by Sheila Dunning | Jul 28, 2014
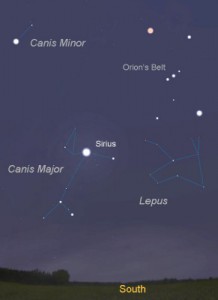
The “Dog Days” are the hottest, muggiest days of summer. In the northern hemisphere, they usually fall between early July and early September. The actual dates vary greatly from region to region, depending on latitude and climate.
In ancient times, when the night sky was un-obscured by artificial lights, the Romans used the stars to keep track of the seasons. The brightest constellation, Canis Major (Large Dog), includes the “dog star”, Sirius. In the summer, Sirius used to rise and set with the sun, leading the ancient Romans to believe that it added heat to the sun. Although the period between July 3 and August 11 is typically the warmest period of the summer, the heat is not due to the added radiation from a far-away star, regardless of its brightness. The heat of summer is a direct result of the earth’s tilt.
Spending time outdoors this time of year is uncomfortable, potentially dangerous, due to the intense heat. However, the chinch bugs are very active in St. Augustine grass, and the summer flowers need water. So, take care of those tasks early in the day and then retreat to the air conditioning to plan your fall planting.
Plant tomato plants in August for tomatoes in October. Varieties such as Phoenix, Florida 91, Solar Set and Heat Wave II are good selections for setting fruit in high temperatures, should summer temperatures continue. Otherwise, try some of the newer UF/IFAS recommended varieties for fall planting in North Florida such as Bella Rosa, Tribute or Finishline. For more information on tomato selection refer to Tomato Cultivars for Production in Florida. For information on other vegetables for fall gardening refer to the Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide. Plan to attend the Fall Gardening program at the Extension office this September.
 Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to Gardening with Annuals in Florida.
Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to Gardening with Annuals in Florida.

Dependable fall blooming perennials include lion’s ear (Leonotis leonurus), pineapple sage (Salvia elegans), firebush (Hamelia patens), cigar plant (Cuphea micropetala), yellowbells (Tecoma stans) and firespike (Odontonema strictum). Also, garden mums (Chrysanthemum sp.) and many different Irises will add color again in the spring. To gain information on perennials for Florida refer to Gardening with Perennials in Florida.
Webster’s second definition of “dog days” is a period of stagnation or inactivity. But, even when the heat forces you to slow down on the labor-intensive work, there is plenty of gardening “activity” to do. Stay in the air conditioning and plan that spectacular fall and winter yard.
by Gary Knox | Jul 21, 2014
Burgundy-leaved crapemyrtle is one of the most exciting breeding accomplishments in years. Unlike previous selections, many new crapemyrtle cultivars have leaves that retain dark burgundy coloration from spring budbreak through fall leaf drop. These plants add bold leaf color to a plant already known for its flower power.
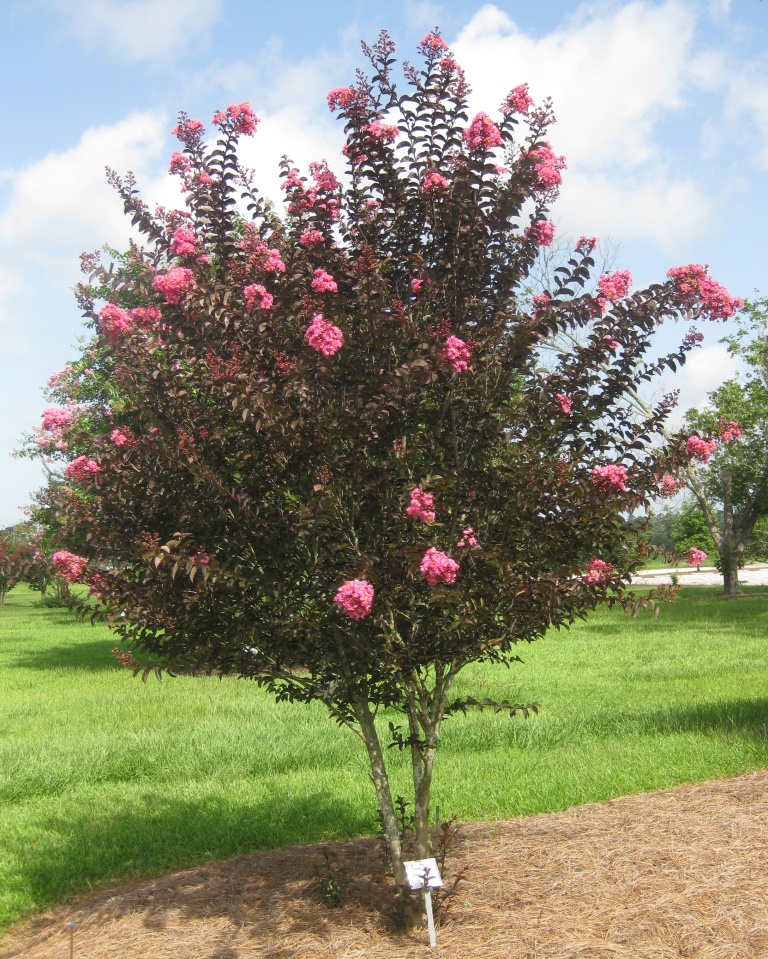

Delta Jazz™ was the first crapemyrtle with burgundy-bronze leaves all summer long. Photo by Gary Knox
As is typical of many new plant introductions, the new crapemyrtles are grouped and sold in series, most of which are patented and/or trademarked. Delta Jazz™ was the first crapemyrtle with burgundy-bronze leaves all summer long. This year Delta Jazz™, with pink flowers, is being joined by Delta Eclipse™ (purple flowers). Future years will see Delta Breeze™ (lavender flowers) and Delta Flame™ (red). All have burgundy to bronze leaves from spring through fall and are expected to be mid-size, maturing at heights of 8 to 12 feet.
Another new series with burgundy leaves confusingly is being sold under two names: the Ebony series and the Black Diamond™ series. ‘Ebony & Ivory’ features white flowers that contrast nicely with dark burgundy leaves on red stems. ‘Ebony Embers’ has red flowers on plants with dark burgundy leaves on purple stems. ‘Ebony Fire’ has flowers that are bright red and its leaves are medium burgundy. ‘Ebony Flame’ has dark red flowers and dark burgundy leaves. Finally, ‘Ebony Glow’ is named for its blush white flowers on dark red stems with dark burgundy leaves. These selections are also sold as Black Diamond™ Pure White, Black Diamond™ Red Hot, Black Diamond™ Crimson Red, Black Diamond™ Best Red and Black Diamond™ Blush, respectively. All are expected to grow 8 feet or more in height (regardless of the name!).

‘Ebony Fire’ is a new crapemyrtle with burgundy leaves and bright red flowers. Photo by Gary Knox
The First Editions® Magic™ series of crapemyrtles includes two new selections with burgundy leaves. Moonlight Magic™ has the darkest burgundy leaves I’ve seen so far. Flowers are white and the burgundy leaves are glossy and narrow on a plant expected to grow to a height of 8 to 10 feet. Maturing at 4 to 6 feet, Midnight Magic™ has leaves that are a dull burgundy while flowers are dark pink. Note that other cultivars in the First Editions® Magic™ series (‘Coral Magic’, ‘Plum Magic’, and ‘Purple Magic’) have green leaves.
These cultivars are too new to know how well they will perform in north Florida and the Gulf Coast. The best place to view these cultivars side by side is at the LSU AgCenter, Hammond Research Station, in Hammond, LA. There, Dr. Allen Owings has developed a beautiful garden where he is evaluating crapemyrtles and many other plants. For more information and to read Dr. Owing’s comments on new crapemyrtles, visit http://www.lsuagcenter.com/en/our_offices/research_stations/Hammond/.
All these new cultivars will have the brightest burgundy leaf color when plants are grown in full sun (at least 6 hours of direct sun each day). Any amount of shade will likely result in pale burgundy or burgundy-green leaves, as well as reduced flowering and growth. As with other crapemyrtles, these new cultivars are tolerant of drought, heat, rain, humidity and all but wet soils. When buying crapemyrtle, place the plant in a location where it can grow to its full height without the need to prune it regularly. After planting, sit back and enjoy these crapemyrtles’ bold burgundy foliage as well as the abundance of colorful flowers!
1Extension Specialist and Professor of Environmental Horticulture, University of Florida/IFAS, North Florida Research and Education Center, Quincy, Florida. gwknox@ufl.edu.

by Beth Bolles | Jul 21, 2014
You hear it all the time. Be sure to read the label before using any pesticide. Honestly though, is this a practice you really follow? It should be.
Sometimes we do not consider pesticides dangerous since we can buy them in most any retail store or garden center. Companies surely would not sell something to an average homeowner that is too toxic or dangerous.
Pesticides are chemicals that are used to kill insects, plants, and sometimes mammals. Even though many of the most dangerous chemicals are not available to homeowners, the products you find on stores shelves should still be used with care and attention. It is important to read the label. If not only to protect yourself, but to protect pets, children, wildlife, and water systems.
Each pesticide that you buy will come with a label. This label contains important information about the product. The following is a guide to the information found on a pesticide label and why it is required by law that you read it.
Active Ingredient: This is the chemical name of the pesticide and the part of the product that is active against the pest. Before buying your pesticide, look at the active ingredient to make sure that you are purchasing the right product for your specific job. You can not always judge a product by the trade name or brand name since several very different pesticides may have the same or very similar brand names.
Signal Words: The pesticide will either have Caution, Warning, or Danger in bold letters on the label. These words tell us the product’s level of toxicity. Caution – slightly toxic, Warning – moderately toxic; Danger – highly toxic. Most homeowner products will carry the Warning or Caution signal words.
Environmental Hazards: Many pesticides are toxic to birds, invertebrates, and mammals. Some products may not be used near water in order to protect wildlife. This section will guide you in ways to prevent damage to animals, groundwater, and soil.
Direction for Use. Each label will state how to apply the product so that it is most effective against the targeted pest. This will include rates, timing of applications, and pests controlled by the product. It is never beneficial to apply more than the label states.

Pesticide labels are the law and must be followed.
Every label will contain additional information on precautions that need to be followed to safely use the pesticide and treatment if there is an accident. Since we are not able to predict when an accident will happen, make sure that you are always prepared by reading any pesticide label you will be using.

by Carrie Stevenson | Jul 21, 2014

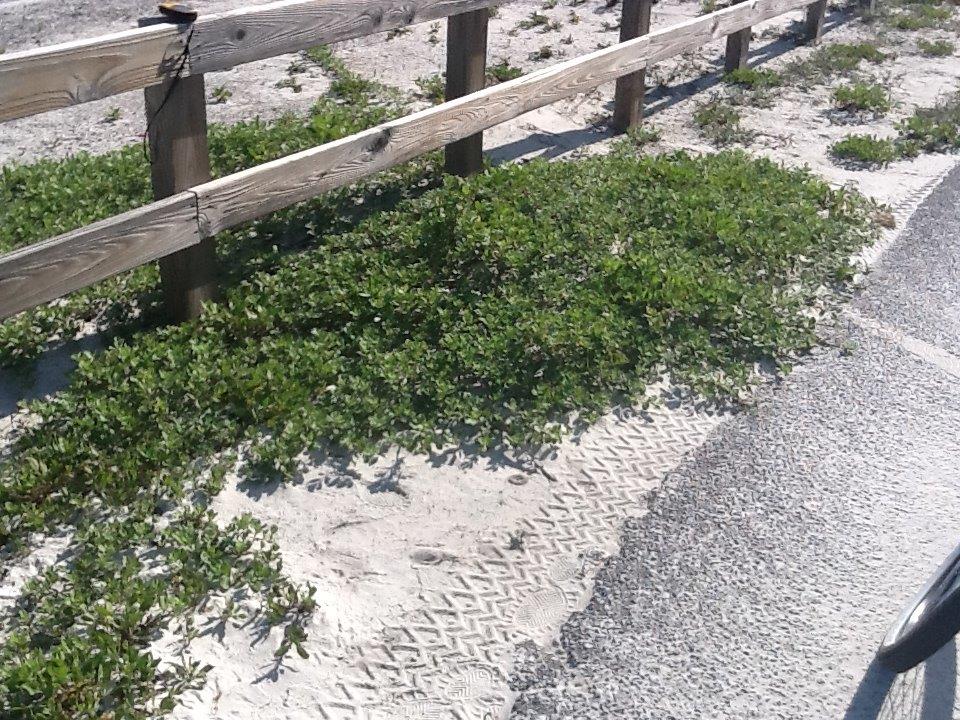
Many beachfront dwellers have intentionally planted beach vitex because of its attractive purple flowers. Photo credit: Rick O’Connor
Now that summer is in full swing, many of us are spending more time on our gorgeous Gulf beaches. Sea turtles are nesting and everyone gets excited at sightings of dolphins, sharks, and the Blue Angels. However, we have another recent visitor to our beaches, and this one isn’t spending money and renting condos. It has moved in from out-of-state and plans to stay, potentially wreaking havoc to our fragile beach dune ecosystems.
Florida is no stranger to invasive species. Reports and stories of pythons, popcorn trees, feral pigs, and others can be found everywhere. As a matter of fact, Florida and Hawaii have more problems with exotic plants and animals than any of the other states.
Beach Vitex (Vitex rotundifolia) is originally from the coastal areas of the western Pacific. It was brought to the United States by North Carolina State University in the 1980’s to restore dunes along coastal Carolina after severe storms. The plant is very salt and drought tolerant and performs well in direct sun and sandy soils; perfect for our coastal beaches. It grows about 3 feet tall and produces branches that extend along the surface of the sand over 60 feet from the tap-root. The flowers are lavender and found in the spring. By midsummer the flowers have dropped and pea-size dark fruit is produced. The fruit is also salt tolerant and can be carried by ocean currents as well as birds. The plant seemed a perfect choice for restoration projects.
And then…
And then it began to overgrow the primary dune system, choking the majority of the native plants including sea oats. The shrub size of the plant and the presence of vertical tap roots in lieu of fibrous ones did not suit it well as a dune forming plant; some studies found that it actually increased the erosion of some dune fields. Beach vitex releases allelopathic compounds, reducing the water content of the soil which stresses native plants thus reducing competition for space. And then there are the sea turtles. Evidence indicates that the growth of this plant over the primary dunes has made it difficult for female turtles to find nesting areas, while fast growing branches grow over incubating nests and make it difficult, if not impossible, for the hatchlings to emerge. The plant has become such a problem that it has been dubbed “Beach Kudzu” and there is a two-state task force to remove it.

Beach vitex grows quickly and can rapidly take over an entire yard or beach dune. Photo credit: Rick O’Connor
Beach vitex has dispersed north to Virginia and south into Georgia. Currently it has been reported in only three Florida counties; Duval, Santa Rosa, and Escambia. Because of the few records in our state it is not currently listed as an invasive plant in Florida. The problem is, most biologists will tell you that the best way to eradicate an invasive species is to get it early. However most do not see the introduction of a new plant or animal as invasive until it becomes established and difficult to remove.
Natural Resource Agents with UF IFAS Extension are tracking the locations along the coast of the panhandle where this plant may exist. If you believe you may have it please let us know so that the location can be recorded. If you are interested in removing the plant we recommend cutting back to the tap-root. Dab the remaining tap-root with Round-Up. It is best if the remaining parts of the plant do not leave the property; if legal it is ok to burn. If you must transport it off the property we recommend it be dried on concrete and then double bagged before removing to the landfill. In many cases it may take several years to completely remove this plant. If you have any questions about this plant please call your local county Extension Office. Special thanks to Sea Grant Agent Rick O’Connor roc1@ufl.edu for use of this article.
by Larry Williams | Jul 15, 2014
Florida Betony (Stachys floridana), commonly called rattlesnake weed, is a Florida native plant. It’s thought to have been confined to Florida until it was moved to other Southeastern states during the 1940s or 1950s in nursery containers. It is now found from Texas to North Carolina. Its square stems are characteristic of the mint family of which it is a member.

Florida Betony foliage & flowers Photo Credits: UF/IFAS Extension
Underground white, fleshy tubers, which resemble a rattlesnake’s rattle in shape, provide the main means of reproduction. Pinkish-purple flowers are followed by a dried fruit that splits open releasing tiny seeds, which are a lesser means of reproduction. The white tubers have been used for hundreds of years as a starchy vegetable and are sometimes boiled like peanuts.
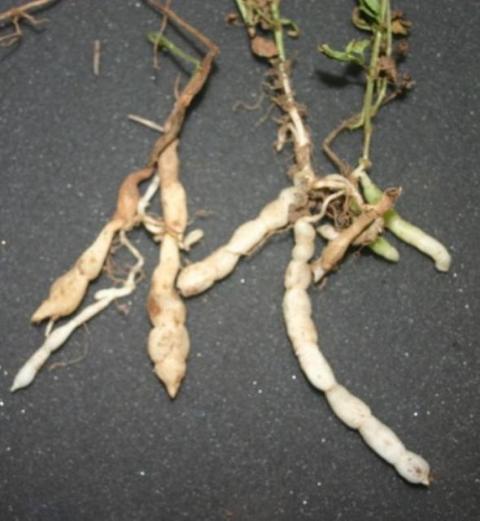

Florida betony weed tubers Photo Credits: UF/IFAS Extension
The tubers make Florida Betony tough to control. Even when above ground foliage and stems are killed due to herbicide use, the tubers allow the regeneration of the plant repeatedly. When attempting to control this weed, it helps to be more persistent than the plant. Many people give up.
Even though it is a perennial, the above-ground portion of the plant grows during fall and spring and becomes dormant during hotter weather.
You can remove the weed by digging, making sure to remove the entire root system (including the tubers). But persistence and patience is required. Herbicide control usually involves repeat applications approved products in lawns. Glyphosate herbicides such as Roundup can be used to control Florida Betony in plant beds. But do not get the herbicide on any green portion of desirable ornamentals.
Always refer to the product’s label for specific uses, application rates and turfgrass tolerance when using any herbicide.
So, why not just dig up the Florida Betony in your lawn and have a native plant feast?
by Larry Williams with content by Matthew Orwat
 Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to Gardening with Annuals in Florida.
Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to Gardening with Annuals in Florida.










