that lists mole crickets on its label. And finally, read the container carefully for use directions, application techniques, irrigation requirements and precautions.

Some times the lawn just gets away from us. It can be completely invaded by weeds or have a devastating disease or insect pest cause total destruction. If your lawn is problem prone there are many cultural practices that can be modified to ensure a successful lawn, but sometimes the lawn is in need of a fresh start and needs to be completely reestablished. If over 50% of the lawn is undesirable than it is time to take action to develop better lawn.
What are the factors that may have caused your lawn to decline so badly? Well here are some common problems that may need to be overcome as you move your lawn into its new era:
As a new lawn is established, correcting these problems will help to ensure the investment will be better taken care of in the future.
Which turf should I choose for my next lawn? Try to answer these questions before you decide:
Here is a publication from Alabama Cooperative Extension to help you choose the correct turfgrass for your next lawn: Selecting Turfgrasses for Home Lawns (while looking at the tables use the South adaptation for the Florida panhandle)
Once the turfgrass type has been chosen, a variety must be chosen. Here are some recommendations:
Get more information on Lawn Management in the Florida Lawn Handbook

It’s too early to fertilize our warm-season lawn grasses now. This includes the use of fertilizers contained in weed-and-feed products.
There are a number of reasons why it’s best to wait to fertilize your lawn.
First, the soil temperature is too cool for grass roots to have access to some of the fertilizer elements. For example, iron and potassium are poorly available until the soil warms up in spring. Some nutrients leach below the grass roots because the lawn can’t use them yet. This results in waste of fertilizer, time and money.
Secondly, fertilizing too soon can induce nutrient deficiencies and off color areas in your lawn. This is one cause for bright yellow areas in lawns during early spring. Nitrogen is readily taken up by the lawn, even under cool soil conditions, and stimulates early green growth. Early lawn growth is dependent on iron also being readily available. However, iron is poorly available under the cool soil conditions of late winter and early spring. Therefore lawns turn yellow in areas due to an iron deficiency caused by an early fertilizer application. Many times, as soil temperatures warm during mid April and May, the iron becomes available and the lawn turns green. So why not avoid this scenario by waiting until mid April to fertilize your lawn?
It takes consistently warm night temperatures to allow the soil to become warm enough for best root growth and optimal uptake of fertilizer.
Thirdly, the young, tender grass roots that are beginning to grow in early spring are easily burned by the fertilizer.
Fourthly, fertilizing too early can stimulate early lawn growth, which is tender and easily injured by a late frost. The average date for our last killing frost is mid March.
Also, be very cautious about using weed-and-feed products that recommend a late winter application. These products are usually high in nitrogen, which will cause your lawn to begin growing too early. If you’re trying to control weeds, it’s best to apply your herbicides separately from fertilizer, anyway.
In North Florida, it’s best to wait until your lawn has completely greened up in spring before applying any fertilizer.
Waiting allows for more efficient use of the fertilizer. You will not injury you lawn by waiting to fertilize but you can certainly injure your lawn by fertilizing too early.
So, have patience, allow your lawn to green up on its own and then fertilize, even if it’s not until mid April or May.

With a few nice late winter days, many people get a good dose of spring fever. But be careful when the fever hits you. Don’t fertilize your lawn too early. The fever may turn into a lawn “headache”.
Wait to fertilize. Fertilizing while the soil is too cool can result in nutrient deficiencies such as iron deficiency causing yellow areas in the lawn. Fertilizing early can result in injury to a lawn’s roots from fertilizer burn. Or tender growth promoted by an early fertilizer application may be injured by a late frost or freeze. Have patience, allow the lawn to green up on its own and then fertilize, even if it’s not until mid April or May.
Get the numbers right. Our lawns need almost the same amount of potassium as compared to nitrogen. Getting this right can make a difference in the long-term health of your lawn. Look for a lawn fertilizer with an analysis such as 8-0-8, 10-0-10, 15-0-15, 18-0-18, 15-2-15, 16-0-8, etc. Look for a fertilizer with a 1:1 ratio of nitrogen to potassium. These numbers provide the buyer important information. The first number is the percent nitrogen (N), the second number is the percent phosphorus (P) and the third number is the percent potassium (K). Adequate potassium has been linked to reduced disease problems, drought and cold tolerance and enhanced root growth.
Use low phosphorus. Lawn grasses use much less phosphorus than nitrogen or potassium. Because of this and because phosphorus has been implicated as a cause for problems in our surface waters, it’s recommended to base phosphorus rates on the results of a reliable soil test. In absence of soil test results, select a fertilizer with 2% or less phosphorus such as 15-2-15, 8-0-8, 16-0-8, etc. It’s best to base P applications on the results of a reliable soil test.
Don’t fertilize too late. The latest month to fertilize our warm season lawn grasses in North Florida as recommended by University of Florida turfgrass researchers is mid September. If you have centipedegrass, it’s recommended to fertilize no later than July.
Measure your lawn. Most homeowners apply too much fertilizer because they do not know the square footage of their lawn. Measure the size of your lawn (front, back and side yard) and err on the side of using less fertilizer than recommended.
So often, homeowners wait until weeds have overtaken their lawns in mid-summer before looking for a course of action to control them. Unfortunately, when weeds get to maturity and start producing flowers and going to seed, they are usually quite difficult to control.
[important]The best strategy is to prevent the weeds from getting established in the first place![/important]

Florida pusley, an annual weed that can be controlled with preemergence herbicides. Photo credit: Mary Derrick UF/IFAS Extension.
When properly applied, a preemergence herbicide forms a chemical barrier on the surface of the soil that kills newly germinated seeds when they grow and contact that barrier. Be sure to follow label directions carefully as it is crucial to apply the correct amount and water it in correctly. The soil surface should not be disturbed after application to ensure that the chemical barrier remains intact.
Keep in mind that preemergence herbicides only prevent annual weeds! They do not control weeds that have already emerged.
In North Florida, the time to apply a preemergence herbicide to your turfgrass is coming soon. As a general rule, March 1 is an ideal time. Another indicator that the time is right is when the daytime temperatures reach 65°F-70°F for 4 to 5 consecutive days as that sustained warmth will prompt weed seeds to germinate. Oftentimes, this is also when azaleas or dogwoods start blooming and that can clue you into when to apply the herbicide. For best results, follow up with a second application in 6 to 9 weeks to control those seeds germinating later in the season.
Always follow the label instructions precisely when applying any herbicide! Ensure that you apply the product at the correct rate, that it is suitable for your specific turfgrass and situation, and that it is watered in correctly. For any pesticide, the label is the law!
If your lawn has problems with winter weeds, make a note on your calendar to apply a preemergence herbicide about October 1 in North Florida or when nighttime temperatures drop to 55°F-60°F for several consecutive days.
For more information on weed control in lawns:
Weed Management Guide for Florida Lawns
For general information on lawn care in Florida:
UF/IFAS Gardening Solutions: Lawns