
by Gary Knox | May 20, 2014

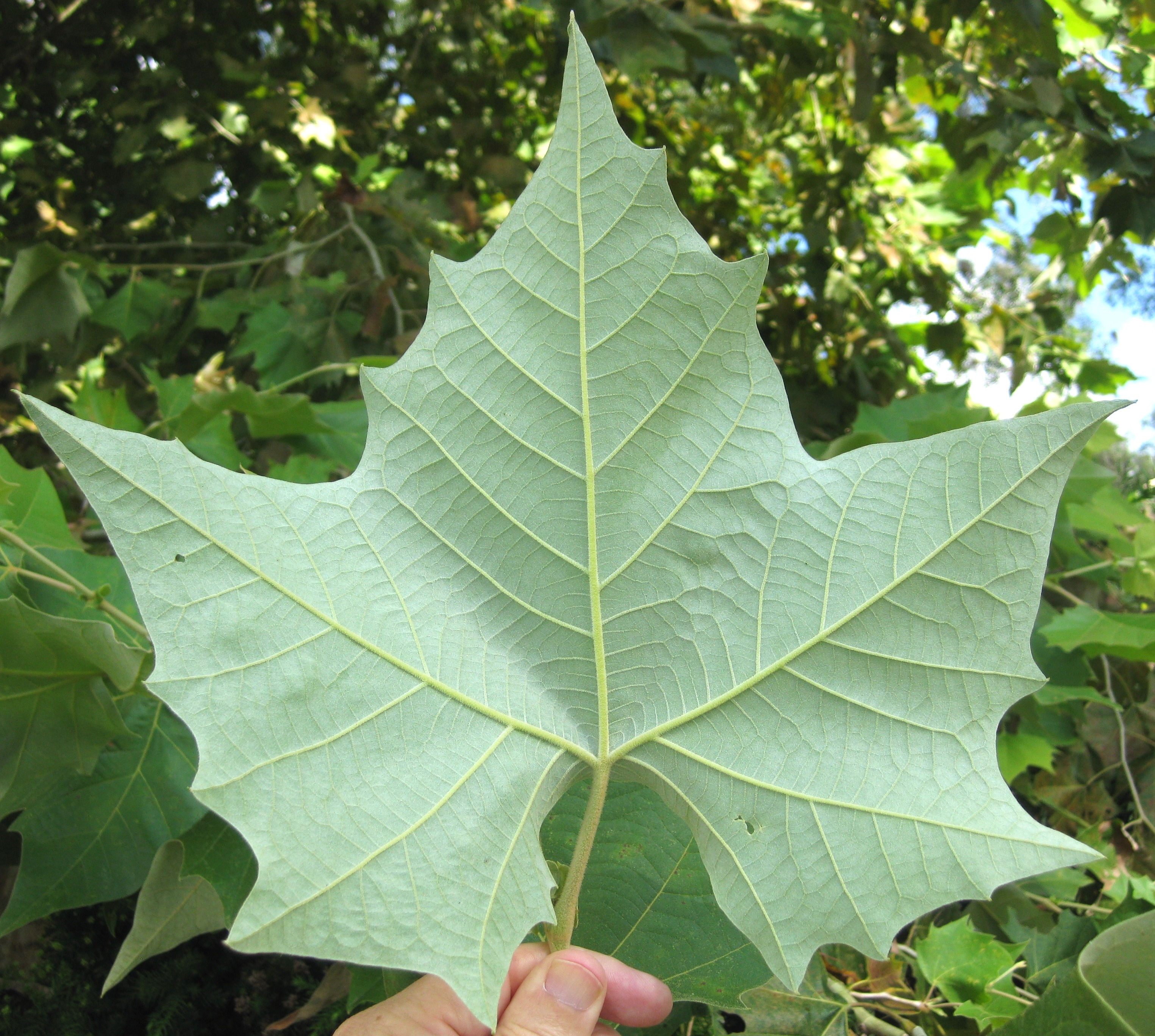
Mexican Sycamore, Platanus mexicana.
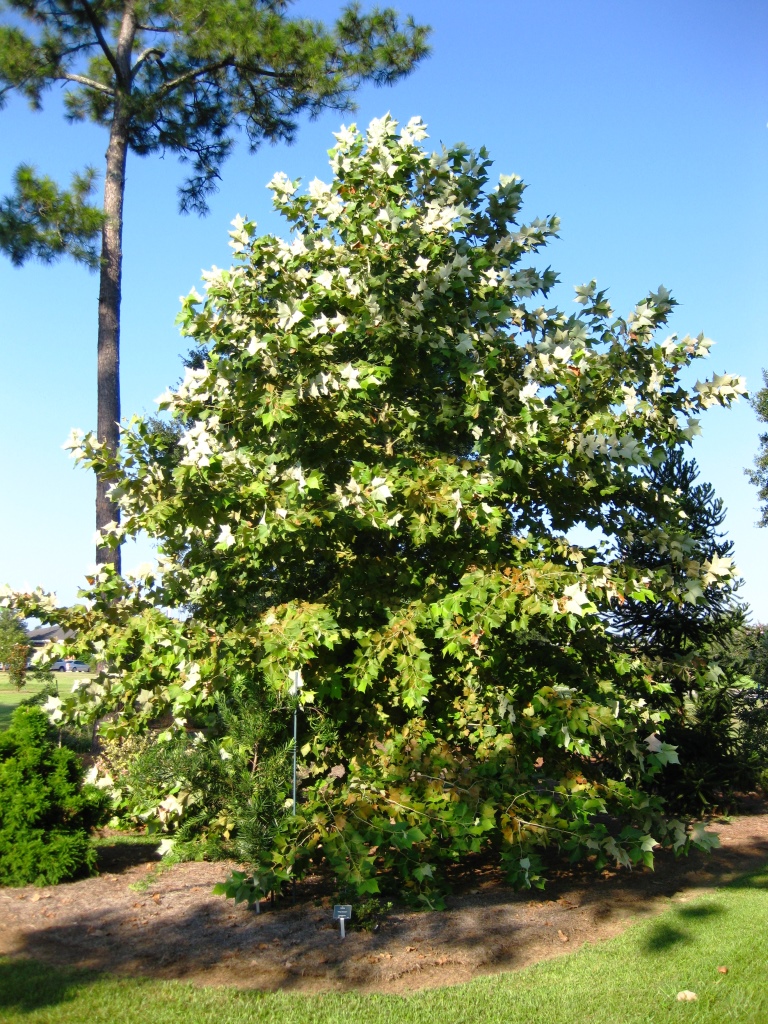
Mexican sycamore (Platanus mexicana) is a fast growing, drought tolerant tree boasting smooth white-and-tan bark and large maple-like leaves with velvety, silver undersides. Native to northeastern and central Mexico, this tree’s cold hardiness is not well defined. However, Mexican sycamore grows well as far north as USDA Cold Hardiness Zone 8b in Texas and Florida.
Mexican sycamore is slightly smaller than our native American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis). While known to grow up to 80 feet or more in the wild, Mexican sycamore typically reaches a mature height of 50 feet in the landscape with a width of about 30 feet. The tree is deciduous with an upright rounded crown. Mexican sycamore grows best in full sun and is adapted to most soils, including alkaline soils. While considered drought tolerant, best success occurs when plants are irrigated until established.
The lobed, maple-like leaves are up to 8 inches wide and olive-green, sometimes turning yellow before falling in December. Leaf undersides of mature trees (at least 4 to 6 years old) develop short, dense, whitish hairs resulting in an attractive silvery appearance. The large leaves can be a nuisance if they fall where leaves must be raked. Like the American sycamore, the aggressive roots and relatively large mature size of this tree suggest it not be used near structures and pavement or under power lines.
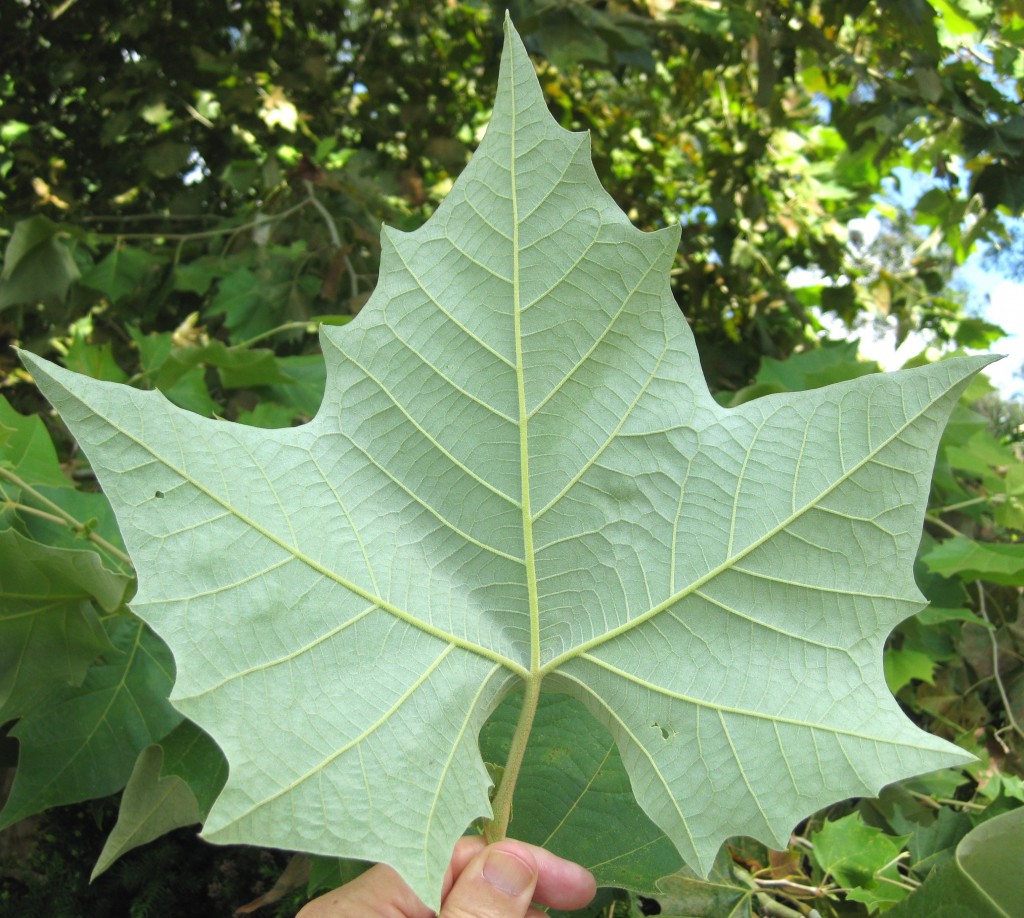

Closeup of the silvery underside of a Mexican Sycamore leaf.
Male and female flowers are borne separately on the same plant from December through February and appear as greenish balls hanging from the branches. Aggregate-like fruit about 1 1/2 inches in diameter follow in April through August.
Mexican sycamore is resistant to bacterial leaf scorch, which can be a problem on American sycamore. This bacterium causes leaves to curl and turn brown and may eventually kill American sycamore. Two occasional fungal diseases affecting Mexican sycamore are anthracnose and powdery mildew. Anthracnose causes moderate to severe leaf drop during cool, wet springs. Initial symptoms are light brown areas forming along the veins of new leaves; if severe, anthracnose can cause cankers as well as leaf drop. Powdery mildew appears as a whitish dust on leaves.
Sycamore lace bugs may feed on leaf undersides in late summer and fall. The feeding results in a stippled appearance on the top of the leaf and black spots of feces on the underside. So far, observations of this tree in Florida suggest infestations of sycamore lace bugs are not as severe as on American sycamore. Aphids may also feed on leaves; they cause little damage to the tree but exude honeydew upon which sooty mold grows and turns leaf surfaces black.
Mexican sycamore is an attractive, smaller statured alternative to American sycamore. Unfortunately, it is not commonly grown by Florida nurseries and may be difficult to find.
Platanus mexicana (Mexican sycamore) has not yet been evaluated using the IFAS Assessment of Non-Native Plants in Florida’s Natural Areas (http://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/assessment/). Without this assessment, the temporary conclusion is that P. mexicana is not a problem species at this time and may be recommended.
by Taylor Vandiver | Apr 29, 2014
Now that spring has finally sprung and summer is well on its way, you may find yourself taking a stroll through your landscape and assessing damage done by late cold spells. However, it may not be a frost problem that has your plants looking worse for the wear. They could be experiencing nutritional imbalances which affect overall plant health. Most cases involving nutrition issues in plants can be linked back to the soil. Therefore, if you suspect a problem I suggest testing your soil to ascertain pH and nutrient levels. You can obtain a soil test kit at your local UF IFAS Extension office. Another way to diagnose your plant damage is to visually catalog its symptoms. Symptoms of mobile nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, tend to reveal themselves on older leaves first. Whereas, immobile nutrient symptoms (i.e. boron and calcium) will show up on newer leaves. These flow charts can help to narrow down which essential element may be lacking in your plant’s diet.
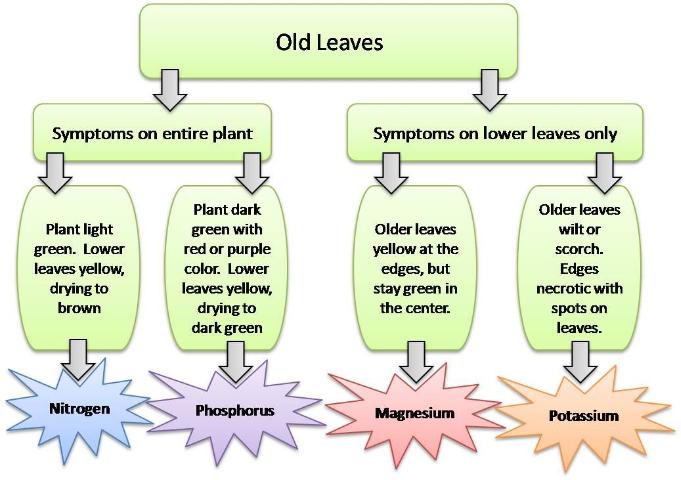
Mobile Nutrient Symptoms.
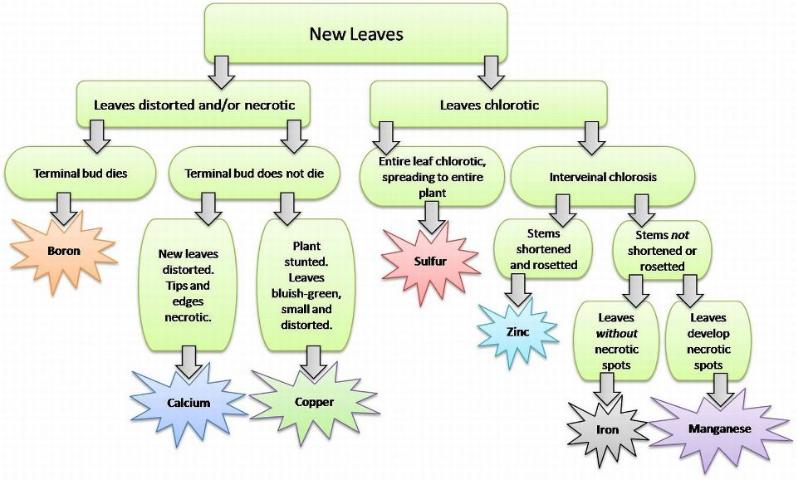
Immobile Nutrient Symptoms.

by Alex Bolques | Mar 25, 2014

Black Titi in bloom. Flower clusters upright at tips of branches. An excellent source of nectar and pollen for honey production. Image: Alex Bolques
Black Titi (also known as Spring Titi or Buckwheat Tree (Cliftonia monophylla (Lam.) Britton ex Sarg. is a native shrub or tree that can be found growing along streams and boggy areas of the Florida Panhandle. It can tolerate acidic wetland soils and once established can also tolerate dry soils in the landscape. Black Titi can reach 15 – 30 feet in height with 3 – 4 inches of trunk diameter. Its bloom period lasts February through March.

Bee visits a Black Titi flower. Image credit: Alex Bolques
Beekeepers love it because it is a wonderful source of nectar and pollen for honey production. Beginning beekeepers may confuse Black Titi with White Titi (also known as Summer Titi or Swamp Titi (Cyrilla racemiflora L.). It should not be grown as a honeybee pollinator plant. The nectar and/or pollen of White Titi can promote a condition known as “Purple brood”, which can be detrimental to honeybee immature stages.The flower of the spring flowering Black Titi is a raceme, a cluster of flowers along a central stem, that appears as an upright cluster on the tip of branches. The flower of the summer flowering White Titi is also a raceme, not as upright, more elongated. Visit the USDA Natural Resource Conservation Service plant database website and click on the image tab to see Black Titi (Buckwheat Tree) or White Titi (Swamp Titi) to view differences in flower morphology.

by Julie McConnell | Feb 18, 2014

Lichen on trunk of oak tree. Image: Julie McConnell, UF/IFAS
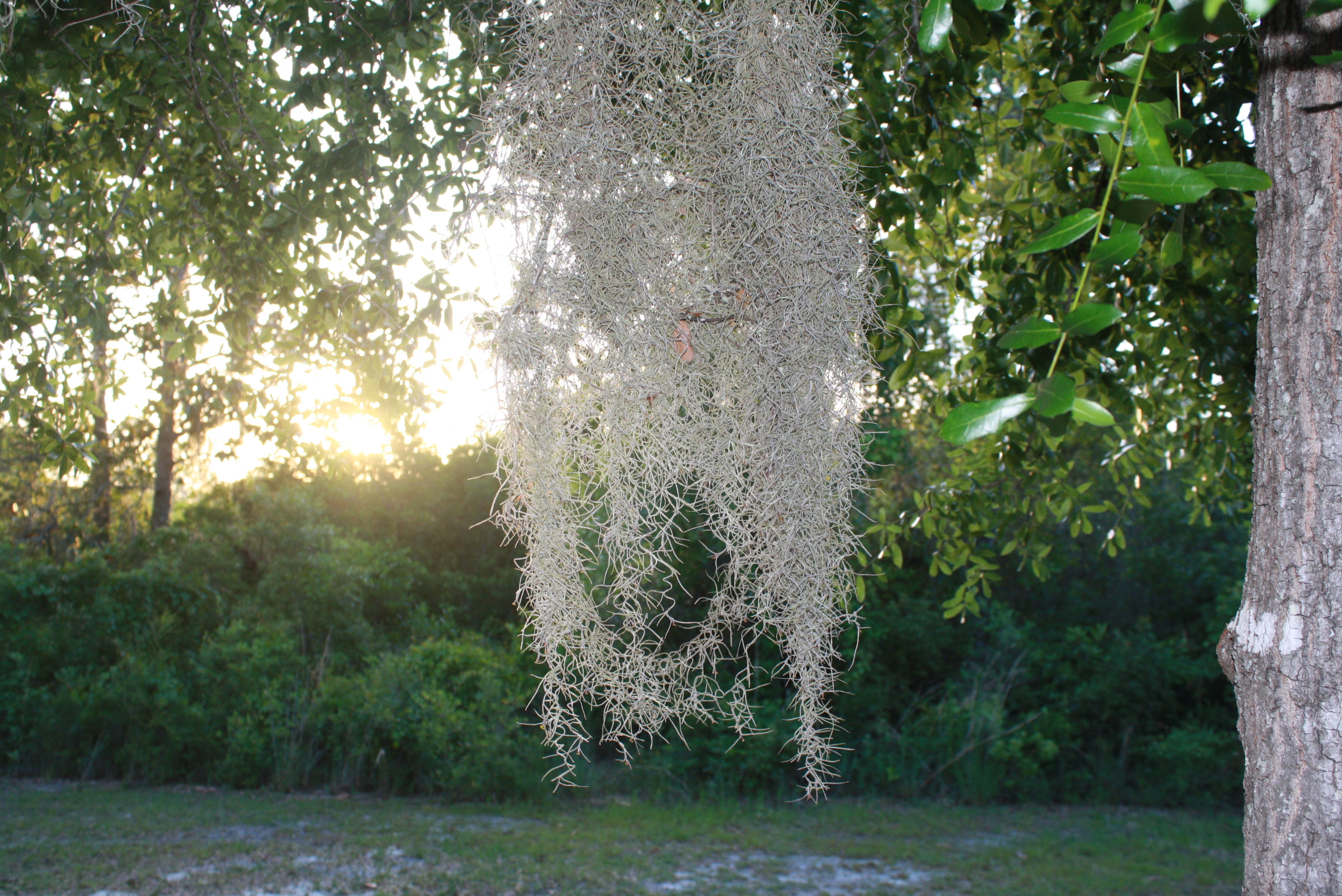
Spanish moss and lichen have earned an inaccurate reputation for damaging trees and shrubs in the Florida landscape. Although they may be found in plants that are in decline or showing stress symptoms, they are simply taking advantage of space available to survive. Both plants are epiphytes and are obtaining moisture and nutrients from the atmosphere rather than from the plants they rest upon.

Spanish moss. Image: Julie McConnell, UF/IFAS
Lichen are more commonly found on plants that are in poor health because they need a plant that is growing slowly and access to sunlight. These conditions can typically be found in thin canopies of trees and shrubs under stress. Although they are firmly attached to the surface of the plant, they are not taking nutrients from the tree or shrub, but rather from the air and other sources such as organic debris and bird excrement. If you find lichen on your landscape plants, look further into what stress factors might be causing the plant to grow slowly such as compacted soil, extreme weather conditions, drought stress, disease or insect pressure.
Spanish moss does not harm trees and many people find it an appealing asset to their landscapes. Common misconceptions about Spanish moss include that the weight causes branches to break and that it is a host site for chiggers. Spanish moss is very light and any additional weight is typically insignificant. Although it may harbor some insects and provide nesting material for birds and other wildlife, Spanish moss in trees is not a site conducive to chiggers because they favor low-lying moist environments.
To read more about Spanish moss, lichens, and other common epiphytes please read the EDIS publication “Spanish Moss, Ball Moss, and Lichens – Harmless Epiphytes.”

by Beth Bolles | Feb 18, 2014
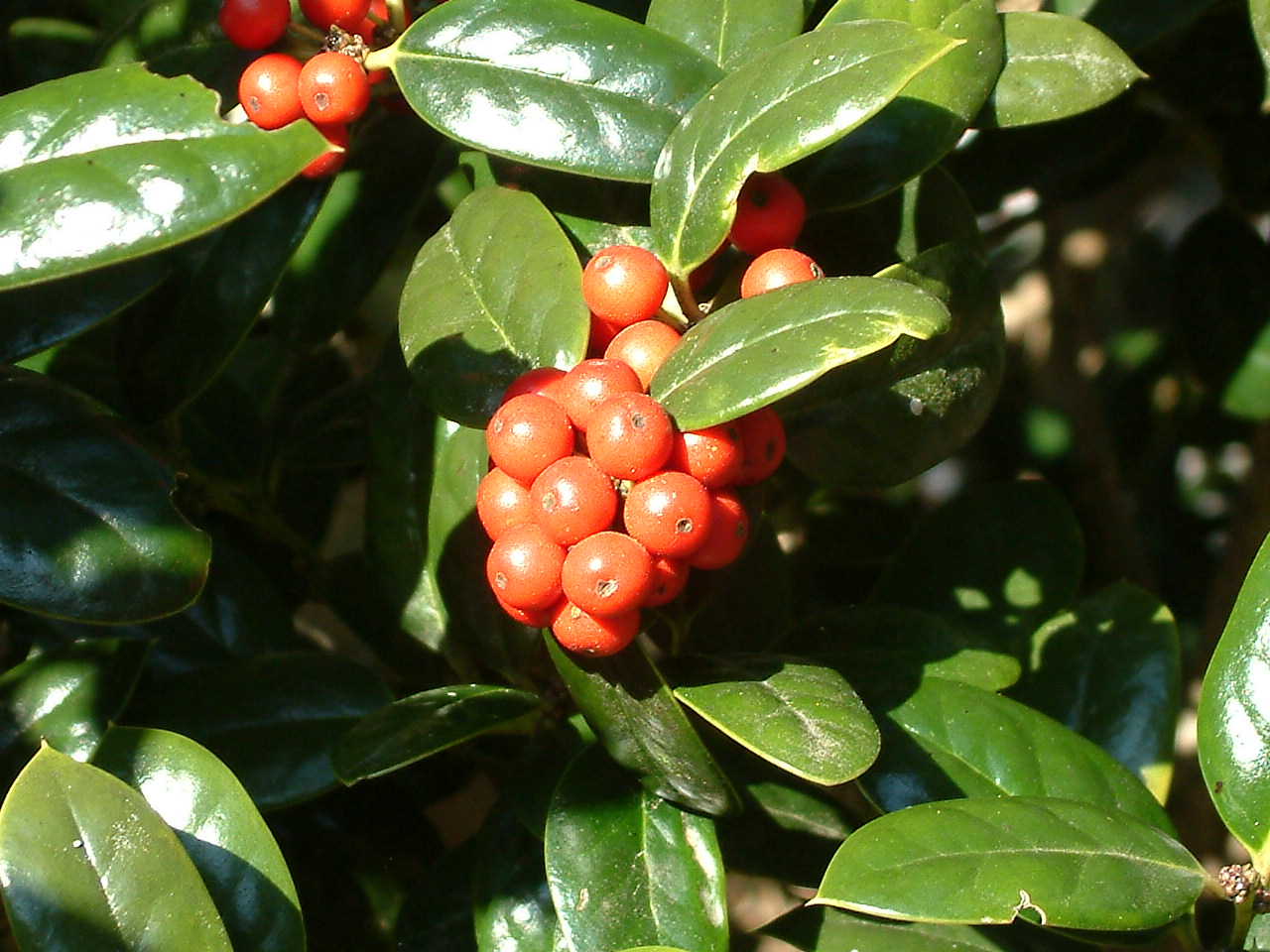
Looking for a new shrub or small tree this year? Interested in one that is low maintenance and offers beautiful green color? Why not try a holly.
Hollies can be found in landscapes throughout North Florida. Many times these plants are used in foundation plantings around homes. They can help make the transition from the hard lines of a home to other parts of the yard. In other landscapes, hollies make an excellent screen, dividing property or blocking a view.
Because hollies are commonplace, they may be overlooked by homeowners who want to add an attractive new plant to the landscape. Hollies have many uses and there are new selections entering the market worth considering.
In general hollies will not need a great amount of maintenance. Once established most species will require only occasional water, fertilizer, and pruning. Many hollies have even grown well under neglected conditions. If you are one that keeps holly plants pruned as hedges, you will need to watch for the scale insect and spray plants with a horticultural oil every year.
When selecting a holly plant, it is good to know a little about the area where you want to place the plant. Hollies vary in size and ability to tolerate wet soil, so it is important to match a species with your specific site. Also consider holly leaf shapes when using the plants in areas where people walk. Some holly leaves are very stiff and sharp and could injury visitors to you home or be a nuisance when you are working in the yard.
If you are interested in the added beauty of holly berries during the year, remember to select a female plant.

Hollies also attract bees to the landscape.
Credit: Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
Tree form hollies that you may select include the American holly (Ilex opaca), Savannah holly (Ilex x attenuata ‘Savannah’), and the Burford holly (Ilex cornuta ‘Burfordii’). All three plants will need well-drained soil. The American and Savannah holly will both reach heights between 20 and 40 feet and have a pyramidal growth form. The Savannah holly leaves will be a lighter green color than the leaves of other holly species. Burford holly has thick dark green leaves and grows about 12-15 feet in height over time.

Burford holly is a beautiful holly that gives birds a place to hide.
Credit: Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
If you have a wet site, consider the Dahoon holly which can be a specimen plant or used as a screen. This plant will develop attractive grayish bark and grow about 20 feet in height with more of a spread than the previously mentioned hollies.
There are medium-sized hollies that make excellent specimen plants about 12 feet in height. ‘Festive’ holly has dark green foliage and forms dense growth in a pyramidal form. The ‘Robin’ holly has a similar growth form but displays beautiful reddish new growth. Both of these plants will need well-drained soil and full sun or partial shade.
For those areas that require smaller evergreen plants, consider a ‘Bordeaux’ yaupon holly. These plants will grow about 4 feet in height and spread and form a dense growth of stiff stems with small leathery leaves. Since these plants keep a naturally round form it is not necessary to shear them. Both hollies will tolerate a wide range of soil conditions and require little maintenance once established.

by Gary Knox | Feb 11, 2014
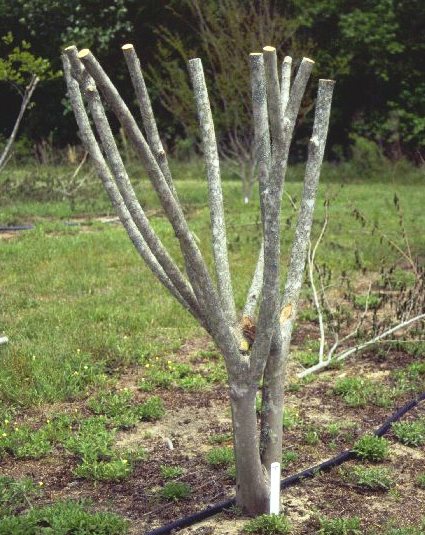
This is the time of year when we often see crapemyrtles unnecessarily topped: main stems that are several years old are cut back, often leaving branch stubs 2 – 5 inches or more in diameter. Topping is sometimes called heading, stubbing, rounding and dehorning.
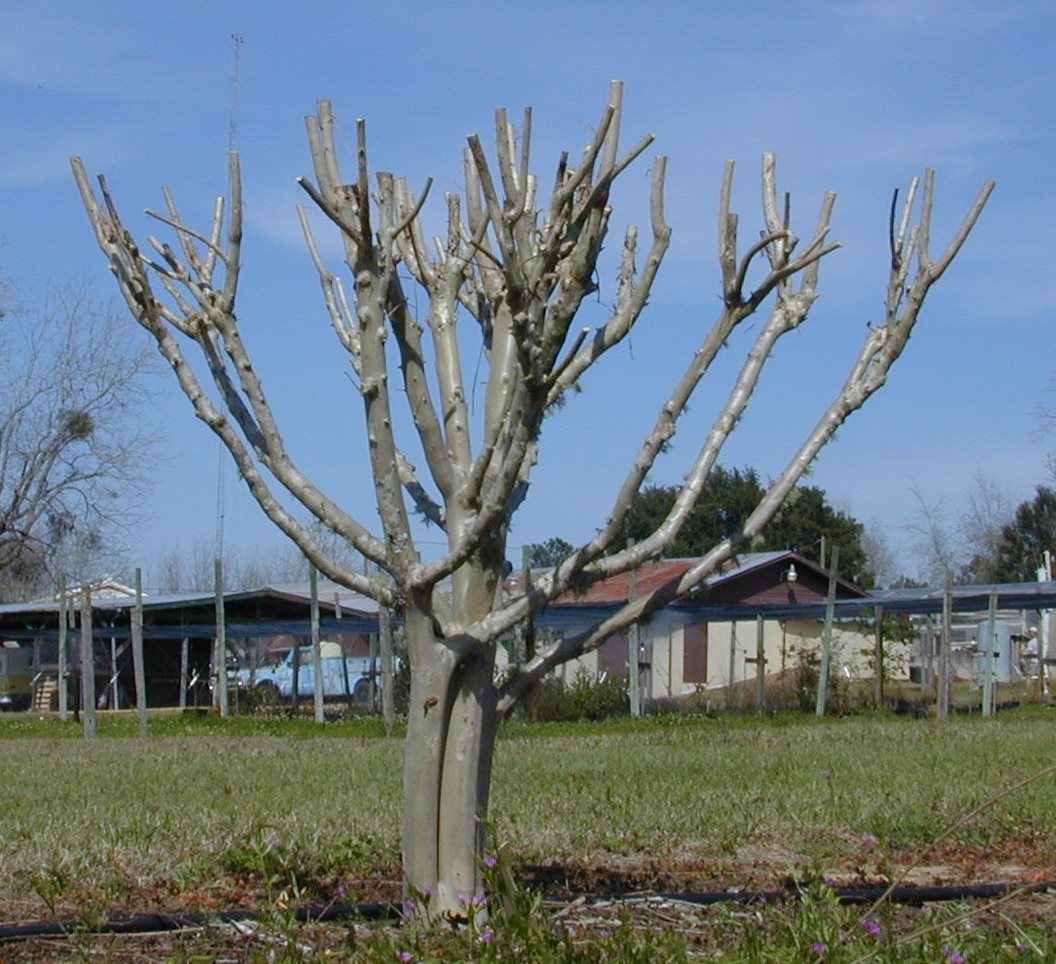

Figure 1. Topping is the drastic removal of large-diameter wood (typically several years old) with the end result of shortening all stems and branches. Topping crapemyrtle is often referred to as “crape murder” because topping usually is not recommended for crapemyrtle. Image Credit Dr. Gary Knox

Figure 2. Topping is the drastic removal of large-diameter wood (typically several years old) with the end result of shortening all stems and branches. Topping crapemyrtle is often referred to as “crape murder” because topping usually is not recommended for crapemyrtle. Image Credit Dr. Gary Knox
In the case of crapemyrtles, another name for this practice is “crape murder”. Topping a crapemyrtle is almost always unnecessary. Because people have seen this done in previous years, home owners often mimic this practice in their own yards, not realizing the unfortunate consequences.
Research at the University of Florida, detailed in this linked publication, found that topping crapemyrtle (“crape murder”) delays flowering up to one month. In other words, unpruned trees may begin flowering in June whereas topped trees don’t flower until July. This research also found topping reduced the number of flowers and shortened the flowering season. Finally, topping stimulated more summer sprouting from roots and stems. Sprouting results in greater maintenance since sprouts are usually removed to maintain an attractive plant appearance.
Unfortunately, landscape professionals and home owners often must maintain crapemyrtles that others planted, and so must deal with the consequences of poor cultivar selection and/or placement. If a crapemyrtle requires routine pruning to fit into its surroundings, it should be replaced with a smaller maturing cultivar. Dwarf crapemyrtles mature at a height of 5 feet; medium crapemyrtle cultivars grow up to about 15 feet in height, and tall or tree-size crapemyrtle cultivars exceed 15 feet and often grow to 20 – 30 feet tall in 10 years.
Best locations for crapemyrtle are areas in full sun with plenty of room for the cultivar size and away from walkways and roads. Proper selection of crapemyrtle cultivar and proper placement in the landscape can result in a low maintenance crapemyrtle without the need for significant pruning.
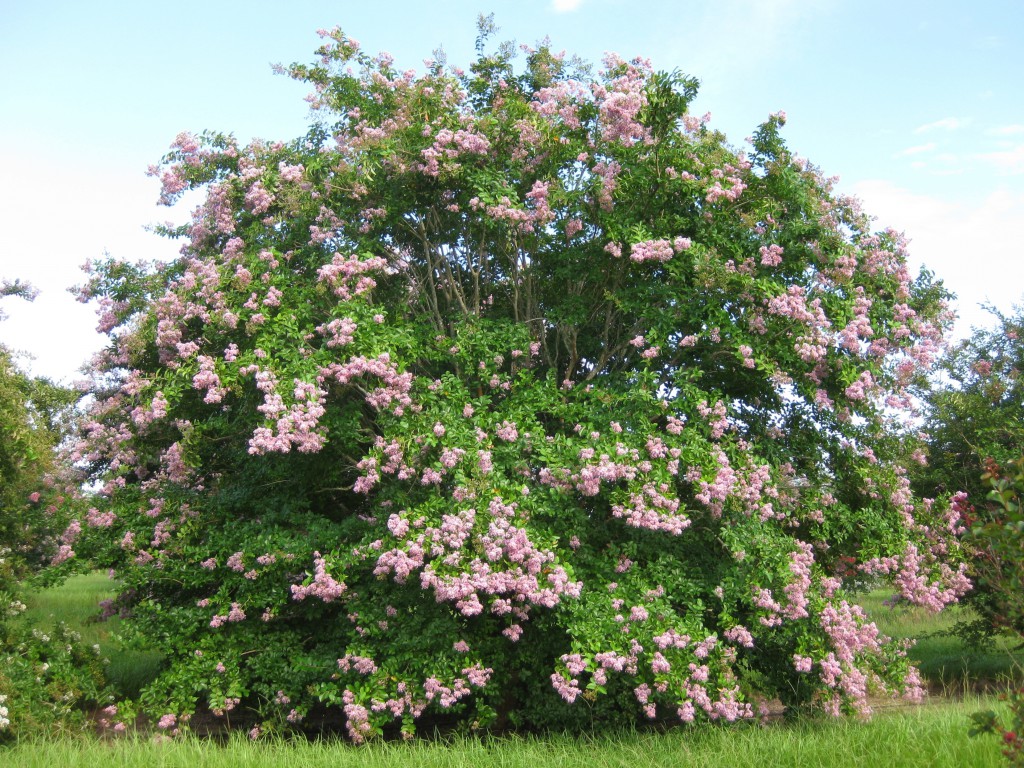

Figure 3. With proper cultivar selection and placement in the landscape, crapemyrtle develops into a beautifully shaped tree that rarely needs pruning. This crapemyrtle is ‘Muskogee’. Image Credit Gary Knox
For more information, see ENH1138, Crapemyrtle Pruning.


















