by Rick O'Connor | Jun 4, 2020
Recently there was a report of high fecal bacteria in a portion of Perdido Bay. I received a few concerned emails about the possible source. Follow up sampling from several agencies in both Florida and Alabama confirmed the bacteria was there, the levels were below both federal and state guidelines (so no advisory issued), and a small algal bloom was also found. It was thought the cause was excessive nutrients and lack of rain.
We hear this a lot.
Excessive nutrients and poor water quality.
What is the connection?
Many people understand the connection, others understand some of it, others still do not understand it. UF IFAS has a program called LAKEWATCH where citizen science volunteers monitor nutrients in some of lakes and estuaries within the state. Here in Escambia County, we have six such volunteers. Some of the six bodies of water have been monitored for many years, others are just starting now, but the data we have shows some interesting issues – many have problems with nitrogen. Let’s look closer.
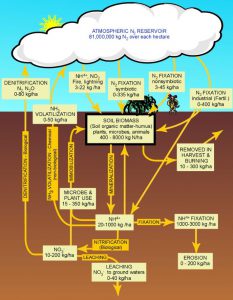
The nitrogen cycle.
Image: University of Florida IFAS
We have all heard of nitrogen. Many will remember from school that it makes up 78% of the air we breathe. In the atmosphere nitrogen is present as a gas (N2). It is very common element found in living creatures – as a matter of fact, we need it. Nitrogen is used to build amnio acids – which builds proteins – which is needed to produce tissue, bone, blood, and more. it is one of the elements found in our DNA and can be used to produce energy. However, it cannot do these in the atmospheric gas form (N2) – it needs to be “converted” or “fixed”.
One method of conversion is the weather. Nitrogen gas are two molecules of nitrogen held together by strong chemical bonds (N2). However, lightning provides enough energy to separate N2 and oxidize it with oxygen in the atmosphere forming nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This NO2 combines with water in the atmosphere to form nitric acid (HNO3). Which can form nitrates (NO3) with the release of the hydrogen and nitrate (NO3) is usable by plants as a fertilizer… a needed nutrient.
But much of the usable nitrates do not come from the atmospheric “fixing” of nitrogen via lightning. It comes from biological “fixing” from microbes. Atmospheric nitrogen can be “fixed” into ammonia (NH3) by bacteria. Another group of bacteria can convert ammonia into nitrite (NO2), and a third group can convert it from nitrite to the usable form we know as nitrate (NO3). Ammonia can also be found in the environment as a waste product of life. As we use nitrogen within bodies it can be converted into ammonia – which can be toxic to us. Our bodies remove this ammonia via urine, and many times we can smell this when we go to the restroom. Nitrogen fixing bacteria can convert this ammonia to nitrites as well and complete the nitrogen cycle.
Once nitrogen has been fixed to the usable nitrate it can be taken up by plants and used within. Animals obtain their needed nitrogen by eating the plants or eating the animals that ate the plants. In both cases, nitrogen is used for protein synthesis in our bodies and unused nitrogen is released into the environment to continue the cycle.
So, what is the connection to water quality?
You might think that excessive nitrogen (nutrients) in the water would be a good thing. Released ammonia, though toxic, could be “fixed” into nitrite and eventually nitrate and recycled back into life. And you would right. Excessive amounts of ammonia though, may not be converted quick enough and a toxic state could occur. We see this in aquaculture ponds and home aquaria a lot.

Members of the herring family are ones who are most often found during a fish kill triggered by hypoxia.
Photo: Madeline
But what about excessive nitrates? Shouldn’t that be good for the plants?
The concept makes sense, but what we see with increase plant growth in aquatic systems is problematic. Excessive plant growth can cause several problems.
1) Too much plant growth at the surface (algae, leafy vegetated material) can block sunlight to the other plants living on the bottom of the waterway. This can cause die off of those plants and a mucky bottom – but there is more.
2) Excessive plant growth at the surface and the middle of the water column can slow water flow. Reduced water flow can negatively impact feeding and reproductive methods for some members of the community, cause stagnation, and decrease dissolved oxygen – but there is more.
3) Plants produce oxygen, which is a good thing, so more plants are better right? Well, they do produce oxygen when the sun is up. When it sets, they begin to respirate just as the animals do. Here excessive plants can remove large amounts of dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water column at night. If the DO levels reach 3.0 µg/L many aquatic organisms begin to stress. We say the water is hypoxic (oxygen starving). When a system becomes hypoxic the animals will (a) come to the surface gasping, (b) some even approach the beach (the famous crab jubilee of Mobile Bay), (c) leave the water body for more open water, (d) die (a fish kill). This is in fact what we call a dead zone. Not always is everything dead, in many cases there is not much alive left – they have moved elsewhere so we say the bottom is “dead”. Here is something else… as the dead fish and (eventually) dead plants settle to the bottom they are decomposed by bacteria. This decomposition process requires dissolved oxygen – you guessed it – the DO drops even further enhancing the problem. In some cases, the DO may drop to 0.0 µg/L. We say the water is now anoxic (NO oxygen). I have only seen this twice. Once in Mobile Bay, and once in Bayou Texar. But I am sure it happens more often. The local environment can enhance (or even cause) this problem as well. Warm water holds less oxygen and much of the oxygen dissolved in water comes from the atmosphere – by way of wave action. So, on hot summer days when the wind is not moving much, and excessive nutrients (nitrogen) is entering the water, you have the perfect storm for a DO problem and possible fish kill.
4) Oh, and there is one other issue… some of the algae that produces these blooms release toxins into the water as a defense. These are known as harmful algal blooms (HABs). Red tide is one of the more famous ones, but blue-green blooms are becoming more familiar. So now you have a possible hypoxic situation with additional toxins in the water that can trigger large fish kills. Some of these HABs situations have killed marine mammals and sea turtles as well.
Though this process can occur naturally (and does) excessive nutrients certainly enhance them, and in some cases, initiate them. So, too much nitrogen in the system can be bad.
So, what does the LAKEWATCH data tell us about the Pensacola Bay system?
Well, first, we have not had volunteers on all bodies of water for the same amount of time. We currently have volunteers monitoring (1) northern Pensacola Bay, (2) Bayou Texar, (3) Bayou Chico, (4) Bayou Grande, (5) Big Lagoon, and (6) lower Perdido Bay. Pensacola Bay has JUST started, and Big Lagoon has not even started yet (COVID-19 issues) – so we only have data from the other four. Bayou Texar has the longest sample period at 13 years.

Lakewatch is a citizen science volunteer supported by the University of Florida IFAS
Second, this program does not sample for just nitrogen, but another key nutrient as well – phosphorus. When you look at a bag of fertilizer you will see a series of numbers looking like: 30-28-14. This would be nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. People adding fertilizer to their lawns should know which nutrient they need the most and can by a fertilizer with a numerical concentration that is best for their lawn. You can have your soil tested at the county extension office. But the point here is that there is more than nitrogen to look at and, as we have learned, more than one form of nitrogen out there. So, what we do at LAKEWATCH is monitor for total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP).
Another parameter monitored is total chlorophyll a (TC). The idea is… if there are excessive amounts of nutrients in the water there will be excessive amounts of algae. You could collect a sample of water and count the number of algal cells in the water – but another way is to measure the amount of chlorophyll in the water as a proxy for the amount of algae. Chlorophyll, of course, is the compound within plants that allows photosynthesis to happen. There is a chemical process used to release the chlorophyll within the cells and you can then use an instrument to measure the amount of chlorophyll in the water.
LAKEWATCH volunteers also monitor water clarity. It is true that clarity can be impacted by sediments in the water as much as an algal bloom, but anything that contributes to less sunlight reaching the bottom can be problematic for some bodies of water. This is done by lowering a disk into the water and measuring the depth at which it “disappears”.
For those not familiar with the term salinity, it is the measure of the amount of dissolved solids in the water – what most people say, “how salty is it?”. For reference, the Gulf of Mexico is usually around
35‰, most open estuaries are between 20-30‰.
Below is a table of the LAKEWATCH data we have as of the spring 2020.
| Year of Sampling |
Body of Water |
Total Phosphorus (µg/L) |
Total Nitrogen (µg/L) |
Total Chlorophyll (µg/L) |
Water Clarity (feet) |
Salinity (‰) |
| 2014 – 2018 |
Bayou Chico |
20-30 |
350 – 600 |
10 – 30 |
2.6 – 4.2 |
7.0 – 8.2 |
| 2012 – 2017 |
Bayou Grande |
16 – 19 |
320 – 340 |
5 -6 |
4.0 – 5.2 |
17 – 18 |
| 2007 – 2018 |
Bayou Texar |
17 – 18 |
600 – 800 |
6 – 8 |
3.4 – 3.8 |
8 – 10 |
| 2014 – 2018 |
Lower Perdido |
15 -16 |
350 – 360 |
5 -6 |
5.3 – 6.1 |
13 -14 |
| STATE AVG. |
(includes lakes) |
25.0 |
309 |
3.7 |
|
|
There are a couple of things that stand out right away
(keep in mind some water bodies have not been monitored very long by LAKEWATCH).
1) Phosphorus is not as big a problem in our part of the state. In the peninsula part of Florida there is a lot of phosphorus in the sediments and much of it is mined. You can see this in the average value for the state. Actually, because of this, many of the central and south Florida lakes are naturally high in phosphorus and this is not considered “polluted”. All that said, there are higher levels of phosphorus in Bayou Chico. Which is interesting. More on solutions in a moment.
2) We have a lot of nitrogen in our waters. Bayou Texar in particular is much higher than the state average. More on this in a moment.
3) We have a little more chlorophyll than the state average, but not alarming.
4) Bayou Grande and lower Perdido are clearer than Bayou’s Texar and Chico.
5) All these bodies of water are less than 20‰. More on this as well.
So, comments…
1) We already discussed the phosphorus issue (or non-issue), but what about Bayou Chico? Phosphorus is NOT introduced to the system from the atmosphere as nitrogen is – rather, it comes from the sediments. High levels of TP would suggest high levels of sediments in the water column (the water clarity data supports this) – which suggest high levels of run-off. The watershed for Bayou Chico is highly urbanized and run-off has historically been a problem.
2) Nitrogen can come from many sources, but when numbers get high – many will hypothesize they are most likely from lawn run-off (fertilizers), or sewage (septic leakage, sanitary sewage overflows, animal waste). There are certainly other possibilities, but this is where most resource managers and agencies begin.
3) Elevated chlorophyll indicates elevated primary production. This is not unusual for an estuary. They are known for their high productivity. Bayou Chico seems have more algae than the others. Most probably due to the increase levels of nutrients entering the watershed.
4) Bayou Grande and lower Perdido Bay have better water clarity than Bayou’s Chico and Texar. Though all four bodies of water have significant coastal and watershed development, Bayou’s Chico and Texar and completely developed as well as their “feeder creeks”. Again, indication of a run-off problem.
5) All four bodies of water have several sources of freshwater input as well as stormwater run-off that has contributed to the lower salinities found here. It is possible that the salinities here were less than 20‰ prior to heavy development.
Possible Solutions….
There is a common theme with each of these – stormwater run-off. Rain that historically fell on the land and percolated into the ground water, now flows off impervious surfaces (streets, driveways, parking lots, even buildings) into drainage pipes and discharges into the waterways. This stormwater carries with it much more than just fertilizers and animal waste, it carries pesticides, oil, grease, solid waste, leaf litter, and much more.
How do you reduce stormwater?
Well, there is not much you can do with impervious surfaces now, but the community should consider alternative materials and plans for future development – what we call “Green Infrastructure”. Green roofs, pervious streets and parking lots, there are a lot of methods that have been developed to help reduce this problem.
Another consideration is Florida Friendly Landscaping. This is landscaping with native plants that require little (or no) water and fertilizer. It also includes plants that can slow run-off and capture nutrients before they reach the waterways and methods of trapping run-off onto your property.
If you happen to live along a waterway, you might consider landscaping your property by restoring some of the natural vegetation along the shoreline – what we call a living shoreline. Studies have shown that these coastal plants can remove a significant amount of nitrogen from the run-off of your property as well as reduce coastal erosion and enhance fisheries by providing habitat.

Closed due to bacteria.
Photo: Rick O’Connor
What about sewage issues?
Unfortunately, most septic systems were not designed to remove nitrogen – so leaks occur and will continue. The only options you have there are (a) maintain your septic by pumping once every five years, (b) consider taping into a nearby sewage line.
Sewers systems are not without their problems. Sanitary sewage overflows do occur and can increase nitrogen in waterways. These are usually caused by cracks in old lines (which need to be replaced), are because we flush things down drains that eventually “clog the arties” and cause overflows. Things such as “flushable wipes”, which are flushable – they go down the drains – but they do not breakdown as toilet paper does and clog lines. Cooking grease and oil, and even milk have been known to clog systems.
Our LAKEWATCH volunteers will continue to sample three stations in each of their bodies of water. We are looking for a volunteer to monitor Escambia Bay. If interested contact me.
If you are interested learning more about green infrastructure, Florida Friendly Landscaping, or living shorelines lines contact your county extension office (850-475-5230 for Escambia County). If interested in issues concerning sanitary sewage overflows or septic issues, contact your county extension office, or (if in Escambia or Santa Rosa counties) visit ECUAs FOG website (Fats, Oils, and Grease) https://ecua.fl.gov/live-green/fats-oils-grease.

by Matt Deitch | May 8, 2020
Urbanization—the process of conversion from forests, grasslands, or agricultural fields to predominantly residential, commercial, and industrial settings—can cause profound changes to the pathways that rainfall takes to become streamflow. This landscape conversion leads to less water infiltrating into soil and more water running directly into streams and other nearby water bodies (such as lakes, wetlands, and bayous). Urban water runoff carries pollutants that have accumulated on the landscape and in soil since the previous rainfall. If the concentrations of pollutants in streams are large enough, they can cause problems for the organisms that live in streams as well as those in the bays and bayous those streams flow into (often called receiving waters).

Stormwater conveyance in Santa Rosa nd Escambia counties.
Photo: Matt Deitch
Local governments play a key role in mitigating the impacts of urbanization on aquatic ecosystems. In northwest Florida, County government is often responsible for limiting pollutant inputs from the network of surface and underground stormwater conveyances known as “municipal separate storm sewer systems” (abbreviated as MS4s). The United States EPA requires urban areas to be regulated as sources of pollutant discharge through their National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (abbreviated NPDES); departments within Escambia County and Santa Rosa County government coordinate the administration of these permits with the US EPA.
The requirements of these MS4 water quality permits vary depending on the population of the area. Permits for medium and large cities or counties having populations greater than 100,000 are categorized as “Phase I” MS4s, while areas with smaller populations are categorized as being “Phase II” MS4s. These two categories have many similar requirements, but also have a few important differences. Permits for both types of MS4s require local agencies to develop methods for community outreach on stormwater pollution issues, controlling runoff from construction sites, and requiring stormwater management in new developments. In addition to the requirements listed above, Phase I MS4s require the implementation of a water quality monitoring program and a plan to reduce pollutants from developed areas.

Stormwater conveyance in Santa Rosa and Escambia counties.
Photo: Matt Deitch
In Spring 2020, the southern portion of Santa Rosa County transitioned from a Phase II MS4 region to Phase I. This means that Santa Rosa County will begin implementation of a surface water monitoring program to evaluate pollutant concentrations in stormwater conveyances (including creeks); and develop plans for reducing pollutants from their MS4s entering the Pensacola Bay System. This program will make important contributions to understanding the effects of urban development on our local streams and estuaries, and improve water quality in the Pensacola Bay System.
This is a great opportunity to remind us of the importance of disposing our personal protective equipment including face masks, plastic gloves, and other single-use items we use to protect ourselves from the coronavirus in the trash after use. Leaving it on the curb or in parking lots means that it can wash into stormwater ponds or creeks and bayous, which can cause problems for the animals that live there.

Stormwater conveyance in Escambia and Santa Rosa counties.
Photo: Matt Deitch

by Matt Deitch | Mar 13, 2020
Flooding and poor water quality are common issues of concern in the Florida Panhandle. Our frequent heavy rains cause water to quickly run off rooftop, parking lot, and driveway surfaces; this runoff water carries with it the chemicals deposited on land surfaces between rain events by direct application (such as landscape fertilizers) as well as through wind and circulation, a process referred to as atmospheric deposition. Surface water that runs off our developed urban and residential landscape is usually routed into stormwater drains and sewers, and then into stormwater detention ponds or directly into surface streams.

Dry stormwater pond in Escambia County.
Photo: Matt Deitch
Conventional methods for dealing with stormwater runoff is through the use of stormwater ponds. Stormwater ponds allow water to slowly infiltrate into the soil before moving to streams or wetlands via shallow groundwater pathways. Typically hidden behind shopping centers or in the back of residential subdivisions, stormwater ponds attenuate flooding by delaying the time when water reaches the stream and are intended to improve water quality through microbial processes (such as denitrification) or plant uptake, particularly focusing on reducing the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus that reaches nearby streams. However, the efficacy of stormwater ponds is highly variable (many do not function as intended), and they often are visually unattractive aspects of a community.

A backyrad rain garden after installation near Navarre FL.
Photo: Nikki Bennett
Stormwater managers in other parts of Florida are increasingly utilizing a suite of management features termed “green infrastructure” as alternatives to stormwater ponds to reduce floodwaters and improve water quality before it enters nearby streams and wetlands. Green infrastructure, which includes features such as rain gardens, green rooftops, rainwater cisterns, bioswales, and permeable pavers, is designed to slow water down and reduce pollutant concentrations by mimicking natural processes of infiltration and biological uptake at its source—off the rooftops, driveways, roads, and parking lots where stormwater first concentrates. As a result, green infrastructure reduces surface runoff that occurs during storm events, leading to less flooding downstream. With the magnitude of peak flow reduced, stormwater runoff is also likely to carry lower amounts of pollutants downstream. In addition to their capacity to reduce flooding and improve water quality, green infrastructure can have many other benefits. It is often visually appealing, with vegetation typically selected to be visually attractive, appropriate for local conditions, and requiring low maintenance.

Rain garden at the VA Central Western Massachusetts Health Care System facility.
Photo: US Air Force
With our frequent rainfall, moderately developed urban areas, and expanding communities, the Florida Panhandle is ideal for using green infrastructure to reduce flooding and improve water quality. Features such as bioswales, rain gardens, and permeable pavement can be added to new development to mitigate stormwater runoff; they can also be added to existing neighborhoods to reduce flooding where roadside areas or other shared spaces allow. In addition to mitigating the effects of rainfall, green infrastructure can also improve property values because of their visual appeal. For green infrastructure techniques to be effective, they require widespread use throughout a neighborhood rather than at a handful of locations; so if it sounds like green infrastructure would benefit your community, talk with your neighbors and reach out to UF IFAS agents to discuss how it could be added to your community!

by Andrea Albertin | Jan 31, 2020

Contact you local county health department office for information on how to test your well water. Image: F. Alvarado Arce
Residents that rely on private wells for home consumption are responsible for ensuring the safety of their own drinking water. The Florida Department of Health (FDOH) recommends private well users test their water once a year for bacteria and nitrate.
Unlike private wells, public water supply systems in Florida are tested regularly to ensure that they are meeting safe drinking water standards.
Where can you have your well water tested?
Your best source of information on how to have your water tested is your local county health department. Most health departments test drinking water and they will let you know exactly what samples need to taken and ho w to submit a sample. You can also submit samples to a certified private lab near you.
Contact information for county health departments can be located at: http://www.floridahealth.gov/programs-and-services/county-health-departments/find-a-county-health-department/index.html
Contact information for private certified laboratories are found at https://fldeploc.dep.state.fl.us/aams/loc_search.asp
Why is it important to test for bacteria?
Labs commonly test for both total coliform bacteria and fecal coliforms (or E. coli specifically). This usually costs about $25 to $30, but can vary depending on where you have your sample analyzed.
- Coliform bacteria are a large, diverse group of bacteria and most species are harmless. But, a positive test for total coliforms shows that bacteria are getting into your well water. They are used as indicators – if coliform bacteria are present, other pathogens that cause diseases may also be getting into your well water. It is easier and cheaper to test for total coliforms than to test for a suite of bacteria and other organisms that can cause health problems.
- Fecal coliform bacteria are a subgroup of coliform bacteria found in human and other warm-blooded animal feces, in food and in the environment. E. coli are one group of fecal coliform bacteria. Most strains of E. coli are harmless, but some strains can cause diarrhea, urinary tract infections, and respiratory illnesses among others.
To ensure safe drinking water, FDOH strongly recommends disinfecting your well if the water tests positive for (1) only total coliform bacteria, or (2) both total coliform and fecal coliform bacteria (or E. coli). Disinfection is usually done through shock chlorination. You can either hire a well operator in your area to disinfect your well or you can do it yourself. Information for how to shock chlorinate your well can be found at http://www.floridahealth.gov/environmental-health/private-well-testing/_documents/well-water-facts-disinfection.pdf
Why is it important to test for nitrate concentration?
High levels of nitrate in drinking water can be dangerous to infants, and can cause “blue baby syndrome” or methemoglobinemia. This is where nitrate interferes with the blood’s capacity to carry oxygen. The Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) allowed for nitrate in drinking water is 10 milligrams nitrate per liter of water (mg/L). It is particularly important to test for nitrate if you have a young infant in the home that is drinking well water or when well water is used to make formula to feed the infant.
If test results come back above 10 mg/L nitrate, use water from a tested source (bottled water or water from a public supply) until the problem is addressed. Nitrates in well water can come from fertilizers applied on land surfaces, animal waste and/or human sewage, such as from a septic tank. Have your well inspected by a professional to identify why elevated nitrate levels are in your well water. You can also consider installing a water treatment system, such as reverse osmosis or distillation units to treat the contaminated water. Before having a system installed, contact your local health department for more information.
In addition to once a year, you should also have your well water tested when:
- The color, taste or odor of your well water changes or if you suspect that someone became sick after drinking well water.
- A new well is drilled or if you have had maintenance done on your existing well
- A flood occurred and your well and/or septic tank were affected
Remember: Bacteria and nitrate are not the only parameters that well water is tested for. Call your local health department to discuss your what they recommend you should get the water tested for, because it can vary depending on where you live.
FDOH maintains an excellent website with many resources for private well users at http://www.floridahealth.gov/environmental-health/private-well-testing/index.html, which includes information on potential contaminants and how to maintain your well to ensure the quality of your well water.

by Andrea Albertin | May 3, 2019

The major goal of the Wakulla Springs Basin Management Action Plan (BMAP) is to reduce nitrogen loads to Wakulla Springs. Septic systems are identified as the primary source of this nitrogen. Photo: A. Albertin
A Basin Management Action Plan, or BMAP, is a management plan developed for a waterbody (like a spring, river, lake, or estuary) that does not meet the water quality standards set by the state. One or more pollutants can impair a waterbody. In Florida, the most common pollutants are nutrients (particularly nitrate), pathogens (fecal coliform bacteria) and mercury.
The goal of the BMAP is to reduce the pollutant load to meet water quality standards set by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP). BMAPS are roadmaps with a list of projects and management action items to reach these standards. FDEP develops them with stakeholder input. Targets are set at 20 years, and progress towards those targets is assessed every five years.
It’s important to understand that a BMAP encompasses the entire land area that contributes water to a given waterbody. For example, the land area that contributes water to Jackson Blue Springs and Merritts Mill Pond (either from surface waters or groundwater flow) is 154 square miles, while the Wakulla Springs Basin covers an area of 1,325 square miles.
BMAPs in the Panhandle
There are 33 adopted BMAPS in the state, and 5 that are pending adoption. Here in the Panhandle, we have three adopted BMAPS. They are the Bayou Chico BMAP in Escambia County, the Wakulla Springs BMAP in Wakulla, Leon, Gadsden and small parts of Jefferson County, and the Jackson Blue/Merritts Mill Pond BMAP in Jackson County. All three are impaired for different reasons.
- Bayou Chico discharges into Pensacola Bay and is polluted by fecal coliform bacteria. The BMAP addresses ways to reduce coliforms from humans and pets, which includes sewer expansion projects, stormwater runoff management, septic tank inspections, pet waste ordinances and a Clean Marina and Boatyard program.
- Wakulla Springs Nitrate from human waste is the main pollutant to Wakulla Springs, and Tallahassee’s wastewater treatment facility and the city’s Southeast Sprayfield were identified as the main sources. Both sites were upgraded (the sprayfield was moved), greatly reducing nitrate contributions to the spring basin. The BMAP is focused on septic systems and septic to sewer hookups.
- Jackson Blue/Merritts Mill Pond Nitrate is also the primary pollutant to the Jackson Blue/Merritts Mill Pond Basin, but nitrogen fertilizer from agriculture is identified as the main source. This BMAP focuses on farmers implementing Best Management Practices (BMPs), land acquisition by the Northwest Florida Water Management District , as well as septic tanks, recognizing their nitrogen contribution to Merritts Mill Pond.
Once all the BMAPS are adopted, FDEP states that almost 14 million acres will be under active basin management, an area that includes more than 6.5 million Floridians.
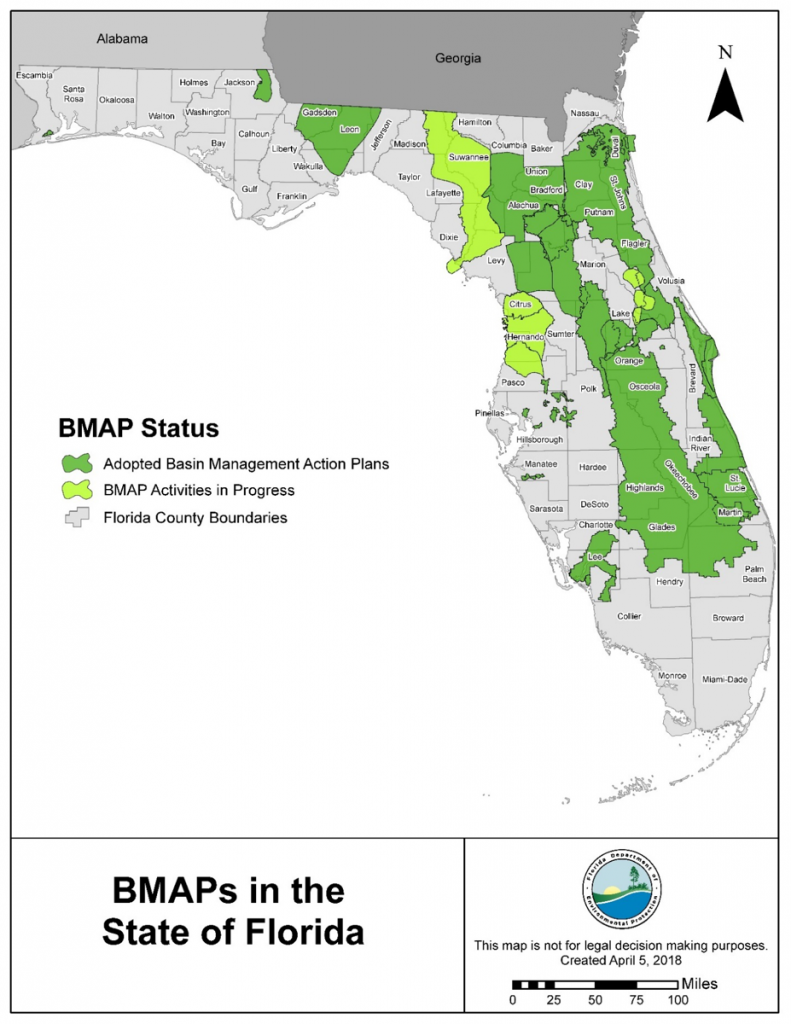
Adopted and pending BMAPS in Florida. Source: FDEP Statewide Annual Report, June 2018
How are residents living in an area with a BMAP affected? It varies by BMAP and specifically land use within its boundaries. For example, in BMAPs where nitrogen from septic systems are found to be a major source of nutrient impairment to a water body, septic to sewer hookups, or septic system upgrades to more advanced treatment units will be required in specific areas. In urban areas where nitrogen fertilizer is an important source, municipalities are required to adopt fertilizer ordinances. Where nitrogen fertilizer from agricultural production is a major source of impairment, producers are required to implement Best Management Practices to reduce nitrogen loads.
More information about BMAPS
For specific information on BMAPS, FDEP has an excellent website: https://floridadep.gov/dear/water-quality-restoration/content/basin-management-action-plans-bmaps All BMAPs (full reports with specific action items listed) can be found there, along with maps, information about upcoming meetings and webinars and other pertinent information.
Your local Health Department Office is the best resource regarding septic systems and any ordinances that may apply to you depending on where you live. Your Water Management District (in the Panhandle it’s the Northwest Florida Water Management District) is also an excellent resource and staff can let you know whether or not you live or farm in an area with a BMAP and how that may affect you.


















