
by Ray Bodrey | Jul 29, 2021
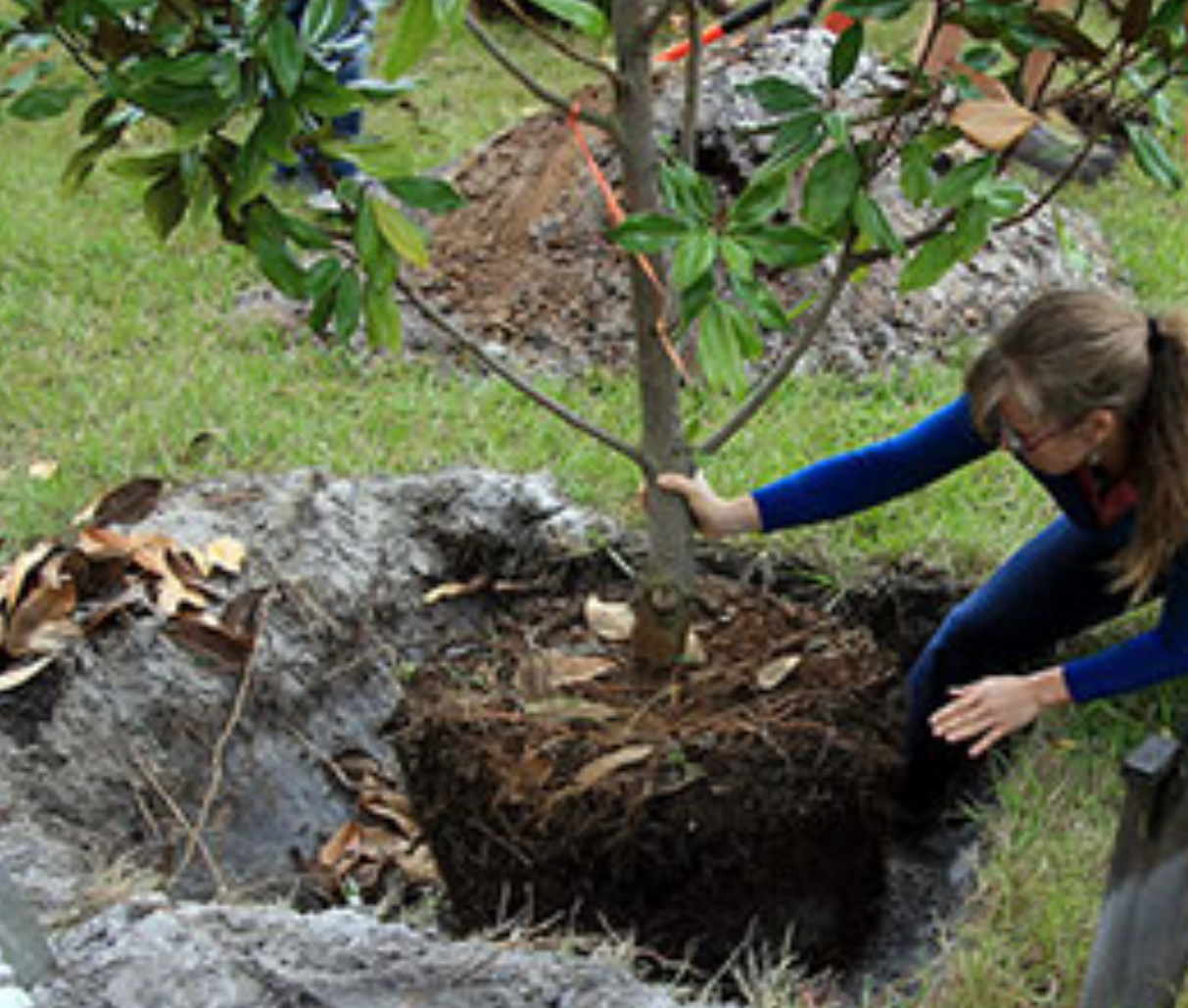
Need tips on planting and caring for trees? The primary focus in care of your newly planted tree is root development. It takes several months for roots to establish and newly planted trees and shrubs do not have a very strong root system. Start by digging the hole in a popcorn bowl shape. Once planted, backfill around the root system, but be careful not to compact the soil as this will hinder root growth. Be sure to keep the topmost area of the root ball exposed, about one to two inches. A layer of mulch will be applied here.
Frequent watering is much needed, especially if you are planting in the summer. Water thoroughly, so that water percolates below the root system. Shallow watering promotes surface root growth, which will make the plant more susceptible to stress during a drought. Concentrate some of the water in a diameter pattern a few feet from the trunk. This will cause the root system to grow towards the water, and thus better establish the root system and anchor the tree.
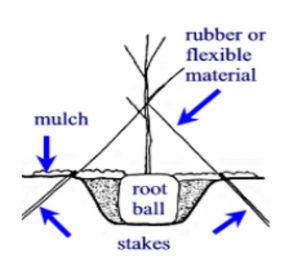
Figure: A Traditional Staking Option. Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS Extension.
Mulch is important in the conservation of soil moisture. Pine needles, bark, wood chips, and other organic materials make a great mulch. A three inch layer of mulch will usually suffice. It’s important to keep the mulch a few inches from the trunk as mulching too close to the tree trunk can cause rot.
You should always prune the bare roots of trees during planting. These exposed roots in containers can be damaged in shipping and removing some of the roots will help trigger growth. Pruning some of the top foliage can also reduce the amount of water needed for the plant to establish, as well. Trees and shrubs grown and shipped in burlap or containers usually need very little pruning.
Newly planted trees often have a difficult time establishing if the root system cannot be held in place. Strong winds and rain can cause the plant to tip over. Avoid this by staking the plant for temporary support. A good rule of thumb to determine staking need is if the trunk diameter measures three inches or less, it probably needs some support! Tie the stake to the plant every six inches from the top. However, only tie the trunk at one spot. Don’t tie too tightly so that the tree has no flexibility. This will stunt the growth of the tree.
Following these tips will help ensure your tree becomes well established in your landscape. For more information please contact your local county extension office.
Information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publication: “Planting and Establishing Trees” by Edward F. Gilman and Laura Sadowiski: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf%5CEP%5CEP31400.pdf
Supporting information also provided by UF/IFAS Extension Forestry Specialist Dr. Patrick Minogue, of the North Florida Research Education Center in Quincy, Florida.

by Larry Williams | Jul 15, 2021
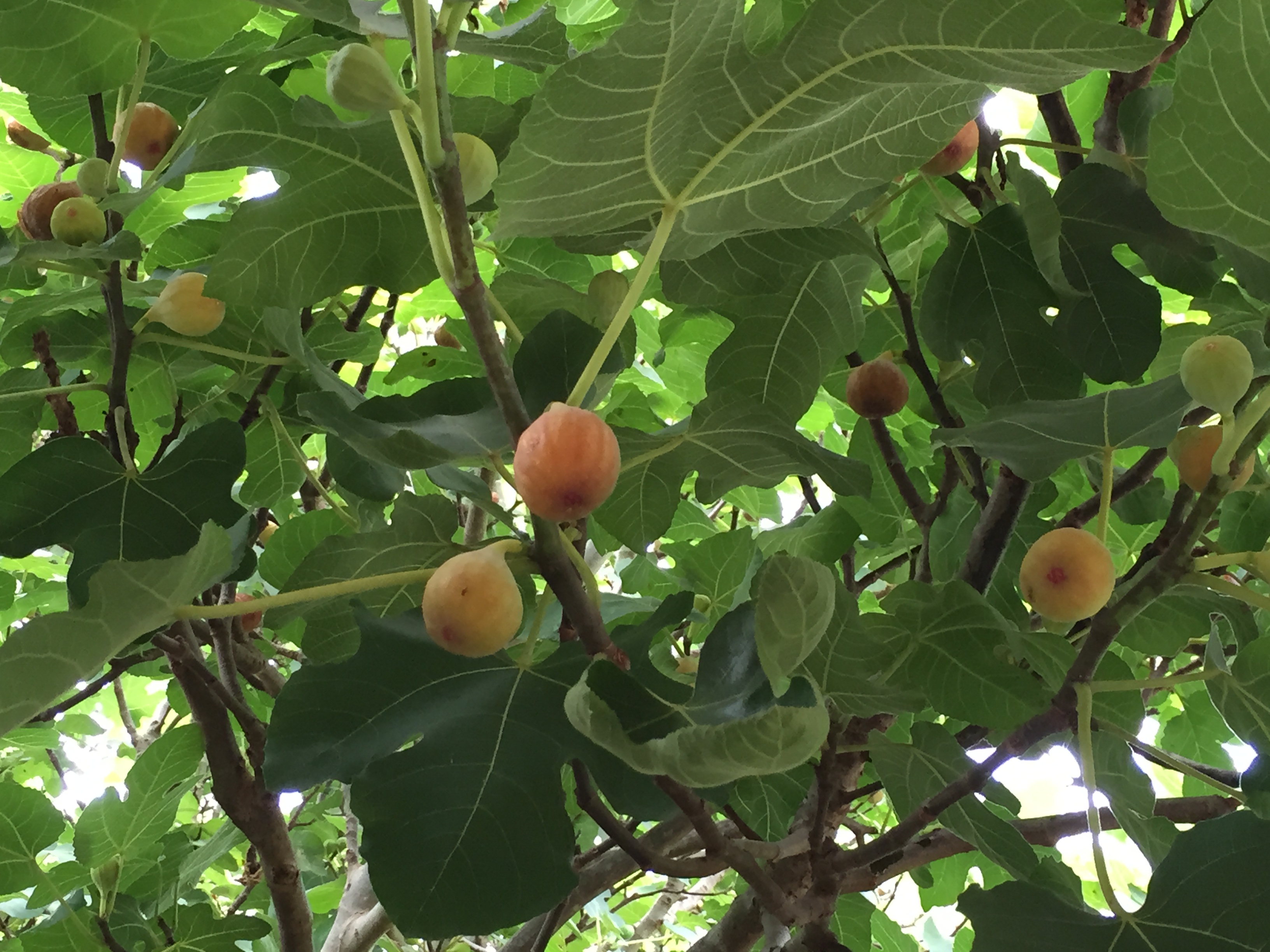
Q. One of my two fig trees has produced a few figs. The other one, which is the largest and healthiest tree, has never had a fig on it. Both where planted six years ago. Why is it not producing?

Mature fig tree with fruit. Photo credit: Larry Williams
A. It may be a matter of age and being overly vigorous. When a fruit tree is younger, it puts most of its energy into producing leaves and shoots. Until the plant becomes mature and slows down in the production of leaves and shoots, it will produce few to no fruit. It may take a year or two more for your tree to slowly and gradually switch from producing mostly leaves and shoots to producing and maturing some fruit. Patience is needed.
Be careful to not overdo it in fertilizing and/or pruning your fig tree. Too much fertilizer, especially nitrogen, or severely pruning the tree will result in the tree becoming overly vigorous at the expense of setting and maturing fruit. This includes fertilizer that the tree may pull up from a nearby lawn area. A tree’s roots will grow outward two to three times beyond its branch spread into adjacent lawn areas.
The end result of being heavy handed with fertilizing and/or overdoing it in pruning is the same – it forces the plant to become overly vigorous in producing leaves and shoots at the expense of producing and maturing fruit.
In addition, the following is taken from an Extension publication on figs and includes the most common reasons for lack of fruiting, in order of importance.
- Young, vigorous plants and over-fertilized plants will often produce fruit that drops off before maturing. If plants are excessively vigorous, stop fertilizing them. Quite often, three of four years may pass before the plant matures a crop because figs have a long juvenile period before producing edible quality fruit.
- Dry, hot periods that occur before ripening can cause poor fruit quality. If this is the case, mulching and supplemental watering during dry spells will reduce the problem.
- The variety Celeste will often drop fruit prematurely in hot weather regardless of the quality of plant care. However, it is still a good variety to grow.
- An infestation of root-knot nematodes can intensify the problem when conditions are as described in item 2.
- You could have a fig tree that requires cross-pollination by a special wasp. This is a rare problem. If this is the case, then it will never set a good crop. The best way to resolve this is to replace the plant with a rooted shoot of a neighbor’s plant you know produces a good crop each year.

by Stephen Greer | Jul 1, 2021

Photo Courtesy: Stephen Greer
Lawn areas come in all sizes and shapes. Some are large open expanses providing long views and others are smaller versions surrounded by shrubs and trees creating a more private and secluded setting. There are a number of reasons for reducing the size of a lawn with some coming into play with your decisions. A home lawn is often an important part of the landscape that provides a place to play outdoors from picnicking, tossing the ball to taking a quite stroll.
Maintaining a healthy lawn is important to an overall performance of this part of the landscape. Several factors are involved in the success in keeping a strong and resilient lawn. Understanding the needs of a grass to remain healthy involve soil testing to address soil pH and nutrient needs plus water challenges. Misuse of fertilizer and over irrigation can be costly to you and to the overall health of the lawn. These decisions can lead to reducing lawn size to managing cost or removing underused areas.
There are big benefits to reducing your lawn from saving time in mowing, trimming and other manicuring needs to saving energy costs involving the lawn mower not to mention reducing pollution from the mower or weed eater. The reduced amounts of pesticides needed to manage weeds and disease to the lawn saves time and money.
Another way to look at the reducing the size of our lawn is there will be more space for expanding plant beds and potential tree placement. These settings increase the opportunities for a more biodiverse landscape providing shelter, protection and food options for birds and other wildlife.

Photo Courtesy: Stephen Greer
The lawn can serve as a transition space that leads from one garden room space to another, while still offering a location to bring the lawn chair out to enjoy all that is around your lawn. Lawns and the landscape are ever changing spaces, especially as your trees and shrubs grow and mature to sizes that can directly impact the lawn performance. Often levels of shade will diminish edges and other areas of the lawn. This often will define the reduction of the lawn size moving going forward. Just remember that lawns and landscapes occupy a three-dimensional space involving the horizontal, vertical and overhead spaces. Just look around and think about what is best for you, your family and the setting.Are you more interested in developing other parts of the landscape? With many of us spending more time at home over the last year plus it gave time to think about the outdoor areas. Growing our own vegetables may be a new or expanding part of the landscape with the use of raised beds or interplanting into the existing landscape. Gardening can assist in reducing stress while at the same time providing that fresh tomato, lettuce, herbs and other fun healthy produce.
What ever your decisions are enjoy the lawn and landscape. For additional information, contact your local University of Florida IFAS Extension office located in your county.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jun 24, 2021
Nutsedge, commonly called “nutgrass”, is one of the most important and difficult to control weed pests in the world. Found in nearly every growing situation, from crop fields and vegetable gardens to landscapes and turfgrass lawns, I bet every person reading this has contended with controlling nutsedge at some point! Nutsedge (a common term to describe several species of weeds in the genus Cyperus) not only reduces curb appeal, but also h as a detrimental effect on desirable plantings around it. Because of its aggressive nature and dense root system, it competes heavily with “good” plants for water, light, and nutrients, causing the plants we are trying to grow to suffer. This is a weed that you definitely do not want in your lawn or landscape!
To keep nutsedge at bay, it’s important to know a few facts about it. First, “nutgrass” is not a grass at all, but a totally different class of plants known as sedges. This is important because selective herbicides used to kill grassy weeds will not affect nutsedge. Though they’re grass look-alikes, sedges can be distinguished by their distinctive triangular shaped stems. You can actually feel the three edges of nutsedge stems. If ever in doubt over whether a weed is a grass or a sedge, remember “sedges have edges”. Most sedges are perennials, dying back to the ground each year in winter and reemerging from tubers, called “nutlets”, that can survive over a foot under the ground! Also, while sedges generally prefer wet areas, they aren’t very particular about where they grow and are equally at home in sand or clay, wet or dry, and sun or shade. All these characteristics make sedges hard to control and cause much consternation amongst gardeners!
The first line of defense in controlling nutsedge is keeping a dense cover over any bare ground. In lawns, this means maintaining a thick, healthy turf as weeds love to enter lawns through thin or patchy areas. This can be accomplished by mowing regularly, fertilizing appropriately based on a soil test, not overirrigating while also not allowing the grass to suffer badly during droughty periods. Easier said than done. In landscape beds, preventative control is a little easier. First, as nutsedge prefers wet areas, only irrigate when it is needed. During much of the year, most established landscapes can get by on rainfall alone. Next, simply maintain a roughly 3” layer of pine straw, wood chips, pine bark, or other natural mulch of your choice. Doing so will reduce all manner of weeds, nutsedge included, and is generally beneficial for ornamental plants as well! I do not recommend landscape fabric as it is a pain to install and remove and is not extremely effective at reducing nutsedge as the sedge’s sharp growing points punch right through most plastic or fabric mulches.
Though mulching and other preventative measures can reduce nutsedge numbers, those methods alone are usually not enough and chemical herbicides are required. Fortunately, in Panhandle lawns and landscapes, there are several excellent, readily available options for sedge control: imazaquin and halosulfuron.
- Imazaquin is the active ingredient in the common product Image Kills Nutsedge and has good activity on most sedge species. It can be applied safely to all the common turfgrass species grown in the area and can even be sprayed right over the top of most common ornamental landscape plants!
- Halosulfuron is the active ingredient in the product Sedgehammer (available online or at specialty landscape supply stores) and several other generic products. Halosulfuron products provide excellent control of all nutsedge species and are safe to use in all turfgrass species found in Florida. While most landscape plants are tolerant of halosulfuron application, use care and try to only spray it on sedge weeds to avoid any unwanted yellowing or damage.
While both products begin working immediately, it may take several weeks to see sedge weeds start suffering and patience is necessary! Though both products are effective, follow up applications 3-4 weeks later are generally necessary to clean up any surviving sedge.
Nutsedge is a nasty little weed that can be difficult, though not impossible to manage. Through some smart cultural practices and timely applications of either imazaquin or halosulfuron, you can keep your lawn and landscapes nutsedge free! For more information about nutsedge control on your property or any other agricultural or horticultural topic, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension office! Happy Gardening!

by Evan Anderson | Jun 24, 2021
There are lots of plant pests out there, and it can take a trained eye to tell which one is doing damage. Many of the insect pests that feed on crops and ornamentals have piercing-sucking mouthparts. These insects do not chew on leaves and leave holes behind; instead, they have a long stylus-like mouthpart they use like a straw to suck out plant juices. Over time this can weaken plants, cause irregular growth as damage builds up on new sprouts, introduce diseases to their hosts, and even cause mold to grow on leaves.
Because they drink so much fluid for their meals, many piercing-sucking insects exude a sugary liquid called honeydew. This liquid drops onto stems and leaves below which can leave them shiny and sticky. Eventually, the coating will grow a light greyish coating of sooty mold, which doesn’t do much harm to the plants itself but is a good indicator that you have an insect problem. You may also notice ants on your plants, working to harvest the honeydew for food. The ants don’t harm the plant, but following are some of the pests that do:

Aphids feeding on a plant stem.

A parasitic wasp emerging from a dead aphid.
Aphids – Found on a wide variety of plants, aphids are fat-bodied little insects that often focus on new, tender growth. Their color depends on the plant they’re feeding on, and they can breed explosively. A female aphid does not need to mate to produce offspring, so a one can produce a lot of children very quickly. Look closely and you might be able to see their cornicles, which look like little tailpipes; these can help identify these pests. Luckily, we have some help in controlling aphids, as they are often parasitized by wasps. If you see large, swollen, brown aphids present, you probably have some wasps working for you.

Ants tending some scale insects on a stem.
Scale Insects – Sometimes appearing to just be a bump on a stem or leaf, scale insects don’t move once they pick a plant to live on. Prolific producers of honeydew, some species grow a waxy shell which can protect them and make them difficult to deal with.

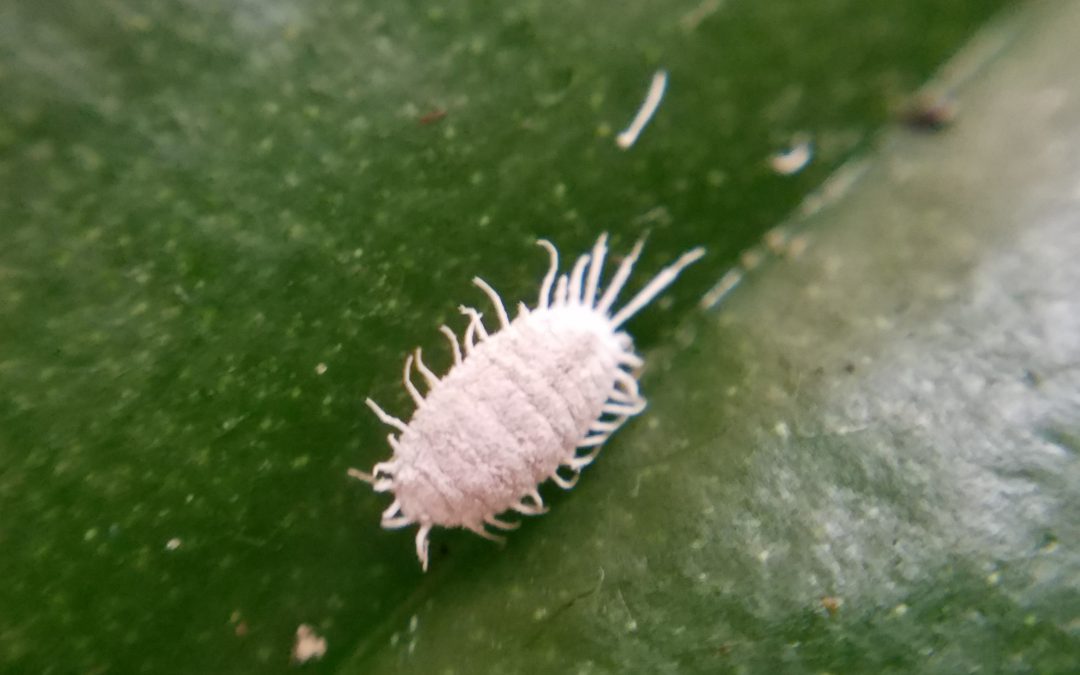
A mealybug.
Mealybugs – If you spy something white and fluffy living on stems or leaves, you might have mealybugs. Soft-bodied insects that are related to scales, they don’t move much. They feed on a wide range of host plants, but can effectively be controlled with a variety of methods once they’re found.

Whiteflies on the underside of a leaf.
Whiteflies – Not true flies, they are truly white in color. Tiny little members of the order Hemiptera (the same order that includes, aphids, scales, and mealybugs), they hang around the undersides of leaves. They enjoy warm weather and can become a problem in greenhouses. They are a bit more difficult to control than some of the other pests listed here.

A psyllid nymph hiding in its waxy coating.
Psyllids and planthoppers – Small jumping insects that affect a variety of plant species, some are responsible for transmitting important plant diseases. Pierce’s disease of grapes and citrus greening, for example, are both vectored by these critters. Young nymphs sometimes secrete a waxy coating which may make them look similar to mealybugs.

A tiny two-spotted spider mite.
Spider Mites – Not an insect but an arachnid, spider mites love hot, dry weather. Almost microscopic in size, the damage they do to leaves is often the first sign that they are present. Looking closely, one might notice tiny webbing where the mites live, or even the mites themselves on the undersides of leaves and on stems.
Many of these pests can be treated with a combination of methods. A sharp jet of water can dislodge some, hand removal can reduce populations even more, and products such as insecticidal soap or horticultural oils can finish them off. Insecticidal soaps are best used on soft-bodied insects such as aphids or mealybugs, while oils such as neem can help suffocate hard scales. Use products such as horticultural oil in the evening during hot weather to avoid damaging plant tissues with intense sunlight. Thorough coverage is important, as these products only control the pests they contact.
For more information on controlling insects, see our EDIS publications, such as Insect Management in the Home Garden or Landscape Integrated Pest Management.
















