
by Blake Thaxton | Jul 21, 2017
Northwest Florida has experienced an enormous amount of rain this summer. The western panhandle has received over 29 inches of rain since the beginning of May according to the Florida Automated Weather Network station at the West Florida Research and Education Center in Jay, Florida. That is 44% of average annual rainfall in less than two months. All of this rain has probably thrown off the normal lawn mowing routine. It is hard to get out and mow the lawn when its pouring buckets or the lawn resembles a swamp. With all of this in mind, there are a couple of mowing pointers that would be useful to implement to address the out of control lawn growth and the challenges posed by not being able to stick to normal mowing schedule.
- Always attempt to mow at the IFAS recommended height for your species of turfgrass. The recommended heights are determined by how quickly the species grow in our climate. The chart below shows the best heights at which to mow your lawn. The fine textured zoysiagrasses are not listed but should be mowed at 0.5 to 1.5 inches. Check the lawn mowers mowing height by measuring the distance from the ground to the bottom of the mowing deck on a flat surface.
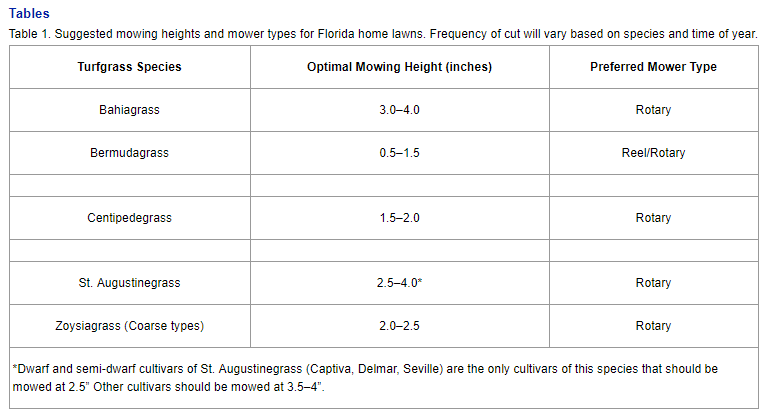
From Mowing Your Florida Lawn: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/LH/LH02800.pdf
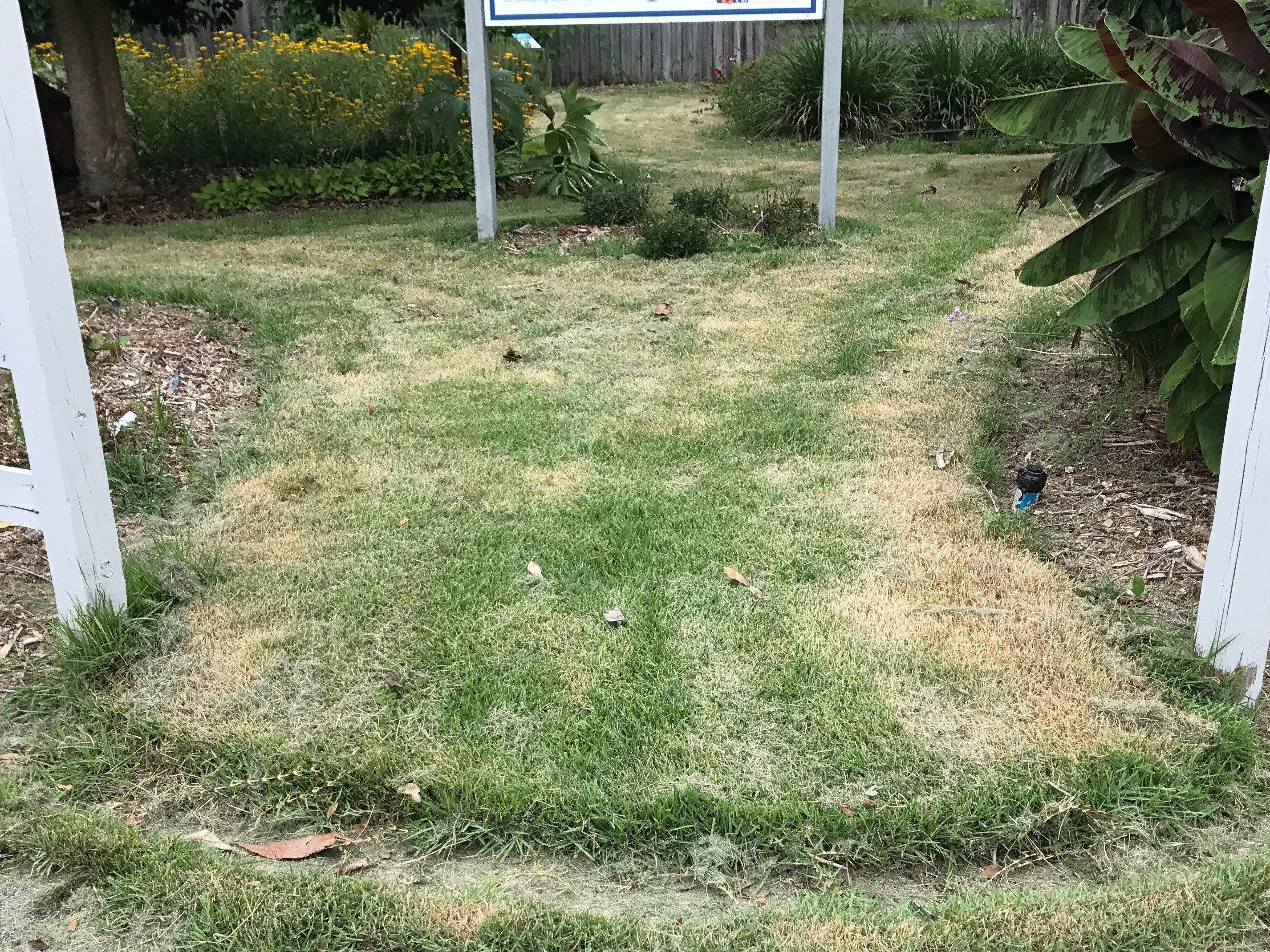
- When you do get out to mow, never remove more than 1/3 of the leaf blade. If you cut to short you will “scalp” the turf and cause a brown look on the lawn. This can be damaging to the turf and allow for weeds to get established by exposing the soil to the sunlight. What is taking place more in northwest Florida is not mowing frequently enough and cutting off excess growth due to the rain. This also can cause scalping so it is very important to mow frequently enough to only remove 1/3 of the leaf blade.

A zoysia lawn that has been “scalped” after excess growth and infrequent mowing. (Photo Credit: Blake Thaxton)
Other practices such as keeping your mower blade sharp, mowing in different directions, and leaving clippings on the ground will help keep a healthy Florida lawn. Please see more information about mowing correctly in Florida in the University of Florida/IFAS Extension publication: Mowing Your Florida Lawn

by Matt Lollar | Jun 29, 2017
Algal leaf spot, also known as green scurf, is commonly found on thick-leaved, evergreen trees and shrubs such as magnolias and camellias. It is in the genus Cephaleuros and happens to be one of the only plant parasitic algae found in the United States. Although commonly found on magnolias and camellias, algal leaf spot has a host range of more than 200 species including Indian hawthorn, holly, and even guava in tropical climates. Algal leaf spot thrives in hot and humid conditions, so it can be found in the Florida Panhandle nearly year round and will be very prevalent after all the rain we’ve had lately.
Symptoms
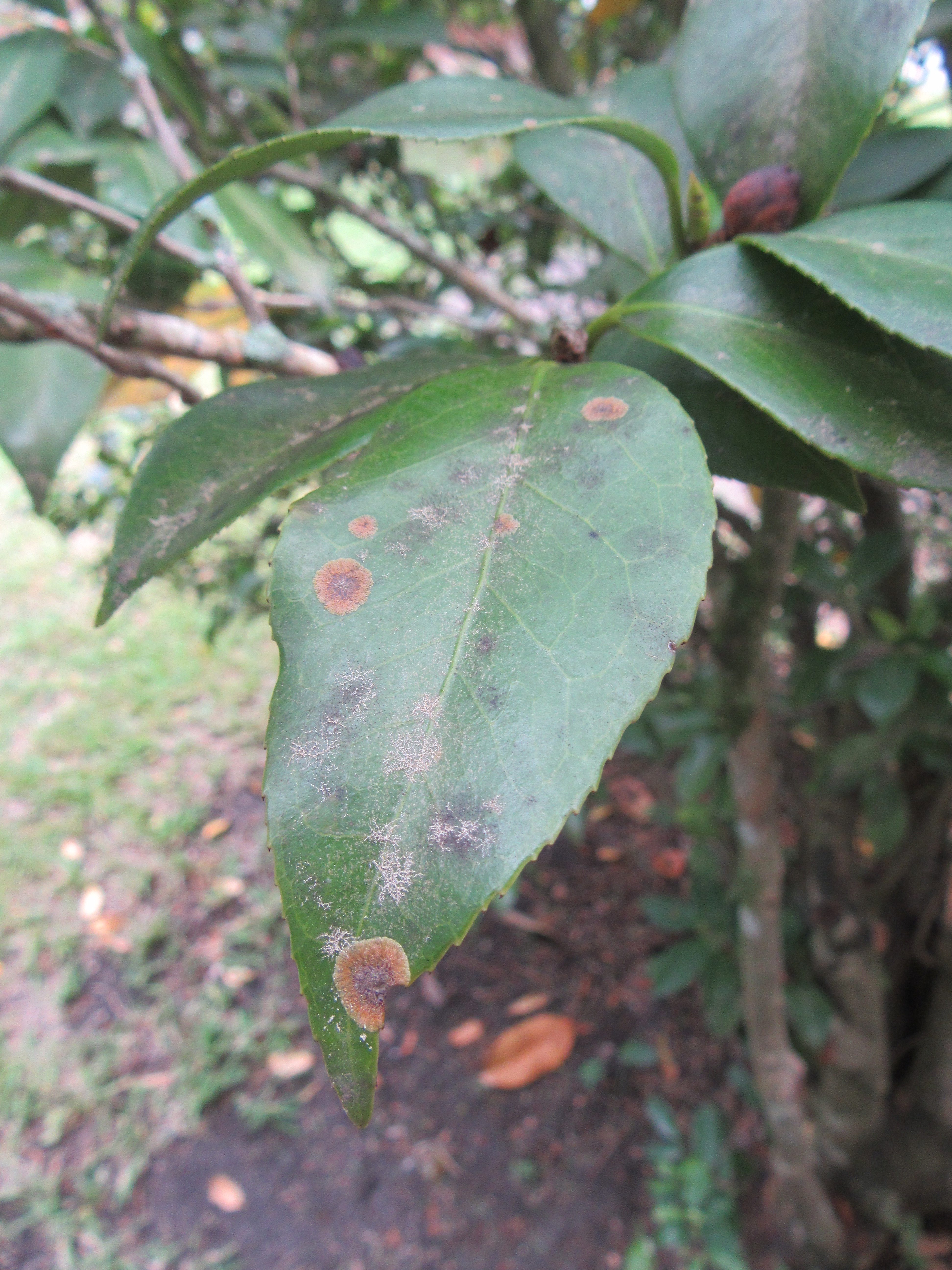
Algal leaf spot is usually found on plant leaves, but it can also affect stems, branches, and fruit. The leaf spots are generally circular in shape with wavy or feathered edges and are raised from the leaf surface. The color of the spots ranges from light green to gray to brown. In the summer, the spots will become more pronounced and reddish, spore-producing structures will develop. In severe cases, leaves will yellow and drop from the plant.
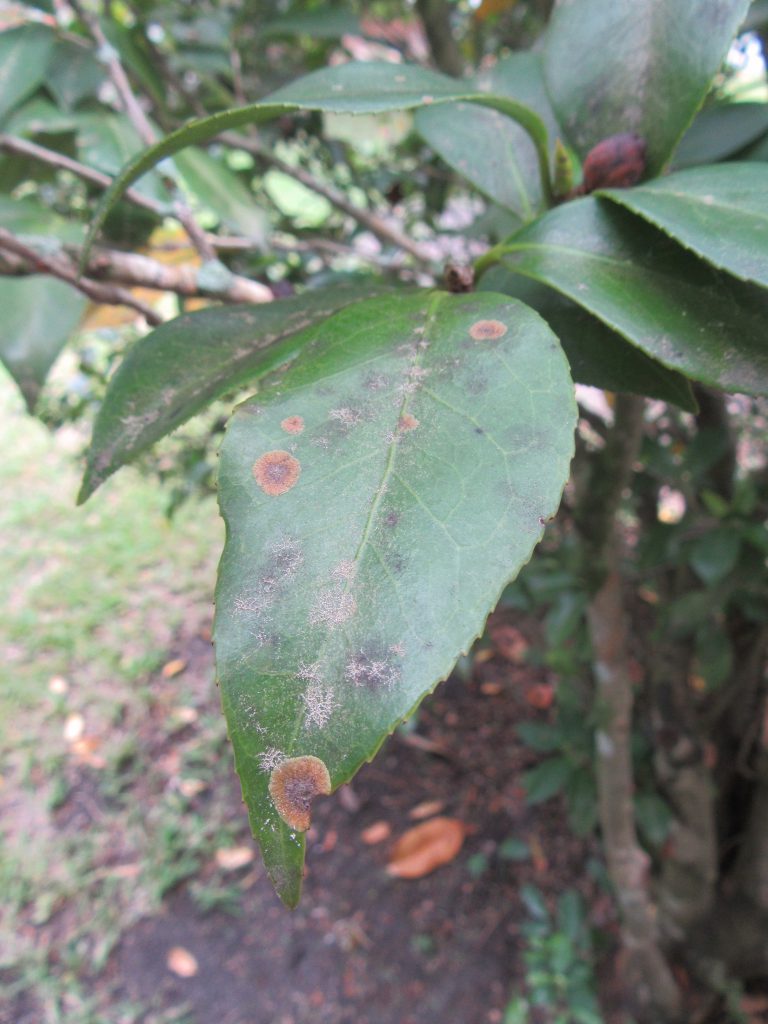

Algal leaf spot on a camellia leaf. Photo Credit: University of Florida/IFAS Extension
The algae can move to the stems and branches in more extreme cases. The algae can infect the stems and branches by entering through a small crack or crevice in the bark. The bark in that area cracks as a canker forms that eventually can girdle the branch, killing it.

Algal leaf spot on a sycamore branch. (Platanus occidentalis). Photo Credit: Florida Division of Plant Industry Archive, Bugwood.org.
Management
In most cases, algal leaf spot is only an aesthetic issue. If only a few leaves are affected, then they can just be removed by hand. \It is important that symptomatic leaves are discarded or composted offsite instead of being left in the mulched area around the trees or shrubs. If symptomatic leaves are left in the same general area then irrigation or rain water can splash the algal spores on healthy leaves and branches. Infected branches can also be removed and pruned.
Preventative measures are recommended for long-term management of algal leaf spot. Growing conditions can be improved by making sure that plants receive the recommended amount of sunlight, water, and fertilizer. Additionally, air circulation around affected plants can be increased by selectively pruning some branches and removing or thinning out nearby shrubs and trees. It is also important to avoid overhead irrigation whenever possible.
Fungicide application may be necessary in severe cases. Copper fungicides such as Southern Ag Liquid Copper Fungicide, Monterey Liqui-Cop Fungicide Concentrate, and Bonide Liquid Copper Fungicide are recommended. Copper may need to be sprayed every 2 weeks if wet conditions persist.
Algal leaf spot isn’t a major pathogen of shrubs and trees, but it can cause significant damage if left untreated. The first step to management is accurate identification of the problem. If you have any uncertainty, feel free to contact your local Extension Office and ask for the Master Gardener Help Desk or your County Horticulture Agent.
by Carrie Stevenson | Jun 2, 2015
Hurricane Season began June 1. While storm experts are predicting a slower year due to El Nino conditions, it only takes a single storm landing nearby to cause millions in damage, uprooting trees and lives.
Tree damage to homes and property can be devastating, and one of the first instincts of many homeowners when they see a big storm in the Gulf is to start trimming limbs and removing trees. However, it is wise to fully evaluate one’s landscape before making an irreversible decision. Trees are crucial for providing shade (i.e. energy savings), wildlife habitat, stormwater management, and maintaining property values.

Downed trees in a row along a hurricane-devastated street. Photo Credit: Mary Duryea, University of Florida
University of Florida researchers Mary Duryea and Eliana Kampf have done extensive studies on the effects of wind on trees and landscapes, and several important lessons stand out. Keep in mind that reducing storm damage often starts at the landscape design/planning stage!
- Select the right plant for the right place.
- Post-hurricane studies in north Florida show that live oak, southern magnolia, sabal palms, and bald cypress stand up well compared to other trees during hurricanes. Pecan, water and laurel oaks, Carolina cherry laurel and sand pine were among the least wind resistant.
- Plant high-quality trees with strong central trunks and balanced branch structure.
- Longleaf pine often survived storms in our area better than other pine species, but monitor pines carefully. Sometimes there is hidden damage and the tree declines over time. Look for signs of stress or poor health, and check closely for insects. Weakened pines may be more susceptible to beetles and diseases.
- Remove hazard trees before the wind does. Have a certified arborist inspect your trees for signs of disease and decay. They are trained to advise you on tree health.
- Trees in a group (at least five) blow down less frequently than single trees.
- Trees should always be given ample room for roots to grow. Roots absorb nutrients, but they are also the anchors for the tree. If large trees are planted where there is limited or restricted area for roots to grow out in all directions, there is a likelihood that the tree may fall during high winds.
- Construction activities within about 20 feet from the trunk of existing trees can cause the tree to blow over more than a decade later.
- Plant a variety of species, ages and layers of trees and shrubs to maintain diversity in your community
- When a tree fails, plant a new one in its place.

by Carrie Stevenson | May 6, 2015
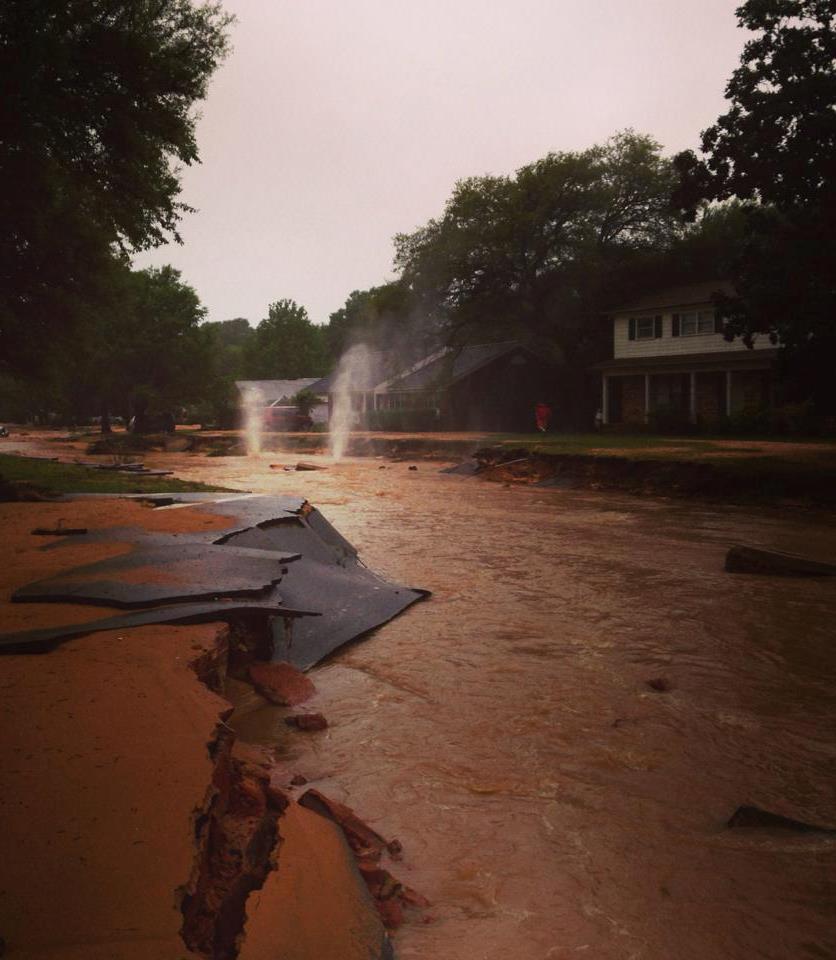
Just over a year ago, southwest Alabama and northwest Florida experienced a devastating storm that left hundreds without access to their homes and businesses, flooded out and stranded by a hurricane-force storm that didn’t come with the luxury of a week’s warning. Rainfall records in Pensacola go back to 1879, and the April 29-30 storm broke them all, estimating just over 20 inches over the two days. Not only was the rainfall heavy, but the torrent was high in both velocity and volume—at one point, a mind-boggling 5.68 inches fell in the span of one hour. That’s half the annual rainfall of many cities in California and Texas!

A residential street in Pensacola became a raging river a year ago during the torrential floods, putting dozens of people out of their homes. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson UF/IFAS Extension.
With every dark storm cloud comes a silver lining, though, and just like the millions pumped into our regional economy from oil spill-related fines, the April 2014 floods have awakened a “greener” ethic among many residents, business owners, and politicians. According to a study just released by an environmental consulting firm, when asked about infrastructure changes and improvements to flooding and stormwater, attendees at community meetings overwhelmingly preferred “low impact” solutions such as expanded green space, cisterns, rain gardens, and stream restoration to “hard” structures such as bigger underground pipes and more pumps. While traditional engineering infrastructure is still crucial to a community that must maintain roads, stormwater ponds, and buildings, I find it encouraging that residents are interested in trying different techniques that have proven successful both here and in other parts of the world.

The new Langley Bell 4-H Center has four large rain barrels around the building, used to collect roof runoff for landscape design. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson UF/IFAS Extension.
So, how does one prepare for unexpected rain and floods? The first thing is to realize that northwest Florida receives the most annual rainfall (over 60”) of any region of the state, and sometimes it seems to come down all at once. Preparing landscapes to handle both frequent and heavy rains is an important place to start. This article will begin a series of articles delving into those “low-impact” stormwater management techniques that can help lessen the impact of the intense storms we experience here in northwest Florida. Many of these practices, such as creating mulch pathways, harvesting rainwater, and installing shoreline vegetative buffers, can be implemented by individual homeowners and help reduce the impact of flooding on a neighborhood and city-wide level

by Taylor Vandiver | Apr 14, 2015
Rain gardens are an easy way to return water to our aquifer, reduce erosion, and help prevent stormwater runoff.
Running down the driveway or patio, rainwater can pick up lawn chemicals and pesticides. A rain garden is basically a low section of the landscape planted with native plants that like to get their “feet” wet. The garden collects rainwater, giving it a chance to “strain” out impurities before draining into the aquifer.

Swamp sunflower. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
They work best when they’re placed at the bottom of downspouts or naturally low spots in the landscape, usually where water tends to puddle. They’re especially useful for collecting runoff from paved surfaces. Rain gardens can be any size or shape and can attract thirsty wildlife.
When selecting plants, you’ll need to consider how much sun your site gets and how much space is available. Make sure you select plants that are not just water-tolerant, but also drought-tolerant for the times between rains.
Rain gardens rely on plants that will survive dry spells but then soak up excess stormwater during Florida’s rainy months, preventing the water from running across your landscape.

Blue flag iris. Photo courtesy UF/IFAS.
Include different types of plants in your rain garden to create a complete and cohesive look that will provide year-round interest. The following is a short list of flowers, shrubs, and grasses that would perform well in a rain garden.
Flowers:
- Blue flag iris
- Goldenrod
- Swamp sunflower
- Spider lily
- Milkweed
Grasses:
- Florida gamma grass
- Muhly grass
- Wiregrass
Shrubs:
- Virginia willow
- Buttonbush
- Wax myrtle
Here is a list of native plants that will do well in your North Florida rain garden. As always consult your local Extension Office for more information. All of the information in this article was provided by UF/IFAS Extension.

by Carrie Stevenson | Mar 17, 2015

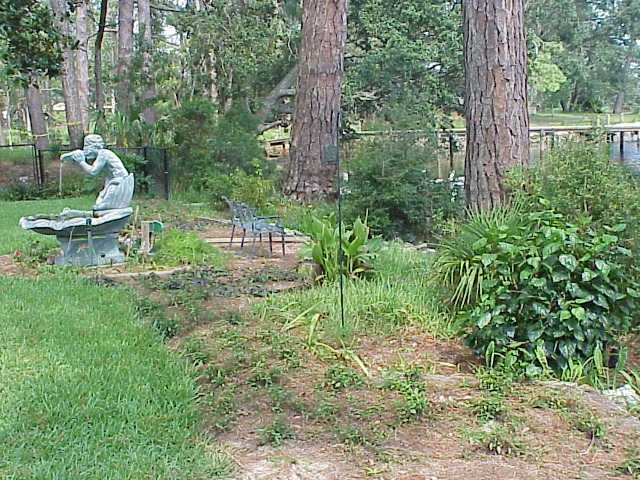
A waterfront buffer zone may include a raised berm with native vegetation to slow runoff from a yard before entering the water. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
A taste of spring weather has arrived, and people will soon be filling the home improvement stores and getting ready for outdoor projects. If you live on the water or near a storm drain, it’s worth considering buffer zones and best management practices for fertilizing and lawn maintenance.
A waterfront buffer zone is an area the length of one’s property line, typically running about 10 feet (although it can be wider) from the edge of a shoreline (or even a storm drain) into the yard. In this area, the homeowner allows native vegetation to grow along the water and uses low-maintenance plants within the buffer. In this zone, no fertilizers or pesticides are used. Some homeowners will build a small berm to divide the area of maintained lawn (uphill) from the downhill waterfront side. This berm may be composed of a mulched area with shrubbery to catch and filter runoff from the more highly maintained lawn. This combination of actions helps treat potentially polluted stormwater runoff before it reaches the water, and keeps homeowners from using chemicals close to the water. It is often quite difficult to grow turf next to the water, anyway, and this takes the pressure off of someone trying to grow the perfect lawn down to the water’s edge. The buffer zones are often quite attractive and can be an excellent transition between managed turf and the waterfront.

Unmaintained dirt roads along creeks are significant sources of sediment, which can harm the bottom-dwelling insects that form the base of the food web. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Erosion prevention is crucial along waterways, as well. An open, non-vegetated lot can contribute a significant amount of sediment to a storm drain, stormwater pond, or natural body of water. Whether grass, trees, or bushes, any kind of vegetation is preferable to soil washing out of a yard and into the water. Sediment is a problem because it causes water clarity to drop, which can prevent seagrasses from getting the sunlight they need. Once settled, underwater sediment can form a stifling layer that chokes out small insects and invertebrates, which live in the soil and form the basis of the aquatic food chain. With no fish food available, fish may die or move out of an area. The most dramatic examples of this can often be found at dirt roads that cross over creeks. If not managed properly, the clay on these roads can nearly bury a small stream.
Other lawn care techniques for protecting the waterfront and preventing stormwater pollution include not mowing along the water, using a deflector shield and staying 3’-10’ away from the water’s edge when fertilizing, and not allowing grass clippings to blow into storm drains. Large amounts of decaying grass in a waterway can use up available oxygen, endangering aquatic organisms. When applying granular fertilizer, be sure to sweep up any spills on concrete so it doesn’t run into a storm drain. When cutting grass, mow at the highest height recommended for your turf to encourage deep rooting and stress tolerance. Healthy turf is better able to withstand drought, pests, and choke out weeds, reducing the frequency of pesticide and water application.
















