
by Blake Thaxton | May 17, 2016
In the last few weeks, more garden pests have arrived! It is a fact of life in northwest Florida that we will have a few things in our garden including heat, moisture (humidity and rainfall), and BUGS! With a cooler spring the arrival of some of the troublesome pests in the garden seemed to be delayed a few weeks. It was nice while it lasted but the insect pests are here to stay until frost in the fall or winter (at least we hope for a frost this year).
There are thousands of insects that you can see in your garden. It’s wise to identify them before making a decision to spray an insecticide or remove them by another method. Insect samples can be taken to your local county extension office for identification.
In this article we will just discuss one of the top insect pests in the vegetable garden, caterpillars, and what you can do about them.

Mature larva of the cabbage looper. Photograph by John L. Capinera, University of Florida.
Beet armyworms, fall armyworms, hornworms, cabbage loopers, southern armyworms, tomato fruitworms, and other caterpillars love to feed on tomato foliage and fruit. They will show up eventually on tomato plants in the garden, if not this year then in the future. These larvae are immature moths and cause a lot of damage if left unchecked. The homeowner can control them effectively with Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI) approved pesticides. A bacterial biological insecticide called Bacillus thuringiensis, also referred to as B.t., can be very effective in controlling these caterpillar pests. B.t. is a stomach toxin to these pests and will cause them to quit eating and starve to death. The key to using B.t. effectively is to routinely apply it before the caterpillars hatch from their eggs as the smaller caterpillars are easiest to control. Larger caterpillars are more difficult to control.
For more information related to using OMRI pesticides:
Organic Vegetable Gardening in Florida
Insecticides for Organic Commercial & Backyard Vegetable Production

by Matt Lollar | Apr 14, 2016

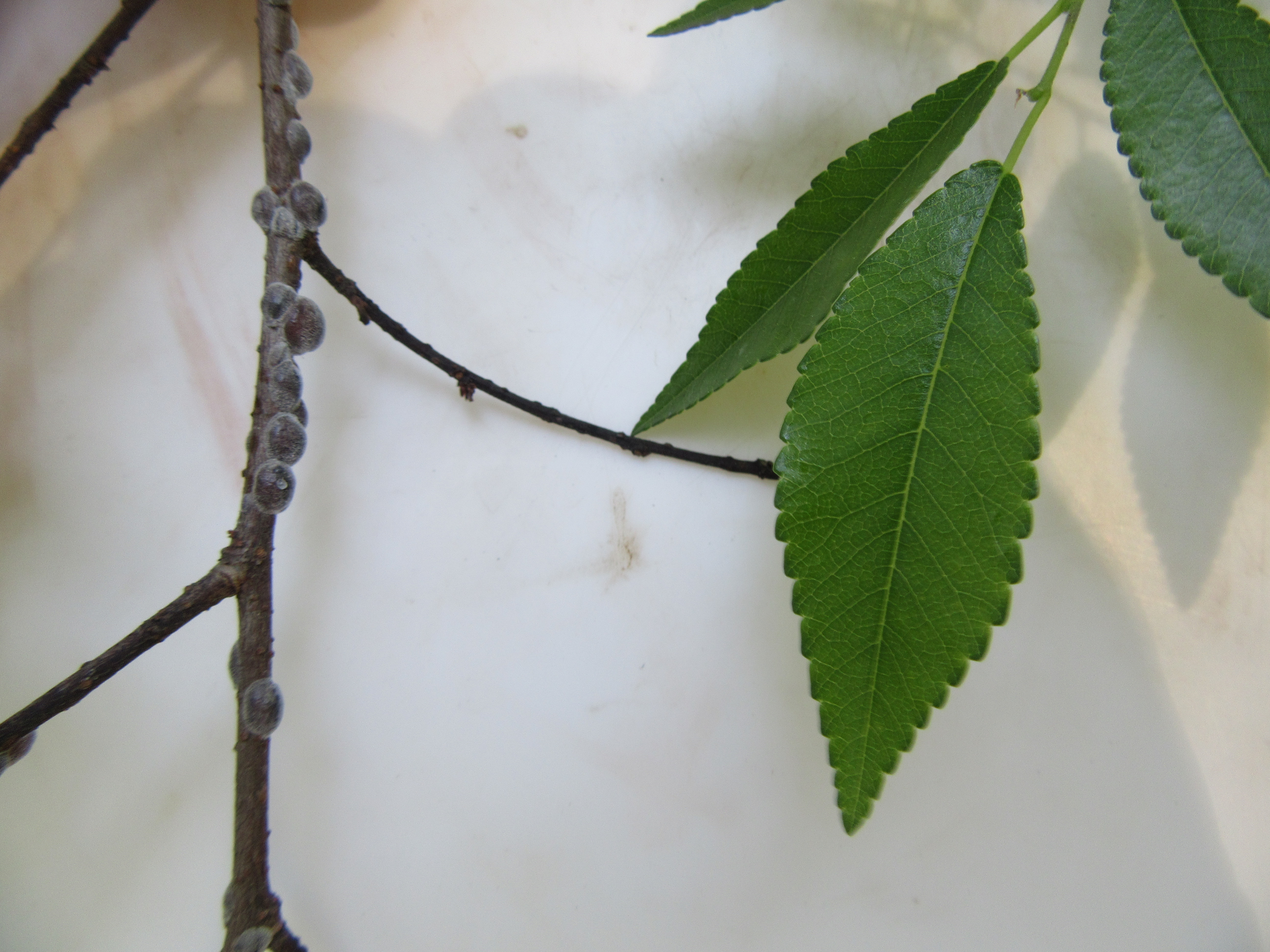
Scales on a Chinese Elm.

Scales on a Chinese Elm.
Last week as I was basking in the shade of the Chinese Elms (Ulmus parvifolia) in my yard, I noticed some strange lumps on the twigs. Upon further investigation, I realized the “lumps” were scales. Scale insects are serious pests of a number of ornamental plants. Here in Florida there are 13 different families of scales with the most common being armored scales, soft scales, and mealybugs. Scales have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Heavy infestations cause extensive leaf yellowing, premature leaf drop, branch dieback, and eventually plant death.
Scale Biology
The life cycle of a scale begins with eggs being laid beneath wax coverings or beneath the adult female. Eggs typically hatch in 1 to 3 weeks. The newly hatched nymphs, called crawlers, move around a plant until they find a spot to feed. Once a feeding site is located, their piercing sucking mouthparts are inserted into the plant and the crawlers begin to feed and grow. The males of many scale species develop wings as adults and fly to other plants to reproduce.

The magnolia white scale. Credits: University of Florida
Armored Scales
Armored scales get their armor by secreting a waxy covering over their bodies that is not attached. The scale lives under this covering and uses it as a protection to feed under. Armored scales can be almost any color or shape and range anywhere from 1/16 to 1/8 inch in diameter. For females, these shapes range from circular to oval to long and slender. The males typically have coverings that are more elongate and smaller than the females. As adults, the males are tiny, winged, gnat-like insects and are rarely seen.

Hemispherical scale on coontie. Credits: Lyle Buss, University of Florida
Soft Scales
Similar to armored scales, soft scales secrete a waxy covering, but it is attached to their bodies. Soft scales can be a number of colors, shapes, and sizes and range anywhere from 1/8 to 1/2 inch in diameter. Their shapes vary from spherical to nearly flat.

Mealybugs. Credits: James Castner, University of Florida
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects that possess a covering of flocculent, white, waxy filaments. They are about 1/8 inch in length and usually pinkish or yellowish in color. Mealybugs have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Mealybug damage produces discolored, wilted, and deformed leaves.
Scale and Mealybug Management
- Cultural Control – Plant inspection prior to purchase or installation is the first line of defense against a scale or mealybug population. Make sure to inspect the undersides of leaves and plant stems. Infested sections of plants can be pruned and plant material should be cleaned from the planting area and discarded. Also, you can increase air flow and decrease humidity by proper installation and pruning. Over-fertilizing can also increase pest populations.

Larva of a brown lacewing. Credits: Lyle Buss, University of Florida.
- Biological Control – Predators, such as ladybugs and green lacewings, are usually present in large enough numbers to suppress scales and mealybugs to a desirable threshold. However, broad-spectrum insecticides and bad weather can reduce predator numbers. Look for signs of predation by inspecting dead scales for jagged holes in their waxy coatings. If predation signs are present, use more selective chemical controls and oils as opposed to broad-spectrum products.
- Chemical Control – Timing is everything when it comes to managing scale and mealybug insects. Crawler activity is more pronounced with the flush of new plant growth in the spring. Before application, prune infested plant parts off first to promote greater penetration of insecticides into the foliage. Contact products (acephate, bifenthrin, carbaryl, etc.) must be applied to inhibit the crawler stages of these insects and systemic products (acetamiprid, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, etc.) can be used on the sessile growth stage. Plants should be sprayed thoroughly to the point of drip or “run off” from leaves, twigs, and stems. Repeated applications may still be necessary even if the timing is right, as crawler populations are often large and crawlers like to hide under old waxy scales. Systemic drenches are also a viable option. With good spray coverage, horticultural oils can kill scales at all stages of growth. Refer to the product label for phytotoxicity and temperature guidelines. Even after successful treatment, the outer coatings of the scales may remain on the plant material for weeks, which can be unsightly. The best way to determine if scales are dead is to squeeze them. They will be dry when squeezed if they are dead and they will ooze liquids if they are living (they were at least alive to the point of being squashed).
For insect identification and additional information on scale control, please see:
A Guide to Scale Insect Identification
UF/IFAS Featured Creatures
Your County Extension Office

by Matt Lollar | Sep 23, 2015
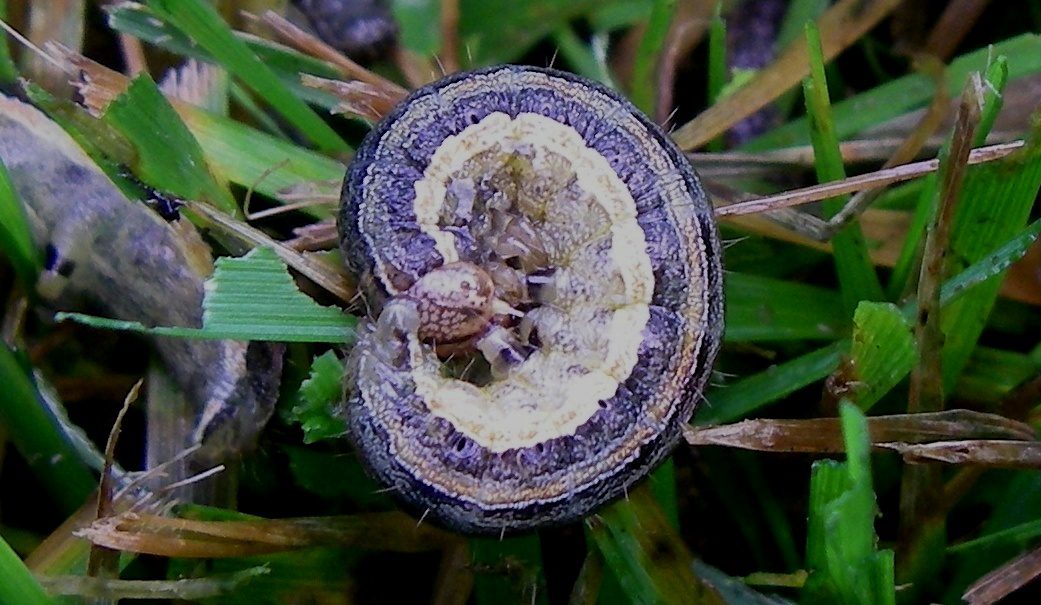
Armyworms come in a wide range of colors and sizes. A few of the prominent species living in Florida are beet, southern, and fall armyworms. And the term “living” is not an exaggeration, because Florida is one of the lucky states where it is warm enough for armyworms to overwinter. They are the snowbirds that never leave!

Armyworm damage on a lawn. Credit: Purdue University
Armyworms are notorious for unanticipated invasions. They feed on most turfgrass species and most vegetable crops, but they prefer grassy vegetable crops such as corn. Armyworms feed in large groups and their feeding has been described as “ground moving” in lawns. They feed during cooler times of the day (morning and evening) and they roll up and rest under the vegetative canopy (in the thatch layer in turf and in the base of leaves in vegetables) during the heat of the day.
Armyworms are difficult to control because of their spontaneity. However, in the lawn they hide in the thatch during the heat of the day. Over watering and fertilization can increase the amount of thatch. It is important to follow UF/IFAS guidelines for home lawn management. A good weed control program can also help to deter armyworms, because weeds serve as an alternate food source.
Numerous chemical control options are available, but softer chemicals such as horticultural oils and insecticides containing the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis are recommended as a first line of defense. Insecticides should be applied in the morning or evening during feeding time. For additional control strategies and basic information please visit the UF/IFAS Armyworm Publication Page.

Armyworm feeding on a young corn plant. Credit: University of Illinois

by Beth Bolles | Aug 26, 2015
It would seem that landscapes are filled with pests ready to devour our favorite plants. We can often see evidence of pest damage in the form of leaf curls, stippled leaves, or chewed holes in foliage. How do plants survive with all the pest threats without intervention from people?
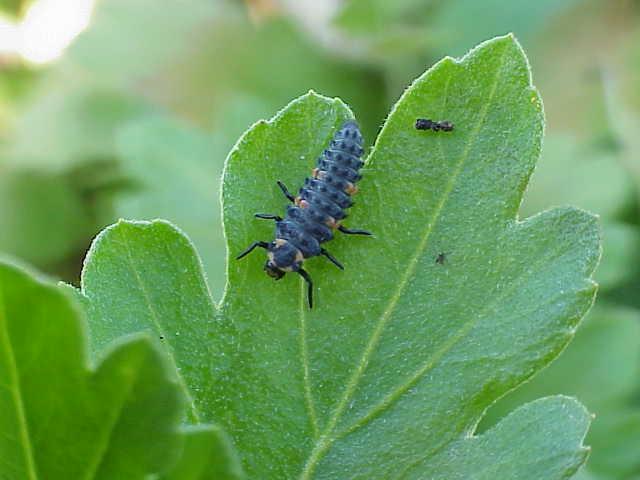
Many plants have their own alert system to help manage a plant-feeding insect attack. When tissues are damaged by plant feeders, the plant releases volatile chemicals that serve as signals for many beneficial insects. Predators such as lady beetles, lacewings, and predatory bugs ‘pick up’ the chemical signals and fly to the injured plants to find their prey.

Ladybeetle larvae will eat many soft-bodied pests.
An interesting part of this occurrence is that the release of chemicals by one plant can stimulate other surrounding plants to build up their chemical defenses against future pest feeding.
The key lesson for all gardeners is that there are many natural processes going on without our knowledge. Instead of immediately applying a broad-spectrum insecticide at the earliest sign of pest feeding on a plant, give the predators a chance to provide you with a free and environmentally sound form of pest control.

by Sheila Dunning | Aug 13, 2015
 University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
University of Florida researchers maintain a constant vigilance on the potential for mosquito-borne illness concerns. UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory in Vero Beach tracks rainfall, groundwater levels, mosquito abundance, wild bird populations and virus transmission to animals including horses and sentinel chickens. When mosquito infection rates reach the levels that can infect humans, alerts are sent out. Through the Florida Department of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health Alert Network issues advisories on a weekly basis to those counties at risk. Such an alert was issued for Gadsden, Polk and Walton Counties for the week of July 19-25, 2015. Unfortunately, the first 2015 confirmed human case of West Nile Virus illness in Florida occurred in Walton County shortly thereafter. It was just another reminder for people to take action to reduce their potential for mosquito development in their landscape.
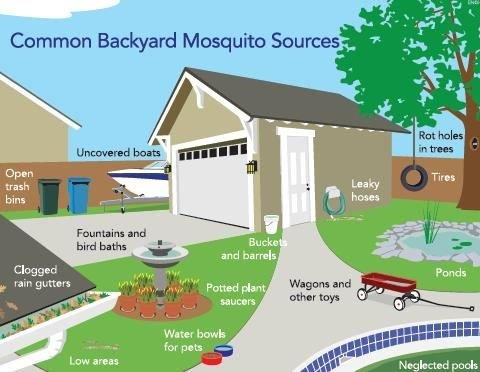
With all the quick afternoon thunderstorms and frequent irrigation events, now is the time to check out where the water is collecting in your yard. The female Culex nigripalpus mosquitoes lay their eggs in temporary flood water pools; even very small ones such as pet watering bowls, bird baths and upturned Magnolia leaves. Dumping out the collection containers every couple of days can greatly reduce the population.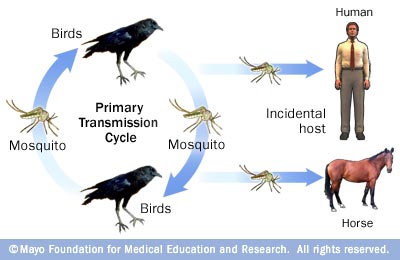
Becoming infected with West Nile Virus is not easy. Mosquitoes usually obtain the virus by feeding on infected wild birds, many of which have migrated from areas that have ongoing West Nile Virus outbreaks. Once the mosquito has drawn infected blood from the bird, the virus goes through a temperature-dependent incubation period within the mosquito. Then, when the infected mosquito “bites” a human or horse the virus mixed in saliva is released into the blood stream of the second host. West Nile Virus is not transmitted from one human to another. Nor is it transmitted from bird to human or from horse to human.
Thanks to a devoted set of researchers and government public health officials, here in Florida we are able to monitor mosquito-borne illnesses quickly and effectively. Additional partners, such as local veterinaries, sentinel bird stations and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) serve as reporters for virus population. Should an individual come across dead birds without an obvious cause, reporting them to the FWC at www.myfwc.com/bird/ is the best thing to do.
 As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:
As for protecting yourself, here are a few pointers:
Stay indoors at dusk (peak mosquito biting time).
If you must be outside, wear long sleeves and pants and/or mosquito repellents containing the active ingredient DEET.
Repair torn door and window screens.
Remove unnecessary outside water sources.
Flush out water collected in outdoor containers every 3-4 days.
Disturb or remove leaf litter, including roof gutters and covers on outdoor equipment.
For additional information, contact your local Extension office about obtaining a free Florida Resident’s Guide to Mosquito Control.


















