
by Rick O'Connor | Sep 21, 2015
A couple of years a few agencies in south Alabama put together something they called the Alabama Birding Trail. It was a relatively simple idea really – they developed a brochure that marked different locations where visitors could enjoy birding in the two county area. They had large signs posted at those locations so that the visitor knew they were at the correct location. There seemed to be a need for this with some vacationers and they provided… It was a big success. More and more visitors were using the trail. It became so popular they that conducted a survey and found that about 40% of the visitors who come to our Gulf coast are looking for outdoor/wildlife adventures to do. Ecotourism is becoming more and more popular.

A heron exploring a local salt marsh for food.
Photo: Molly O’Connor
The panhandle is no different. Each year hundreds of thousands to millions of visitors come to our beaches. There is no doubt that we have some of the most beautiful beaches in the world, and they are a huge draw, but we have a lot of outdoor adventures to provide them as well. From scalloping in St. Joe, to snorkeling the jetties in Panama City, to fishing in Destin, to paddling in Navarre, to dolphin cruises in Pensacola the panhandle provides a wide variety of activities for both the local residents and visitors to enjoy – and employment for many.
So what does this have to do with estuaries?
Well, for most of these businesses a healthy wildlife population is needed. A dolphin cruise with no dolphin is not much. Visitors coming to stay on our beaches will certainly enjoy the white sand and emerald waters. They will return home with pictures and stories of how beautiful it was and how they hope to return – but if they saw a sea turtle that week, or went snorkeling and found thousands of tropical fish to view, or kayaked over a lagoon and found horseshoe crabs or stingrays… the stories get better and their urge to return grows. Wildlife and healthy estuaries are good for business – for everyone.

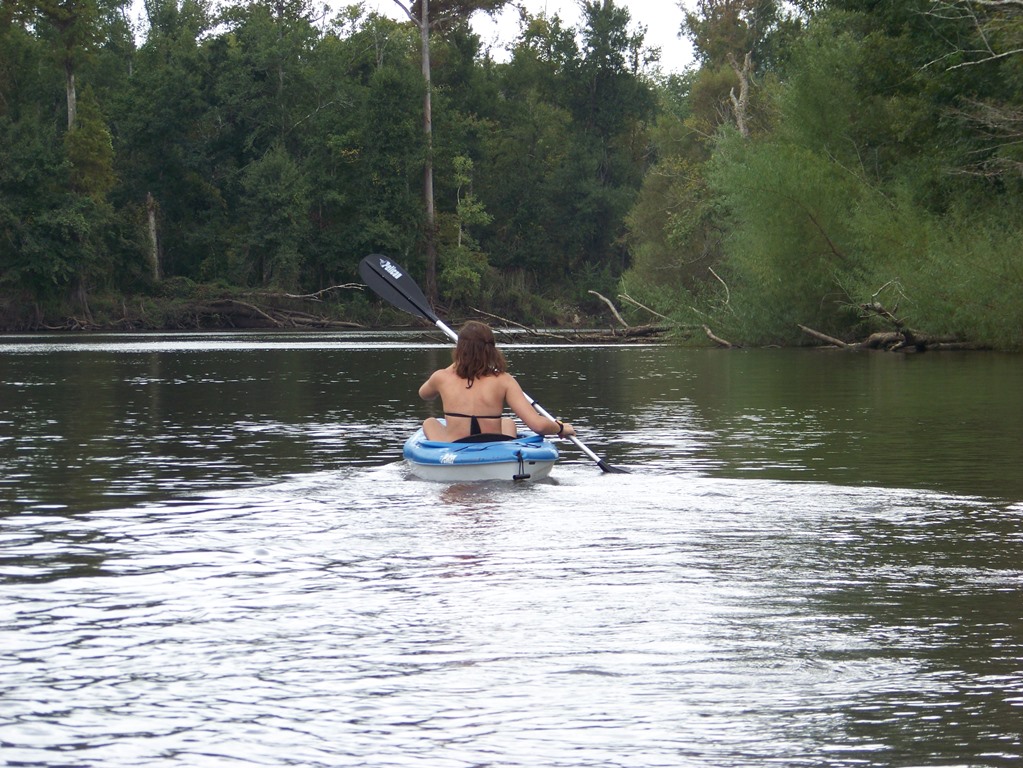
Paddling Blackwater River.
Photo: Adventures Unlimited
In 2014 the Escambia and Santa Rosa county extension offices launched a program called Naturally EscaRosa to help both locals and visitors locate both agritourism and ecotourism businesses in the two county area. The sight provides information on camping, hiking, fishing, sailing, snorkeling, biking, wildlife viewing, and farm tours (of which the popularity is growing across the country). Most of these depend on a healthy bay. Health advisories, fish kills, and loss or degradation of habitat are all problematic for the ecotourism industry. Snorkeling and finding no scallops, paddling over a lagoon and seeing no wildlife, or a slow fishing day on a charter will obviously hurt business – and remember the spin-off’s such as hotels and restaurants as well.
Estuaries have certainly benefitted this industry. From providing a nursery ground for the species we are trying to view or catch, to paddling through a peaceful salt marsh to get away from the hustle and bustle of everyday life, estuaries have been an important part of our lives. And the sunsets… don’t forget the sunsets.

Spadefish on a panhandle snorkel reef.
Photo: Navarre Beach Snorkel
We encourage all locals and visitors to get out and enjoy the beauty of our bays. As the beach season ends the crowds are down, the weather is cooler, and it is a perfect time to venture out. For information about different activities in your area contact your local tourism board, or your county extension office.

by Rick O'Connor | Aug 7, 2015

The elongated body of the Golden Orb Weaver. Photo: Molly O’Connor
TELL ME NO! Please tell me these huge spiders are not a part of our summer. People are afraid snakes… that’s a given – but there are just as many afraid of spiders. Honestly, after years of leading field hikes into the north Florida environment, when we encounter a spider web on the trail I have heard more screams from the boys than from the girls. But most are afraid and there nothing is more terrorizing than the huge, almost hand-size, Golden Orb Weaver (or banana spider).
The Golden Orb Weaver is one of 180 species of orb weavers from around the world; one from Australia is large enough to feed on small birds. The local species is Nephila clavipes and is found throughout the southeastern United States; in the warmer months it may reach as far north as New England. Female Orb Weavers are the really big ones you find on the webs. Their body lengths can reach 2” (not including the extended legs) and the males are much smaller at 0.02”. They have long inward pointing legs with hair-like tuffs at the joints. These are very useful in web building. They have the typical “red/yellow/black” coloration of a venomous animal and their mimics; but N. clavipes is no mimic… though mild, they do have venom. There is another orb weaver spider that is large a constructs large webs. This is the Black and Yellow Argiope (Agriope aurantia). One way to distinguish this spider from the Golden Orb is the “zig-zag” pattern it adds to its’ web near the center (where the spider spends a lot of its time).

The zig-zag pattern of the Black and Yellow Argiope spider helps to distinguish from the Golden Orb. Photo: Molly O’Connor
The name “Golden Orb” does not come from their body coloration but from the color of the silk produced for their webs. It is believed that the yellow/golden color of this silk makes it difficult for others to see in open sunny areas. Many hikers can attest to this… they are hard to see, until you become entangled… then become aware the large spider is very close and heading your way… then the scream. N. clavipes can actually adjust the hue of yellow in the silk to match the sunlight conditions where it is building its web. It is amazing to see how quickly they replace their large webs, over 3 feet in diameter, after they have been removed by people. Actually they mend and move their webs regularly. They tend to build them off ground, at eye level to the tree tops, in open areas near a line of trees. I have actually seen one build the web across a dirt road between two stands of pines as if it were going to try and capture a truck! Though species of Orb Weavers feed on small birds and snakes, N. clavipes prefers flying insects. They do not wrap their prey in silk for later feeding, as many spiders do, but rather consume them almost immediately. This may be because of a small slivery spider called Argyrodes. This spider feeds on the captured food of other spiders. N. clavipes feeding may be an adaptation to combat this kleptoparasitic spider. Another interesting behavior I have noticed is when the heavy rains come. I have noticed the web remains but the spiders leave. I am not sure where they go, most likely a hiding spot nearby, but they do leave.
The fear of spiders is most likely similar to the fear of snakes… they are venomous. Venom is used to kill prey and many times is not strong enough to kill humans, but the fact that some species can kill makes folks a bit nervous. Despite local tales that say otherwise, the venom of N. clavipes is mild. It is a neurotoxin, which can be potent, but the bite from this spider is not lethal. The typical response is pain and redness at the site of the bite, blisters may form, but it is actually less potent than a bee sting.
Like many other species of spiders, the Golden Orb Weaver is a beneficial backyard creature consuming hundreds of biting (in some cases disease carrying) insects. The large webs can be a nuisance around backyard patios and swimming pools but they can easily be moved to other locations with a rake or broom. We have many of them in our yard, one out of my office window, and enjoy watching them work. They are good panhandle neighbors.
For more information on these beneficial creatures visit:
http://okeechobee.ifas.ufl.edu/News%20columns/Orbweaver.spiders.htm
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in017
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in467

by Rick O'Connor | Jul 17, 2015
The air temperatures are in the high ‘90’s and the heat indices are reaching over 100°F; heck the inland water temperatures are in the high ‘80’s – it’s just hot out there! But our barrier island wildlife friends are doing okay, they have had to deal with this many times before. Deep burrows and nocturnal movement lead the list of behavior adaptations to cope but some still scurry around during daylight hours.

People visiting the Gulf coast during the summer.
I typically begin my monthly hikes along the Gulf shore to see what is out and about; this month there were humans… and lots of them. This is the time of year that vacationers visit our islands. Traffic is bad, nowhere to park, long lines, etc. But it is part of living on the Gulf coast. We are glad to have visitors to our part of the state. We do ask that each evening they take their chairs, tents, and trash with them. Have fun.

This plant, Redroot, grows in the wetter areas of the secondary dune.

Seaside Rosemary
During these hot days of summer this flower was blooming all throughout the freshwater bogs of the secondary dunes. The plant is called REDROOT and it is really pretty. I did not see any insects near it but it was in the warm part of the day that I made my hike this month. The round shaped SEASIDE ROSEMARY is one of my favorite plants on the island. The odor it gives off reminds me of camping out there when I was a kid and of the natural beach in general. I have been told that Native Americans did use it when cooking, but can’t verify that. This is a neat plant either way. I believe there are male and female plants in this species and they have a low tolerance of fire and vehicle traffic.

The new, young seeds of the common sea oat.

Though it appears small, this is the same species of pine that grows tall inland.
The most famous plant on our barrier islands is the SEA OAT. However most think of them in the primary dune fields only. They actually grow all across the island as long as their seeds fall in a place where the wind is good, usually at the tops of dunes. As many know the roots and rhizomes of this plant are important in stabilizing the dunes, hence the reason why in most states it is illegal to remove any part of the plant. This PINE is the same type found growing 40 feet up in your yard but here on the beach salt spray and wind stunt their growth. Also the moving sand covers much of the trunk, making the tree appear much smaller than it really is. Pines are quite common on the island.

The tall trees are covered by quartz sand forming the tertiary dune system.

The expanse of marshes that make up Big Sabine on Santa Rosa Island.
The large trees of the barrier island system are typically found in the TERTIARY DUNE field. Here we see pine, oak, and magnolia all growing forming dunes that can reach 50 feet high in some places. Behind large tertiary dunes are the marshes of BIG SABINE. These marsh systems are some of the most biologically productive systems on the planet. 95% of our commercially valuable seafood species spend most, if not all, of their lives here. We will focus on this ecosystem in another edition of this series Discovering the Panhandle.

The red cones of the Sweet bay identify this as a relative of the magnolia.

The “mystery tracks” we have been seeing since January now show the small tracks of a mammal; probably armadillo.
This SWEET BAY is a member of the magnolia family and the small red cones show why. I had not seen the cones until now, so guess they like the heat and rain. WE HAVE SOLVED THE MYSTERY TRACK… knew we would. If you have read the other additions in this series you may recall we have found a track that appeared to be a “slide” coming out of the marsh and into a man-made pond from the old hatchery. Never could determine what was causing this but saw it each month of the year. However this month you could see the individual tracks of a mammal; I am guessing armadillo but could be opossum or raccoon as well. Cool… got that one behind us. On to other discoveries.

Acres and acres of Black Needlerush indicate this is a salt marsh.

Bulrush and other plants indicate that this is not salt water, but a freshwater marsh.
Marshes differ from swamps in that they are predominantly grasses, not trees. Salt marshes, as you would expect, have salt water. Fresh water the opposite… yep. The photo on the left is the salt marsh. The grass species are different and help determine if the water is fresh or brackish. Next year we will do a whole series in this ecosystem – it is pretty cool.
Until next month… enjoy our barrier islands.

by Rick O'Connor | May 29, 2015
This month there were many more plants flowering… it is true that April showers do bring May flowers. May not only brings more flowers but more tourists. Everyone is out enjoying the weather, including some wildlife. I was happy to include Florida Master Naturalist Paul Bennett on this hike and he was very helpful identifying plants. Thanks Paul!

Tent set up on Pensacola beach to protect from the sun. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Sign altering and educating folks that this is a sea turtle nest. Photo: Rick O’Connor
It is sea turtle nesting season all along the Florida Panhandle. The season begins in May and ends in October. This time of the season the females are heading up the beach looking for good nesting locations near dunes. There are five species of marine turtles that inhabit the northern Gulf and there are records of each species nesting here. They emerge at night and move towards the dunes where they excavate a deep cavity to lay about 100 eggs. The nest is covered and she returns to the water. The incubation period is between 60-70 days and the temperature of the nest determines the sex of the hatchling; the warmer eggs becoming females. It is illegal to disturb a sea turtle nest.
This tent was occupied when I was there but all too often they are left overnight so folks can return the same spot the following day. Tents and chairs are barriers for both nesting females and emerging hatchlings. If at all possible, remove these for the evening. In some counties it is required. Another problem is artificial lighting. Adult turtles are distracted, and many times abort the nesting activity due to bright lights. Most panhandle counties have a lighting ordinance that requires homes to use turtle friendly lighting. To learn more about the turtle friendly lighting program and local ordinances contact your county Sea Grant Agent at the local Extension office or visit http://myfwc.com/wildlifehabitats/managed/sea-turtles/lighting/.

This county sign marks a public snorkel reef and also educates everyone about lionfish. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Mangrove seed washed ashore. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Summer means swimming and in many local counties there are interesting snorkel reefs nearby. We asked that everyone keep an eye out for the invasive lionfish as they enjoy their day. If one is spotted be aware they do have venomous, though not deadly, spines and please contact your local Sea Grant Agent at the county Extension office to let them know. If you are in Escambia County you can log your sighting at www.lionfishmap.org and FWC has a lionfish app for reporting; http://myfwc.com/news/news-releases/2014/may/28/lionfish-app/
The seed is of a red mangrove tree. These are common coastal plants in south Florida and elsewhere in the tropics. The red mangroves drops their seeds (propagules) into the water to drift in the currents to new locations. They frequently wash upon our shores and sometimes take root, but they do not last during our colder winters.

This Whitlow-Wort, also known as “square flower”. Common dune plant. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Track of an unidentified snake crossing a dune. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The flower to the left is the Whitlow-Wort, or as some locals call it… “square flower”. The track is of a snake but could not find it so I am not sure which species. The weather warms quickly here along the Gulf coast. A few months ago we may have been able to find this animal but with the increasing heat they were in a cool place somewhere. Snake encounters this time of year are typically at dawn and dusk.

The seed pod of a milkweed. Photo: Rick O’Connor

An open seed pod of a milkweed releasing seeds. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The milkweed bloomed a few months ago but here in May we find both the seed pods and, in the photo to the right, the “dandelion-like” seeds being released. This is one of the plants used by the migrating monarchs, which we should see later in the year.

Marsh Pink, a flower found in the wetter areas of the island.

Narrow-leaved Sagittaria. Another water loving plant.
Here are two of the many flowers we saw today. Both of these were found in the freshwater ponds located in the swale areas of the barrier island. The flower to the left is known as Marsh Pink. The one to the right is Narrow-leaved Sagittaria.

The yellow vine called “Love Vine”; correct name is Dodder.

It is good to see bees on the island.
This orange-yellow stringy vine is called “Love Vine” but there is not much love here; this is a parasitic plant called Dodder. This is the first we have seen of it this year and expect to see more. Many residents on the island believe it to be an non-native invasive plant but it is actually a native and quite common out there. I have also seen it in the north end of Escambia County.
We did see a few bees today and this is a good sign. There have been reports in recent years of the decline of our native bees and the impact that has had on gardening and commercial horticulture. In addition to seeing bees Paul and I also came across the famous yellow fly. These were encountered near the marsh on the sound side of the island. Loads of fun there!

The “bed” made by an unknown animal that has been frequenting this location all year. Photo: Rick O’Connor

This scat pile was near the location of the “bed” and along the drag marks made by this animal.
If you have been following this series since we began in January you may recall the strange “bedding” and drag marks we have encountered near the marsh (you can read other issues on this website). I have seen these drag marks, and apparent bedding areas, every month except last. I showed them to Paul and we are still not sure what is making them. Again, whatever it is seems to move from one body of water to another. We cannot find in foot tracks to help identify it… but we will!
The photo to the right is of a large scat pile approximately 15-16” across. It was relatively fresh and contained crab and shrimp shell parts. Not sure if it was left by the same animal that continually makes the drags but was in the same location so…

The pretty, but invasive, beach vitex. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Many of the plants on our barrier islands are blooming now, and so is this one. This is Beach Vitex (Vitex rotundifolia). It is an invasive/not-recommended plant. Currently we are only aware of 22 properties in Escambia County that have it. Sea Grant is currently working with the SEAS program at the University of West Florida to assist in removing them. If you believe you have this plant and would like advice on how to remove contact your local Sea Grant Agent at the county Extension office.
Let’s see what shows up in June!

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 17, 2015
As we left the winter months and headed into spring I was expecting a lot of new blooms, new animal tracks, and more live encounters with wildlife… and then the rain began. I do not know if the entire panhandle has been getting what Pensacola has but the rain has been nonstop for over a week now. I track rain days for a water quality project and for the first three months of 2015 the number of days during a month where it rained was between 23-30%. We are about half way through April and so far it has rained 61% of the days. WELL… rain or shine we will make this hike and see what is happening on our barrier island.

Hole left by a sand castle architect. These can be problems for wildlife and rescue vehicles. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The first thing I noticed when I began the trip along the Gulf was this large hole left by a sand castle architect. These can be problematic for some forms of wildlife, including sea turtles, but they can also be a problem for rescue and turtle watch vehicles. Please enjoy the beach and make awesome sand castles, but when you are finished please fill the hole.

Sargassum is floating form of brown algae. Notice the “air bladders” (pneumatocyst) Photo: Rick O’Connor

A tropical seed commonly referred to as a sea bean. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The line of seaweed and debris along the surf zone is called wrack. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The line of seaweed and debris that washes ashore during storms is called the wrack. For the most part it is natural material and provides the nutrients needed for many of the high energy shoreline plants to grow. Many of the beach animals found in the berm and primary dune depend on this wrack as well. Many locals and visitors find this material and eye sore and, at times, producing an unpleasant odor. But this material is an important part of the beach ecology. Sargassum is a drifting member of the brown algae, sometimes called “gulfweed”. It possess small air bladder structures called pneumatocysts that allow it to remain at the surface of the open Gulf where the sunlight is. These large offshore mats of Sargassum have been targets for local fishermen for decades. Many small invertebrates live in these drifting mats and these are targets for small fish, which in turn are targets for even larger sport fish. They are also the hideaway for sea turtle hatchlings. When the little guys head for the Gulf after hatching this is where they are heading. Large ocean currents, including the Gulf Stream, push Sargassum into large mats in the middle of the open ocean. The area within the Atlantic where this happens in known as the Sargasso Sea. If you get a chance this summer, grab a small hand net and mask when the Sargassum is just offshore. Collecting you may find a lot of cool interesting creatures. Sea Beans is a generic word for a variety of tropical seeds that wash ashore in the northern Gulf. Some of these may sprout, including mangroves, but most will not make it through our winters.
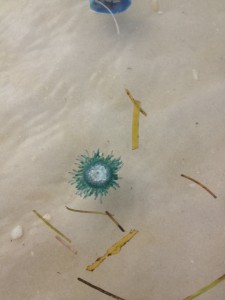
The Blue Button Jellyfish is a tropical cousin of the Portuguese man-of-war. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Portuguese Man-of-War is one of the more venomous jellyfish in Florida waters. Photo: Rick O’Connor.

A variety of shorebirds utilize the wrack. Photo: Rick O’Connor
One of the more venomous jellyfish in Florida waters is now making its way onto our shores. The Portuguese man-of-war, named for the many “guns” this animal possess, is well known by locals but not so much by some of our visitors. The man-of-war is actually not one animal but a colony of sedentary polyp jellyfish that produce an inflated bag which floats at the surface carrying them across the sea. The dark blue tentacles hang down into the water column where passing fish are stung and consumed. Each of the polyps have connecting stomachs which helps move the food around to the whole colony. The sting of this jellyfish is quite painful and should be avoided. When they arrive life guards will usually fly a purple flag.
Their close cousins, the Blue Button Jelly, is very similar to the man-of-war albeit they are much smaller and the venom is not as potent. They are more tropical and not common along the northern Gulf but in recent years more have been washing ashore; they are here now.

A variety of plastics ends up in the Gulf. Each is a potential problem for marine life. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Pieces of plastic ribbon resemble jellyfish tentacles and are frequently consumed by sea turtles. Photo: Rick O’Connor
One of the bigger issues are oceans are facing are discarded plastics. These materials takes years to decompose and are found in all oceans and seas. Even some distant isolated islands have huge piles of this form of marine debris. Plastics can entangle marine organisms or they may actually swallow it, plugging their digestive system and eventually starving them. We encourage locals and visitors alike to help with this problem by taking your trash with you and discarding it in a location where it will not reach the Gulf.

This ephemeral pond formed around a small dune which becomes a temporary island. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Chinese tallow is an invasive species the entire state is dealing with. Photo: Rick O’Connor
With the heavy rains of the last week ephemeral ponds have formed on parts of the island. These small pockets of freshwater can be “manna from heaven” for many island residents, particularly the amphibians. I have been hiking this section of Pensacola beach for years, leading field trips for all sorts of groups. I have never seen this Chinese Tallow until today. Also known as the “popcorn tree” due to its unique looking fruit, this plant is listed as an invasive in the state of Florida and is very aggressive. I did not see any others and will seek permission to remove it before it spreads to other dunes and out competes the native plants.

One of the few plants blooming in April, the Spiderwort is a common weed in many lawns. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The blossoms of Conradina first appeared in February. They are all but gone this time of year. Photo: Rick O’Connor
I was actually expecting more flowers to be in bloom this month but there were few. The Conradina, which have been in bloom since February, have lost most of its blossoms. The “new kids on the block” are the Spiderwort, the Primrose, the Sandhill Milkweed, and the Devil’s Joint Cactus.

There are a variety of primrose that grow on our barrier islands. They are beginning to bloom now. Photo: Rick O’Connor

New growth on a pine tree. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Sandhill Milkweed. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The Sandhill Milkweed is one of the plants used by the monarch butterfly to gain fuel for their great flight across the Gulf to Mexico. The milky toxic sap of this plant is consumed by the monarch caterpillar but it does not harm it. The chemical toxins therefore become a defense for the monarch and the butterfly has earned the respect of many birds; though it may be a trial and error learning experience.

A decomposing log is a microhabitat for many organisms. Photo: Rick O’Connor

New growth on a live oak. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Most environmental centers, state and federal parks, leave fallen trees where they lie. The tree is actually a storage house of nutrients and full of cavities that can be used by a lot of organisms within the beach community.

The mysterious “drags” we have seen the last three months were not to be found in April. Photo: Rick O’Connor.

The beautiful yellow bloom of the Devil-Joint cactus. Photo: Rick O’Connor
This month the weather was warm enough for me to venture into the Salt Marsh. Salt marshes are wetlands but differ from swamps in that the dominate plants are grasses, not trees. Our local salt marsh is dominated by two species of grass, the Smooth Cordgrass, and the Black Needlerush. There are many other plants that exist here but these are the most common. This particular marsh is dominated by Black Needlerush. Salt marshes are one of the most productive systems on the planet, producing tons of organic material annually. 90% of the commercially valuable marine species spend part or all of their lives here. There are many unique species to this system as well. Today the water was crystal clear but I saw few fish. I expect as it gets warmer we will see more. It is very possible that with the heavy rains that they have moved to deeper, saltier spots in the Sound.

It’s warm enough to enter the salt marsh. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The marsh periwinkle is one of the more common mollusk found in our salt marsh. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The Marsh Periwinkle is an interesting guy. This snail will crawl up the stalks of marsh plants during high tide to avoid predators like blue crab and diamondback terrapins. Both of these predators appear to be on the decline and it will be interesting to see how this impacts the ecology of the marsh. At low tide the periwinkles descend and feed on the organic leaf litter on the muddy bottom.

This dewberry has flowered and the dark fruit will be ready next month. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Gracilaria is a common epiphytic red algae growing in our seagrass beds. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Black Needlerush is one of the two dominant plants of our salt marshes. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Though it has a white appearance, Gracilaria is a member of the red algae group. This algae grows on seagrasses as Spanish moss grows on oaks. The plant is usually kept in check by herbivorous grazers, such as green sea turtles, but in recent decades the number of predators have declined and the amount of nutrient runoff has increased. This has sparked a increase in the growth of this algae and, in some cases, to the determent of the seagrass itself.

This eroded pine tree gives evidence of the ever changing shorelines of our barrier islands. Photo: Rick O’Connor

This submerged mound of peat is the remnants of a salt marsh which is now below sea level. Photo: Rick O’Connor
These photos of peat and the eroded tree are indications of a changing shoreline. Due to storms, boat wake, and time, the shoreline of Santa Rosa Island, like all barrier islands, is changing. Peat is actually the remnants of an old salt marsh that has now pass the high tide line and is within the Sound.

Trash left behind by those enjoying the beach. Photo: Rick O’Connor

We encourage those who pack it in… to pack it out. Photo: Rick O’Connor
As the weather has warmed and spring break has fallen upon us I have noticed an increase in the amount of trash on this hike, both the Gulf of Sound sides. We encourage locals to take their trash with them and encourage visitors to do the same. Let’s try to keep our waste out of our waters.
I am expecting some animal nesting in May. We will see what we find. Until then.

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 10, 2015
The American Alligator is an icon in the state of Florida. Viewed on the program “Swamp People” and as the mascot of the University of Florida, most visitors to our state view this animal more on television than in the wild; but they are certainly there. In need of mates and calories from the lack of eating over the winter, alligators and other reptiles become more active this time of year. Visitors and residents alike should be a little more cautious.

Alligator basking on the Escambia River; photo: Molly O’Connor
Like most predators, alligators seek food that will provide them energy. Generally predators will target prey that will cost them very little energy to capture and kill. Obviously small alligators will feed on small prey but adult alligators feed on smaller prey than many think. Fish, turtles, snakes, small mammals and birds make up the bulk of their diet. If the opportunity presents itself, and they do not have to expend too much energy, alligators will certainly take larger mammals and birds.
For humans the bigger problem has been the loss of pets and livestock. Small dogs are certainly easier prey than a human, and with the loss of habitat encounters with humans and their pets have increased. Since 1948 FWC has estimated about 300 alligator attacks on humans directly, less than 10% of these were fatal. As more alligators are forced into suburban areas more encounters have occurred. In the last 10 years 16,000 nuisance alligator calls have been reported to the FWC. As with other wildlife, like coyotes, many of these animals are living in ditches and other watering holes where they seek fish and turtles. However if we visit such places, particularly with our pets, these animals may certainly make an attempt to grab them. If you feel an alligator is a nuisance and could be a potential problem you can call FWC at (866) FWC-GATOR; (866) 392-4286). Folks should be aware that FWC does not relocate nuisance alligators, they will be destroyed. Currently FWC issues about 7000 permits for alligator control across the state.
A couple of safety notes if you live near waterways with alligators.
- Do not swim in these locations at night; alligators are more active hunters between dusk and dawn
- Try to discard fish remains after cleaning in another location besides the water; if these locations have a few alligators they will certainly learn this habitat and hang around the boat ramp more.
- DO NOT FEED alligators; help us let visiting tourists know this and that it is illegal in our state. Alligators fed by humans will eventually lose their natural fear of us and this could bring on problems.
These are awesome animals. We should better understand their natural history so that we can exist with them. For more information on alligators in your area contact your county extension office.



































































