
by Sheila Dunning | Oct 10, 2019
 Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
This spring, scientists from World Wildlife Fund Mexico estimated the population size of the overwintering Monarchs to be 6.05 hectacres of trees covered in orange. As the weather warmed, the butterflies headed north towards Canada (about three weeks early). It’s an impressive 2,000 mile adventure for an animal weighing less than 1 gram. Those butterflies west of the Rocky Mountains headed up California; while the eastern insects traveled over the “corn belt” and into New England. When August brought cooler days, all the Monarchs headed back south.
What the 2018 Monarch Watch data revealed was alarming. The returning eastern Monarch butterfly population had increased by 144 percent, the highest count since 2006. But, the count still represented a decline of 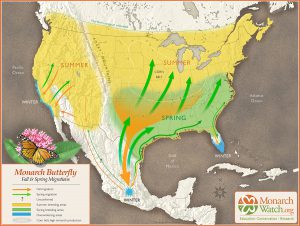 90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
Scientists estimate that 6 hectacres is the threshold to be out of the immediate danger of migratory collapse. To put things in scale: A single winter storm in January 2002 killed an estimated 500 million Monarchs in their Mexico home. However, with recent changes on the status of the Endangered Species Act, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has delayed its decision until December 2020. One more year of data may be helpful to monarch conservation efforts.
 Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
There is something more you can do to increase the success of the butterflies along their migratory path – plant more Milkweed (Asclepias spp.). It’s the only plant the Monarch caterpillar will eat. When they leave their hibernation in Mexico around February or March, the adults must find Milkweed all along the path to Canada in order to lay their eggs. Butterflies only live two to six weeks. They must mate and lay eggs along the way in order for the population to continue its flight. Each generation must have Milkweed about every 700 miles. Check with the local nurseries for plants. Though orange is the most common native species, Milkweed comes in many colors and leaf shapes.

by Shep Eubanks | Sep 13, 2019

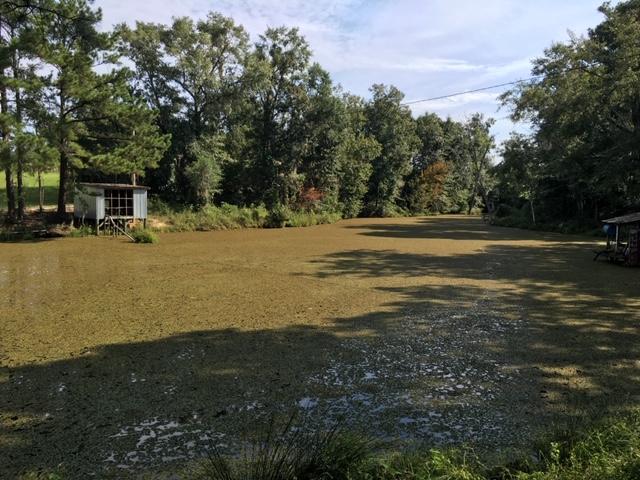
Common Salvinia Covering Farm pond in Gadsden County
Photo Credit – Shep Eubanks UF/IFAS Gadsden County Extension

Close up of common Salvinia
Photo Credit – Shep Eubanks UF/IFAS Gadsden County Extension
Aquatic weed problems are common in the panhandle of Florida. Common Salvinia (Salvinia minima) is a persistent invasive weed problem found in many ponds in Gadsden County. There are ten species of salvinia in the tropical Americas but none are native to Florida. They are actually floating ferns that measure about 3/4 inch in length. Typically it is found in still waters that contain high organic matter. It can be found free-floating or in the mud. The leaves are round to somewhat broadly elliptic, (0.4–1 in long), with the upper surface having 4-pronged hairs and the lower surface is hairy. It commonly occurs in freshwater ponds and swamps from the peninsula to the central panhandle of Florida.
Reproduction is by spores, or fragmentation of plants, and it can proliferate rapidly allowing it to be an aggressive invasive species. When these colonies cover the surface of a pond as pictured above they need to be controlled as the risk of oxygen depletion and fish kill is a possibility. If the pond is heavily infested with weeds, it may be possible (depending on the herbicide chosen) to treat the pond in sections and let each section decompose for about two weeks before treating another section. Aeration, particularly at night, for several days after treatment may help control the oxygen depletion.
Control measures include raking or seining, but remember that fragmentation propagates the plant. Grass carp will consume salvinia but are usually not effective for total control. Chemical control measures include :carfentrazone, diquat, fluridone, flumioxazin, glyphosate, imazamox, and penoxsulam.
For more information reference these IFAS publications:
Efficacy of Herbicide Active ingredients Against Aquatic Weeds
Common salvinia
For help with controlling Common salvinia consult with your local Extension Agent for weed control recommendations, as needed.

by Erik Lovestrand | May 31, 2019
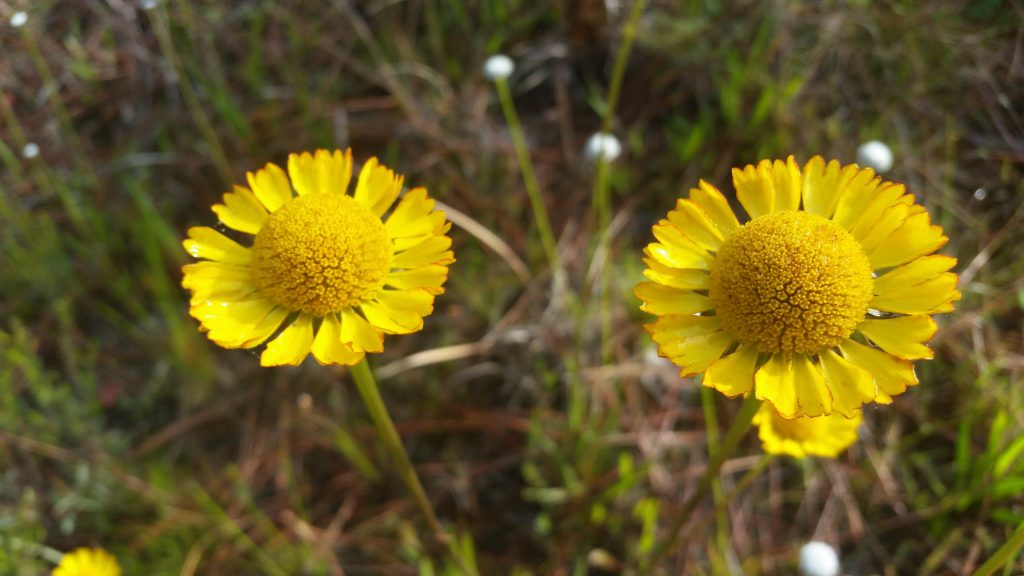

Yellow asters such as sneezeweed bloom profusely during summertime in the flatwoods.
Our coastal habitats are some of the most beautiful on the planet. Where else can you have the breathtaking, wide open vistas of our salt marshes, the incredible productivity of our nearshore bays, and the expansive pinelands in the adjacent uplands. Year-round opportunities abound to be outside and enjoy the natural resources we are blessed with. Just go prepared for the inevitable encounter with some of our bloodsucking flies and midges that are part of the package deal. A pair of binoculars, snacks, water and proper clothing provide the makings of a great day out, but I would also recommend a picture-taking device of some sort. I’ve basically given up on the heavier camera gear and the notion of getting long-distance close-ups. I now rely on my cell phone or a small digital camera; mainly for taking photos of flowers, bugs, and anything else that doesn’t require stealth and patience to shoot.
One of the best habitats to explore during this time of year for capturing memorable images is the upland pine flatwoods that is so abundant in the Florida Panhandle. There is no shortage of public lands that display some of the most well-managed pineland landscapes in the nation. Pineland ecosystems in the Southeast have been intimately linked with a natural fire regime, long before Europeans came on the scene. Successional cycles of increasing shrubby growth over time and the ability of the landscape to carry a fire after a lightning strike, have allowed these areas to develop with the “park-like” vista of a pine tree savanna in many cases. When fire is excluded by people, these ecosystems gradually convert to more hardwood species that tend to shade-out herbaceous growth on the ground and reduce the opportunity for new pine seedlings to become established. Professional land managers who work hard to mimic natural fire cycles on the lands they manage produce some astounding results. I can attest, as many of the areas where I hunt turkeys each spring are chosen more for the beauty of the landscape than the abundance of gobblers. Although fewer gobblers is not typically the ideal hunting scenario, the silver lining comes in the form of less competition with other hunters.
This spring I hunted in part of the St. Marks National Wildlife Refuge and had a nice mix of fairly recently burned pinelands to explore. Some were burned this spring, and was just starting to green-up with newly emerging grasses and forbs. Other areas were burned a year or two ago and you would never know it except for the charred bark on tree trunks. These areas recover to full greenery in a very short time. The foot-high wild blueberry bushes were loaded with green berries for summer wildlife feasts to come, and the photo opportunities for wildflowers abounded. Fire is so important in retaining a high species diversity in these habitats. Opening up the canopy allows sunlight to filter through to the forest floor and the recycling of nutrients in the ash supports many unique plants. There are several terrestrial orchids that bloom in the wetter soils (grass pink, colic root, lady’s tresses, etc.), and yellow flowers are prolific right now (St. John’s wort, sneeze weed, candy root and many more). I even saw some parrot pitcher plants in one wet spot, noticeable mainly by their tall maroon flowers. Fetterbush and staggerbush are also blooming with small flowers that look similar to blueberry blooms. The difference in scent of these two Lyonia shrubs is an easy way to tell them apart with fetterbush having a strong musky (not totally unpleasant) smell, while staggerbush (rusty Lyonia) has one of the sweetest, most pleasant smells of spring in the flatwoods.
So, while I did have the opportunity to chase around a gobbler this spring (who easily out-maneuvered me), I truly enjoyed my week of annual leave spent reconnecting with something that we too often take for granted. Take time to locate the state parks, national wildlife refuges, state forests and other public lands in your region. Then go outside. I mean it; none of us should miss the chance of a lifetime to see what we really have here.
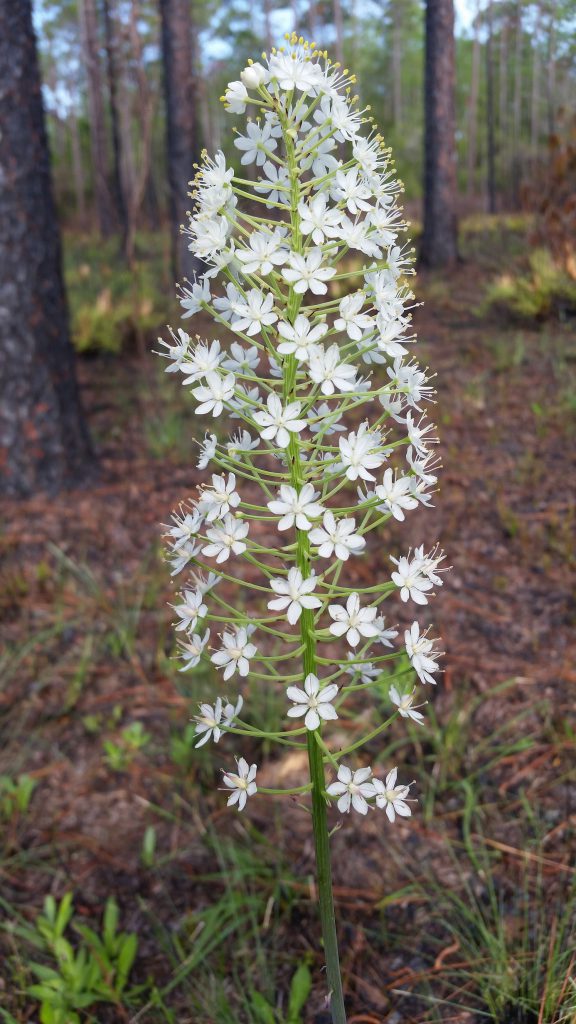

Crow poison, also know as Osceola’s plume shows up in wet flatwoods, most noticeably after a fire.

by Sheila Dunning | Apr 18, 2019

Young Longleaf Pine
All of Florida’s ecosystems contain pine trees. There are seven native species in the state; Sand, Slash, Spruce, Shortleaf, Loblolly, Longleaf, and Pond. Each species grows best in its particular environment. Pines are highly important to wildlife habitats as food and shelter. Several species are equally valuable to Florida’s economy. Slash, Loblolly, and Longleaf are cultivated and managed to provide useful products such as paper, industrial chemicals, and lumber. All pines are evergreens, meaning they keep foliage year-round. The leaves emerge from the axil of each scale leaf into long slender needles clustered together in bundles. Needles are produced at the growing tips of each branch and remain on the tree for several years before turning reddish-brown and falling off. The bundles are referred to as “fascicles”. The length and number of needles in each fascicle is one way to help identify the different pine species.
A handy rule of thumb is that pines starting with “S” have needles in twos, while pines starting with “L” have needles in threes. And slash pine, which starts with “SL” has needles in twos and threes. The pond pine is also a three-needled fascicle. Pay attention to their length and the number that are held in a fascicle. Because the numbers per fascicle may vary, be sure to check several fascicles to get an overall sense for the plant! Longleaf has the longest needle, measuring over 10 inches. While sand pine has the shortest needles at around 2 inches in length. Pine cones are also a means for identification. Typically the longer the needle, the bigger the cone. But, they also vary in attachment and “spinyness’.

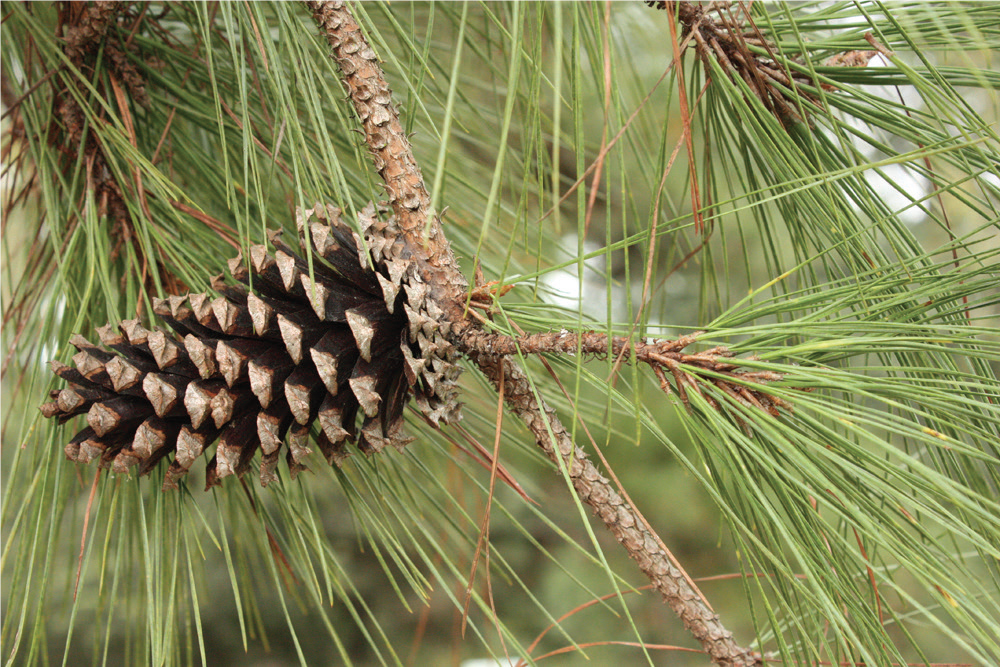
Cone of Loblolly Pine, attached directly to the stem
The outer (dorsal) surface of each seed cone scale has a diamond-shaped bulge, or “umbo,” formed by the first year’s growth. The umbo may or may not be armored with a “prickle,” a sharp point but not quite a spine or thorn, at the tip. As the seed cone continues to grow and expand, the exposed area at the end of each scale grows as well. The larger diamond-shaped area around the umbo, formed in the second year of growth, is called the “apophysis.” The shapes of the prickle, umbo, and apophysis can be helpful in identification. The male and female cones are separate structures, but both are present on the same plant. Pollen is produced by male cones and is carried by the wind to female cones where it fertilizes the ovules. Seeds develop and mature inside the female cones (also called the seed cones) for two years, protected by a series of tightly overlapping woody scales. Some pines open their seed cones after two years to release the seeds, while other pines continue to keep their cones tightly closed past maturity and release seeds in response to the heat of a forest fire.
To learn more about Florida’s pines and helpful hint on identification go to:
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/fr/fr00300.pdf

by Sheila Dunning | Dec 19, 2018
 Throughout history the evergreen tree has been a symbol of life. “Not only green when summer’s here, but also when it’s cold and dreary” as the Christmas carol “O Tannenbaum” says. After such devastating tree losses in the Panhandle this year, this winter is a prime time for installing more native evergreens.
Throughout history the evergreen tree has been a symbol of life. “Not only green when summer’s here, but also when it’s cold and dreary” as the Christmas carol “O Tannenbaum” says. After such devastating tree losses in the Panhandle this year, this winter is a prime time for installing more native evergreens.
While supporting the cut Christmas tree industry does create jobs and puts money into local economics, every few years considering adding to the urban forest by purchasing a living tree. Native evergreen trees such as Redcedar make a nice Christmas tree that can be planted following the holidays. The dense growth and attractive foliage make Redcedar a favorite for windbreaks, screens and wildlife cover. The heavy berry production provides a favorite food source for migrating Cedar Waxwing birds. Its high salt-tolerance makes it ideal for coastal locations. Their natural pyramidal-shape creates the traditional Christmas tree form, but can be easily pruned as a street tree.
Two species, Juniperus virginiana and Juniperus silicicola are native to Northwest Florida. Many botanists do not separate the two, but as they mature, Juniperus silicicola takes on a softer, more informal look. For those interested in creating a different look, maybe a Holly (Ilex,sp.) or Magnolia with full-to-the-ground branches could be your Christmas tree.
When planning for using a live Christmas tree there are a few things to consider. The tree needs sunlight, so restrict its inside time to less than a week. Make sure there is a catch basin for water under the tree, but never allow water to remain in the tray and don’t add fertilizer. Locate your tree in the coolest part of the room and away from heating ducts and fireplaces. After Christmas, install the new tree in an open, sunny part of the yard. After a few years you will be able to admire the living fence with all the wonderful memories of many years of holiday celebrations. Don’t forget to watch for the Cedar Waxwings in the Redcedar.

by Scott Jackson | May 25, 2018
By L. Scott Jackson and Julie B. McConnell, UF/IFAS Extension Bay County
Northwest Florida’s pristine natural world is being threaten by a group of non-native plants and animals known collectively as invasive species. Exotic invasive species originate from other continents and have adverse impacts on our native habitats and species. Many of these problem non-natives have nothing to keep them in check since there’s nothing that eats or preys on them in their “new world”. One of the most problematic and widespread invasive plants we have in our local area is air potato vine.
Air potato vine originated in Asia and Africa. It was brought to Florida in the early 1900s. People moved this plant with them using it for food and traditional medicine. However, raw forms of air potato are toxic and consumption is not recommended. This quick growing vine reproduces from tubers or “potatoes”. The potato drops from the vine and grows into the soil to start new vines. Air potato is especially a problem in disturbed areas like utility easements, which can provide easy entry into forests. Significant tree damage can occur in areas with heavy air potato infestation because vines can entirely cover large trees. Some sources report vine growth rates up to eight inches per day!
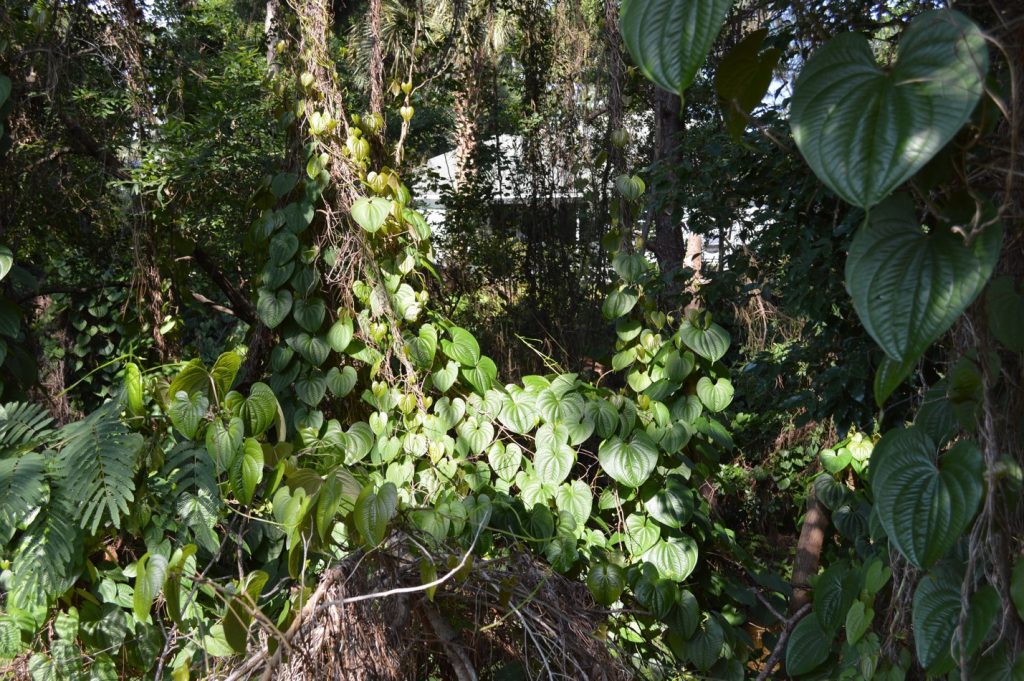

Air Potato vines covering native shrubs and trees in Bay County, Florida. (Photo by L. Scott Jackson)
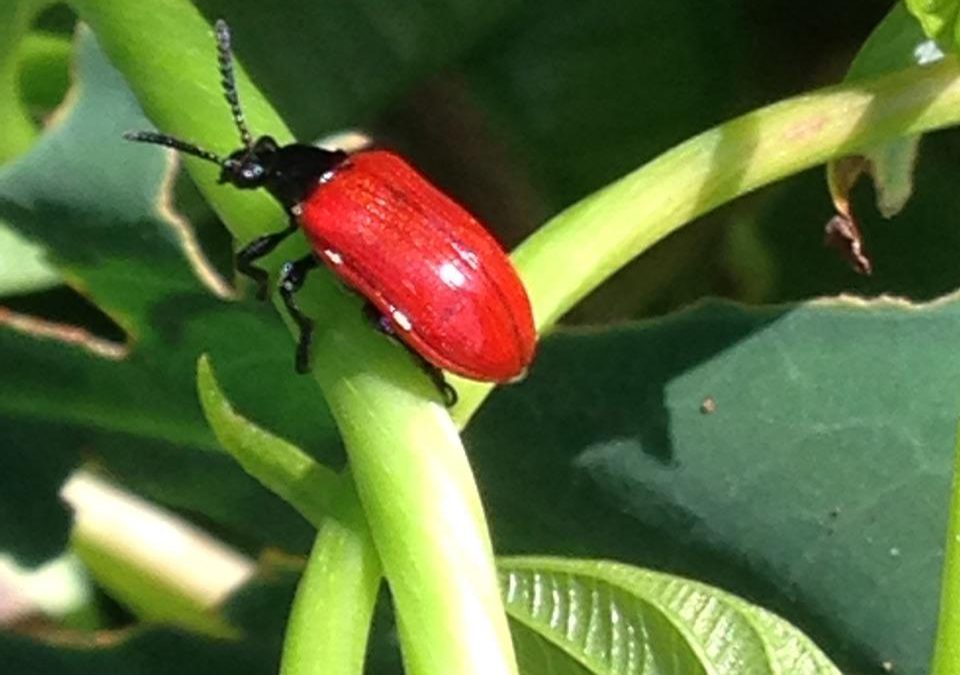
Mechanical removal of vines and potatoes from the soil is one control method. Additionally, herbicides are often used to remediate areas dominated by air potato vine but this runs the risk of affecting non-target plants underneath the vine. A new tool for control was introduced to Florida in 2011, the air potato leaf beetle. Air potato beetle releases have been monitored and evaluated by United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) researchers and scientists for several years.

Air Potato Beetle crawling on leaf stem. Beetles eat leaves curtailing the growth and impact of air potato. (Photo by Julie B. McConnell)
Air potato beetles target only air potato leaves making them a perfect candidate for biological control. Biological controls aid in the management of target invasive species. Complete eradication is not expected, however suppression and reduced spread of air potato vine is realistic.
UF/IFAS Extension Bay County will host the Air Potato Challenge on June 6, 2018. Citizen scientist will receive air potato beetles and training regarding introduction of beetles into their private property infested with air potato vine. Pre-registration is recommended to receive the air potato beetles. Please visit http://bit.ly/bayairpotato
In conjunction with the Air Potato Challenge, UF/IFAS Extension Bay County will be hosting an invasive species awareness workshop. Dr. Steve Johnson, UF/IFAS Associate Professor of Wildlife Ecology, will be presenting “Exotic Invaders: Reptiles and Amphibians of Concern in Northwest Florida”. Additionally, experts from UF/IFAS Extension, Florida Fish and Wildlife, and the Science and Discovery center will have live exhibits featuring invasive reptiles, lionfish, and plants. For more information visit http://bay.ifas.ufl.edu or call the UF/IFAS Extension Bay County Office at 850-784-6105.

Flyer for Air Potato Challenge and Invasive Species Workshop June 6 2018

 Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be. 90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing. Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.















