by Sheila Dunning | Nov 11, 2013

It doesn’t take expert gardeners or landscapers to create a Florida-friendly yard. All it takes is a willingness to learn and a desire to build a beautiful yard that helps protect Florida’s environment. Florida-friendly landscaping is now part of state law. Florida Statute 373.185 prohibits government entities and homeowners associations from enacting or enforcing any governing document to prevent homeowners from implementing Florida-friendly landscaping (FFL) principles. A guideline to ease the development of a manual can be found at this link on the Florida Yards and Neighborhoods website. “Florida-Friendly Landscape Guidance Models for Ordinances, Covenants, and Restrictions.”  Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device.
Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device.
 Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.
Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.

by Carrie Stevenson | Oct 7, 2013
After severe weather of any kind, homeowners must often spend a considerable amount of time dealing with impacts to their landscapes. Below are a few lessons we have learned from hurricanes and tropical storms in the past. Many thanks to fellow agent Beth Bolles for her contributions to this article.
Dealing with Toppled Trees
It may be difficult to turn an uprooted favorite tree into firewood, but this is probably the best choice. A small or young tree may be replanted successfully if done immediately. These trees will require bracing for up to two years until the root systems regrow and are able to support themselves. If the roots have been exposed for an extended period of time, don’t try and save the tree. Exposed roots should be covered with soil or moist burlap for protection from drying out. Large or older trees will typically not survive this ordeal even with the best of care. Because the root system is compromised, attempting to keep the tree may create a hazard down the road with the next storm.

If a tree is completely uprooted, its odds of recovery are severely limited and it is best to remove the tree. Photo courtesy Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension
When removing fallen trees, think ahead about whether you plan to remove stumps. It’s a lot easier to pull instead of dig stumps out of the ground, so leave a four-foot stump to make your life easier. Be careful using power equipment like chain saws. It may be better to hire a professional to deal with removing large trees, especially around power lines.
Exposed Roots or Leaning Trees
Any exposed roots should be covered immediately. Cover roots with nearby soil at the same level roots were originally growing. Do not bank the soil higher because this will cut off oxygen supplies to roots in an already oxygen deprived, saturated soil.
If small trees are leaning and need straightening, they can be staked and treated like a newly planted tree. Larger trees with trunks greater than six inches in diameter can be saved but should be removed if they are a hazard to structures, power lines, or roadways. Reset the trees with stakes or guy wires for support. Trees with trunks measuring less than two inches in diameter can be supported with two or three forty-eight inch, two inch by two inch wood stakes placed one foot outside of the root ball inserted eighteen inches into the ground. Larger trees should be anchored with three or four guy wires or cables. Cover guy wires that are in contact with the trunk with rubber hoses to prevent damage.

A leaning, partially uprooted tree may recover if it is righted and its roots are covered back with soil. Photo courtesty Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension
Replace the soil around the area and firm to assure there are no air pockets around the roots. Make sure the top root coming off the trunk is level with the existing soil. If many trees were swaying back and forth during the wind, there may be air pockets underneath the trees. If this is obvious, add soil and water to eliminate any air pockets. If root damage is obvious, do not fertilize at this time because salts in the fertilizer may damage new feeder roots.
Broken Branches
Broken branches should be removed from trees and shrubs as soon as possible to prevent tearing into trunk wood. Make clean cuts just outside of the branch collar to avoid damaging the trunk. If these are large branches, make three separate cuts to prevent tearing. Make the first cut on the underside of the branch about fifteen inches from the trunk and one-third through the branch. The second cut is made from the top, a few inches out from the first cut. This cut should remove the weight of the branch so the next one will not rip the trunk. The remaining stub can be held while the last cut is made. Make the last cut just outside the branch bark ridge and end outside the trunk collar (swollen area on lower side of branch). This is not a flush cut with the trunk and should leave a small protrusion on the trunk. Do not use wound dressing on the cut surface, as this practice is no longer recommended.
If trees lost all of their branches, it is advisable to remove the tree. The natural shape is gone and trees like pines will typically not recover. Some trees may lose the majority of their leaves, but these will flush back out so they should be okay.
Repairing Lawns
Keep a close eye on lawns for disease problems due to all the rain. Brown patch and take-all root rot would be the major concerns. Rake and remove all debris to give lawns a chance to dry out. If lawn areas are damaged, now is the time to replace with plugs or sod so they can establish before winter. Sod webworms are bad now so don’t mistake this damage for diseases. If adult moths are obvious and grass blades are closely cropped, this is due to caterpillar damage…not disease.
Watering
Most soils are saturated and irrigation systems should be in the off-mode. If there is standing water around trees or in other low areas, use a hose to siphon water to a retention pond or a better-drained area. Once soils dry out and the sun comes out, keep a close eye on plants as they may require more frequent irrigation because of root damage. Coastal areas flooded with saltwater may experience damage from extended exposure to high salinity; it is recommended to run a sprinkler system to flush out a lawn after the water retreats.
If you have questions, contact your local UF IFAS Extension Office!

by Carrie Stevenson | Jul 29, 2013
Few things move a local homeowner into action faster than a big storm moving into the Gulf of Mexico. After filling up at gas stations and running out to home improvement stores, many start trimming limbs and removing trees.
The destructive tornadoes in the Midwest this spring may cause anxiety about having mature trees in a yard. It is true that falling trees and limbs can cause damage to a home and property. However, it is wise to look closely at a landscape before making a permanent decision. It’s also important to do this before the stress of a looming storm is at hand. Trees are very important for providing shade (i.e. energy savings), wildlife habitat, storm-water management, and maintaining property values.
University of Florida / IFAS researchers have done long-term studies on the effects of wind on trees and landscapes, and several important lessons stand out. Keep in mind that reducing storm damage often starts at the landscape design / planning stage!

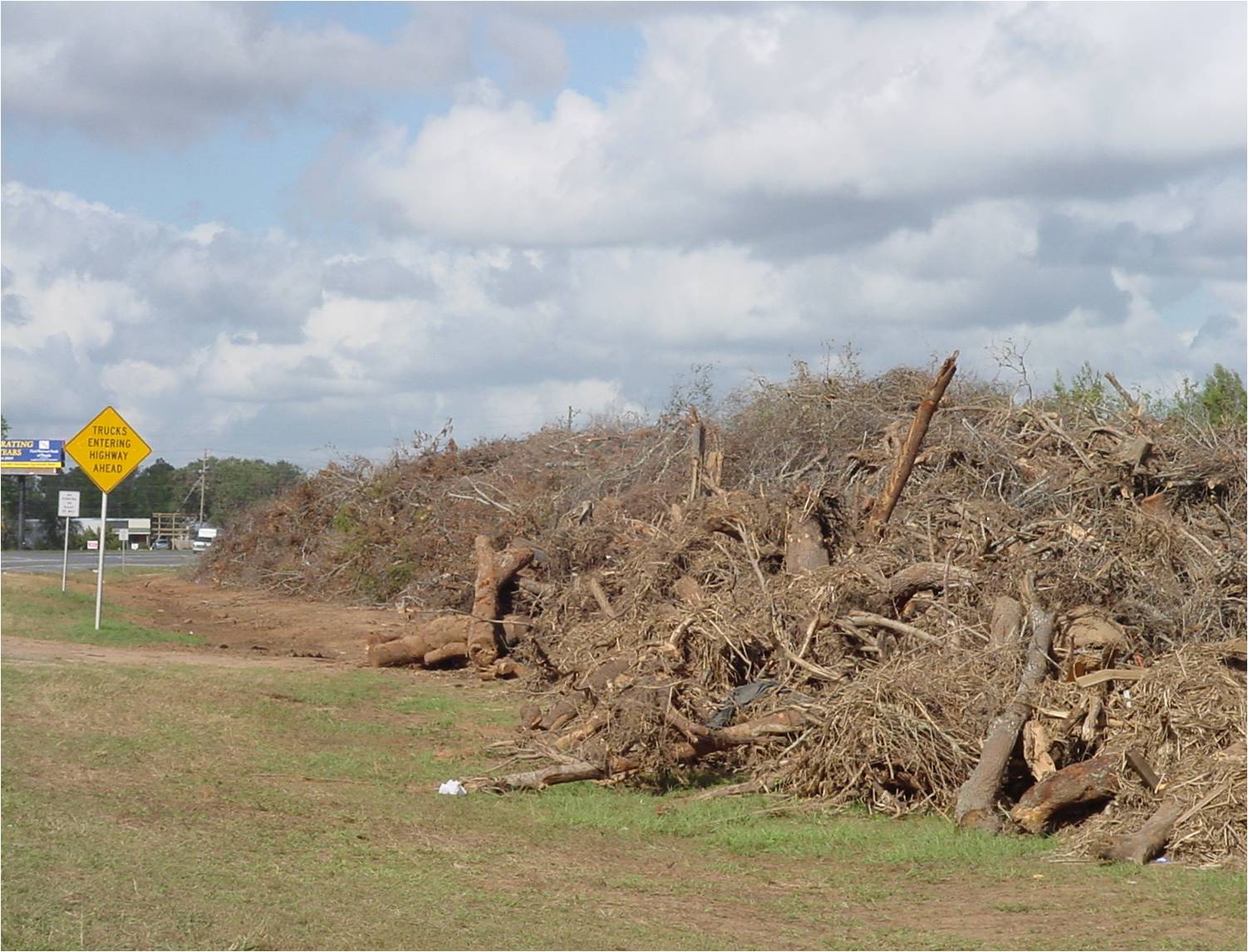
After a hurricane, piles of vegetative debris are common sights. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Below are several tips for protecting your home and landscape in case of a storm.
- Plant high-quality trees with single trunks and strong branches. Branch attachment angles can affect whether a large branch will split from a tree. Branches angling straighter out from a tree (wide angles) are stronger than those pointing almost directly up (tight angles).
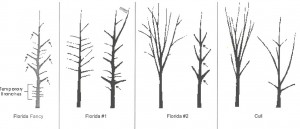
“Florida fancy” is the best quality of tree, with quality decreasing to “cull” level. Notice the difference in branch angles and direction between each group. Figure courtesy FDACS, Division of Plant Industry
- Trees that have had regular pruning are less likely to fail than neglected trees. The UF horticulture website has detailed information on correct pruning, or you can contact your County Extension Agent for tips.
- Post-hurricane studies in North Florida show that Live Oak, Southern magnolia, Sabal Palm, and Bald Cypress stand up well compared to other trees during hurricanes. Pecan, Water and Laurel Oak, Carolina Cherry Laurel and Sand Pine were among the least wind resistant. UF has a list of trees and their hurricane endurance based on a study conducted after the 2004 hurricane season.

The classic Southern magnolia tree earns high marks in wind resistance. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
- Plant a variety of species, ages and layers of trees to maintain diversity in the yard and neighborhood.- Trees with decayed trunks are very dangerous in winds. Disease causing decay can come up from the roots or enter through improper pruning cuts. Remove hazard trees before the wind does. Have a certified arborist inspect trees for signs of disease and decay. They are trained to provide advice on tree health.
- Watch pines carefully. Sometimes there is hidden damage and the tree declines over time. Look for signs of stress or poor health, such as unusual dark stains or small holes on trunks, dropping leaves, or piles of sawdust at the tree’s base. Check closely for insects. Weakened pines may be more susceptible to beetles and diseases. Long-leaf pines often survive storms in our area better than other species.
- Trees in a group (at least five) blow down less frequently than single trees.
- Trees should always be given plenty of room for roots to grow. Roots absorb nutrients, but they are also the anchors for the tree. If large trees are planted without enough space for roots to grow out in all directions, there is a likelihood that the tree may fall during high winds.
- Construction activities within about 20 feet from the trunk of existing trees can cause the tree to blow over more than 10 years later.
- When a tree is removed or dies, plant a new one in its place.

by Blake Thaxton | Jun 4, 2013

As of January 2014 all companies applying fertilizer, commercially “for hire”, will be required to hold a fertilizer applicators license. In order to obtain this license you must first become GI-BMP certified.
2014 isn’t that far away. Take the time to attend class this summer. Don’t wait to the last minute and have to scramble to find a training close to home.
What are Green Industries Best Management Practices?
GI-BMPs teach environmentally safe landscaping practices that help conserve and protect Florida’s
ground and surface waters and natural resources. This science-based educational program for
Green Industry professionals is brought to you by the UF/IFAS Florida-Friendly LandscapingTM
program and the Florida Department of Environmental Protection. Other FAQs about GI-BMPs
June 28th – Santa Rosa County
Navarre Community Center: 1917 Navarre School Rd Navarre, FL 32566
For more information email Blake Thaxton at bthaxton@ufl.edu
 Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device.
Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device. Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.
Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.









