
by Beth Bolles | Jun 23, 2014
In our area of Florida, soils will vary in the amount of nutrients they hold. In general, we think of our soils as nutrient poor because sand is often the highest component. Sandy soils have large pore spaces and the particles themselves do not ‘attract’ many of our nutrients. Therefore needed plant nutrients can leave a sandy soil quickly, especially when rainfall or irrigation is prevalent.
There are areas along the Panhandle that do have more quality soils that have the ability to retain some nutrients. Also, frequent fertilizer or lime applications in home landscapes can create soils with abundance of certain nutrients over time .
One nutrient that may become prevalent in routinely fertilized soils is phosphorus. We know that phosphorus is one of the big three nutrients needed by plants in order to grow and flourish. When we routinely apply phosphorus to garden beds or lawns, it can build up. Phosphorus is a nutrient that does not leave the soil as readily as other nutrients. It binds to other elements to hang around. If we keep adding phosphorus to the soil, even though there is plenty there, problems can occur. One negative impact is the potential for soils with phosphorus to wash away and pollute local water systems.
Phosphorus is absolutely necessary for plant growth. It is needed for the energy transfer which is involved in plant growth functions. Phosphorus is also important for flower and fruit formation, and root growth.

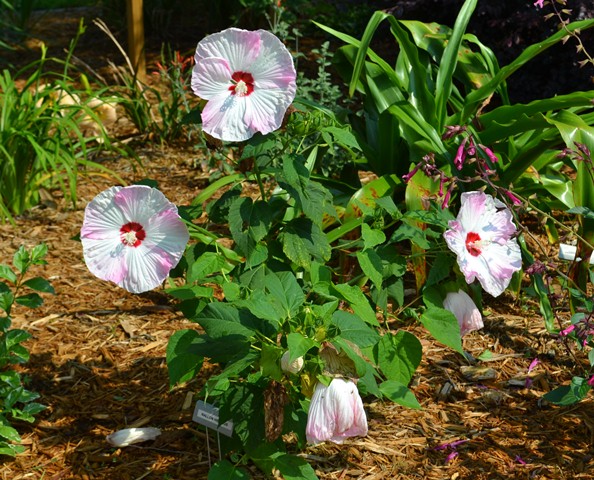
Flowering plants benefit from fertilizer but make sure your soil needs the nutrients before an application. Photo: Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Escambia Extension
There can be too much of a good thing. The key to remember, as with any nutrient, is make sure it is needed before applying it to your soil. Plant growth will not be improved beyond what is normal by adding more of any nutrient. Before you grab the bloom promoter or starter fertilizer with high phosphorus, run a soil test to accurately determine what is really needed in your soil.
by Sheila Dunning | Jun 17, 2014
 The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions.
The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions.
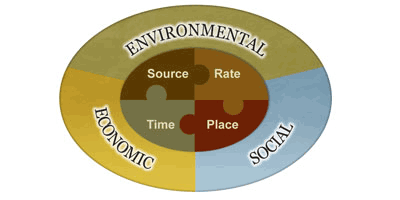
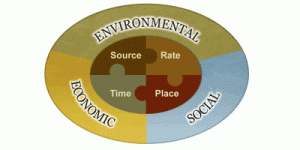
If you haven’t submitted a soil test since the storm, now is the time to do so. It’s time to apply a summer fertilizer, but it needs to address all the nutrient deficiencies created from the excess rain. Soil test kits can be obtained from your County Extension office. When you get the results from the University of Florida Lab, it is important to remember the 4 Rs when applying fertilizer. It needs to be the Right Source, applied at the Right Rate, at the Right Time, and over the Right Place.
Best Management Practices (BMPs) have been developed to allow individuals to make conscientious decisions regarding fertilizer selection that will reduce the risk of water contamination. The Right Source for a BMP-compliant fertilizer is one that contains a portion of slow-release (water insoluble) nitrogen with little to no phosphorus, and a potassium level similar to the nitrogen percentage (e.g. 15-0-15, that contains 5% coated nitrogen). However, a soil test is the only way to accurately identify the specific nutrients your landscape is lacking. Many soil tests indicate a need for phosphate and currently it is illegal to apply more than 0.25 pounds per 1,000 sq. ft. without a soil test verifying the need.
Next, the fertilizer must be applied at the Right Rate. In order to do that, you must know the square footage of your property and how much you can spread using the settings on your equipment. Individuals walk at varied speeds and the product recommended rates are based on 1,000 sq.ft. areas. For information on calibrating application equipment refer to  the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).
the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).
The Right Time for applying fertilizer is when the plants are actively growing and beginning to show nutrient deficiencies. Summer, when rainfall and irrigation is frequent, is often a typical application time. The Right Place is only on living plant areas. Be cautious to avoid getting fertilizer on the sidewalk, driveway and street. A deflector on your spreader is very helpful. Otherwise, be sure to sweep or blow the fertilizer back onto the grass or into the landscape beds. Avoid having fertilizer end up in any water body.





