Catfish…
There are a lot of fish found along the Florida panhandle that many are not aware of, but catfish are not one of them. Whether a saltwater angler who captures one of those slimy hardhead catfish to a lover of freshwater fried catfish – this is a creature most have encountered and are well aware of.
Growing up fishing along the Gulf of Mexico, the “catfish” was one of our nemesis. Slinging your cut-bait out on a line, if you were fishing near the bottom, you were likely to catch one of these. Reeling in a slimy barb-invested creature, they would swallow your bait well beyond the lip of their mouths and it would begin a long ordeal on how to de-hooked this bottom feeder that was too greasy to eat. Many surf fishermen would toss their bodies up on the beach with the idea that removing it would somehow reduce their population. Obviously, that plan did not work but ghost crabs will drag their carcasses over to their burrows where they would consume them and leave the head skull that gives this species of catfish it’s common name “hardhead” catfish, or “steelhead” catfish. This hard skull has bones whose shape remind you of Jesus being crucified and was sold in novelty stores as the “crucifix fish”.
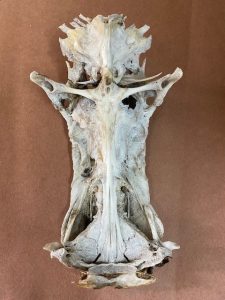
The bones in the skull of the hardhead catfish resemble the crucifixion of Christ and are sold as “crucifix fish”.
Photo: Rick O’Connor
When I attended college in southeast Alabama a group of friends wanted to go out for fried catfish. I, knowing the above about saltwater catfish, replied “why?… no…, you don’t eat catfish”. They assured me you did and so off we went to a local restaurant who sold them. Fried catfish quickly became one of my favorites. A fried catfish sandwich with slaw and beans is something I always look forward to. At that time, I was not aware of the freshwater catfish, nor the catfish farms that produce much of the fish for my sandwiches. I now have also become aware of the method of catching freshwater catfish called “noodling” – which is not something I plan to take up.
Worldwide, there are 36 families and about 3000 species of what are called catfish1. Most are bottom feeders with flatten heads to burrow through the substrate gulping their prey instead of biting it. Most possess “whiskers” – called barbels, which are appendages that can detect chemicals in the environment (smell or taste) helping them to detect prey that is buried or hard to find in murky waters. These barbels resemble whiskers and give them their common name “catfish”.
They lack scales, giving them the slimy feel when removing them from your hook, and also have a reduced swim bladder causing them to sink in the water – thus they spend much of their time on the bottom. The mucous of their skin helps in absorbing dissolved oxygen through the skin allowing them to live in water where dissolved oxygen may be too low for other types of fish1.
They are also famous for their serrated spines. Usually found on the dorsal and pectoral fins, these spines can be quite painful if stepped on, or handled incorrectly. Some species can produce a venom introduced when these spines penetrate a potential predator which have put some folks in the hospital1.
The size range of catfish is large; from about five inches to almost six feet. In North America, the largest captured was a blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) at 130 pounds. The largest flathead catfish (Pylodictis olivaris) was 123 pounds. But the monster of this group is the Mekong catfish of southeast Asia weighing in at over 600 pounds.
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission lists six species of catfish in the Florida panhandle area. However, they are focusing on species that people like to catch2.

This large blue catfish is being weighed by FWC researchers. Photo: Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission
The Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) is found throughout Florida and also in many river systems of the eastern United States. It has found few barriers dispersing through these river systems. They are not typically bottom feeders having a more carnivorous diet.
The Flathead Catfish (Pylodictis olivaris) are relatively new to Florida and are currently reported in the Escambia and Apalachicola rivers. They prefer these slow-moving alluvial rivers.
The Blue Catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) were first reported in the Escambia and Yellow Rivers, there are now records of them in the Apalachicola. These catfish prefer faster moving rivers with sand/gravel bottoms and seem to concentrate towards the lower ends of major tributaries.
The White Catfish (Amerius catus) is found in rivers and streams statewide, and even in some brackish systems.
The Yellow Bullhead (Amerius natalis) are most often found in slow moving heavily vegetated systems like ponds, lakes, and reservoirs. It is reported to be more tolerant of poor water conditions.
The Brown Bullhead (Amerius nebulosus) live in similar conditions to the Yellow Bullhead.
The dispersal of freshwater catfish is interesting. How do they get from the Escambia to the Apalachicola Rivers without swimming into the Gulf and up new rivers? The answer most probably comes from small tributaries further upstream that can, eventually, connect them to a new river system. Scientists know that eggs deposited on the bottom can be moved by birds who feed in each of the systems carrying the eggs with them as they do. And you cannot rule out movement by humans, whether intentionally or accidentally.
On the saltwater side of things, there are two species – though the blue catfish has been reported in the upper portions of some estuaries in low salinities in the western Gulf of Mexico. The marine species are the hardhead catfish (Arius felis), sometimes known as the “steelhead” or the “sea catfish” – and the gafftop (Bagre marinus), also known as the gafftopsail catfish3.
The hardhead catfish is very familiar with anglers along the Gulf coast. This is the one I was referring to at the beginning of this article. It is considered inedible and a nuisance by most. They are common in estuaries and the shallow portions of the open sea from Massachusetts to Mexico. They are reported to have an average length of two feet, though most I have captured are smaller. Like many catfish, they possess serrated spines on their dorsal and pectoral fins. Their distribution seems to be limited by salinity.
The gafftop is also reported to have a mean length of two feet, and most that I have captured are closer to that. At one point in time, we were longlining for juvenile sharks in Pensacola Bay and caught numerous of these thinking they were small bull sharks as we pulled the lines in, until we saw the long barbels extending from them. I remember this being a very slimy fish, covered with mucous, and not fun to take off the hooks. It is reported to have good food value, though I have not eaten one. They differ from the hardheads mainly in their extended rays from the dorsal and pectoral fins. The habitat and range are similar to hardheads, though they have been reported as far south as Panama.
The diversity of freshwater catfish in the U.S. goes beyond what has been reported here. This group has been found on most continents and have been very successful. There are plenty of local catfish farms where you can try your luck, have them cleaned, and enjoy a good meal.
References
1 Catfish. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catfish.
2 Catfish. Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission. https://myfwc.com/fishing/freshwater/sites-forecasts/catfish/.
3 Hoese, H.D., R.H. Moore. 1977. Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico; Texas, Louisiana, and Adjacent Waters. Texas A&M Press. College Station TX. Pp. 327.
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 5 – Reproduction - January 12, 2026
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 4 – Thermoregulation - December 29, 2025
- Rattlesnakes on Our Barrier Islands; Part 3 – Envenomation - December 22, 2025



