
Native trees, like this Live Oak (Quercus virginiana), provide habitat for various insects fed upon by birds. Source: James Holland, Bugwood.org
Planting native plants is a topic many north Florida gardeners, and subscribers to Gardening in the Panhandle, have seen covered in various ways and formats. It doesn’t take a great leap of understanding to realize that native plants are highly valued by our wildlife, which have adapted to living with these plants for millennia. However, we also get a lot of information about the latest, greatest landscape plant variety, many of which are non-native, and are lured to purchase them by their beautiful flowers and/or foliage. In the wake of Hurricane Michael, the importance of selecting native plants for the landscape becomes apparent when you look around and see whole forests severely disturbed. Furthermore, recent research has shown how much our native wildlife prefer native plants and need them for the best chances of survival.
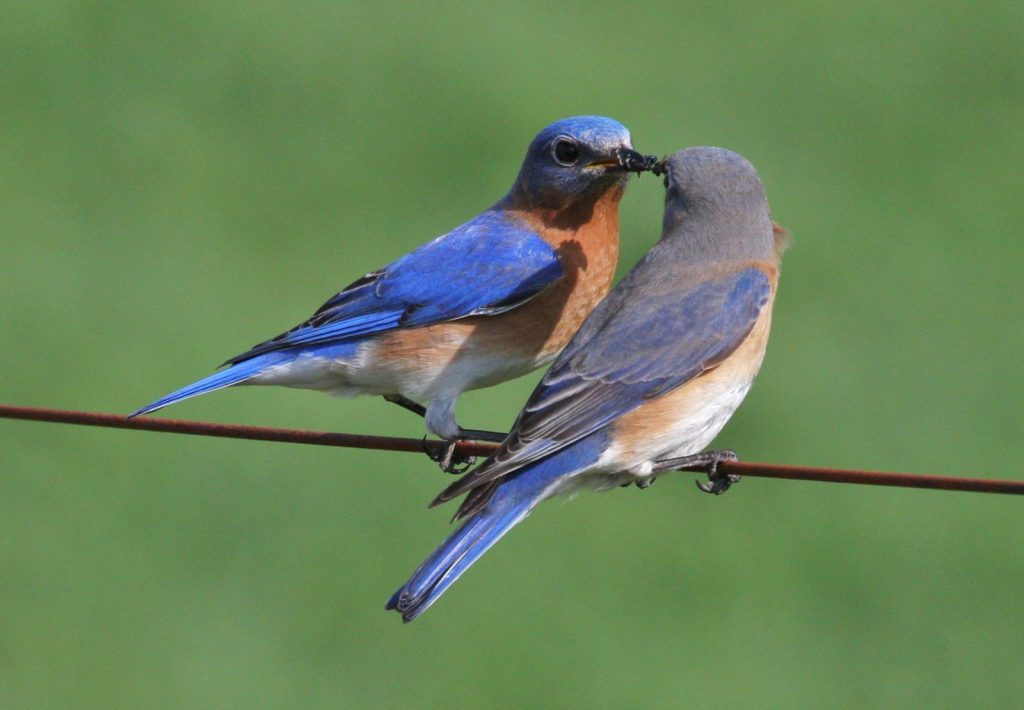

Eastern bluebirds are an example of a bird that relies on insects. Source: Sandysphotos, Creative Commons.
Why Native Plants?
It’s not that non-native ornamental plants are “bad”, unless they’re the terrible invasive, exotic species like kudzu, Chine privet, etc., it’s just that the food chains that support our wildlife are adapted to native plants. A recent report published in the National Proceedings of Science found that chickadees had far better success fledging young when they foraged landscape areas containing 70% or more native plant cover. The reason for their success was that the insects they feed on utilize native species more than non-native plant species. Does that mean non-natives provide no value? Not necessarily. Non-native ornamental plants can be important sources of nectar and pollen and, as you know from experience dealing with pest problems on non-native plants, they also support insects. Native plants just support more of an abundance of these insects.
Following a large disturbance like Hurricane Michael, many insects, birds, and other wildlife will likely see a decrease in numbers and/or reproductive success due to the loss and/or disruption of native plant ecosystems. As stated in the recent report, restoration of urban areas should prioritize native plants to support local food webs.
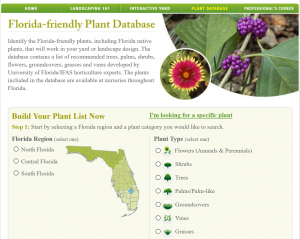
The deactivated_site website is a great resource to find native trees for your area. Source: Screenshot, deactivated_site.
The deactivated_site website is an easy way to start putting together a list of potential plants. The website’s Florida-Friendly Plant Database allows users to select the area of Florida they live in, site conditions, plant type (tree, shrub, etc.), and to specify native plants only. It then searches the database for plants that meet those conditions and creates a list of species, along with photos and care information. If you’re thinking about how these trees hold up to storms, you can cross-check that list with UF/IFAS’s Wind and Trees EDIS publication. Of course, if you have any questions along the way, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office.
- When to Worry About Your Citrus During Cold Weather - December 18, 2025
- A Tale of Two Hoses - November 13, 2025
- Anthracnose and Aster Yellowing Diseases Recently Diagnosed - August 28, 2025
