
by Carrie Stevenson | May 1, 2017

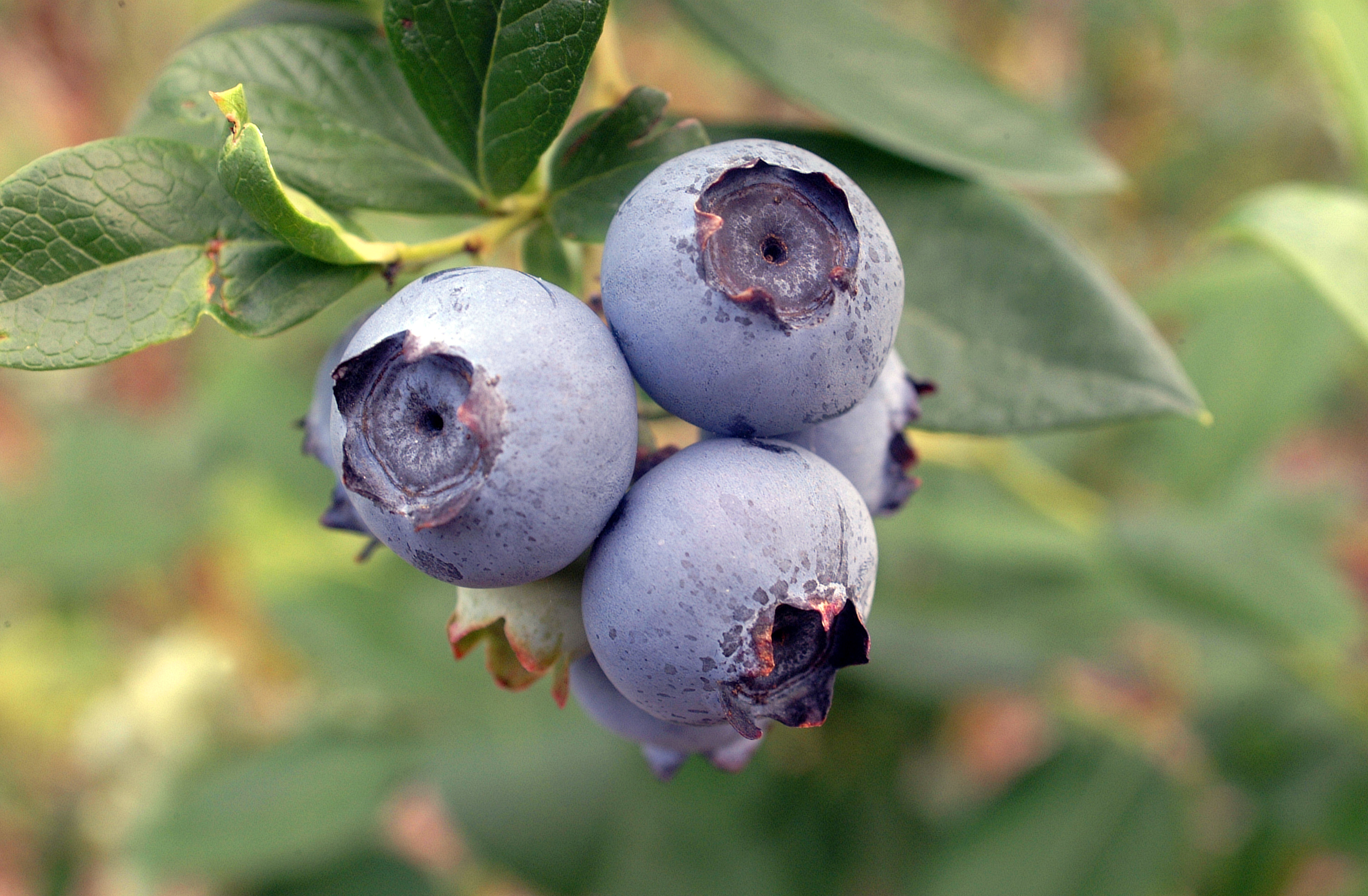
The Southeastern blueberry bee uses buzz pollination on a blueberry plant. Photo credit: Tyler Jones, UF IFAS.
This time of year, blueberry bushes are flowering and small fruit are coming onto the wild and cultivated bushes in north Florida. Many of us, myself included, look forward to the late-spring harvest of blueberries, taking our children out to u-pick operations and digging out family recipes for blueberry-filled desserts.
What many do not know, however, is that there’s a specialized bee that literally lives for this season. During the last few weeks, this little insect has been furiously pollinating blueberry bushes during its short, single-purpose lifetime.
The Southeastern blueberry bee, Habropoda labriosa is active only in mid-March to April when blueberry plants are in flower. They are smaller than bumblebees, and the yellow patches on their heads can differentiate males. Blueberry pollen is heavy and sticky, so it is not blown by the wind, and the flower anatomy is such that pollen from the male anther will not just fall onto the female stigma. Blueberry bees must instead attach themselves to the flower and rapidly vibrate their flight muscles, shaking the pollen out. Moving to the next flower, the bee’s vibrations will drop pollen from the first flower onto the next one. This phenomenon is called “sonicating” or ‘buzz pollination” and is the most effective method of creating a prolific blueberry crop.
Blueberry bees do not form hives, but create solitary nests in open, sunny, high ground. Females will dig a tunnel with a brood chamber large enough for one larva, filling it with nectar and pollen. After laying an egg, the female seals the chamber and the next generation is ready. The species produces only one generation of adults per year.
By the time we are picking fresh blueberries next month, you probably won’t see any blueberry bees around. However, we should all consider these insects’ short-lived but vitally important role in Florida’s $82 million/year blueberry industry!
For more information, check out the beautifully illustrated USDA Forest Service publication, “Bee Basics—An Introduction to our Native Bees,” or North Carolina State University’s entomology website.
by Julie McConnell | May 1, 2017

American Dog Tick. Photo: L. Buss, UF/IFAS
You’ve probably heard some tips to prevent picking up ticks in the past, but did you ever wonder why some work and others don’t? Understanding the life cycle and behavior of common ticks can help you succeed with your prevention measures.
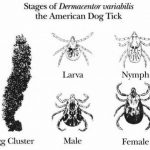
Life Cycle of American Dog Tick. Credit: Centers for Disease Control
A general life cycle for ticks includes four life stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. The egg hatches into larva which require a blood meal to molt into a nymph which again requires a blood meal before molting to an adult.
The adult female also requires blood feeding in order to produce eggs, which she lays in high numbers – some species lay up to 6,500 eggs!
Because blood is required for development, ticks have to be resourceful in finding hosts. Knowing this can help you understand why some tips work better than others.
Tick Tips
-
Wear clothing that covers skin and avoid sitting on the ground or logs in brushy areas. Adult ticks exhibit a behavior called “questing” where they climb to the top of grasses and vegetation with their forelegs extended and wait for a host to come by. The American Dog Tick‘s primary host are dogs, but they will also target cattle, horses, and humans.
-
Apply repellents to exposed skin and clothing (different products are labeled for where they are applied, follow all directions). These chemicals repel ticks and can reduce likelihood of tick attachment, but ticks have been known to crawl over treated areas to access untreated body parts.
-
Keep grass and vegetation maintained and clean up debris that may harbor small mammals and rodents. Early in the tick life cycle it targets smaller animals for blood and they can
hide or shelter in debris piles and vegetation.
-
Always shower and check yourself for ticks after being in areas where ticks may live, especially when temperatures are warm. Nymphs can be less than 1 mm long, so check carefully!
For instructions on how to properly remove a tick that has embedded, visit UF Health Tick Removal.

Female Lone Star tick that has not fed. Photo: L. Buss, UF/IFAS

Lone Star Tick female engorged on blood. Photo: L. Buss, UF/IFAS
by Beth Bolles | May 1, 2017
We may shy away from drama in our lives but drama in the garden is always welcome. One plant series that will be a prominent feature in any garden bed is the Amazon Dianthus series.

Amazon Dianthus series is showy in the garden or in a container. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
Although we normally consider Fall the time to plant dianthus, the Amazon Series developed by PanAmerican Seed company can be planted in Spring for blooms that extend into Summer. This is the combination of two dianthus and the results are plants with striking colors and longer blooming cycles.
The Amazon series comes in a few bright colors including Amazon Neon Cherry, Amazon Neon Pink, and Amazon Rose Magic. Flowers are held on stems about 1.5-2′ tall and foliage is an attractive dark green. Plants are generally low maintenance but be sure to deadhead flowers as they fade. Plants will need rich, well drained soil and full sun.

Neon Cherry. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County

Neon Pink. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
If you don’t have room for the Amazon dianthus series in your landscape, plants will also grow well in containers to brighten a patio or deck.
by Mark Tancig | Apr 24, 2017

Source: UF/IFAS.
Impatiens are a very popular annual, bedding plant that provide a nice burst of color in the landscape. The traditional Impatiens (Impatiens walleriana), or touch-me-not, is the one that most gardeners know as needing part shade, but there are also the New Guinea Impatiens (Impatiens hawkeri) that are able to tolerate more sun. In addition to being able to withstand more sunlight, the New Guinea Impatiens also have larger flowers and leaves. Another highlight of the New Guinea impatiens is their increased resistance to downy mildew, a major concern for growers of touch-me-nots, especially in south Florida.
While native to the Old World, Impatiens are not known to invade Florida natural areas but may reproduce by seed. Touch-me-nots are known to spread easily be seed. An interesting fact about Impatiens is their bursting seed pods that can send seeds several feet from the parent plant. This characteristic is what led to the scientific name Impatiens – for impatient – and one of the common names – touch-me-not.
May is a good time to plant Impatiens in north Florida. They prefer slightly acidic soil and should be planted at a 12-18 inch spacing. Impatiens work well as a border planting or in mass plantings. While New Guinea Impatiens tolerate more sun, they still would prefer some afternoon shade. Those growing in full sun will need extra care to ensure they remain well watered. An all-purpose plant food can be applied at monthly intervals for best performance.
Some common varieties of touch-me-nots include ‘Accent’, ‘Blitz’, ‘Carousel’, ‘Dazzler’, ‘Impact’, ‘Impulse’, and ‘Super Elfins’. Common New Guinea Impatiens varieties include ‘Celebration Candy Pink’, ‘Celebration Light Lavender’, ‘Nebulus’, ‘Equinox’, ‘Sunglow’, and ‘Tango’. The newer ‘Sunpatiens’ variety is quite popular and comes in different forms – compact, spreading, and vigorous.

Source: UF/IFAS.
If you have any questions regarding Impatiens, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office or visit our EDIS website at www.edis.ifas.ufl.edu.
by Ray Bodrey | Apr 24, 2017
If you haven’t already, it’s time to prepare the garden space for the summer bounty of fresh vegetables. The following information will help you get started. Just remember, as the soil preparation goes, so goes the vegetable production.

Figure 1: Planting Vegetables in Prepared Soil.
Credit: Tyler Jones, UF/IFAS.
By far the most physical part of vegetable gardening is soil preparation. This is the foundation that your garden is built on, so let’s not cut corners at this stage. Plain and simple, poor soil prep will result in poor garden performance. Before you begin prep, it is a good idea to have a soil sample analyzed. With a soil analysis complete, a more customized fertilizer and application may be recommended for your needs. However, a complete fertilizer like 8-8-8 or 10-10-10 can be used as general purpose. Also, pH can be determined through this test. If the soil is too acidic for vegetables, then a liming requirement may be needed. pH is key information, especially regarding planting time. If one needs lime, it is recommended to wait at least a month before planting to allow the lime to adjust soil pH. Generally, a small amount of lime can be added to a garden space regardless, as lime also contains the vital micronutrients calcium and magnesium. Contact your local extension office for more information on soil testing.
To begin the garden prep, one will first need to remove the weeds from the space. The next step is to turn the soil. This will help aerate the soil and accelerate soil decomposition which leads to higher organic matter. Turing the soil will also eliminate any soil compaction issues that would stifle seed germination. With sandy soils throughout the Panhandle, one will most likely need to amend by spreading a rich organic compost in the space. An application of fertilizer can be mixed in at this stage as well. Always follow the manufacturer’s label regarding application directions. Once complete, the soil should then be turned by digging down six to eight inches. A large garden will require a motorized tiller, but hand-held implements should be fine for smaller spaces.
After the soil is turned, be sure to break up any clods and rake so that the area is level. The soil should be of a fine texture by this point. Again, this makes seed germination much easier and will assist in further root development of transplants.
To have a vegetable garden that all will envy, it begins with soil prep. Remember, not only does a vegetable garden provide nutrition, but it also provides for exercise, a feeling of accomplishment and even could save you a few bucks. Please contact your local county extension office for more information.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publication: “Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide” by Sydney Park Brown, Danielle Treadwell, J. M. Stephens and Susan Webb: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/VH/VH02100.pdf
Information on garden plot preparation was also provided by Emeritus Vegetable Specialist Jim Stephens, of The University of Florida’s Institute of Food and Agricultural Science.
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.












