by Sheila Dunning | Jun 28, 2018
 National Pollinator Week is only recognized in June, but efforts to encourage pollinators shouldn’t end then.
National Pollinator Week is only recognized in June, but efforts to encourage pollinators shouldn’t end then.
Pollination occurs when pollen grains are moved between two flowers of the same species, or within a single flower, by wind or animals that are pollinators. Successful pollination, which may require visits by multiple pollinators to a single flower, results in healthy fruit and fertile seeds, allowing plants to reproduce. Without pollinators, we simply wouldn’t have many crops!
Worldwide, approximately 1,000 plants grown for food, beverages, fibers, spices, and medicines need to be pollinated by animals in order to produce the goods on which we depend. Foods and beverages produced with the help of pollinators include blueberries, chocolate, coffee, melons, peaches, pumpkins, vanilla, and almonds.
About 75% of all flowering plants rely on animal pollinators and over 200,000 species of animals act as pollinators. Of those, about 1,000 are hummingbirds, bats, and small mammals. The rest are insects such as beetles, bees, ants, wasps, butterflies, and moths. Western honey bees are the most common.
Most species of bees don’t sting. Although all female bees are physically capable of stinging, most bee species native to the U.S. are “solitary bees,” that is, not living in colonies and don’t sting unless they are physically threatened or injured. Only honey bees are defensive and may chase someone who disturbs their hive.
It is wise, though, to avoid disturbing any bee or insect nest.
What everyone can do for pollinators:
Watch for pollinators. Get connected with nature. Take a walk, experience the landscape and look for pollinators which are most active midday in sunny, planted areas.
Reduce your impact. Reduce or eliminate your pesticide use, increase green spaces, and minimize impervious surfaces.
Plant for pollinators. Create pollinator-friendly habitat with native flowering plants that supply pollinators with nectar, pollen, and homes. For a list of plant choices go to: http://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/design/gardening-with-wildlife/bee-plants.html
What you can do to create a pollinator-friendly habitat:
Design your garden so that there is a continuous succession of plants flowering from spring through fall. Check for the species or cultivars best suited to your area.
Plant native to your region using plants that provide nectar for adults plus food for insect larvae, such as milkweed for monarchs. If you do use non-native plants, choose ones that don’t spread easily, since these could become invasive.
Select old-fashioned varieties of flowers whenever possible because breeding has caused some modern blooms to lose their fragrance and/or the nectar/pollen needed to attract and feed pollinators.
Install ‘houses’ for bats and native bees. For examples go to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw290 or http://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/design/gardening-with-wildlife/pollinator-hotels.html
Avoid pesticides, even so-called “natural” ones such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). If you must use them, use the most selective and least toxic ones and apply them at night when most pollinators aren’t active.
Supply water for all wildlife. A dripping faucet or a suspended container with a pinhole in the bottom is sufficient for some insects. Other wildlife need a small dish of water.
Provide water for butterflies without letting it become a mosquito breeding area. Refill containers daily or bury a shallow plant saucer to its rim in a sunny area, fill it with coarse pine bark, sand or stones and fill to overflowing with water.
Fun facts:
A tiny fly (a “midge”) no bigger than a pinhead is responsible for the world’s supply of chocolate
One out of every three mouthfuls of food we eat is delivered to us by pollinators.

by Carrie Stevenson | Feb 23, 2017

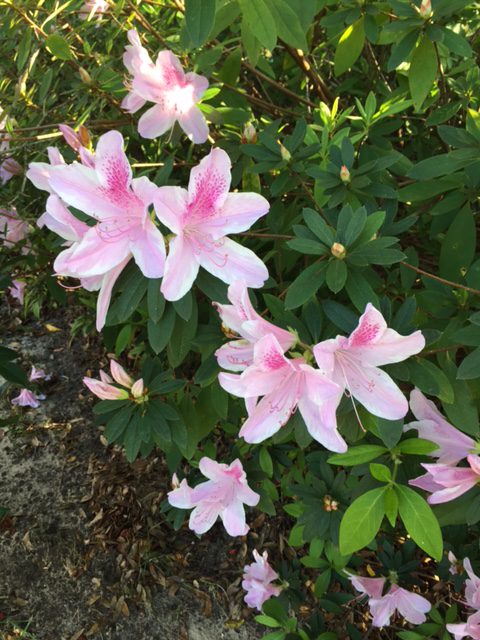
Azaleas have been in full bloom this year since mid-February. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
It’s mid-February, and regardless of the groundhog’s prediction, spring seems to have arrived in northwest Florida. In my neighborhood, all the azaleas have bloomed. While beautiful, it’s something that usually doesn’t happen around here until well into March!
According to NOAA and NASA climate data, 2016 was the hottest year globally on record, followed by the previous hottest years, 2015 and 2014. In fact, 16 of the 17 warmest years documented (since official record keeping began in 1880) have been since 2001. The United States also experienced a record-setting year of natural disasters in 2016, ranging from floods to droughts and wildfires.
As the warming trend continues, gardeners, farmers, and wildlife managers alike will find it necessary to adjust their long-held practices. When plants bloom or put on fruit early, these changes can have real economic and commercial impacts. Farmers compete on a global scale to get products to market, and if northern climates start experiencing warmer temperatures, Florida farmers could lose their competitive edge.

Juvenile bats are vulnerable and therefore protected by state laws during late spring through summer in Florida. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
In natural systems, a change in migration or hatching could affect the success of a protected species’ survival. The time frames for these life stages are often legally protected by state or federal laws. For example, in Florida, bats cannot be “excluded” from a building between the April 16-August 14 due to the maternity season. Beach re-nourishment projects are restricted and heavily monitored during sea turtle nesting from May-October. If these time frames start skewing earlier in the year due to changing temperatures and early onset of spring and summer, laws or common practices might need to be evaluated and changed.
In response to these changes in weather patterns, the interesting science of phenology (not to be confused with the brain-mapping “science” of phrenology) has regained popularity in recent years. Phenology is the study of when annual events in the natural world begin—the first hatching of shorebirds, the blooming of spring flowers, the migration of butterflies. For many years, both amateur and professional naturalists have kept records of these phenomena, observing them for pure scientific interest. Now, phenology research has become real-time documentation of a changing world. There are several national networks of citizen scientists making observations and recording them online, including Project Budburst, FrogWatch USA, and the National Phenology Network. If you enjoy spending time outdoors, consider joining one of the many phenology networks and contributing to the larger body of scientific observation. The more we understand about climate-related changes, the better we can prepare and adapt.

by Carrie Stevenson | Feb 3, 2016
Do you love the outdoors? Wish you knew more about the plants and animals native to our area?

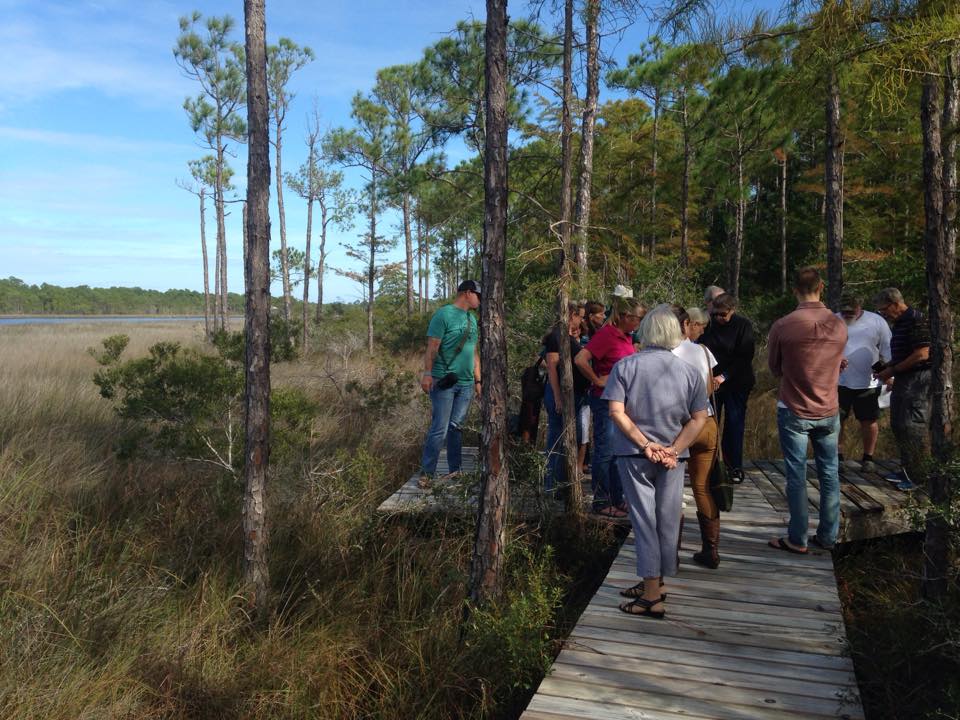
Master Naturalist Jerry Patee leads classmates along his project: a wetland boardwalk in Perdido Key. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
The Florida Master Naturalist Program is a course offered by Extension agents throughout the state, including the northwestern counties. Three different modules—Freshwater Wetlands, Coastal, and Uplands—are offered. They include 40 hours of instruction time on ecosystems, plant identification, animal ecology, and how humans live within the environment. Each class includes 2-3 field trips which may entail hikes, paddling, or tours of local museums and parks. Adult students are expected to produce an educational project at the end of the course, which may vary from a display or presentation to a skit or full-blown nature trail.

Proud Master Naturalist students at their graduation. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Several Master Naturalists have recently brought their projects to life. Several years ago, Charlie Lurton created a plan to build living shorelines in Bayou Grande behind homes in his neighborhood. The project was approved by state and federal environmental regulatory agencies and oyster reefs and planting have recently begun. Jerry Patee, also an Escambia County Master Gardener, worked with his church to create a boardwalk trail through wetlands to a pristine view of Bayou Garcon in Perdido Key.
Master Naturalist students vary in backgrounds from retired military and teachers to new residents and college students. Many Master Gardeners find the courses a helpful addition to their training, and utilize their newly gained knowledge when working with clientele. At completion, students receive an official Florida Master Naturalist certificate, pin, and patch. Several Panhandle courses will be offered this spring—check out the FMNP website to see when a class will be offered near you!
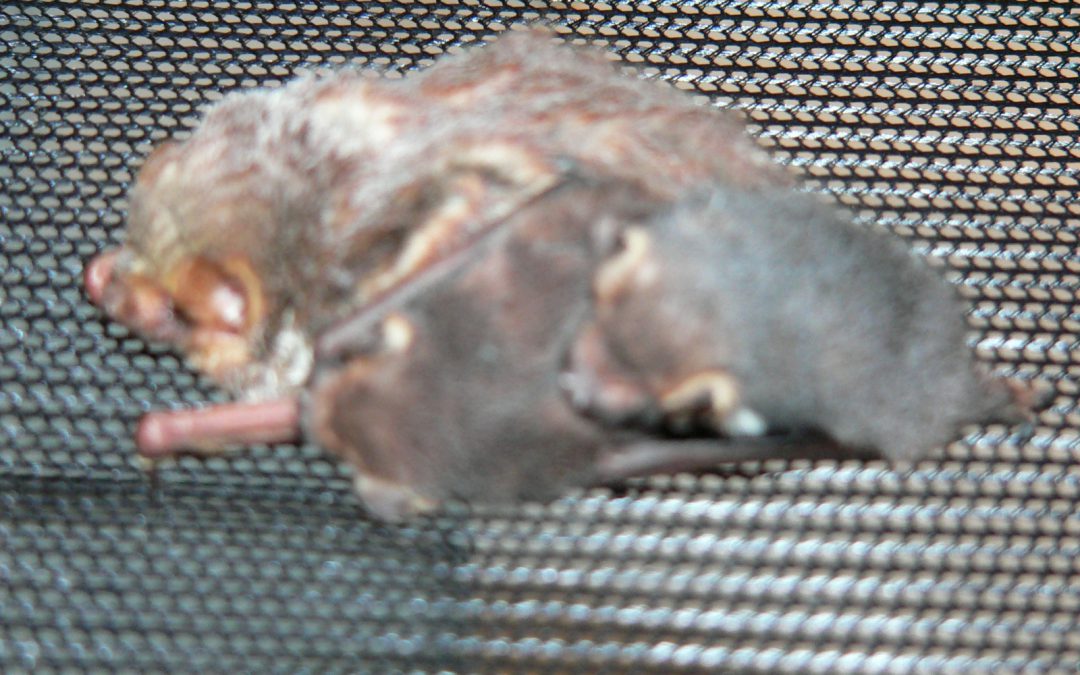
by Carrie Stevenson | Apr 7, 2015

These young Seminole bat pups were separated from their mother and extremely vulnerable in the wild. The local Wildlife Sanctuary nursed them to health. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
 As spring commences and young wildlife of all species are born, everyone’s favorite flying, furry mammal begins roosting season. Ideally, bats will find homes in trees, caves, abandoned buildings, and bat houses, but sometimes they end up in a home. I receive calls often about how to best remove or exclude a group of bats living in an attic or garage. While there are countless benefits (most notably, efficient insect control) to having bats in one’s landscape or neighborhood, most people prefer they not share their own home with them.
As spring commences and young wildlife of all species are born, everyone’s favorite flying, furry mammal begins roosting season. Ideally, bats will find homes in trees, caves, abandoned buildings, and bat houses, but sometimes they end up in a home. I receive calls often about how to best remove or exclude a group of bats living in an attic or garage. While there are countless benefits (most notably, efficient insect control) to having bats in one’s landscape or neighborhood, most people prefer they not share their own home with them.
Bats have a slow reproductive cycle and declining populations in the United States, and are protected by several state laws. According to Florida Administrative Code 68A-9.010 under “Taking Nuisance Wildlife,” it is illegal in Florida to prevent bats from returning to any roosting location from April 16 to August 14. Female bats typically give birth during maternity season to one pup (or rarely, 2-3), which clings to the mother’s fur to nurse for their first few weeks and months of life. Being nocturnal, this means mothers and babies will be inside a dwelling during the day. Typically, if a homeowner is trying to exclude bats from a home, they will put up netting or seal a hole in an attic entry in the evening after bats have flown off to feed on insects at night. However, if this is done during roosting season, young bats left back in the roost while mothers are hunting can get trapped inside a building and will not survive.
This obviously has the potential to cause conflict between homeowners and the bat population. The Florida Fish & Wildlife Conservation Commission has regulatory oversight for bat-related issues, and they will work with citizens to arrange a positive outcome for both the property owner and the animals involved. Bats play an important role the ecosystem as efficient controllers of insect populations.
Unfortunately, bat populations are declining in North America due to a devastating disease called white-nose syndrome and loss of habitat. However, you can help these fascinating animals by installing a bat house in your yard. Keep in mind that bats attracted to bat houses prefer to be in open areas away from trees (where their predators hide), and the house should be installed at least 12 feet in the air. Bat houses can be purchased or built rather simply—keep an eye out for Extension workshops near you, or visit the UF Wildlife Ecology publication, “Effective Bat Houses for Florida” or Bat Conservation International’s website for simple instructions.
To learn more about bats and how to help them, visit this website or contact me or your local County Extension office!

by Julie McConnell | Jan 13, 2015

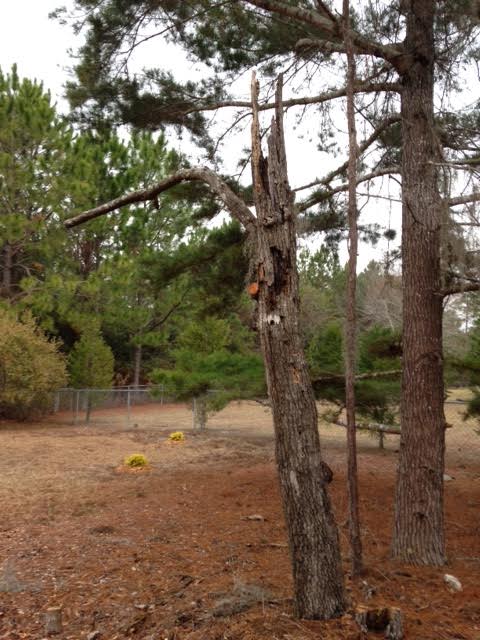
This dead oak tree was trimmed up to make it neater. It is ready for a wildlife resident! Photo: JMcConnell, UF/IFAS
One of the management issues that any landowner will face at some point is what to do when a tree dies in the landscape. The logical response is “cut it down,” but depending on the location and the size of the tree, that may not be necessary and you could be removing potential wildlife habitat.
With any other major decisions about your landscape, always consider safety first. If the tree is in a location where it could damage property or cause harm to people or domesticated animals then it should be properly removed. But what about those trees that are along wood lines or in the far reaches of the yard and not threatening person or property?
Consider leaving the entire tree or modifying it to make it more aesthetically pleasing yet still useful to wildlife. Weak branches or unstable tops may be removed to make the snag less of a risk or to look a little neater.
Some examples of animals that may use dead trees in the landscape are birds, bats, squirrels, frogs, and lizards. Besides the obvious cavity dwelling creatures such as woodpeckers, owls, and bats that are attracted to decaying trees, other animals will be drawn for other reasons. Dead trees in the landscape will become inhabited by insects and fungi which are terrific food sources for birds, mammals, amphibians, and reptiles!
To learn more about providing wildlife habitats in your landscape, please see the EDIS publications listed below or contact your local extension office.
Helping Cavity-nesters in Florida
A Birds-Eye View: How Birds Select Habitat
Dead Wood: Key to Enhancing Wildlife Diversity in Forests

by Carrie Stevenson | Sep 30, 2014
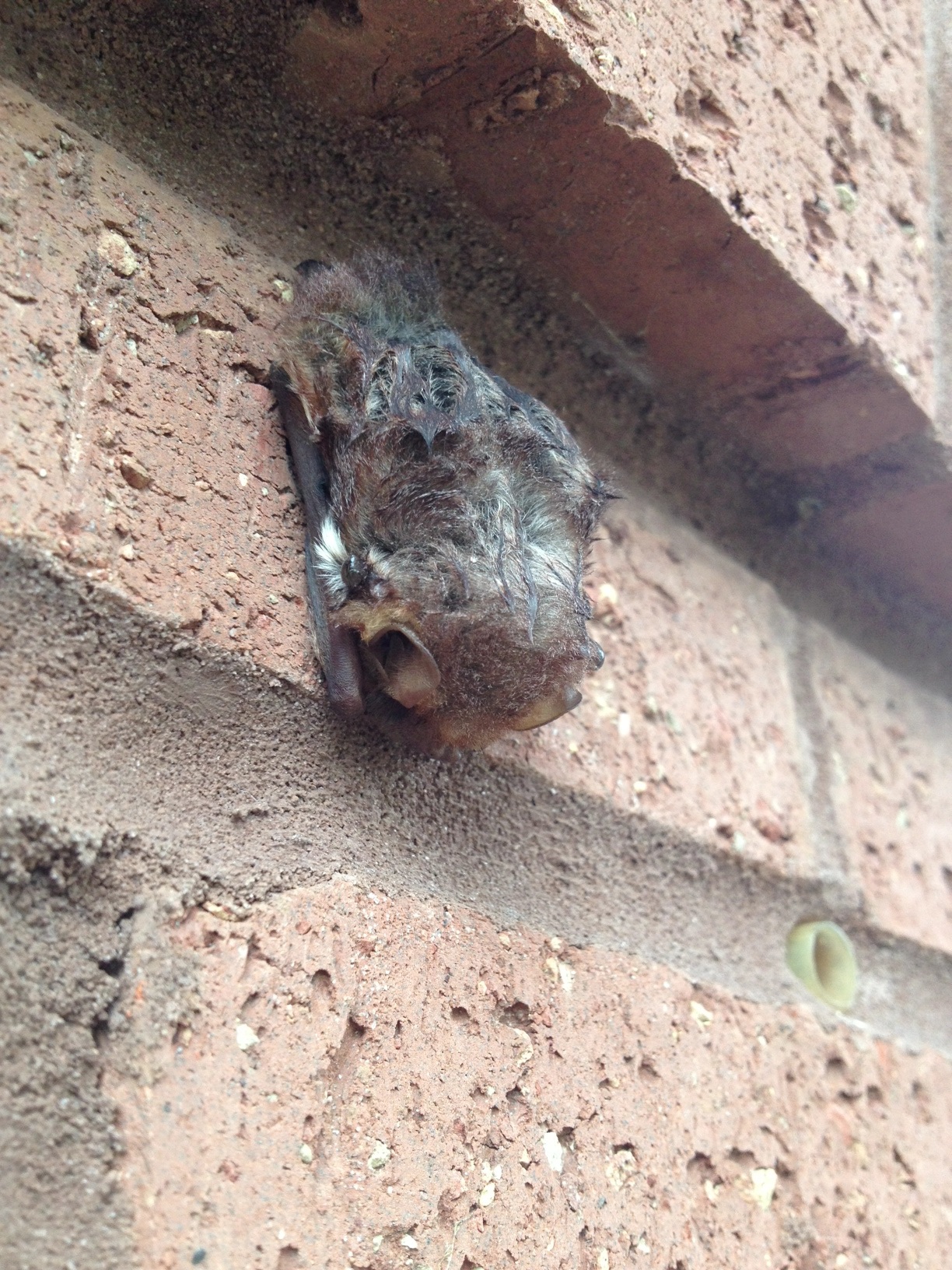
Last week, the Okaloosa County Health Department issued a rabies alert after three bats were determined to have the illness. A “drive-through” rabies vaccine clinic was organized for pets, and warnings were issued throughout the region about making contact with wild animals. One radio broadcast played an interview in which a health department staffer urged people “not to attract wildlife to your yard.” While they were focusing on unsecured trash and pet food, I found this advice unsettling, for as an Extension Agent I’ve promoted the practice of attracting wildlife to yards for many years—birds, butterflies, and even (especially) bats. Raccoons, not bats, have the greatest incidence of rabies (based on data collected from 1992-2011), by a factor of almost seven times that of bats. In the scare of a rabies outbreak, it can be easy to overreact or overlook the many benefits that wildlife provide to our neighborhoods.
There are, of course, practical ways to go about living with wildlife without endangering your health or that of your family and pets (including making sure pets have the rabies vaccine).
Use Caution around Injured Wildlife
Most wildlife rescue organizations do not have the staff to pick up injured animals and ask those who find one to bring them in. However, sick or injured animals may respond aggressively as an intuitive protective measure. If you are taking an animal to a wildlife rehabilitator, be sure to approach it gently and use a blanket or large towel to pick up the animal, and place it gently in a box with a ventilated lid. Great information on responding to injured or deserted animals can be found at the Wildlife Sanctuary of Northwest Florida website. Keep in mind that bats are flying animals and spend almost no time on the ground. They do not chase people and are primarily concerned with catching insect prey. If you find a bat on the ground, it is most likely sick. County animal control or private wildlife responders can also help if you are concerned about interacting with a sick animal.

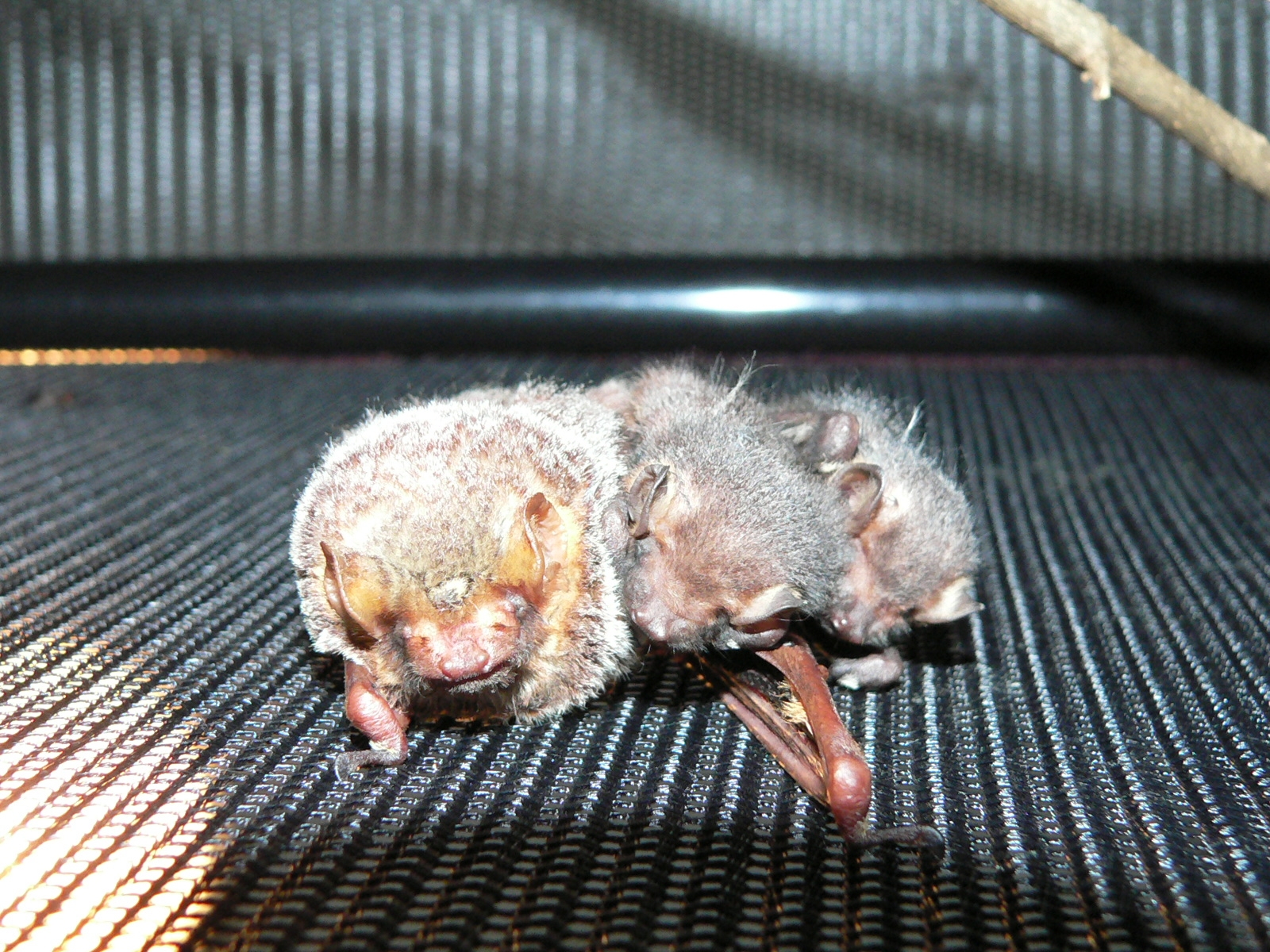
These twin Seminole bat pups were found on the ground with their mother and nursed back to health at the Wildlife Sanctuary of Northwest Florida. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Use Care When Retrieving Dead Animals
When bird flu, West Nile or rabies hits an area, health departments sometimes ask that suspect animals be reported for testing to confirm the cause of death. Even if you are just disposing of the animal, be sure to use gloves and place the animal in a sealable plastic bag to prevent spreading germs, and wash your hands after handling it. If burying, place at least three feet deep and away from wells or water sources.
Enjoy Wildlife from a Distance
Disturbing healthy animals while they are feeding or resting can cause unnecessary stress and reduce their hunting success. Animals’ natural behaviors are fascinating to watch, so be sure and do so from a respectful distance to allow them to interact normally with their environment.
 National Pollinator Week is only recognized in June, but efforts to encourage pollinators shouldn’t end then.
National Pollinator Week is only recognized in June, but efforts to encourage pollinators shouldn’t end then.











