
by Matthew Orwat | Oct 10, 2017

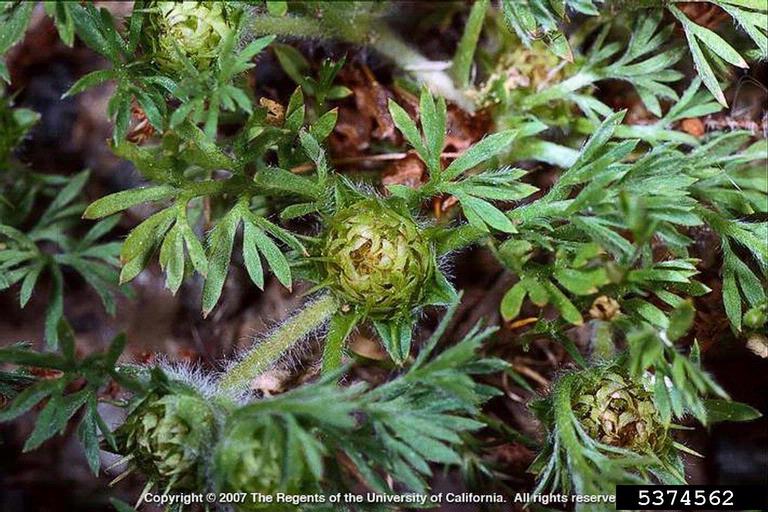
Burweed, Soliva Sessilis. – Image Credit: Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org. Creative Commons License
On the top of my list of lawn related annoyances is stepping into a patch of burweed, Soliva sessilis, which is in the sunflower family and is also known as spurweed. The leaves are opposite along the stem and sometimes resemble parsley. The main ways in which burweed can irk the casual gardener are sticking to socks, sneaking in with the dog, or littering flower beds with its nuisance. It can also hide in the house and reappear when shoes are removed. This causes pain in both the foot and the ear.
Lawn burweed has been an especially noticeable problem in lawns. Over the years, extension offices throughout Northwest Florida have been fielding many questions and finding solutions to lawn burweed infestations!
Maintaining a healthy vigorous lawn will prevent weeds from taking over. If your lawn is reasonably healthy and only a few instances of this weed exist, try to mechanically remove them and encourage the lawn to outgrow them.
If an infestation of burweed occurred last year on a specific patch of turf, take note. The best time to apply pre-emergent herbicides to control burweed is in October, when nighttime temperatures drop to between 55-60 degrees F for a few consecutive nights. A widely used pre-emergence product for burweed control is isoxaben, which is sold under the brand name of Gallery as well as others. It prevents the weed from emerging from the ground when it germinates and can be used on St. Augustine, centipede, bahia and zoysia lawns, as well as in ornamental shrub beds. In northwest Florida, this herbicide needs to be applied in October for best results. A second application later in the season might be warranted. For more information about control, please consult this excellent article on lawn burweed management.
Now is the time to control burweed before it gets started. As temperatures cool burweed seed will germinate, as it is a winter annual. In cases where it is already coming up, control with post-emergent herbicide may be warranted.
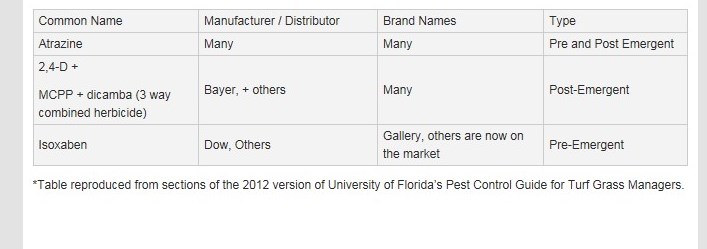
The active ingredients mentioned above are present in a variety of ‘trade name’ products* available from your local garden center, farm supply or co-op. Be sure to read label instructions carefully and contact your local extension office for any assistance. I hope all the northwest Florida lawn managers prevent burweed this fall so that lawns will be burweed free next spring.
Happy Gardening!

by Sheila Dunning | Feb 3, 2017
 Remember last summer? The hot, dry days. Grass drying up and turning brown. Yet, the weeds are green and doing fine. However, every herbicide label warns against applying when the temperatures are above 85 degrees and especially under drought conditions. Those weeds flourished and dispersed seed everywhere. Now, they are just sitting there ready to sprout again.
Remember last summer? The hot, dry days. Grass drying up and turning brown. Yet, the weeds are green and doing fine. However, every herbicide label warns against applying when the temperatures are above 85 degrees and especially under drought conditions. Those weeds flourished and dispersed seed everywhere. Now, they are just sitting there ready to sprout again.
It’s time to start thinking about weed prevention. Pre-emergent herbicides need to be applied prior to seed germination. Late winter is the time to focus on summer annual weeds. The narrow window of application is challenging. Homeowners often wait too late into spring to put out preventative products. A general rule of thumb for pre-emergent herbicide timing is February 15 – March 1 in North Florida.
However, weed seeds germinate in response to soil temperature, not calendar dates. By monitoring day time temperatures, one can determine a more effective application date. When there are 4-5 consecutive days that reach 65 to 70 degrees weeds will germinate. This generally coincides with the first blooms appearing on azaleas and dogwood. With a warm winter it may occur as early as mid-January.
Some of the active ingredients in pre-emergent herbicides include dithiopyr, isoxaben, oryzalin, pendimethalin, prodiamine and simazine. Always read the label for specific weed controlled and observe all directions, restrictions and precautions.
Weed and feed products that contain nitrogen are not suitable as pre-emergent herbicides. Irrigation before and after application is necessary to activate these products. The chemical binds to soil particles, creating a barrier that remains effective for 6-12 weeks. Reapplication will be necessary for season long control, especially with constantly fluctuating winter temperatures. Now is the time to purchase pre-emergent herbicides and prepare to apply them. For more information on weed control in lawns go to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep141

by Matthew Orwat | May 12, 2016

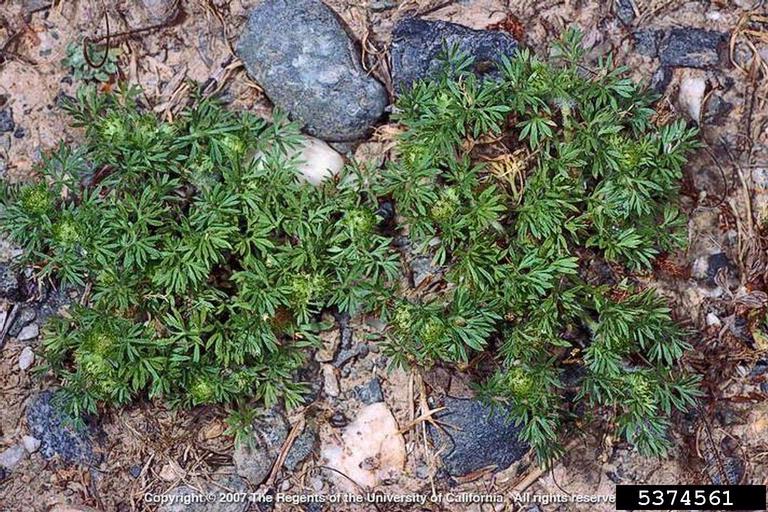
Burweed, Soliva Sessilis. – Image Credit: Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org. Creative Commons License
This spring, lawn burweed has been an especially noticeable problem in lawns. Extension offices throughout Northwest Florida have been fielding many questions and finding solutions to lawn burweed infestations!
On the top of my list of lawn related annoyances is stepping into a patch of burweed, Soliva sessilis, which is in the sunflower family and is also known as spurweed. The leaves are opposite along the stem and sometimes resemble parsley. The main ways in which burweed can irk the casual gardener are sticking to socks, sneaking in with the dog, or littering flower beds with its nuisance. It can also hide in the house and reappear when shoes are removed. This causes pain in both the foot and the ear.
Aside from herbicides, maintaining a healthy vigorous lawn will prevent weeds from taking over. If your lawn is reasonably healthy and only a few instances of this weed exist, try to mechanically remove them and encourage the lawn to outgrow them.
If cultural methods aren’t sufficient, science has given us several options to control this irksome pest. Herbicides containing the active ingredients dicamba, 2,4-D or atrazine are good at controlling burweed as a post emergence control when applied from December through March. Be careful to use reduced rates on centipede and St. Augustine lawns, and never use more than the labeled rate since injury can occur when using these products on these species. Later applications have less effect on burweed because as it matures it is harder to control. Additionally the burs, once present on the lawn, are hard to remove. As the daytime temperatures rise to 90ºF, some of these herbicides may cause lawn damage. Try to keep the spray residue outside of the root zone of desirable plants to avoid injury and always follow label directions.
Be aware that burweed reproduces by seed, so mowing it down will only increase the problem by burying the seed for fall germination. Although we are now in the month of May, control of actively growing burweed might still be warranted if it is still flowering and setting seed. As temperatures warm up burweed will die, as it is a winter annual. In cases where it is already dying, control is not warranted since the natural cycle of winter annuals is concluding.
If an infestation of burweed has occurred this year, take note. The best time to apply pre-emergent herbicides to control burweed is in October. A widely used preemergence product for burweed control is isoxaben, which is sold under the brand name of Gallery as well as others. It prevents the weed from emerging from the ground when it germinates and can be used on St. Augustine, centipede, bahia and zoysia lawns, as well as in ornamental shrub beds. In northwest Florida, this herbicide needs to be applied in October for best results. A second application later in the season might be warranted. For more information about control, please consult this excellent article on lawn burweed management.
The active ingredients mentioned above are present in a variety of ‘trade name’ products* available from your local garden center, farm supply or co-op. Be sure to read label instructions carefully and contact your local extension office for any assistance. I hope all the northwest Florida lawn managers prevent burweed during the upcoming fall so that lawns will be burweed free next spring.
Happy Gardening!

by Larry Williams | Sep 2, 2013
Despite the fact that winter annual weeds are not currently growing, we are approaching the best time to prevent them from being seen in our North Florida lawns.

Carolina Geranium
Common winter annual weeds include annual bluegrass (Poa annua), chickweed, henbit, hop clover, lawn burweed and Carolina or wild geranium.
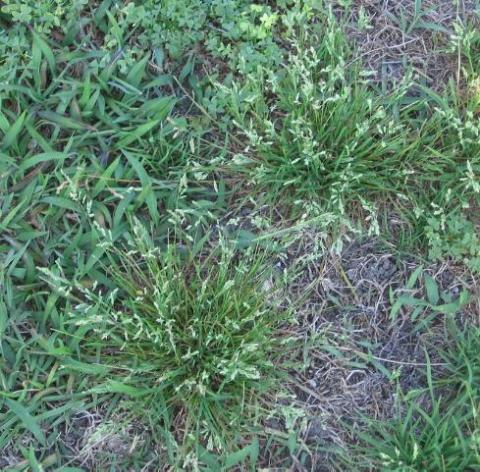

Annual Bluegrass Photo Credits: UF/IFAS
These and other winter annual weeds germinate from seeds in late fall and early winter. The little seedlings go unnoticed but continue to slowly grow through the colder winter months. Approaching spring, as day length becomes longer and soil temperatures warm, these previously inconspicuous weeds put on a growth spurt.

Lawn Burweed:
Close up of parsley-like leaves. Note sharp spines in leaf axils.
Photo Credits: Weeds of Southern Turfgrasses
During spring, the winter weeds may outgrow the lawn grass in our North Florida yards. They begin producing numerous flowers followed by thousands of seeds. For example, one chickweed plant can produce over 15,000 seeds.
In late spring or early summer with the onset of higher temperatures, the parent plants that started their lives from seeds the previous fall will die. But they leave behind a multitude of seed. These seed last the hot summer months dormant in your lawn. Then, in late fall and early winter, they germinate, beginning the entire cycle again.
Late September to early October, when nighttime temperatures drop to 55° to 60°F for several consecutive nights, is the time to apply a pre-emergence herbicide to interrupt the cycle of life for these winter annual weeds. This is just before seedlings emerge.
For season-long control, a second application may be needed about nine weeks after initial application. Not every lawn needs an application of pre-emergence herbicide. If your lawn has had no problem with winter annual weeds, there’s probably no need to apply a pre-emergence herbicide. Use pre-emergence herbicides only on lawns that have been established for at least a year. Many preemergence products interfere with grass seed germination. So, delay reseeding 6 to 16 weeks after application. This also applies to over-seeding a lawn with rye grass seed. Always follow label directions and precautions when using any pesticide, including herbicides.For specific pre-emergence herbicide recommendations, please consult this Weed Management Guide.









