In the final segment of this 3 part series on worms we will discuss the largest, most commonly encountered members of the worm world… the Annelids.
Annelids differ from the other two groups of worms we have discussed in that they have segmented bodies. They are largest of the worms and the most anatomically complexed. The fluids of their coelomic cavity serve as a skeleton which supports muscle movement and increases locomotion. The annelids include marine forms called Polychaetes, the earthworms, and the leeches.
POLYCHAETES
Polychaetes are the most diverse group of annelids and most live in the marine environment. They differ from earthworms and leeches in that they have appendages called parapodia and do not possess a clitellum. In size they range from 1 mm (0.04”) to 3 m (10’) but most are around 10 cm (4”). Many species display beautiful coloration and some possess toxic spines.
There are 3 basic life forms of polychaetes; free-swimming, sedentary, and boring. The free-swimming polychaetes are found swimming in the water column, crawling across the seabed, or burrowing beneath the sediments. Some species are responsible for the “volcanoes” people see when exploring the bottom of our local bays. Most sedentary polychaetes produce tubes within which they live. Some tubes are made of elastic organic material and others are hard, stony, and calcareous. “Tubeworms” rarely leave their tubes but extend appendages from the tube to collect their food. Most feed on organic material either in the water column or on the seabed but some species collect and consume small invertebrates. There are commensal polychaetes but parasitism is rare. All polychaetes have gills and a closed circulatory system and some have a small heart. As with the other Annelids, polychaetes do have a small brain and are aware of light, touch, and smell; most species dislike light. Reproduction involves males and females who release their gametes in the water where fertilization occurs and drifting larva form.
EARTHWORMS
Aside from parasitic tapeworms and leeches, earthworms are one of the more commonly recognized varieties of worms. Many folks actually raise earthworms for their gardens or for fish bait; a process known as vermiculture. Earthworms differ from polychaetes in that they do not have parapodia but DO possess a clitellum, which is used in reproduction. Though most live in the upper layers of the soil there are freshwater species within this group. They are found in all soils, except those in deserts, and can number over 700 individuals / m2. The number of earthworms within the soil is dependent on several factures including the amount of organic matter, the amount of moisture, soil texture, and soil pH. Scientists are not sure why earthworms surface during heavy rains but it has been suggested that the heavy drops hitting the ground can generate vibrations similar to those of an approaching mole; a reason many think “fiddling” for worms works. Earthworms can significantly improve soil conditions by consuming soil and adding organics via their waste, or castings. Unlike polychaetes, earthworms lack gills and take in oxygen through their skin, one reason why they most live in moist soils. Another difference between them and polychaetes is in reproduction. Aquatic polychaetes can release their gametes into the water where they are fertilized but terrestrial earthworms cannot do this. Instead two worms will entangle and exchange gametes; there are no male and females in this group. The fertilized eggs are encased in a mucous cocoon secreted by the clitellum.
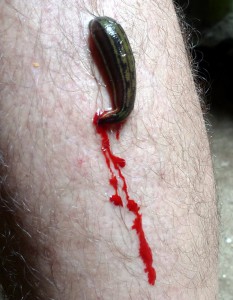
LEECHES
Here is another creepy worm… leeches. Leeches are segmented, and thus annelids, and like earthworms they lack the parapodia found in polychaetes and possess a clitellum for reproduction. Most leeches are quite small, 5 cm (2”) but there is one from the Amazon that reaches 30 cm (12”). Most are very colorful and mimic items within the water, such as leaves. They differ from earthworms in that they are flatter and actually lack a complete coelomic cavity; which most annelids do have. They also possess “suckers” at the head and tail ends.
Leeches prefer calm, shallow water but are not fans low pH tannic rivers. If conditions are favorable their numbers can be quite high, as many as 10,000 / m2. They are found worldwide but are more common in the northern temperate zones of the planet; North America and Europe.
Some species feed by using an extending proboscis which they insert and remove body fluids, but most actually have jaws with teeth and use them to rip flesh to cause bleeding, cutting as frequently as 2 slices/second. Those with teeth possess an anesthesia that numbs the area where the bite occurs. Both those with and without teeth possess hirudin, which is an anticoagulant, allowing free-bleeding until the worm is full. Those who feed on blood tend to prey on vertebrates and most species are specific to a particular type of vertebrate. It is known they can detect the smell of a human and will actually swim towards one who is standing still in the water. It takes several hundred days for a leech to digest a full meal of blood and so they feed only once or twice a year. They remove most of the water from the blood once they swallow and require the assistance of bacteria in their guts to breakdown the proteins. They can detect day and night, and prefer to hide from the light. However when it is feeding time they are actually attracted to daylight to increase their chance of finding a host. Vibrations, scent, even water temperature (signaling the presence of warm blooded animals) can stimulate a leech to move towards a potential prey. Leeches, like earthworms, reproduce using a clitellum and develop a cocoon.
Though most find worms a disgusting group of creatures to be avoided, they are actually very successful animals and many species are beneficial to our environment. We hope you learned something from this series and will try and learn more.
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 5 – Reproduction - January 12, 2026
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 4 – Thermoregulation - December 29, 2025
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 3 – Envenomation - December 22, 2025