Hurricanes and floods: Meeting the resource needs of private well owners

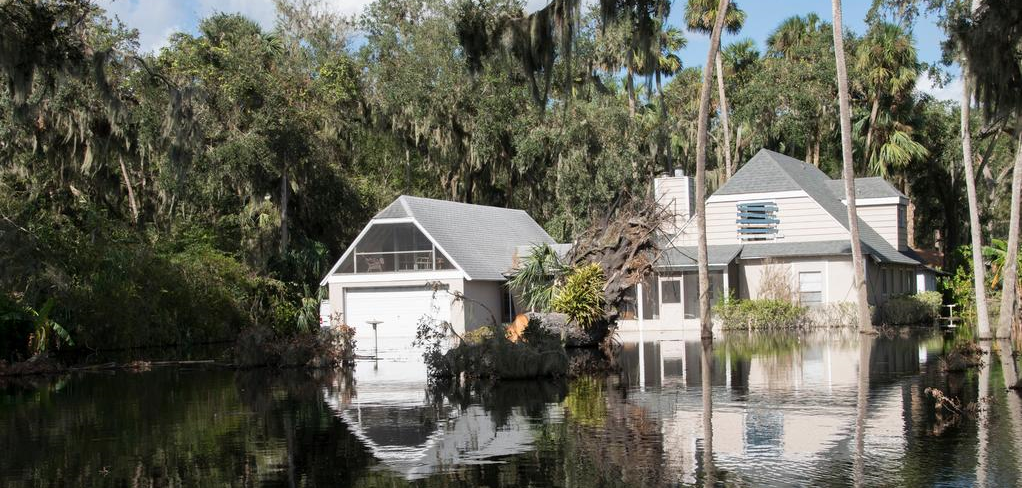
Flooding along the South Prong of the Black Creek River in Clay County on September 13, 2017. Photo credit: Tim Donovan, Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC).
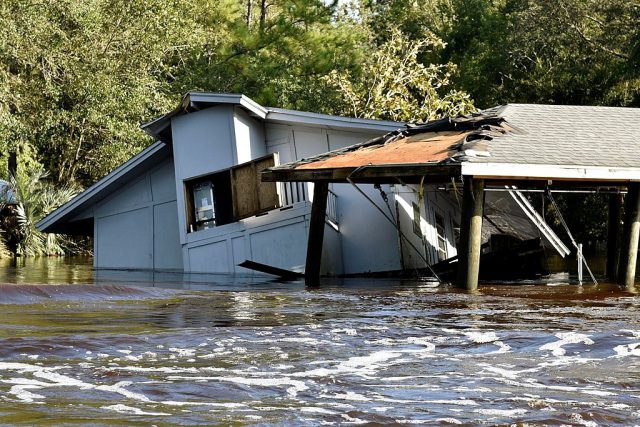
As hurricane season is upon us again, I wanted to share the results of work that UF/IFAS Extension staff did with collaborators from Virginia Tech and Texas A&M University to help private well owners impacted by Hurricanes Irma and Harvey last year. This work highlights just how important it is to be prepared for this year’s hurricane season and to make sure that if flooding does occur, those that depend on private wells for household use take the proper precautions to ensure the safety of their drinking water.
About 2.5 million Floridians (approximately 12% of the population) rely on private wells for home consumption. While public water systems are regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to ensure safe drinking water, private wells are not regulated. Private well users are responsible for ensuring the safety of their own water.
Hurricanes Irma and Harvey
In response to widespread damage and flooding caused by Hurricane Harvey in Texas and Irma in Florida in August and September 2017, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University (VT) received a Rapid Research Response Grant from the National Science Foundation to offer free well water testing to homeowners impacted by flooding.
They partnered with Texas A&M AgriLife Extension’s Well Owner Network (run by Diane Boellstorff and Drew Gholson) and us, at UF/IFAS Extension to provide this service. The effort at VT was led by members of Marc Edward’s lab in the Civil Engineering Department: Kelsey Pieper, Kristine Mapili, William Rhoads, and Greg House.
VT made 1,200 sampling kits available in Texas and 500 in Florida, and offered free analysis for total coliform bacteria and E. coli as well as other parameters, including nitrate, lead, arsenic, iron, chloride, sodium, manganese, copper, fluoride, sulfate, and hardness (calcium and magnesium). Homeowners were also asked to complete a needs assessment questionnaire regarding their well system characteristics, knowledge of proper maintenance and testing, perceptions of the safety of their water and how to best engage them in future outreach and education efforts.
Response in the aftermath of Irma
Although the sampling kits were available, a major challenge in the wake of Irma was getting the word out as counties were just beginning to assess damage and many areas were without power. We coordinated the sampling effort out of Quincy, Florida, where I am based, and spread the word to extension agents in the rest of the state primarily through a group texting app, by telephone and by word of mouth. Extension agents in 6 affected counties (Lee, Pasco, Sarasota, Marion, Clay and Putnam) responded with a need for sample kits, and they in turn advertised sampling to their residents through press releases.
Residents picked up sampling kits and returned water samples and surveys on specified days and the samples were shipped overnight and analyzed at VT, in Blacksburg, VA. Anyone from nearby counties was welcome to submit samples as well. This effort complemented free well water sampling offered by multiple county health departments throughout the state.
In all, 179 water samples from Florida were analyzed at VT and results of the bacterial analysis are shown in the table below. Of 154 valid samples, 58 (38%) tested positive for total coliform bacteria, and 3 (2%) tested positive for E. coli. Results of the inorganic parameters and the needs assessment questionnaire are still being analyzed.
Table 1. Bacterial analysis of private wells in Florida after Hurricane Irma.
| County | Number of samples (n) | Positive for total coliform (n) | Positive total coliform (%) | Positive for E. coli (n) | Positive for E. coli (%) |
| Citrus | 1 | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| Clay | 13 | 5 | 38% | 0 | 0% |
| Hernando | 2 | 1 | 50% | 0 | 0% |
| Hillsborough | 1 | 1 | 100% | 0 | 0% |
| Marion | 19 | 5 | 26% | 1 | 5% |
| Monroe | 1 | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| Pasco | 40 | 19 | 48% | 1 | 3% |
| Putnam | 61 | 19 | 31% | 0 | 0% |
| Sarasota | 16 | 8 | 50% | 1 | 6% |
| Overall | 154 | 58 | 38% | 3 | 2% |
Of 630 samples analyzed in Texas over the course of 7 weeks post-Hurricane Harvey, 293 samples (47% of wells) tested positive for total coliform bacteria and 75 samples (2%) tested positive for E. coli.
What to do if pathogens are found
Following Florida Department of Health (FDOH) guidelines, we recommended well disinfection to residents whose samples tested positive for total coliform bacteria, or both total coliform and E. coli. This is generally done through shock chlorination by either hiring a well operator or by doing it yourself. The FDOH website provides information on potential contaminants, how to shock chlorinate a well and how to maintain your well to ensure the quality of your well water (http://www.floridahealth.gov/environmental-health/private-well-testing/index.html).
UF/IFAS extension agents that led the sampling efforts in their respective counties were: Roy Beckford – Lee County; Brad Burbaugh – Clay County; Whitney Elmore – Pasco County; Sharon Treen – Putnam and Flagler Counties; Abbey Tyrna – Sarasota County and Yilin Zhuang – Marion County.
We at IFAS Extension are working on using results from this sampling effort and the needs assessment questionnaire filled out by residents to develop the UF/IFAS Florida Well Owner Network. Our goal is to provide residents with educational materials and classes to address gaps in knowledge regarding well maintenance, the importance of testing and recommended treatments when pathogens and other contaminants are present.
Remember: Get your well water tested if flooding occurs
It’s important to remember that if any flooding occurs on your property that affects your well and/or septic system, you should have your well water tested in a certified laboratory for pathogens (total coliform bacteria and E. coli) and any other parameters your local health department may recommend.
Most county health departments accept samples for water testing. You can also submit samples to a certified commercial lab near you. Contact your county health department for information about what to have your water tested for and how to take and submit the sample.
Contact information for county health departments can be found online at: http://www.floridahealth.gov/programs-and-services/county-health-departments/find-a-county-health-department/index.html
You can search for laboratories near you certified by FDOH here: https://fldeploc.dep.state.fl.us/aams/loc_search.asp This includes county health department labs as well as commercial labs, university labs and others.
You should also have your well water tested at any time when:
- The color, taste or odor of your well water changes or if you suspect that someone became sick after drinking your well water
- A new well is drilled or if you have had maintenance done on your existing well
Testing well water once a year is good practice to ensure the safety of your household’s drinking water.