
by Sheila Dunning | Oct 10, 2019
 Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
This spring, scientists from World Wildlife Fund Mexico estimated the population size of the overwintering Monarchs to be 6.05 hectacres of trees covered in orange. As the weather warmed, the butterflies headed north towards Canada (about three weeks early). It’s an impressive 2,000 mile adventure for an animal weighing less than 1 gram. Those butterflies west of the Rocky Mountains headed up California; while the eastern insects traveled over the “corn belt” and into New England. When August brought cooler days, all the Monarchs headed back south.
What the 2018 Monarch Watch data revealed was alarming. The returning eastern Monarch butterfly population had increased by 144 percent, the highest count since 2006. But, the count still represented a decline of 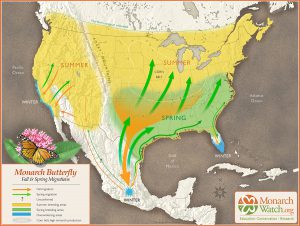 90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
Scientists estimate that 6 hectacres is the threshold to be out of the immediate danger of migratory collapse. To put things in scale: A single winter storm in January 2002 killed an estimated 500 million Monarchs in their Mexico home. However, with recent changes on the status of the Endangered Species Act, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has delayed its decision until December 2020. One more year of data may be helpful to monarch conservation efforts.
 Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
There is something more you can do to increase the success of the butterflies along their migratory path – plant more Milkweed (Asclepias spp.). It’s the only plant the Monarch caterpillar will eat. When they leave their hibernation in Mexico around February or March, the adults must find Milkweed all along the path to Canada in order to lay their eggs. Butterflies only live two to six weeks. They must mate and lay eggs along the way in order for the population to continue its flight. Each generation must have Milkweed about every 700 miles. Check with the local nurseries for plants. Though orange is the most common native species, Milkweed comes in many colors and leaf shapes.

by Mark Mauldin | Oct 10, 2019
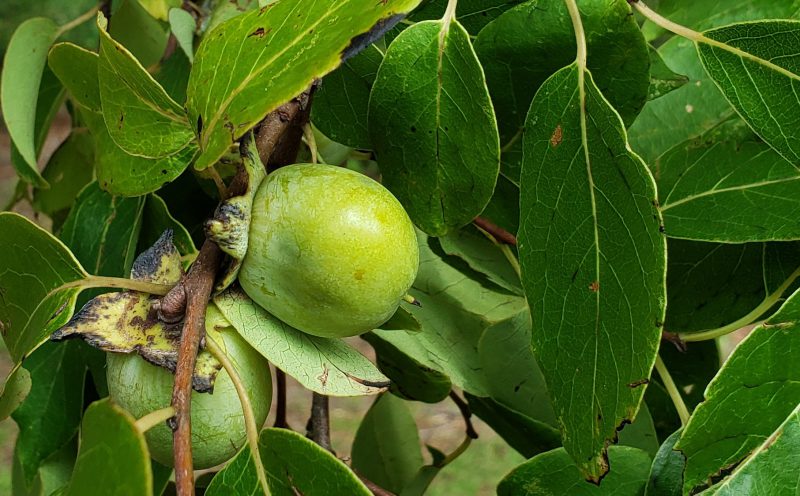

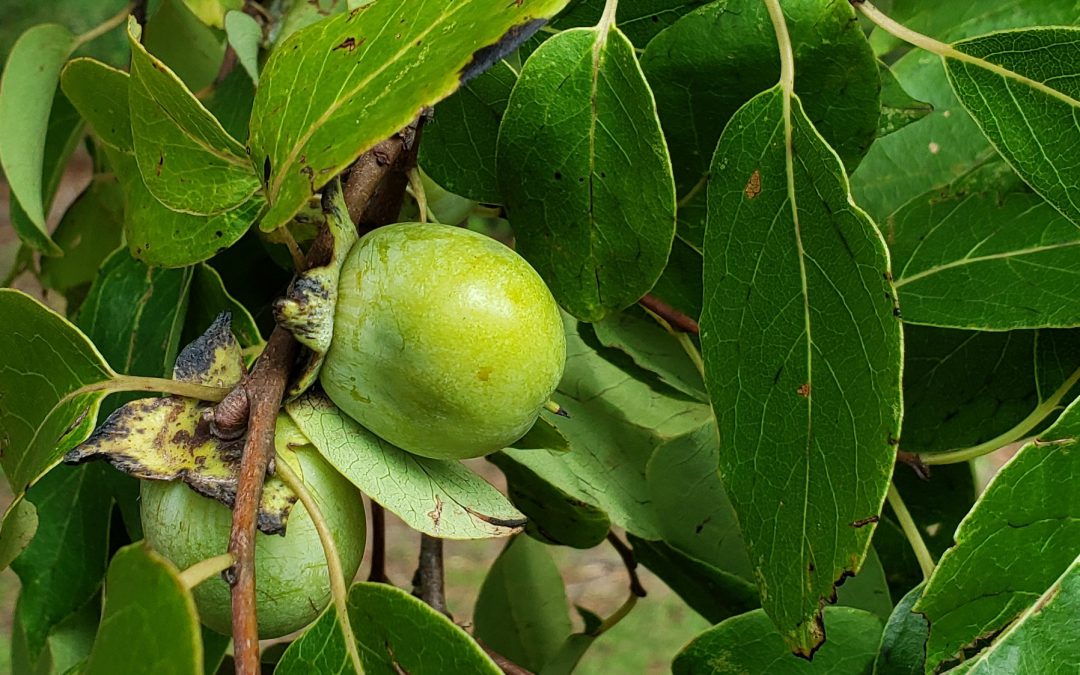
Protecting and promoting plants that produce soft mast, like this wild persimmon, can be a crucial step in improving wildlife habitat. Note: This time of year persimmons will be orange, the picture was taken earlier in the summer.
Photo Credit: Mark Mauldin
Landowners frequently prioritize wildlife abundance and diversity in their management goals. This is often related to a desired recreational activity (hunting, bird watching, etc.).
In order to successfully meet wildlife related management goals, landowners need to understand that animals frequent specific areas based largely on the quantity, quality and diversity of the food and cover resources available. Implementing management strategies that improve wildlife habitat will lead to greater wildlife abundance and diversity.
Herbivorous wildlife feed on plants, mostly in the form of forages and mast crops. All wildlife species have preferences in terms of habitat, especially food sources. Identifying these preferences and managing habitat to meet them will promote the abundance of the desired species.
Herbaceous plants, leaves, buds, etc. – serve as forages for many wildlife species. Promoting their growth and diversity is essential for improving wildlife habitat. Three common habitat management practices that promote forage growth include:
1) Create forest openings and edges; forested areas with multiple species and/or stand ages, areas left unforested allowing for increased herbaceous plant growth.
2) Thinning; open forest canopy allowing more light to hit the ground increasing herbaceous plant growth and diversity.
3) Prescribed fire; recycle nutrients, greatly improve the nutritional quality of herbage and browse, suppress woody understory growth.
Mast – the seeds and fruits of trees and shrubs – is often one of the most important wildlife food sources on a property.
Hard mast includes shelled seeds, like acorns and hickory nuts and is generally produced in the fall and serves as a wildlife food source during the winter.
Soft mast includes fruits, like blackberries and persimmons, and is generally produced in the warmer months, providing vital nutrition when wildlife species are reproducing and/or migrating.
Making management decisions that protect and promote mast producing trees will encourage wildlife populations.
Landowners can make supplemental plantings to increase the quantity and quality of the nutrition available to wildlife. These supplemental plantings (food plots/forage crops and mast producing trees) can be quite expensive and should be well planned to help maximize the return on investment.
Key points to remember to help ensure the success of supplemental wildlife plantings.
- Select species/varieties that are well adapted to the site.
- Take soil samples and make recommended soil amendments prior to planting.
- Make plantings in areas already frequented by wildlife (edges, openings, etc.).
- Food plots should be between 1 and 5 acres. Long, narrow designs that maximize proximity to cover are generally more effective.
Habitat management and other wildlife related topics are being featured this year in the UF/IFAS building at the Sunbelt Ag Expo. Make plans to attend “North America’s Premiere Farm Show” and stop by the UF/IFAS building, get some peanuts and orange juice and learn more about Florida’s Wildlife.
 If you have any questions about the topics mentioned above, contact your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Office or check out the additional articles listed on the page linked below.
If you have any questions about the topics mentioned above, contact your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Office or check out the additional articles listed on the page linked below.
EDIS – Wildlife Forages
A significant portion of this article was summarized from Establishing and Maintaining Wildlife Food Sources by Chris Demers et al.

by Erik Lovestrand | May 31, 2019
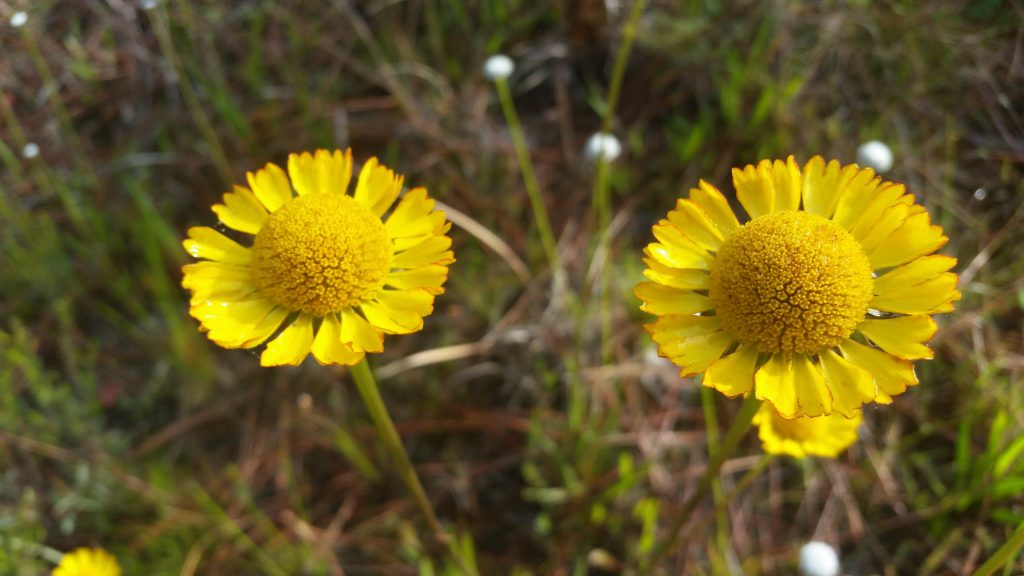

Yellow asters such as sneezeweed bloom profusely during summertime in the flatwoods.
Our coastal habitats are some of the most beautiful on the planet. Where else can you have the breathtaking, wide open vistas of our salt marshes, the incredible productivity of our nearshore bays, and the expansive pinelands in the adjacent uplands. Year-round opportunities abound to be outside and enjoy the natural resources we are blessed with. Just go prepared for the inevitable encounter with some of our bloodsucking flies and midges that are part of the package deal. A pair of binoculars, snacks, water and proper clothing provide the makings of a great day out, but I would also recommend a picture-taking device of some sort. I’ve basically given up on the heavier camera gear and the notion of getting long-distance close-ups. I now rely on my cell phone or a small digital camera; mainly for taking photos of flowers, bugs, and anything else that doesn’t require stealth and patience to shoot.
One of the best habitats to explore during this time of year for capturing memorable images is the upland pine flatwoods that is so abundant in the Florida Panhandle. There is no shortage of public lands that display some of the most well-managed pineland landscapes in the nation. Pineland ecosystems in the Southeast have been intimately linked with a natural fire regime, long before Europeans came on the scene. Successional cycles of increasing shrubby growth over time and the ability of the landscape to carry a fire after a lightning strike, have allowed these areas to develop with the “park-like” vista of a pine tree savanna in many cases. When fire is excluded by people, these ecosystems gradually convert to more hardwood species that tend to shade-out herbaceous growth on the ground and reduce the opportunity for new pine seedlings to become established. Professional land managers who work hard to mimic natural fire cycles on the lands they manage produce some astounding results. I can attest, as many of the areas where I hunt turkeys each spring are chosen more for the beauty of the landscape than the abundance of gobblers. Although fewer gobblers is not typically the ideal hunting scenario, the silver lining comes in the form of less competition with other hunters.
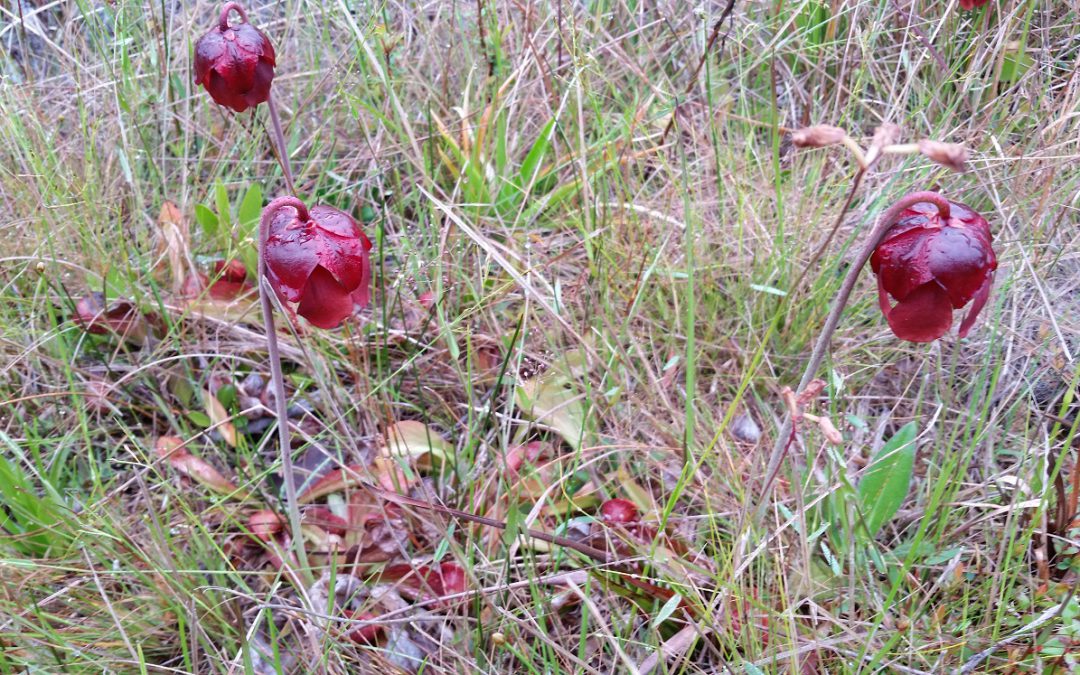
This spring I hunted in part of the St. Marks National Wildlife Refuge and had a nice mix of fairly recently burned pinelands to explore. Some were burned this spring, and was just starting to green-up with newly emerging grasses and forbs. Other areas were burned a year or two ago and you would never know it except for the charred bark on tree trunks. These areas recover to full greenery in a very short time. The foot-high wild blueberry bushes were loaded with green berries for summer wildlife feasts to come, and the photo opportunities for wildflowers abounded. Fire is so important in retaining a high species diversity in these habitats. Opening up the canopy allows sunlight to filter through to the forest floor and the recycling of nutrients in the ash supports many unique plants. There are several terrestrial orchids that bloom in the wetter soils (grass pink, colic root, lady’s tresses, etc.), and yellow flowers are prolific right now (St. John’s wort, sneeze weed, candy root and many more). I even saw some parrot pitcher plants in one wet spot, noticeable mainly by their tall maroon flowers. Fetterbush and staggerbush are also blooming with small flowers that look similar to blueberry blooms. The difference in scent of these two Lyonia shrubs is an easy way to tell them apart with fetterbush having a strong musky (not totally unpleasant) smell, while staggerbush (rusty Lyonia) has one of the sweetest, most pleasant smells of spring in the flatwoods.
So, while I did have the opportunity to chase around a gobbler this spring (who easily out-maneuvered me), I truly enjoyed my week of annual leave spent reconnecting with something that we too often take for granted. Take time to locate the state parks, national wildlife refuges, state forests and other public lands in your region. Then go outside. I mean it; none of us should miss the chance of a lifetime to see what we really have here.
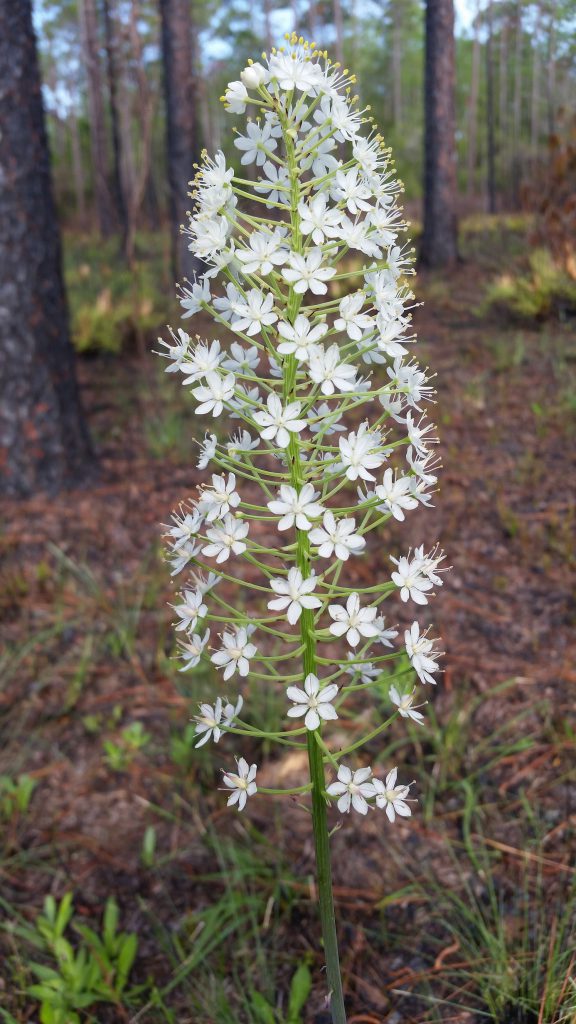

Crow poison, also know as Osceola’s plume shows up in wet flatwoods, most noticeably after a fire.

by Sheila Dunning | Apr 18, 2019

Young Longleaf Pine
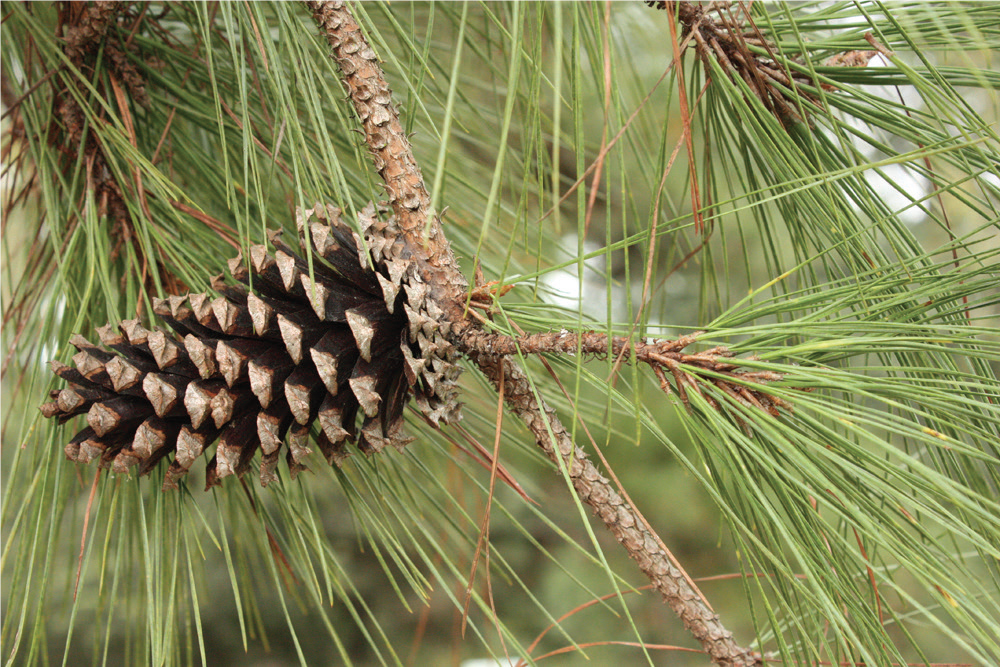
All of Florida’s ecosystems contain pine trees. There are seven native species in the state; Sand, Slash, Spruce, Shortleaf, Loblolly, Longleaf, and Pond. Each species grows best in its particular environment. Pines are highly important to wildlife habitats as food and shelter. Several species are equally valuable to Florida’s economy. Slash, Loblolly, and Longleaf are cultivated and managed to provide useful products such as paper, industrial chemicals, and lumber. All pines are evergreens, meaning they keep foliage year-round. The leaves emerge from the axil of each scale leaf into long slender needles clustered together in bundles. Needles are produced at the growing tips of each branch and remain on the tree for several years before turning reddish-brown and falling off. The bundles are referred to as “fascicles”. The length and number of needles in each fascicle is one way to help identify the different pine species.
A handy rule of thumb is that pines starting with “S” have needles in twos, while pines starting with “L” have needles in threes. And slash pine, which starts with “SL” has needles in twos and threes. The pond pine is also a three-needled fascicle. Pay attention to their length and the number that are held in a fascicle. Because the numbers per fascicle may vary, be sure to check several fascicles to get an overall sense for the plant! Longleaf has the longest needle, measuring over 10 inches. While sand pine has the shortest needles at around 2 inches in length. Pine cones are also a means for identification. Typically the longer the needle, the bigger the cone. But, they also vary in attachment and “spinyness’.

Cone of Loblolly Pine, attached directly to the stem
The outer (dorsal) surface of each seed cone scale has a diamond-shaped bulge, or “umbo,” formed by the first year’s growth. The umbo may or may not be armored with a “prickle,” a sharp point but not quite a spine or thorn, at the tip. As the seed cone continues to grow and expand, the exposed area at the end of each scale grows as well. The larger diamond-shaped area around the umbo, formed in the second year of growth, is called the “apophysis.” The shapes of the prickle, umbo, and apophysis can be helpful in identification. The male and female cones are separate structures, but both are present on the same plant. Pollen is produced by male cones and is carried by the wind to female cones where it fertilizes the ovules. Seeds develop and mature inside the female cones (also called the seed cones) for two years, protected by a series of tightly overlapping woody scales. Some pines open their seed cones after two years to release the seeds, while other pines continue to keep their cones tightly closed past maturity and release seeds in response to the heat of a forest fire.
To learn more about Florida’s pines and helpful hint on identification go to:
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/fr/fr00300.pdf

by Andrea Albertin | Mar 20, 2019
By Vance Crain and Andrea Albertin
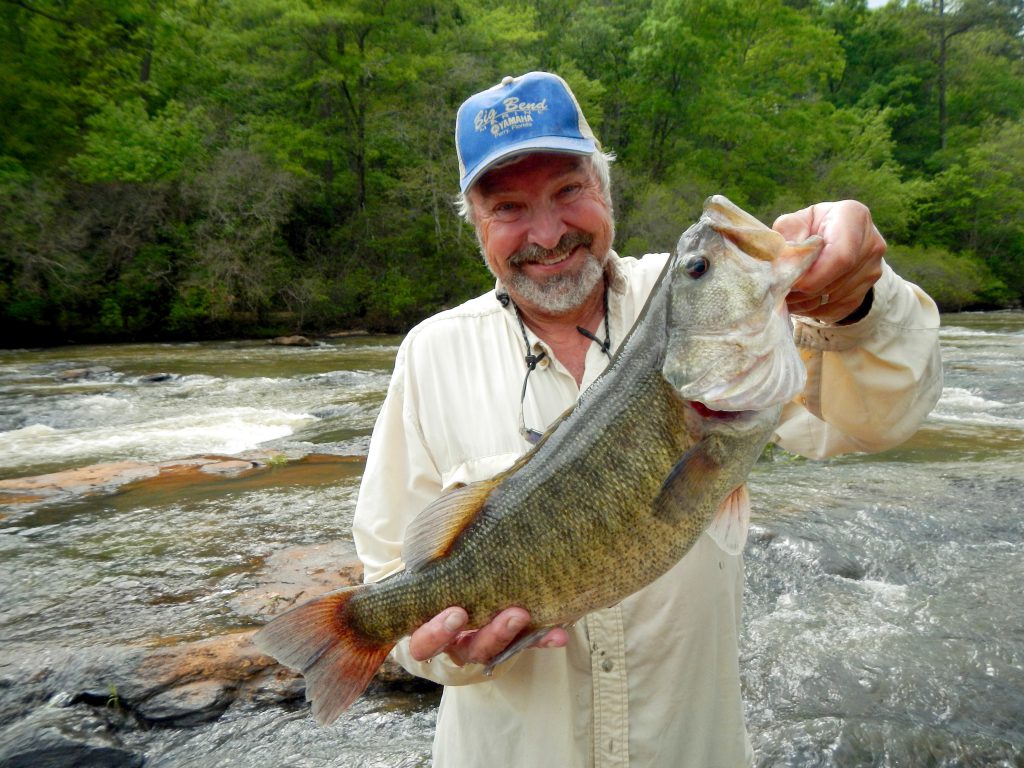

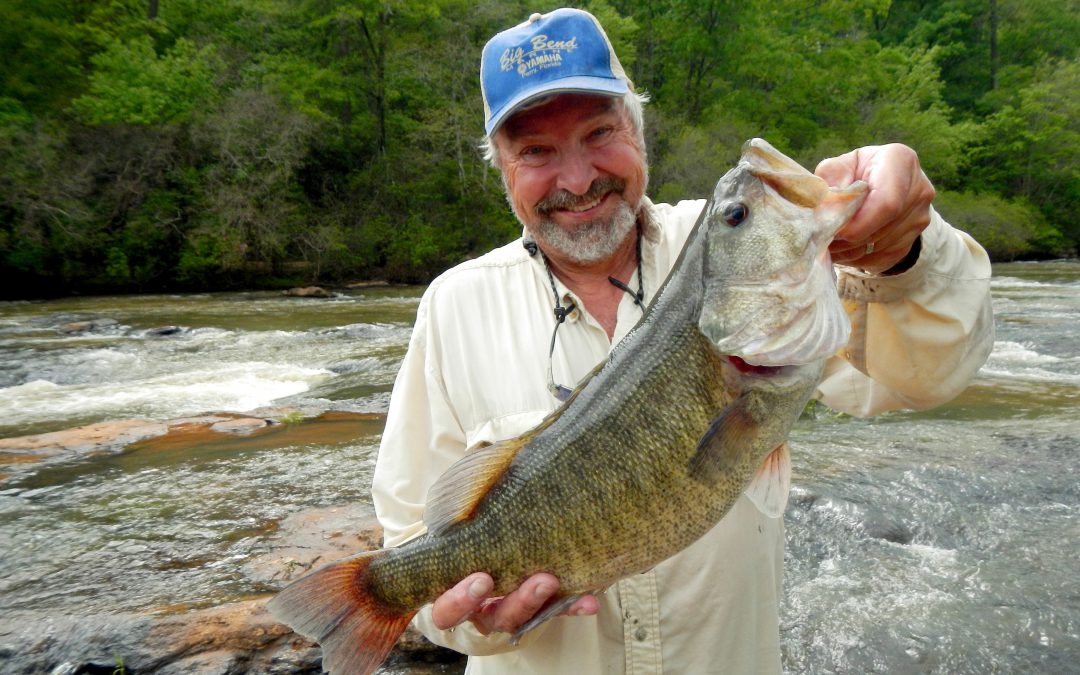
Fisherman with a large Shoal Bass in the Apalachicola-Chattahootchee-Flint River Basin. Photo credit: S. Sammons
Along the Chipola River in Florida’s Panhandle, farmers are doing their part to protect critical Shoal Bass habitat by implementing agricultural Best Management Practices (BMPs) that reduce sediment and nutrient runoff, and help conserve water.
Florida’s Shoal Bass
Lurking in the clear spring-fed Chipola River among limerock shoals and eel grass, is a predatory powerhouse, perfectly camouflaged in green and olive with tiger stripes along its body. The Shoal Bass (a species of Black Bass) tips the scale at just under 6 lbs. But what it lacks in size, it makes up for in power. Unlike any other bass, and found nowhere else in Florida, anglers travel long distances for a chance to pursue it. Floating along the swift current, rocks, and shoals will make you feel like you’ve been transported hundreds of miles away to the Georgia Piedmont, and it’s only the Live Oaks and palms overhanging the river that remind you that you’re still in Florida, and in a truly unique place.
Native to only one river basin in the world, the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint (ACF) River Basin, habitat loss is putting this species at risk. The Shoal Bass is a fluvial specialist, which means it can only survive in flowing water. Dams and reservoirs have eliminated habitat and isolated populations. Sediment runoff into waterways smothers habitat and prevents the species from reproducing.
In the Chipola River, the population is stable but its range is limited. Some of the most robust Shoal Bass numbers are found in a 6.5-mile section between the Peacock Bridge and Johnny Boy boat ramp. The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission has turned this section into a Shoal Bass catch and release only zone to protect the population. However, impacts from agricultural production and ranching, like erosion and nutrient runoff can degrade the habitat needed for the Shoal Bass to spawn.
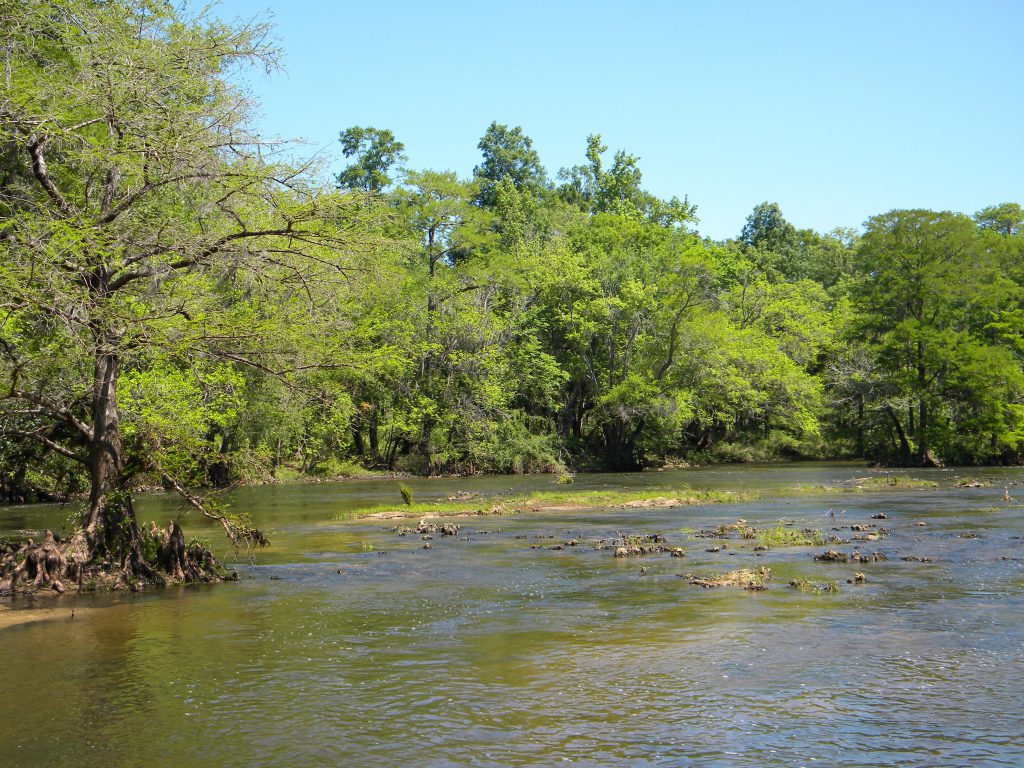

Preferred Shoal Bass habitat, a shoal in the Chipola River. Photo credit: V. Crain
Shoal Bass habitat conservation and BMPs
In 2010, the Southeast Aquatic Resources Partnership (SARP), the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and a group of scientists (the Black Bass Committee) developed the Native Black Bass Initiative. The goal of the initiative is to increase research and the protection of three Black Bass species native to the Southeast, including the Shoal Bass. It also defined the Shoal Bass as a keystone species, meaning protection of this apex predators’ habitat benefits a host of other threatened and endangered species.
Along the Chipola River, farmers are teaming up with SARP and other partners to protect Shoal Bass habitat and improve farming operations through BMP implementation. A major goal is to protect the river’s riparian zones (the areas along the borders). When healthy, these areas act like sponges by absorbing nutrients and sediment runoff. Livestock often degrade riparian zones by trampling vegetation and destroying the streambank when they go down to a river to drink. Farmers are installing alternative water supplies, like water wells and troughs in fields, and fencing out cattle from waterways to protect these buffer areas and improve water quality. Row crop farmers are helping conserve water in the river basin by using advanced irrigation technologies like soil moisture sensors to better inform irrigation scheduling and variable rate irrigation to increase irrigation efficiency. Cost-share funding from SARP, the USDA-NRCS and FDACS provide resources and technical expertise for farmers to implement these BMPs.
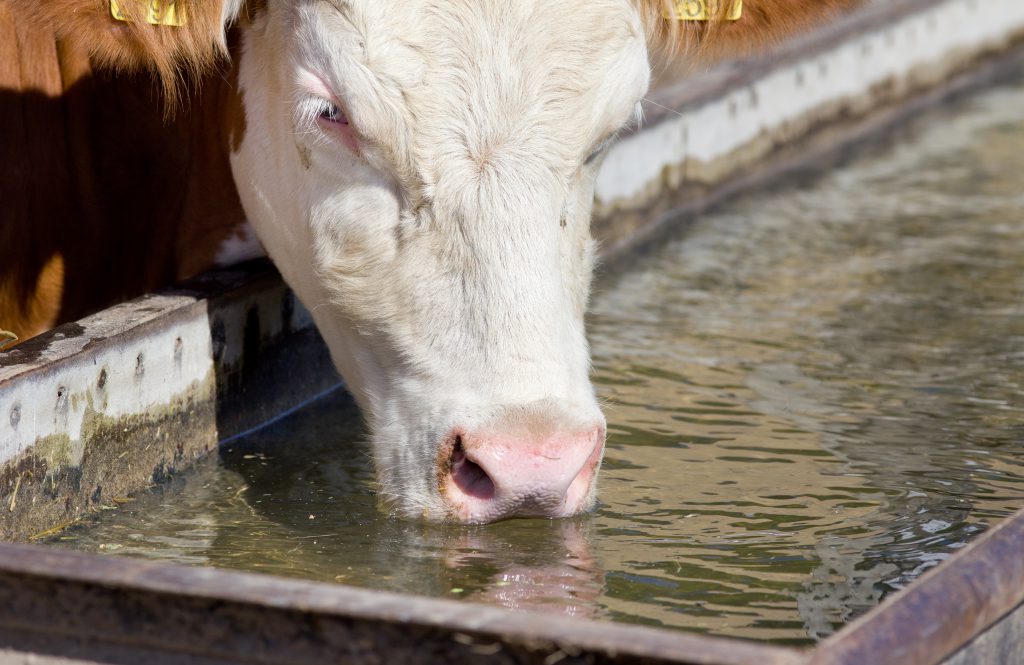

Holstein drinking from a water trough in the field, instead of going down to the river to get water which can cause erosion and problems with water quality. Photo credit: V. Crain
By working together in the Chipola River Basin, farmers, fisheries scientists and resource managers are helping ensure that critical habitat for Shoal Bass remains healthy. Not only is this important for the species and resource, but it will ensure that future generations can continue to enjoy this unique river and seeing one of these fish. So the next time you catch a Shoal Bass, thank a farmer.
For more information about BMPs and cost-share opportunities available for farmers and ranchers, contact your local FDACS field technician: https://www.freshfromflorida.com/Divisions-Offices/Agricultural-Water-Policy/Organization-Staff and NRCS field office USDA-NRCS field office: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/fl/contact/local/ For questions regarding the Native Black Bass Initiative or Shoal Bass habitat conservation, contact Vance Crain at vance@southeastaquatics.net
Vance Crain is the Native Black Bass Initiative Coordinator for the Southeast Aquatic Resource Partnership (SARP).

by Sheila Dunning | Dec 19, 2018
 Throughout history the evergreen tree has been a symbol of life. “Not only green when summer’s here, but also when it’s cold and dreary” as the Christmas carol “O Tannenbaum” says. After such devastating tree losses in the Panhandle this year, this winter is a prime time for installing more native evergreens.
Throughout history the evergreen tree has been a symbol of life. “Not only green when summer’s here, but also when it’s cold and dreary” as the Christmas carol “O Tannenbaum” says. After such devastating tree losses in the Panhandle this year, this winter is a prime time for installing more native evergreens.
While supporting the cut Christmas tree industry does create jobs and puts money into local economics, every few years considering adding to the urban forest by purchasing a living tree. Native evergreen trees such as Redcedar make a nice Christmas tree that can be planted following the holidays. The dense growth and attractive foliage make Redcedar a favorite for windbreaks, screens and wildlife cover. The heavy berry production provides a favorite food source for migrating Cedar Waxwing birds. Its high salt-tolerance makes it ideal for coastal locations. Their natural pyramidal-shape creates the traditional Christmas tree form, but can be easily pruned as a street tree.
Two species, Juniperus virginiana and Juniperus silicicola are native to Northwest Florida. Many botanists do not separate the two, but as they mature, Juniperus silicicola takes on a softer, more informal look. For those interested in creating a different look, maybe a Holly (Ilex,sp.) or Magnolia with full-to-the-ground branches could be your Christmas tree.
When planning for using a live Christmas tree there are a few things to consider. The tree needs sunlight, so restrict its inside time to less than a week. Make sure there is a catch basin for water under the tree, but never allow water to remain in the tray and don’t add fertilizer. Locate your tree in the coolest part of the room and away from heating ducts and fireplaces. After Christmas, install the new tree in an open, sunny part of the yard. After a few years you will be able to admire the living fence with all the wonderful memories of many years of holiday celebrations. Don’t forget to watch for the Cedar Waxwings in the Redcedar.

 Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be. 90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing. Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
















