
by Sheila Dunning | Nov 4, 2021

Chewing caterpillar damage on St. Augustinegrass Photo by: Steven Arthurs, UF
Tropical sod webworm larvae are destructive pests of warm season turfgrasses in the southeastern U.S. especially in the fall. Commonly referred to as a worm, they are truly caterpillars, the larvae of a moth. Larval feeding damage reduces turfgrass aesthetics, vigor, photosynthesis and density, which is very evident on finer-bladed grasses such as bermudagrass and zoysiagrass. Feeding damage is possible on all grass types however. Adults, a dull brown colored moth about ¾ inch long, rest in sheltered and shrubby areas during the day and are active at dusk. Females deposit clusters of 10-35 eggs on the upper surface of grass blades. The eggs hatch in 3-4 days and develop from a 1 mm long caterpillar to one over 11 mm long through six instars within 21 to 47 days, depending on temperature. Larval feeding occurs at night, leaving the grass looking ragged, shortened and missing.

Sod webworm on soil surface
Photo by: Steven Arthurs, UF
Control should be against damaging larvae, not the flying moths. However, insecticidal soap applications to moth harboring areas can reduce re-population frequency. Soil-drenching soap flushes can be used to find the caterpillars, especially in dry and hot grass areas. Bacterial-based insecticides, such as Bt, Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki or Spinosad, will control sod webworm caterpillars without impacting beneficial species as long as they are applied with each flush of grass growth.
Fall armyworms are also active when the weather turns cooler. They feed any time of the day or night, but are most active early in the morning or late in the evening. The 1 ½ inch long gray and white moth lays about 1,000 eggs in multiple masses on any vegetation. Two to 10 days later, the small caterpillar hatches and begins to grow to nearly 2 inches long over a two week period. The fall armyworm is easily recognized by its dark head marked with a distinct pale-colored inverted Y and the long black stripe running along each side of its body. These aggressive feeders “march” rapidly across grassed areas consuming every above-ground plant part. While bacterial-based insecticides will reduce the numbers, control of armyworms usually requires synthetic insecticides.

Armyworm
Photo by: Jim Castner, UF
The good news is that grass “worms” can be controlled and the blades will grow back. The damage may be devastating to see, but usually not a permanent problem.
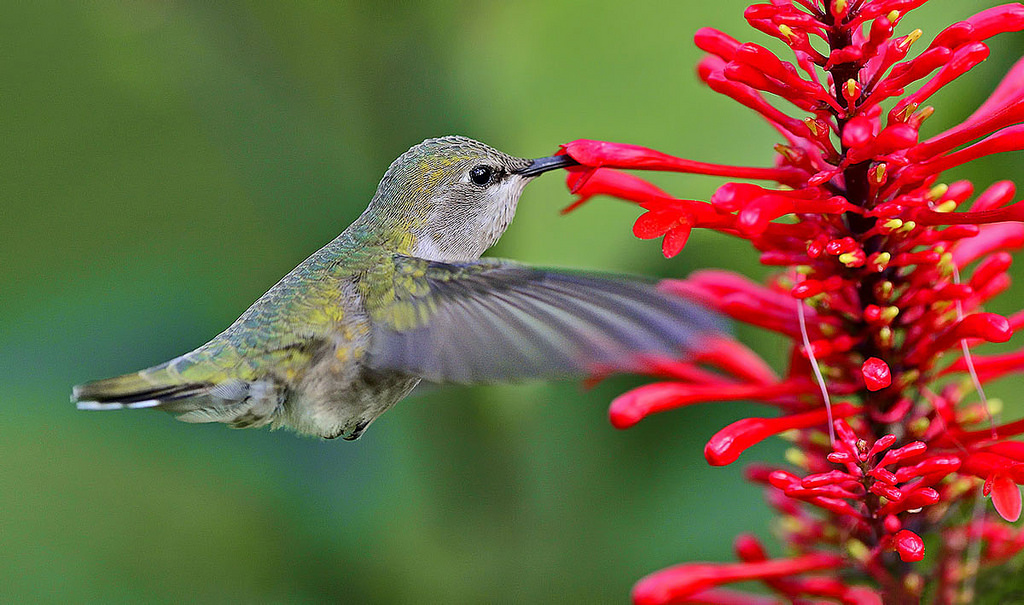

by Sheila Dunning | Oct 4, 2021
 Looking to add something to brighten your landscape this autumn? Firespike (Odontonema strictum) is a prolific fall bloomer with red tubular flowers that are very popular with hummingbirds and butterflies. Its glossy dark green leaves make an attractive large plant that will grow quite well in dense shade to partial sunlight.
Looking to add something to brighten your landscape this autumn? Firespike (Odontonema strictum) is a prolific fall bloomer with red tubular flowers that are very popular with hummingbirds and butterflies. Its glossy dark green leaves make an attractive large plant that will grow quite well in dense shade to partial sunlight.
In frost-free areas firespike grows as an evergreen semi-woody shrub, spreads by underground sprouts and enlarging to form a thicket. In zones 8 and 9 it usually dies back to the ground in winter and re-sprouts in spring, producing strikingly beautiful 9-12 inch panicles of crimson flowers beginning at the end of summer and lasting into the winter each year.
 Firespike is native to open, semi-forested areas of Central America. It has escaped cultivation and become established in disturbed hammocks throughout peninsular Florida, but hasn’t presented an invasive problem. Here in the panhandle, firespike will remain a tender perennial for most locations. It can be grown on a wide range of moderately fertile, sandy soils and is quite drought tolerant. Firespike may be best utilized in the landscape in a mass planting. Plants can be spaced about 2 feet apart to fill in the area quickly. It is one of only a few flowering plants that give good, red color in a partially shaded site. The lovely flowers make firespike an excellent candidate for the cutting garden and is a “must-have” for southern butterfly and hummingbird gardens. Additional plants can be propagated from firespike by division or cuttings. However, white-tailed deer love firespike too, and will eat the leaves, so be prepared to fence it off from “Bambi”.
Firespike is native to open, semi-forested areas of Central America. It has escaped cultivation and become established in disturbed hammocks throughout peninsular Florida, but hasn’t presented an invasive problem. Here in the panhandle, firespike will remain a tender perennial for most locations. It can be grown on a wide range of moderately fertile, sandy soils and is quite drought tolerant. Firespike may be best utilized in the landscape in a mass planting. Plants can be spaced about 2 feet apart to fill in the area quickly. It is one of only a few flowering plants that give good, red color in a partially shaded site. The lovely flowers make firespike an excellent candidate for the cutting garden and is a “must-have” for southern butterfly and hummingbird gardens. Additional plants can be propagated from firespike by division or cuttings. However, white-tailed deer love firespike too, and will eat the leaves, so be prepared to fence it off from “Bambi”.
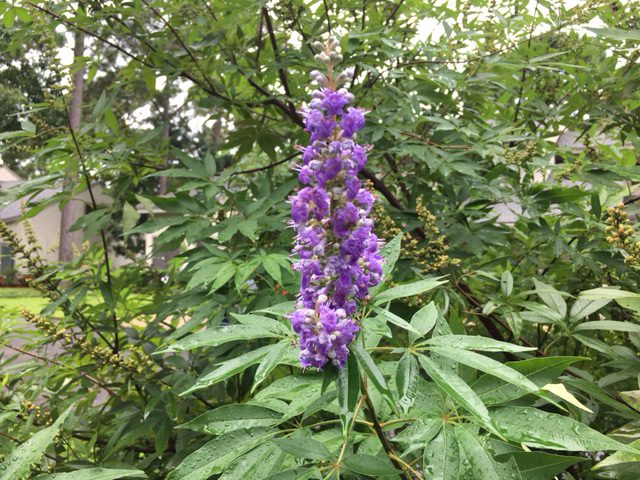

by Sheila Dunning | Aug 26, 2021

Photos by Sheila Dunning
The showy chaste tree makes an attractive specimen as the centerpiece of your landscape bed or in a large container on the deck. Much more of them are being seen since the Florida Department of Transportation has recognized the tree as a desirable median planting. Easy-to-grow, drought resistant, and attractive to butterflies and bees, Vitex agnus-castus is a multi-stemmed small tree with fragrant, upwardly-pointing lavender blooms and gray-green foliage. The chaste tree’s palmately divided leaves resemble those of the marijuana (Cannabis sativa) plant; its flowers can be mistaken for butterfly bush (Buddleia sp.); and the dry, darkened drupes can be used for seasoning, similar to black pepper, making it a conversation piece for those unfamiliar with the tree.
Vitex , with its sage-scented leaves that were once believed to have a sedative effect, has the common name “Chastetree” since Athenian women used the leaves in their beds to keep themselves chaste during the feasts of Ceres, a Roman festival held on April 12. In modern times, the tree is more often planted where beekeepers visit in order to promote excellent honey production or simply included in the landscape for the enjoyment of its showy, summer display of violet panicles.
Chaste tree is native to woodlands and dry areas of southern Europe and western Asia. It will thrive in almost any soil that has good drainage, prefers full sun or light shade, and can even tolerate moderate salt air. Vitex is a sprawling plant that grows 10-20 feet high and wide, that looks best unpruned. If pruning is desired to control the size, it should be done in the winter, since it is a deciduous tree and the blooms form on new wood. The chaste tree can take care of itself, but can be pushed to faster growth with light applications of fertilizer in spring and early summer and by mulching around the plant. There are no pests of major concern associated with this species, but, root rot can cause decline in soils that are kept too moist.
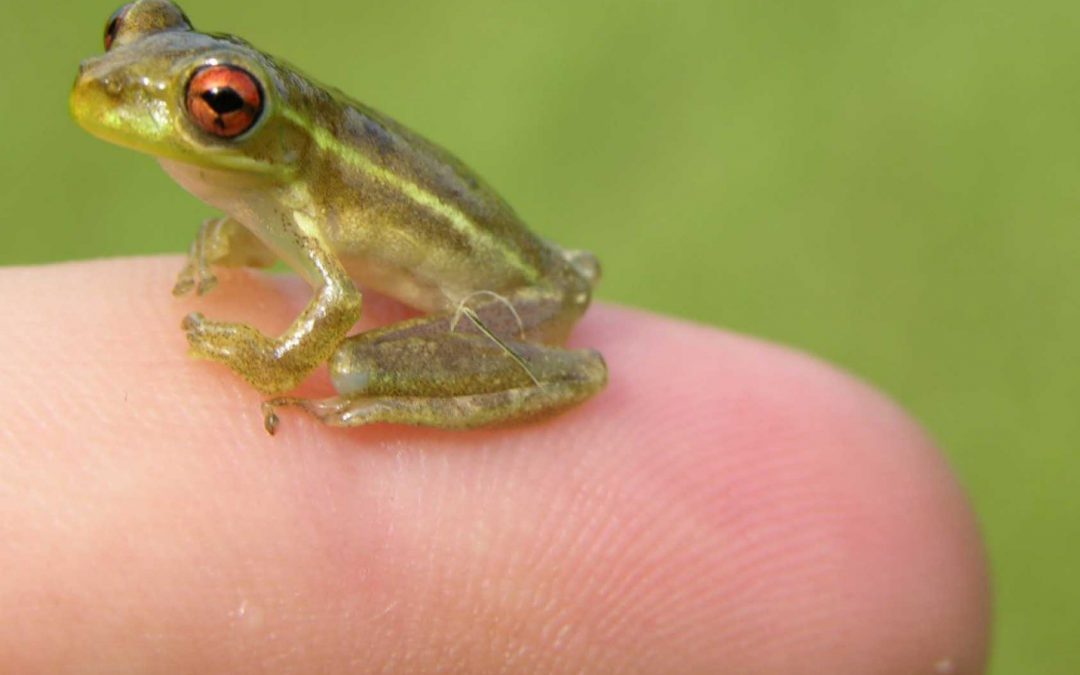

by Sheila Dunning | Jul 15, 2021

Photo by Dr. Steve Johnson
Treefrog calls are often heard with each rain event. But, how about a “snoring raspy” call that begins after a day time light rain? That may be a male Cuban treefrog trying to attract the girls. Cuban treefrogs breed predominately in the spring and summer. Reproduction is largely stimulated by rainfall, especially warm summer rains such as those associated with tropical weather systems and intense thunderstorms.
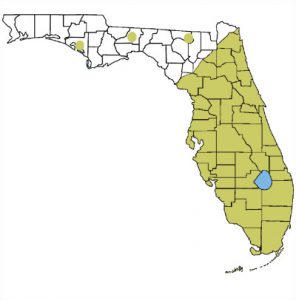
Range of Cuban treefrogs
The Cuban treefrog, Osteopilus septentrionalis, was accidently introduced to Florida in the 1920’s as a stowaway in shipping crates from the Caribbean. Over the last hundred years, the invasive frog has managed to spread throughout Florida and the Southeastern U.S. by hitchhiking on ornamental plants, motorized vehicles, and boats. Though occasional cold winters have created temporary population setbacks, new generations of Cuban treefrogs continue to be reported in north Florida, including the Panhandle.
An invasive species is generally defined as a plant, animal or microbe that is found outside of its native range, where it negatively impacts the ecology, economy or quality of human life. Cuban treefrogs come out at night to feed on snails, millipedes, spiders and a vast array of insects. But, they are also predators of several Florida native frogs, lizards and snakes. Tadpoles of the invasive Cuban treefrog have been shown to inhibit the growth and development of native Southern toad and green treefrog tadpoles when all of the species are in the same water body. Additionally, a large female Cuban treefrog can lay over 10,000 eggs per season in very small amounts of water.
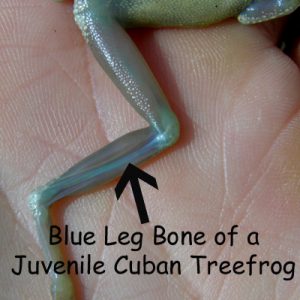 Panhandle citizens can help manage the invasive Cuban treefrog by learning to identify them and reduce their numbers. All treefrogs have expanded pads on the ends of their toes. Cuban treefrogs have exceptionally large toepads. They also have a “big eyed” appearance due to their oversized bulging eyes. Cuban treefrogs may exceed 6 inches in length, have warty-looking skin with possible blotches, bands or stripes, and vary greatly in color. However, they can be distinguished from other treefrogs. Cuban treefrogs have a yellowish wash where their front and rear legs are attached to their body. Juvenile Cuban treefrogs have red eyes and blue bones visible through the skin of their hind legs. The skin of the Cuban treefrog produces a sticky secretion that can cause a burning or itching sensation if it contacts the eyes or nose of certain individuals. It is recommended to wear gloves and wash your hands after handling Cuban treefrogs.
Panhandle citizens can help manage the invasive Cuban treefrog by learning to identify them and reduce their numbers. All treefrogs have expanded pads on the ends of their toes. Cuban treefrogs have exceptionally large toepads. They also have a “big eyed” appearance due to their oversized bulging eyes. Cuban treefrogs may exceed 6 inches in length, have warty-looking skin with possible blotches, bands or stripes, and vary greatly in color. However, they can be distinguished from other treefrogs. Cuban treefrogs have a yellowish wash where their front and rear legs are attached to their body. Juvenile Cuban treefrogs have red eyes and blue bones visible through the skin of their hind legs. The skin of the Cuban treefrog produces a sticky secretion that can cause a burning or itching sensation if it contacts the eyes or nose of certain individuals. It is recommended to wear gloves and wash your hands after handling Cuban treefrogs.
It is important to document the locations of Cuban treefrogs in the Panhandle. By placing short sections of PVC pipe in the ground around your home and garden will provide hiding places for treefrogs that enables you to monitor for Cuban treefrogs. Cut 10 foot sections of 1.5-inch-diameter PVC pipe into approximately three-foot-long sections and push them into the ground about 3-4 inches. To remove a frog from a pipe, place a clear sandwich bag over the top end, pull the pipe from the ground, and insert a dowel rod in the other end to scare the frog into the baggie. If you suspect you have seen one, take a picture and send it to Dr. Steve Johnson at tadpole@ufl.edu. Include your name, date, and location. Dr. Johnson can verify the identity. If it is a Cuban treefrog, upload the information by going to http://www.eddmaps.org/ and click the “Report Sightings” tab.
Once identified as a Cuban treefrog, it should be euthanized humanly. To do that, the Cuban treefrog in a plastic sandwich bag can be placed into the refrigerator for 3-4 hours then transferred to the freezer for an additional 24 hours. Alternatively, a 1-inch stripe benzocaine-containing ointment (like Orajel) to the frog’s back to chemically anesthetize it before placing it into a freezer. After freezing, remove the bagged frog from the freezer and dispose of in the trash. Ornamental ponds should also be monitored for Cuban treefrog egg masses especially after a heavy rain. The morning after a rain, use a small-mesh aquarium net to scoop out masses of eggs floating on the surface of the pond and simply discard them on the ground to dry out. Various objects that can collect water found throughout your yard need to be dumped out regularly to reduce breeding spots for both Cuban treefrogs and mosquitoes.
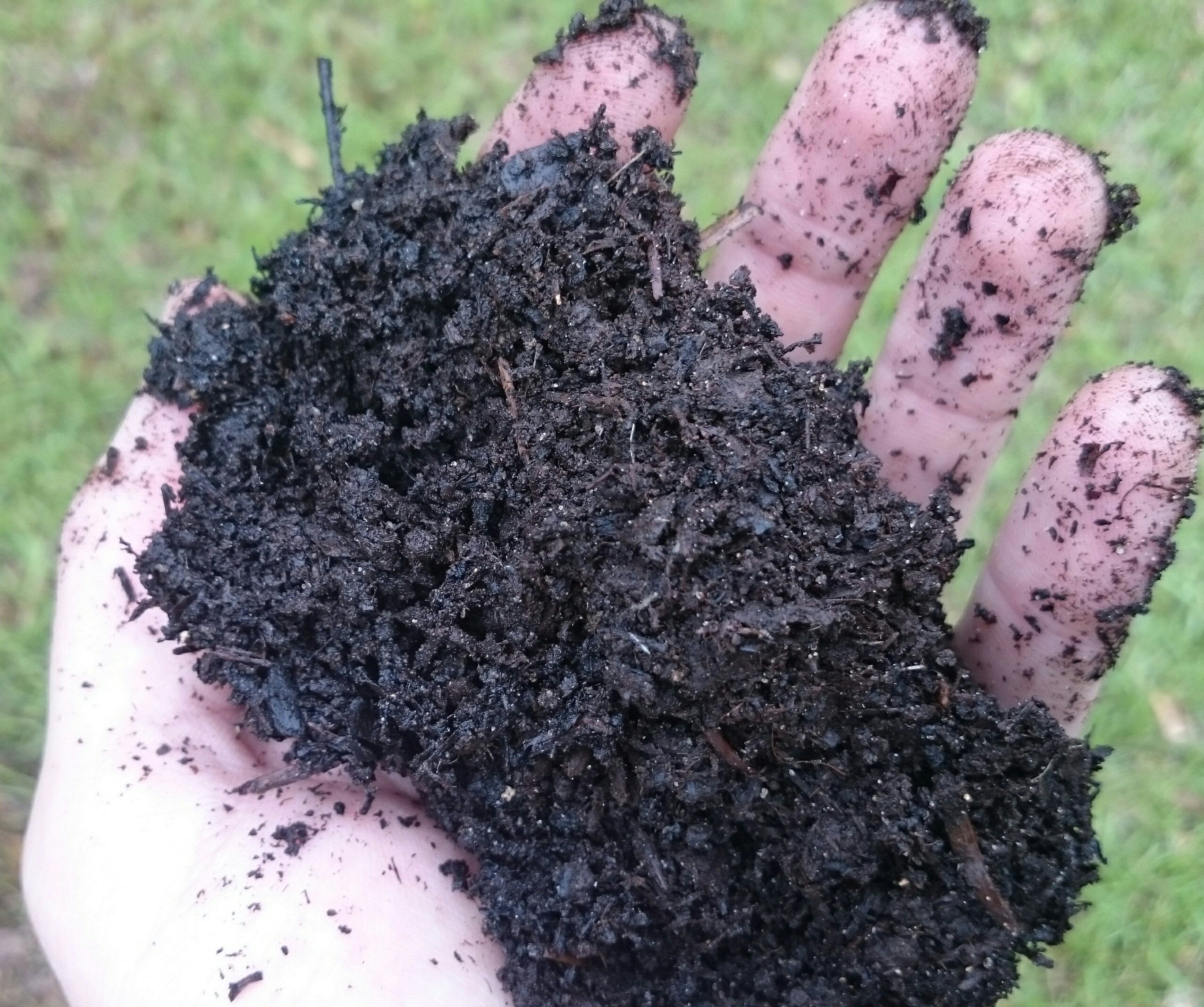

by Sheila Dunning | Jun 10, 2021
Potting soil, potting mix, garden soil, topsoil. The bags are all sitting side-by-side on the shelf at the garden center. Your challenge is to figure out which one you need for your project. What’s the difference? To begin with, none of them are dirt. The Soil Science Society of America defines dirt as “displaced soil”, the dead nuisance material left on your hands after working with soil. Soil is a blend of sand, silt, clay and organic matter. It is alive with nutrient and water holding components. But, all soil is not equal.
Soil contains decayed organic remains. It may be composted leaf tissue and/or microorganisms. The terms potting soil and
 potting mix are often used interchangeably, but there is a significant difference. Potting soil contains compost or the flora responsible for the breakdown process. Potting mix is soil-less. It is a blend of sphagnum moss, coir, bark, perlite and/or vermiculite. While these are natural occurring materials, they are in their original state. No decomposition has occurred. In the absence of compost, the resulting potting mix is sterile and free of fungus spores and insect eggs. Potting mixes are excellent choices for container growing, especially for house plants. The sphagnum moss, coir and bark hold and release water and nutrients, while the vermiculite or perlite keep the mix loose and well-drained. Some blended products add microbes, which then requires the word soil be added to the packaging. These are still suitable for potted plants.
potting mix are often used interchangeably, but there is a significant difference. Potting soil contains compost or the flora responsible for the breakdown process. Potting mix is soil-less. It is a blend of sphagnum moss, coir, bark, perlite and/or vermiculite. While these are natural occurring materials, they are in their original state. No decomposition has occurred. In the absence of compost, the resulting potting mix is sterile and free of fungus spores and insect eggs. Potting mixes are excellent choices for container growing, especially for house plants. The sphagnum moss, coir and bark hold and release water and nutrients, while the vermiculite or perlite keep the mix loose and well-drained. Some blended products add microbes, which then requires the word soil be added to the packaging. These are still suitable for potted plants.
But, if the potting soil is made from mostly compost, the potential of having poor drainage and fungus gnat problems increases substantially. The only containers these type of potting soils should be used in are raised gardens. Depending on the compost source, these soils can sour, grow mushrooms or become extremely hard. 
 Garden soil is a blend of soil and soilless ingredients. It can be used in very large containers (24” or greater) or added to native soils to enrich planting areas.
Garden soil is a blend of soil and soilless ingredients. It can be used in very large containers (24” or greater) or added to native soils to enrich planting areas.
Then there is topsoil. It varies widely in composition and quality. Use it to fill holes in the yard, build berms or mix it will compost to increase water retention in dry garden areas. 
So, when standing in the store comparing prices, don’t let price dictate your purchase. To keep your containerized plants doing well, do some bag reading. Choose the product that has aged forest products, sphagnum moss and perlite. Use the soils made from bio-solids and composted materials to improve the sand in the yard. When you’re done, go wash the dirt off your hands.


















 potting mix are often used interchangeably, but there is a significant difference. Potting soil contains compost or the flora responsible for the breakdown process. Potting mix is soil-less. It is a blend of sphagnum moss, coir, bark, perlite and/or vermiculite. While these are natural occurring materials, they are in their original state. No decomposition has occurred. In the absence of compost, the resulting potting mix is sterile and free of fungus spores and insect eggs. Potting mixes are excellent choices for container growing, especially for house plants. The sphagnum moss, coir and bark hold and release water and nutrients, while the vermiculite or perlite keep the mix loose and well-drained. Some blended products add microbes, which then requires the word soil be added to the packaging. These are still suitable for potted plants.
potting mix are often used interchangeably, but there is a significant difference. Potting soil contains compost or the flora responsible for the breakdown process. Potting mix is soil-less. It is a blend of sphagnum moss, coir, bark, perlite and/or vermiculite. While these are natural occurring materials, they are in their original state. No decomposition has occurred. In the absence of compost, the resulting potting mix is sterile and free of fungus spores and insect eggs. Potting mixes are excellent choices for container growing, especially for house plants. The sphagnum moss, coir and bark hold and release water and nutrients, while the vermiculite or perlite keep the mix loose and well-drained. Some blended products add microbes, which then requires the word soil be added to the packaging. These are still suitable for potted plants.

