by Ray Bodrey | May 4, 2018

Figure 1: Florida Betony, Stachys floridana. Credit: UF/IFAS Range Cattle Research & Education Center.
If you look closely at your yard, there is a good chance that you will find a plant that, depending on who you ask, is considered either a native wildflower or a weed and there are more than a few species that fit this description. If, upon even closer inspection, you find a plant with root tubers that resemble egg casings or even a rattlesnake’s rattle, you’ve stumbled upon Florida Betony.
Stachys floridana is a perennial broadleaf commonly referred to as rattlesnake weed due to it’s fleshy, white, segmented underground tubers. The plant has an erect stem with leaves that are opposite, shovel-shaped and coarsely serrated. The plant structure is very similar to mint. Flowers, emerging in late spring, are pinkish-purple in color. These inflorescences will also produce fruit, consisting of four nutlets. However, reproduction of the plant and it’s propensity to spread through lawns and gardens primarily occurs through dense root tuber development. Florida Betony’s growing range was originally confined to the state of Florida, but the commercial nursery trade played a major hand in dispersing the plant across the Southeast in the mid-1900’s. It can now be found as far west as Texas and as far north as North Carolina.

Figure 2: Tubers of the Florida Betony. Credit: Jill Bebee, UF/IFAS Gulf County Master Gardener.It can now be found as far west as Texas and as far north as North Carolina.
This time of year is when Florida Betony thrives. The moderate temperatures of fall and spring are the prime growing periods for Betony. In the heat of the summer, the above-ground structure of the plant will struggle and often disappear completely, only to reemerge in the fall. As a lawn weed, managing tuber development is key to controlling this plant. Applying herbicide to the leaves and stalk may seem at first to have conquered the weed. However, in most cases the tuber will simply regenerate. Glyphosate (Roundup) can be used effectively for control in ornamental plant beds where no turf is present. Be careful when spraying herbicides around trees, shrubs and other desirable plants as any foliar contact will cause phytotoxicity. If you have an infestation of Florida Betony in your turfed areas, there are a few options for control. Regular applications of three way broadleaf herbicides, such as mixtures of 2-4D, Dicamba and Mecoprop, are effective at suppressing this pesky plant. For more information and options, please contact your local county extension office or see the supporting information links below. Always refer to the product label for specific uses, precautions and application rates when using any herbicide.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the following the UF/IFAS EDIS publication, “Florida Betony Biology and Management in Turf” by J. Bryan Unruh, Ramon G. Leon, and Darcy E. P. Telenko: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP38800.pdf
by Larry Williams | Apr 16, 2018

Cold injury to lawn. Photo Credit: Larry Williams
Patience, warmer soil temperature and correct lawn management will solve many spring lawn problems.
Many spring dead spots in lawns are caused by something that happened the previous growing season or winter. For example, a late application of a high-nitrogen fertilizer can decrease winter survival. It’s best to not fertilize our lawns after early September.
An insect or disease problem during fall many times goes unseen as the grass is beginning to go dormant. The following spring, as the lawn begins to green up, evidence of a fall pest is clearly visible by brown dead, grass. The pest may not be present or active during spring.
Poor maintenance practices may be to blame for spring dead spots. Over-watering, shallow watering (watering frequently for short periods), mowing too low, too much fertilizer and herbicide injury can result in poor lawn performance come springtime.
Regardless of cause, problem areas within lawns are slow to recover during spring due to frequent cool night temperatures. Frequent cool nights keep the root zone cool.
Cool soil temperature doesn’t allow rapid root regeneration in spring, which inhibits top growth in your lawn. Cool soil also decreases availability of some needed nutrients. For example, poor availability of iron because of cool soil is a common cause for bright yellow areas within lawns, especially in centipedegrass. Cool soil also decreases availability of phosphorus and potassium, which can result in reddish-purple grass blades, intermingled throughout the yard. As soil temperature increases, availability of nutrients improves and the yellow and purple areas turn green.
Have patience with your lawn and follow good maintenance practices this spring. Provide ½ to 1 inch of water when the grass shows signs of wilt. Fertilize and lime based on the results of a reliable soil test. And, mow at a high setting. Good lawn maintenance info is provided at the YourFloridaLawn website.
Consistently warmer nights will allow the soil temperature to warm, which will improve turf root growth, nutrient availability and lawn recovery. During many years in North Florida, it’s well into the month of May before our lawns begin to recover.
If the lawn has not made a comeback by late spring or early summer, it may be time to consider reworking and replanting the dead areas or maybe consider replacing them with something other than grass, if practical.

by Ray Bodrey | Mar 21, 2018
I imagine many of you have had plant loss due to this recent cold snap. Like myself, you’ll be busy this spring replanting areas. Want to have a more sustainable landscape and attract birds & butterflies? Consider a Florida-Friendly Landscape.

Figure 1: Florida-Friendly Landscaping.
Credit: Tyler Jones, UF/IFAS Communications.
So, what is “Florida-Friendly”? These are plants that are either native to Florida or non-invasive species, and are low maintenance. One can convert their landscape to “Florida-Friendly” simply by changing the way you take care of your yard. A Florida-Friendly Landscape has 9 major principles:
- Right plant, right place – Select plants that match a site’s soil, light, water, and climatic conditions. Buy quality plants that welcome wildlife, consider plant size when you make your purchase, and aim for a diversity of trees, shrubs, groundcovers, and flowers.
- Water efficiently – Watch for signs of wilt before you irrigate, be a weather watcher (don’t irrigate if it’s going to rain), and water early in the morning if you can, following any restrictions in your area. Check your irrigation system regularly; repair any leaks, clogs, or breaks; and make sure all sprinklers are irrigating your plants, not the sidewalk!
- Fertilize appropriately – Fertilize according to UF/IFAS recommended rates and application timings to prevent leaching—fertilizer leaking down through the soil rather than being absorbed by plant roots. Look for fertilizers with slow-release nitrogen and little or no phosphorous, unless your soil test indicates need (as many Florida Panhandle soils are phosphorous poor). Never fertilize within 10 feet of any water body, and don’t fertilize before a heavy rain.
- Mulch – Retains soil moisture, protects plants, and inhibits weed growth. It gives your landscape a neat, uniform appearance and is a great Florida-Friendly choice for hard-to-mow slopes and shady spots. Keep a 2- to 3-inch-deep layer of mulch on plant beds. Always leave at least 2 inches of space around tree trunks to prevent rot. Create self-mulching areas under your trees by letting fallen leaves lie.
- Attract wildlife – By providing food, water, and shelter for birds, butterflies, bats, and others, you can help these displaced Floridians while bringing beauty and benefits to your home landscape. Select plants with seeds, fruit, foliage, flowers, or berries that animals can eat.
- Manage yard pests responsibly – Concerns for human and environmental health have led scientists to recommend Integrated Pest Management (IPM), a strategy that helps gardeners manage pests with as few chemicals as possible. Don’t treat by default—some of the insects you see may be beneficial, actually helping to control pest insect populations. Spot-treat only, rather than blanket spraying, and use selective rather than broad-spectrum insecticides.
- Recycle – Landscape maintenance activities like mowing, pruning, and raking generate yard waste that you can recycle to save money. Decomposed organic matter, like pruned branches or grass clippings, releases nutrients back to the soil in a form that plants can easily use. Try composting, combining “green” (nitrogen-rich) and “brown” (carbon-rich) materials, such as grass clippings, weeds, plant trimmings, egg shells, coffee grounds, tea bags, twigs and branches, pine needles, corncobs, and shredded cardboard.
- Reduce Stormwater – Florida’s waterways are vulnerable to everything we put on our home landscapes. Fertilizers and pesticides can leach through the soil or run off into storm drains. Along with landscape debris and eroded soil, these can wreak havoc on our water quality and the fragile ecosystems our water resources support. Creating shallow rain gardens, or shaping the earth on slopes with berms (rises) and swales (dips), can help slow runoff from heavy rains and allow the water time to soak into the ground. Make sure your downspout is pointed into the garden, not towards a sidewalk or driveway. Wherever possible, maintain permeable walkways, driveways, and patios of brick, gravel, earth, or crushed shell, to allow rain to soak into the ground.
- Protect the waterfront – Florida boasts over 10,000 miles of rivers and streams, about 7,800 lakes, more than 700 freshwater springs, and the U.S.’s second-longest coastline. Even if you don’t live immediately on one of these water bodies, you do live in what’s known as a watershed (a drainage area). What you do in your home landscape has much further-reaching consequences than you might think. One of the most important steps you can take to protect any water body is maintaining a 10-foot “maintenance-free zone” around it. Do not mow, fertilize, or use pesticides in this zone. A stormwater pond or canal can become an aesthetically pleasing and lively place, edged with plants and home to wildlife. Work with your neighbors or homeowner association to make your stormwater pond a Florida-Friendly neighborhood amenity.
For more information on Florida-Friendly Landscaping please contact your local county extension office.
The information for this article can be found in the following the UF/IFAS publication, “The Florida Yards & Neighborhoods Handbook”: & website.

by Mary Salinas | Aug 25, 2017
After you have chosen the right fertilizer, fungicide, herbicide or insecticide to apply to your landscape, the question becomes: how much do I buy? Labels on these products will tell you how many square feet it will cover – so that leads to the next question: how many square feet of lawn do I have?
Here’s an easy way to determine your square footage. This online tool from Sod Solutions uses GIS mapping to figure it out from the comfort of your lounge chair.
On this front page, search for your address.
A bird’s eye view of your property comes up. Zoom in by using the + sign in the lower right corner of the screen.
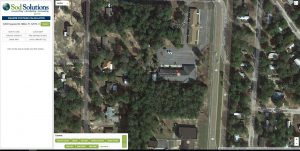
Plot points on the area you want to measure. This makes it so easy to measure those curved and odd-shaped areas!

The calculation of the area in square feet, yards, and acres is displayed on the left side. The perimeter is also calculated; that might be handy for determining the length of a fence line.
For more information:
Your Florida Lawn website
The Florida Fertilizer Label
Interpreting Pesticide Label Wording
by Mark Tancig | Apr 24, 2017

Source: UF/IFAS.
Impatiens are a very popular annual, bedding plant that provide a nice burst of color in the landscape. The traditional Impatiens (Impatiens walleriana), or touch-me-not, is the one that most gardeners know as needing part shade, but there are also the New Guinea Impatiens (Impatiens hawkeri) that are able to tolerate more sun. In addition to being able to withstand more sunlight, the New Guinea Impatiens also have larger flowers and leaves. Another highlight of the New Guinea impatiens is their increased resistance to downy mildew, a major concern for growers of touch-me-nots, especially in south Florida.
While native to the Old World, Impatiens are not known to invade Florida natural areas but may reproduce by seed. Touch-me-nots are known to spread easily be seed. An interesting fact about Impatiens is their bursting seed pods that can send seeds several feet from the parent plant. This characteristic is what led to the scientific name Impatiens – for impatient – and one of the common names – touch-me-not.
May is a good time to plant Impatiens in north Florida. They prefer slightly acidic soil and should be planted at a 12-18 inch spacing. Impatiens work well as a border planting or in mass plantings. While New Guinea Impatiens tolerate more sun, they still would prefer some afternoon shade. Those growing in full sun will need extra care to ensure they remain well watered. An all-purpose plant food can be applied at monthly intervals for best performance.
Some common varieties of touch-me-nots include ‘Accent’, ‘Blitz’, ‘Carousel’, ‘Dazzler’, ‘Impact’, ‘Impulse’, and ‘Super Elfins’. Common New Guinea Impatiens varieties include ‘Celebration Candy Pink’, ‘Celebration Light Lavender’, ‘Nebulus’, ‘Equinox’, ‘Sunglow’, and ‘Tango’. The newer ‘Sunpatiens’ variety is quite popular and comes in different forms – compact, spreading, and vigorous.

Source: UF/IFAS.
If you have any questions regarding Impatiens, please contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office or visit our EDIS website at www.edis.ifas.ufl.edu.











