
by Ray Bodrey | Oct 14, 2021
Tree dieback is a complex syndrome and slow developing. Dieback is essentially a process in which trees lose leaves and limbs. This usually occurs as a result of severe stress to the tree’s bark or root system, but could be a result of a declining life cycle.
It’s important to note that there is a significant balance between a tree’s root system and the number of leaves and limbs it can support. For example, if a tree loses part of its root system, possibly due to disease or lawn equipment damage, the tree will forfeit a portion of its leaves. Dieback doesn’t happen overnight, though. It’s a slow process, with larger trees taking much longer time for signs of stress to emerge. However, a large tree root system is very sensitive to damage, whereas a small tree will adapt quickly and is much more resilient to damage. So, what can be done to prevent dieback in trees?
First and foremost, trees, like all living things, have a natural life cycle. Regardless of how you care for your trees, dieback will occur. The most important management measure in extending the life of a tree is to protect the root system and bark.
With each passing year, a tree grows new bark in the rejuvenation process. The bark replacement process inevitably becomes more difficult as the tree gets older and in turn the tree is more and more susceptible to dieback. If the bark becomes damaged, especially later in the tree’s life cycle, then fungi and insects have a much greater chance to cause serious harm. Treating bark damage with a wound dressing to prevent decay is the recommended procedure.

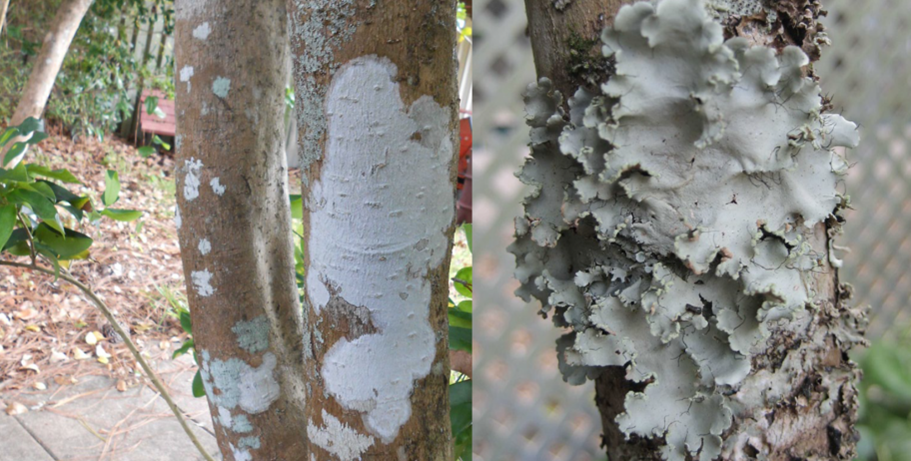
Lichens come in many forms and are commonly blamed for the decline and death of trees and shrubs, however they do not cause harm. Credit. Sydney Park Brown and Joseph Sewards, UF/IFAS.
A common misconception is that epiphytes, such as lichens and Spanish moss, are tree diseases. Epiphytes are known as “air plants” and thrive in the Panhandle. They survive on moisture and nutrients in the atmosphere and are harmless to trees. However, a tree that becomes inundated with epiphytes may be an indicator of excessive soil moisture, which may lead to root rot.
Lawn weed killers can have detrimental effects to trees, even if the application seems to be from a safe distance. When using a weed killer near a tree’s root system, confirm on the label that the product is designed to kill green growth only. It can’t be overstated that excessively fertilizing an old tree will greatly accelerate the decline of the tree. Some may think this will stimulate a tree and extend its life, but instead it will do the opposite. Young trees can tolerate fertilizer applications, as they need crown growth. Older trees will simply become top heavy, and structural damage will likely occur.
Don’t forget, trees need space too. A mature tree forced to occupy a small space will simply not adapt. Be sure to have adequate spacing when planting younger trees and shrubs in the vicinity of older trees. Also, keep your trees pruned away from touching structures and utilities.
Tree dieback is a complex issue to manage. By following these measures, you can help extend the life of your trees and continue to have a picturesque landscape.
For more information on tree dieback, contact your local county extension office.
Please visit Florida Friendly Landscaping, http://fyn.ifas.ufl.edu/, for more information on maintaining your landscape.
For more general information on lichens, please see UF/IFAS EDIS document “Spanish Moss, Ball Moss and Lichens-Harmless Epiphytes” by Joe Sewards and Dr. Sydney Park Brown: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP48500.pdf
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Pat Williams | Sep 9, 2021
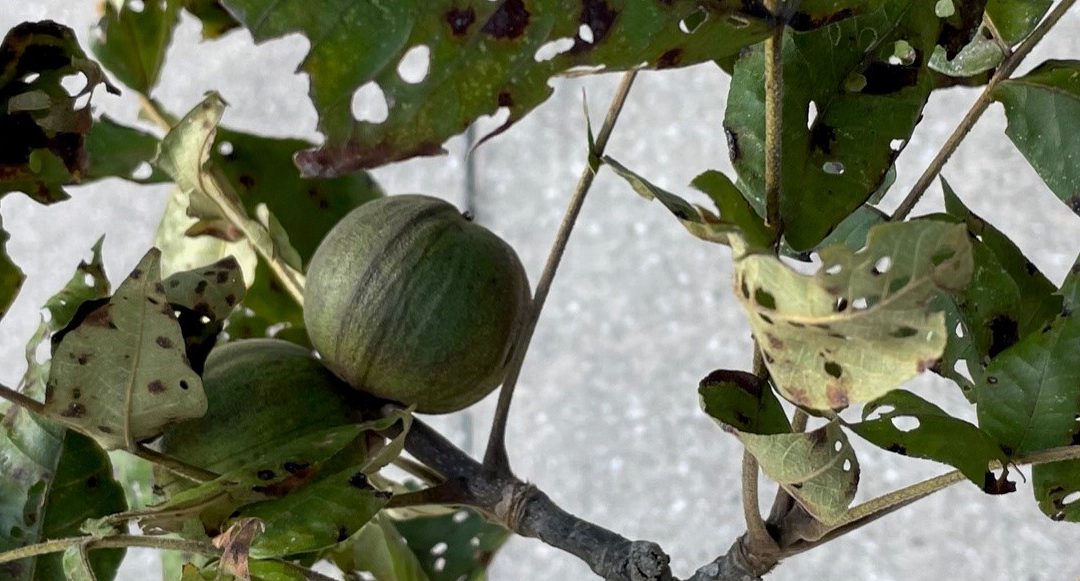
As homeowners, we do value our trees and no one wants to lose a shade tree especially on the house’s south side in Florida. On a recent site visit, a hickory tree had multiple concerns. Upon closer inspection, the tree had a bacterial infection about 30” off the ground with a smelly, black-brown ooze seeping forth. The leaf canopy was riddled with beetle holes and leaf margins were chewed by caterpillars. When leaves were viewed under the microscope, thrips (insects) and spider mites were found running around. The biggest homeowner cosmetic concern arose from hickory anthracnose (fungus) and upon closer inspection found the leaves to have hickory midge fly galls. The obvious question is should the tree come down? I’ll have you read the whole article before giving you the answer.
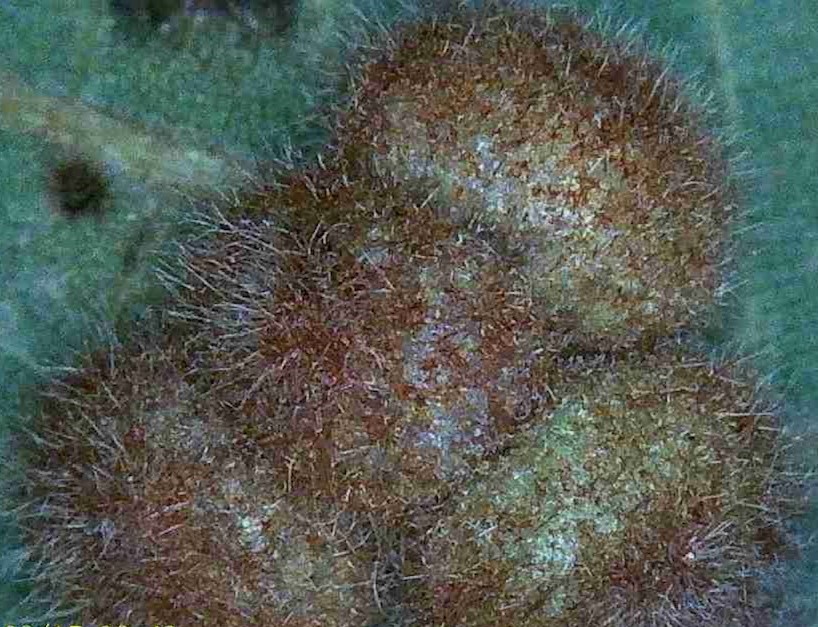

Each hickory gall is approximately 3/16″ wide.
Hickory anthracnose or leaf spot as seen in the banner photo is caused by a fungal infection during the wet summer months in Florida. The homeowner can usually recognize the disease by the large reddish brown spots on the upper leaf surface (sending a sample to the NFREC Plant Pathology Lab will confirm the diagnosis) and brownish spots with no formal shape on the bottom. Be sure to rake and remove all leaves to prevent your disease from overwintering close to the tree thus reducing infection next year.
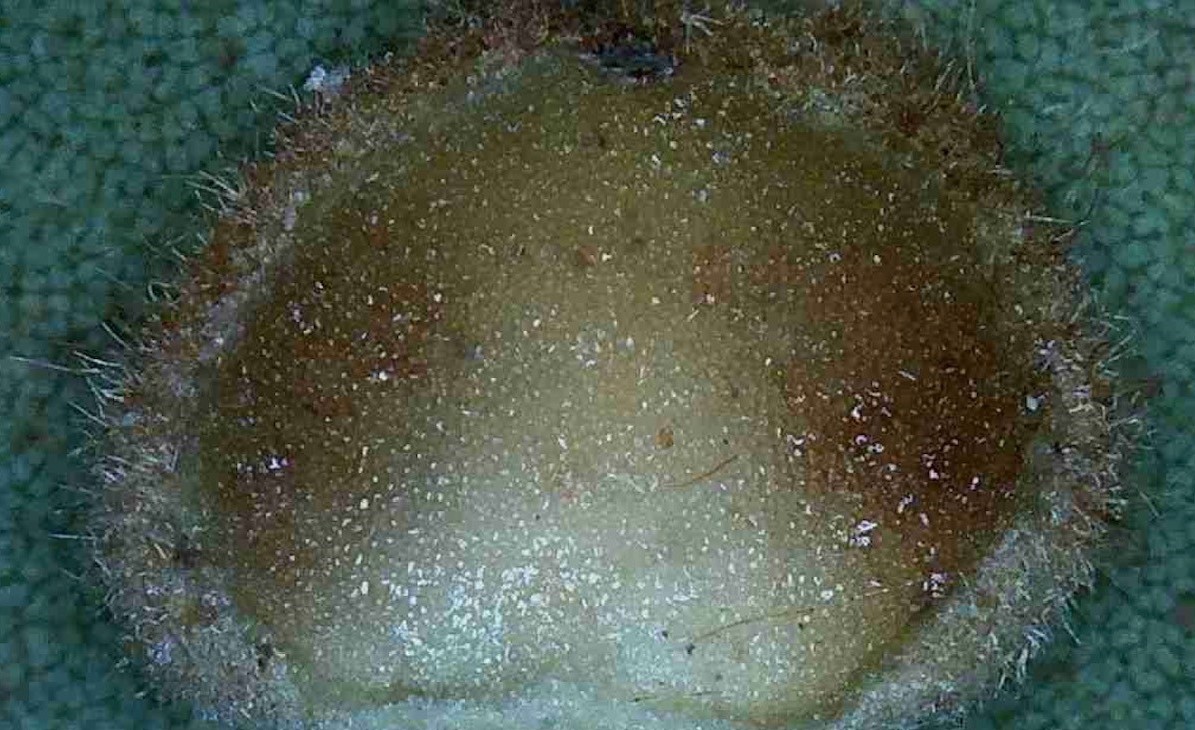
A hickory gall has been cut in half to show the leaf tissue.
The fungus can be lessened by good cultural practices and appropriate fungicidal applications. Please remember it is best left to professionals when spraying a large tree. This alone is not cause to remove your tree.
Hickory gall is caused by the hickory midge fly, an insect that lays eggs in the leaf tissue. The plant responds by building up tissue around each egg almost like the oyster when forming a pearl.
As the gall tissue grows, eggs hatch and larva start to feed on this tissue. The larva will continue to
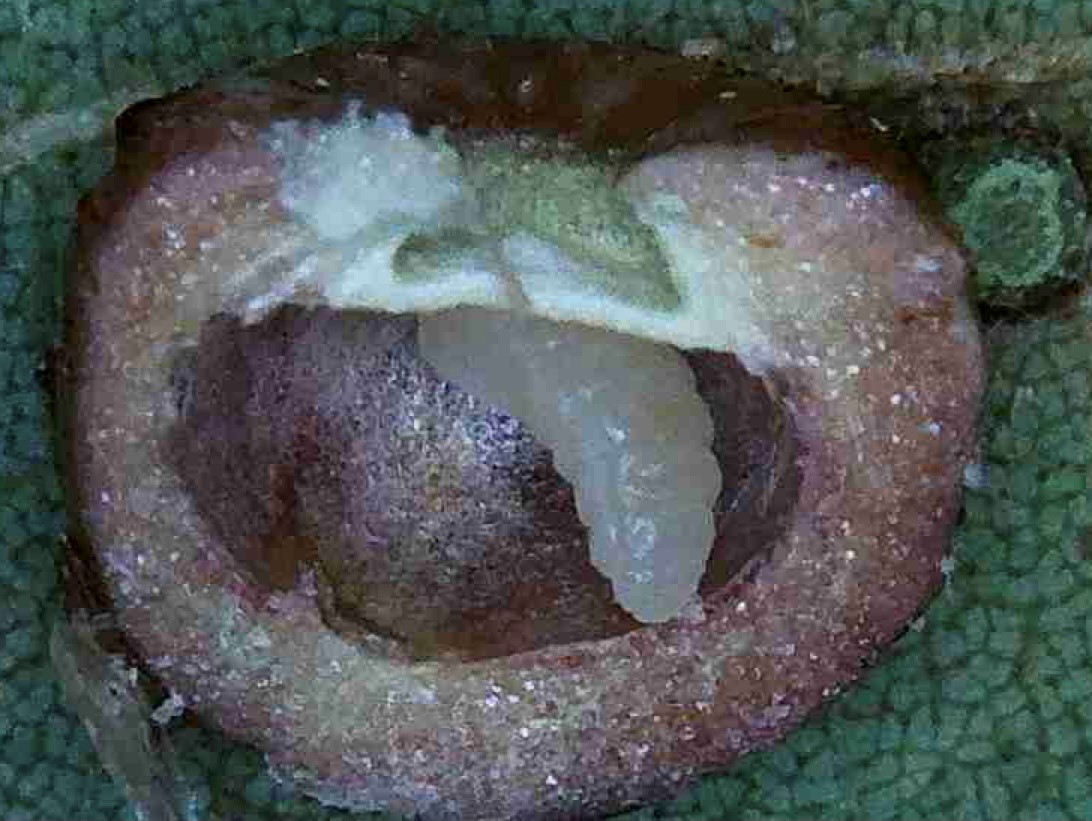
The larva has eaten all soft material inside the gall and is ready to pupate.
feed until it is ready to pupate within the gall. After forming a pupa, the midge fly will eventually emerge as an adult and females will continue to lay eggs on other leaves. The galls are more of a cosmetic damage and because your hickory leaves will fall from the tree as winter comes, the galls will normally not cause enough damage to worry about each year. Once again good cultural practices and disposal of each year’s leaves will reduce the gall numbers next year.
In a large tree with many leaves, foliar feeding by beetles and caterpillars do cause damage though the leaves will still produce enough food (photosynthesis) to keep the tree alive. Most of us never climb our trees to look at leaves to see the small insects/mites and there are more than enough leaves to maintain tree health.
The biggest concern during my site visit was their tree’s bacterial infection. A knife blade was pushed into the wound area and went in less than 1/4″. The homeowner was instructed to look at bactericide applications. In the end, this hickory tree with so many problems is still shading the home and helping cool the house. It is still giving refuge to wildlife and beneficial insects. When in doubt give our trees the benefit and keep them in place. Remember your local Extension agent is set up to make site visits and saving a tree is time well spent.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Sep 9, 2021
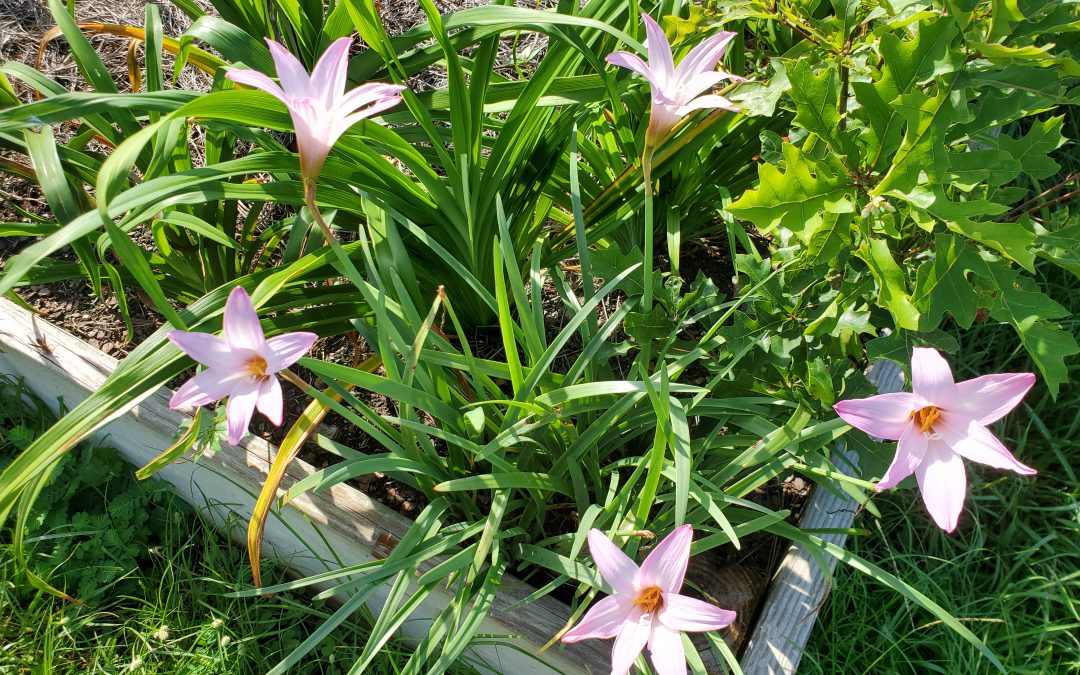
Bulbs are my favorite class of ornamental plants. They generally are low maintenance, come back reliably year after year, and sport the showiest flowers around. While many bulbs like Daylily, Crinum and Amaryllis are very common in Panhandle landscapes, there is a lesser-known genus of bulbs that is well worth your time and garden space, the Rainlily (Zephyranthes spp.).
Rainlily, aptly named for its habit of blooming shortly after summer rainfall events and a member of the Amaryllis family of bulbs, is a perfect little plant for Panhandle yards for several reasons. The plant’s genus name, Zephyranthes – which translates to English as “flowers of the western winds”, hints at the beauty awaiting those who plant this lovely little bulb. From late spring until the frosts of fall, Rainlily rewards gardeners with flushes of trumpet-shaped flowers in shades of white, pink, and yellow, with some hybrids offering even more exotic colors. While these individual flowers typically only persist for a day or two, they are produced in “flushes” that last several days, extending the show. Though Rainlily flowers are the main event for the genus, beneath the blooms, plants also offer attractive, grass-like, evergreen foliage. These aesthetic attributes lend themselves to Rainlily being used in a variety of ways in landscapes, from massing for summer color ala Daylilies, to use around the edges of beds as a showy border like Liriope or other “border” type grassy plants.

Unknown Rainlily species blooming in a raised bed. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Continuing along the list of Rainlily attributes, the genus doesn’t require much in the way of care from gardeners either. Most species of Rainlily, including the Florida native Z. atamasca, have no serious pests and are right at home in full sun to part shade. Once established, plants are exceedingly low-maintenance and won’t require any supplemental irrigation or fertilizer! Some Rainlily species like Z. candida even make excellent water or ditch garden plants, preferring to have their feet wet most of the year – putting them right at home in the Panhandle this year. And finally, all Zephyranthes spp. do very well in containers and raised beds also, adding versatility to their use in your landscape!
The one drawback of Rainlily is that they can be somewhat difficult to find for sale. As these bulbs are an uncommon sight in most garden centers, to source a specific Zephyranthes species or cultivar, one is probably going to need to purchase from a specialty internet or mail-order nursery. As with other passalong-type bulbs though, the absolute best and most rewarding way to obtain Rainlily is to get a dormant season bulb division from a friend or fellow gardener who grows them. There are many excellent unnamed or forgotten Zephyranthes cultivars and seedlings flourishing in gardens across the South, waiting to be passed around to the next generation of folks who will appreciate them!
Even if you must go to some lengths to get a Rainlily in your garden, I highly recommend doing so! You’ll be rewarded with years of low-maintenance summer color after the dreariest of rainy days and will be able to pass these “flowers of the western wind” on to the next gardening generation. For more information on growing, sourcing, or propagating Rainlilies, check out this EDIS publication by Dr. Gary Knox of the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC) or contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office! Happy Gardening!

by Stephen Greer | Aug 11, 2021
One big goal of establishing a home lawn and landscape is to enjoy an attractive setting for family and friends, while also helping manage healthy soils and plants. Soil compaction at these sites can cause multiple problems for quality plants establishment and growth. Soil is an incredibly important resource creating the foundation for plants and water absorption.

Photo courtesy: Stephen Greer, UF IFAS
Soils are composed of many different things, including minerals. In Florida, these minerals often include sand of differing sizes and clay in the northern area of the counties in the panhandle of Florida. Soil is also composed of organic matter, nutrients, microorganisms and others. When soil compacts, the air spaces between the sand or clay are compressed, reducing the space between the mineral particles. This can occur anytime during the landscape and lawn construction phase or during long term maintenance of the area with equipment that could include tractors, mowers, and trucks.
What can be done to reduce soil compaction? There are steps that can be taken to help reduce this serious situation. Make a plan on how to best approach a given land area with the equipment needed to accomplish the landscape of your dreams. Where should heavy equipment travel and how much impact they will have to the soils, trees, and other plants already existing and others to be planted? At times heavy plywood may be needed to distribute the tire weight load over a larger area, reducing soil compaction by a tire directly on the soil. Once the big equipment use is complete, look at ways to reduce the areas that were compacted. Incorporating organic matter such as compost, pine bark, mulch, and others by tilling the soil and mixing it with the existing soil can help. Anytime the soil provides improved air space, root will better grow and penetrate larger areas of the soil and plants will be healthier.
Even light foot traffic over the same area over and over will slowly compact soils. Take a look at golf course at the end of cart paths or during a tournament with people walking over the same areas. The grass is damaged from the leaves at the surface to the roots below. Plugging these areas or possibly tilling and reestablishing these sites to reduce the compacted soils may be necessary.

Photo courtesy: Stephen Greer, UF IFAS
Water absorption is another area to plan for, as heavy rains do occur in Florida. Having landscapes and lawns that are properly managed allow increased water infiltration into the soil is critically important. Water runoff from the site is reduced or at least slowed to allow the nutrient from fertilizers used for the plant to have more time to be absorbed into the soil and taken up by the plants. This reduces the opportunity for nitrogen, phosphorus, and other nutrients to enter water areas such as ponds, creeks, lagoons, rivers and bays. Even if you are miles from an open water source, movement of water runoff can enter ditches and work their way to these open water areas, ultimately impacting drinking water, wildlife, and unwanted aquatic plant growth.
Plan ahead and talk with experts that can help with developing a plan. Contact your local Extension office for assistance!

by Daniel J. Leonard | Aug 5, 2021
The number one request all would-be gardeners and budding landscape enthusiasts have is “I want something that I don’t have to take care of, tolerates the heat, blooms, and comes back every year”. That is a tall order in our climate but not an impossible one, especially if one is willing to take a step back in time and consider an old Southern passalong plant, Garden Phlox (Phlox paniculata)!

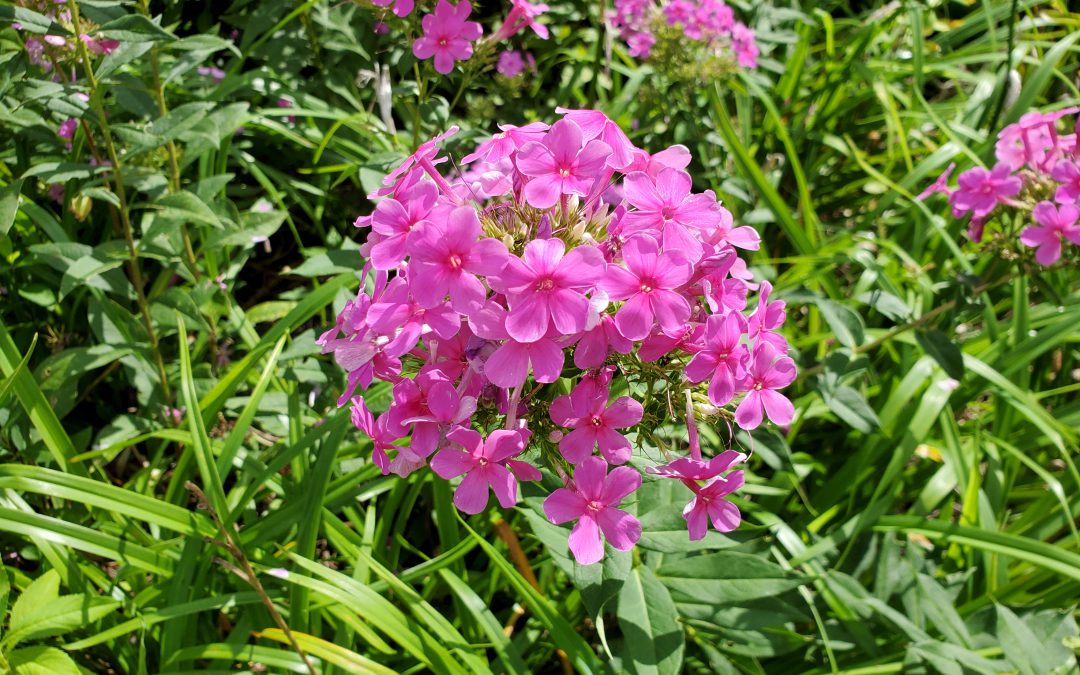
Garden Phlox (Phlox paniculata) in a Calhoun County landscape. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
This old heirloom perennial is an outstanding ornamental for Panhandle landscapes. Every spring, Garden Phlox emerges from a long winter sleep and shoots its attractive bright green foliage straight up, reaching 3-5’ in height. After hiding inconspicuously in the landscape all spring, Phlox then blasts into fiery magenta bloom during the heat of summer, beginning the show in late June. While individual Phlox flowers are only 1” wide or so, they are held prominently above the plant’s foliage in large clusters up to 8” in diameter and are about as eye-catching as flowers come. The flower show continues through July and August until finally fading out as fall rolls around. Plants then set seed and ready themselves for winter dormancy, repeating the cycle the following spring. A bonus, though individual Phlox plantings start off as small, solitary clumps, they slowly expand over the years, never over-aggressively or unwanted, into a mass of color that becomes the focal point of any landscape they occupy!
In addition to being gorgeous, Phlox is adaptable and demands very little from gardeners. The species prefers to be sited in full, blazing sun but can also handle partial shade. Just remember, the more shade Phlox is in, the fewer flowers it will produce. Site accordingly. Phlox is also extremely drought tolerant, thriving in most any semi-fertile well-drained soil. Though it can handle drought like a champ, Phlox will languish if planted in a frequently damp location. If water stands on the planting site for more than an hour or so after a big rain event, it is most likely too wet for Phlox to thrive. Once established, Phlox is not a heavy feeder either. A light application of a general-purpose fertilizer after spring emergence from winter dormancy will sustain the plants’ growth and flowering all summer long!

Clump of Garden Phlox in a Calhoun County landscape. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Though the ornamental and low-maintenance attributes of plain Garden Phlox make it sound like a perfect landscape plant, it is uncommon in the modern nursery trade, having fallen out of favor as many old plants often do. The species is still a familiar site around old home places, cemeteries, abandoned buildings, and the like throughout the South, but is difficult to find in most commercial nurseries. The primary reason for this is that the commercially available modern Phlox hybrids sporting exotic flower colors and shapes are not tolerant of our growing conditions. These new Garden Phlox hybrids were bred to perform in the milder conditions of more norther climes and are extremely susceptible to the many fungal diseases brought on by Florida’s heat and humidity of summer, particularly Powdery Mildew. It’s best to avoid these newcomers and stick to the old variety with its pink flowers and ironclad constitution. Plain old Garden Phlox can be found in some independent and native plant nurseries, but the best and most rewarding method of acquisition is to make friends with someone that already has a clump and dig up a piece of theirs!
If you have been looking for a low-maintenance, high impact perennial to add to your landscape, old-fashioned Garden Phlox might be just the plant for you! For more information on Garden Phlox, other landscape perennials, passalong plants or any other horticultural topic, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension Office. Happy Gardening!














