The unwanted guest- Flea beetle
Having trouble with flea beetles? Tired of them showing up unannounced? Do not be alarmed here are a few tips to get rid of the unwanted guest in your garden.
Description: Flea beetles vary in appearance, where colors range from black to tan, with other, brighter colors mixed. They may also have a solid, striped, or spotted pattern depending on the species. Beetles are tiny with large hind legs which allow them to jump like fleas when disturbed.
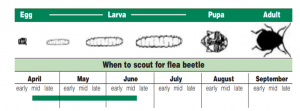
Lifecycle: These unwanted guests will overwinter as adults in the soil or beneath plant debris and become active in early spring when temperatures reach 50°F, and begin feeding on weeds or early-planted crops. Eggs are laid by adult flea beetles normally around May in the soil or at the base of host plants. After 7-14 days eggs will hatch and larvae will feed and develop on various plant parts. They pupate in the soil for 11-13 days before emerging as adults.
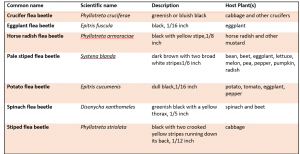
Host plants: Some species attack a wide range of plants, while others target only certain plant families. (Table 1). In the garden, several vegetable crops are eaten by these pests, particularly those in the Brassica family.
Scouting: Adult flea beetles are particularly active on warm, sunny days. To identify damages, scout every 1-2 days in newly planted fields, since it is easier to identify the damages than to see the beetles themselves. Flea beetle populations can be monitored with yellow sticky traps.
Damage: Adult beetles feed on foliage, producing shot holes in the leaves, especially new leaves which will have a lacy appearance. Additionally, in leafy crops like lettuce or spinach, the holes can reduce the quality of the leaves.
Management / Control strategies:
- In the spring delay transplanting or planting by a couple weeks if possible.
- In the fall, till the garden to uncover any hiding flea beetles.
- Plant “push” or repellant crops such as catnip, sage, mint, hyssop, nasturtium, and basil.
- Use a “trap crop” such as radishes, taking the pest’ focus off more valuable plants.
- Dusting leaves with plain talcum powder repels flea beetles on tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and other plants.
- Insecticides may be used early in the season.
- Water deters adult flea beetles. Any watering should be done in mid-day.
- Planting after adults have emerged or crop rotation can help minimize flea beetle damage.
- Apply commercially available nematodes that feed on flea beetle eggs, larvae, and pupae.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publications EENY-721/IN1238: Flea Beetles of the Genus Altica: Altica spp. (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelid) (ufl.edu); https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/ORN/BEETLES/flea_beetle.html and https://extension.uga.edu/content/dam/extension/programs-and-services/integrated-pest-management/documents/insect-pdfs/fleabeetles.pdf
- “Stink and Pretty”: The Pedagogy of Marigolds - May 22, 2025
- The Bold and the Beautiful in Your Landscape – Snapdragons - April 10, 2025
- Should You Be Concerned About the Grizzled Mantis? - February 27, 2025