
by Laura Tiu | May 22, 2020
Have you ever been on a walk, passed a beautiful flowering bush, and wondered what it was? Well, wonder no more! You can become an expert naturalist by using an easy smartphone app, iNaturalist. With one easy download, you can connect with others to identify species and document their occurrence.
iNaturalist is a community of naturalists, citizen scientists and biologists working together to share observations of biodiversity and map the occurrence. Parents need to know that iNaturalist is an online community that allows users age 13 and older to share pictures and locations of the living things they see around them. While considered very safe, like any online network, teens should be cautious with sharing.
Getting started is easy. All you need to do is create an account at iNaturalist.org and download their free iNaturalist app to your smartphone (Android or iOS). You can then start making your own nature observations, upload them to iNaturalist where you can share your discoveries with others, and also let other iNaturalist users help identify what you have seen.
iNaturalist is a great way to connect with nature and generate scientifically valuable biodiversity data. You can use it for your own personal fulfillment, or as part of a group. You can even use the project feature which allows you to have a central page that displays all the observations made within a location, or all observations made by a group. Why not organize your neighbors, club, or friends and challenge them to post their observations?

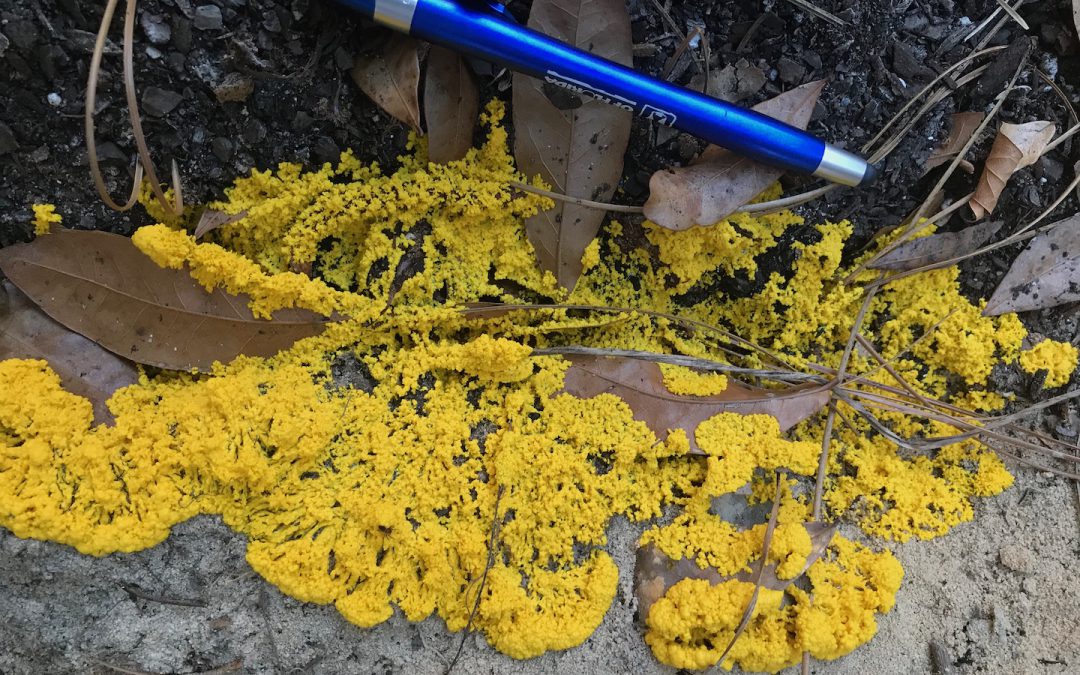
Mystery blob in the garden. Can you figure out what it is? Photo: Laura Tiu
I recently used iNaturalist to identify a bright yellow blob that sprung up in my garden overnight. I won’t spoil the surprise by telling you what it is. Why don’t you head on over to iNaturalist.org and see if you can figure it out? It will be your first step to becoming an expert naturalist.

by Chris Verlinde | May 1, 2020

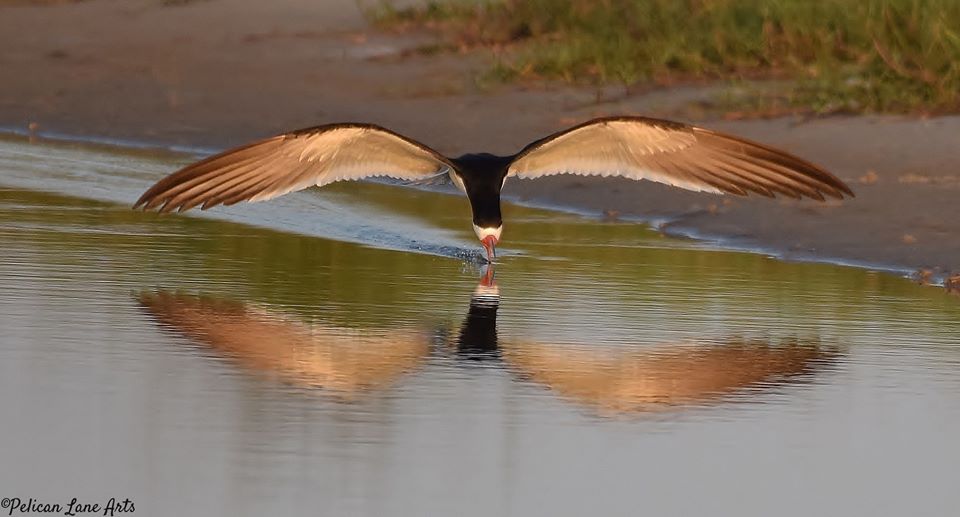
Black Skimmers foraging for fish. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
Black Skimmers and Least Terns, state listed species of seabirds, have returned along the coastal areas of the northern Gulf of Mexico! These colorful, dynamic birds are fun to watch, which can be done without disturbing the them.

Shorebirds foraging. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.

Black Skimmer with a fish. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
What is the difference between a seabird and shorebird?
Among other behaviors, their foraging habits are the easiest way to distinguish between the two. The seabirds depend on the open water to forage on fish and small invertebrates. The shorebirds are the camouflaged birds that can found along the shore, using their specialized beaks to poke in the sandy areas to forage for invertebrates.
Both seabirds and shorebirds nest on our local beaches, spoil islands, and artificial habitats such as gravel rooftops. Many of these birds are listed as endangered or threatened species by state and federal agencies.

Juvenile Black Skimmer learning to forage. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
Adult black skimmers are easily identified by their long, black and orange bills, black upper body and white underside. They are most active in the early morning and evening while feeding. You can watch them swoop and skim along the water at many locations along the Gulf Coast. Watch for their tell-tale skimming as they skim the surface of the water with their beaks open, foraging for small fish and invertebrates. The lower mandible (beak) is longer than the upper mandible, this adaptation allows these birds to be efficient at catching their prey.

Least Tern “dive bombing” a Black Skimmer that is too close to the Least Tern nest. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
Adult breeding least terns are much smaller birds with a white underside and a grey-upper body. Their bill is yellow, they have a white forehead and a black stripe across their eyes. Just above the tail feathers, there are two dark primary feathers that appear to look like a black tip at the back end of the bird. Terns feed by diving down to the water to grab their prey. They also use this “dive-bombing” technique to ward off predators, pets and humans from their nests, eggs and chicks.

Least Tern with chicks. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
Both Black Skimmers and Least Terns nest in colonies, which means they nest with many other birds. Black skimmers and Least Terns nest in sandy areas along the beach. They create a “scrape” in the sand. The birds lay their eggs in the shallow depression, the eggs blend into the beach sand and are very hard to see by humans and predators. In order to avoid disturbing the birds when they are sitting on their nests, known nesting areas are temporarily roped off by Audubon and/or Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) representatives. This is done to protect the birds while they are nesting, caring for the babies and as the babies begin to learn to fly and forage for themselves.
Threats to these beautiful acrobats include loss of habitat, which means less space for the birds to rest, nest and forage. Disturbances from human caused activities such as:
- walking through nesting grounds
- allowing pets to run off-leash in nesting areas
- feral cats and other predators
- litter
- driving on the beach
- fireworks and other loud noises
Audubon and FWC rope-off nesting areas to protect the birds, their eggs and chicks. These nesting areas have signage asking visitors to stay out of nesting zones, so the chicks have a better chance of surviving. When a bird is disturbed off their nest, there is increased vulnerability to predators, heat and the parents may not return to the nest.

Black Skimmer feeding a chick. Photo Credit: Jan Trzepacz, Pelican Lane Arts.
To observe these birds, stay a safe distance away, zoom in with a telescope, phone, camera or binoculars, you may see a fluffy little chick! Let’s all work to give the birds some space.
Special thanks to Jan Trzepacz of Pelican Lane Arts for the use of these beautiful photos.
To learn about the Audubon Shorebird program on Navarre Beach, FL check out the Relax on Navarre Beach Facebook webinar presentation by Caroline Stahala, Audubon Western Florida Panhandle Shorebird Program Coordinator:
In some areas these birds nest close to the road. These areas have temporarily reduced speed limits, please drive the speed limit to avoid hitting a chick. If you are interested in receiving a “chick magnet” for your car,  to show you support bird conservation, please send an email to: chrismv@ufl.edu, Please put “chick magnet” in the subject line. Please allow 2 weeks to receive your magnet in the mail. Limited quantities available.
to show you support bird conservation, please send an email to: chrismv@ufl.edu, Please put “chick magnet” in the subject line. Please allow 2 weeks to receive your magnet in the mail. Limited quantities available.

by Mark Mauldin | Oct 10, 2019

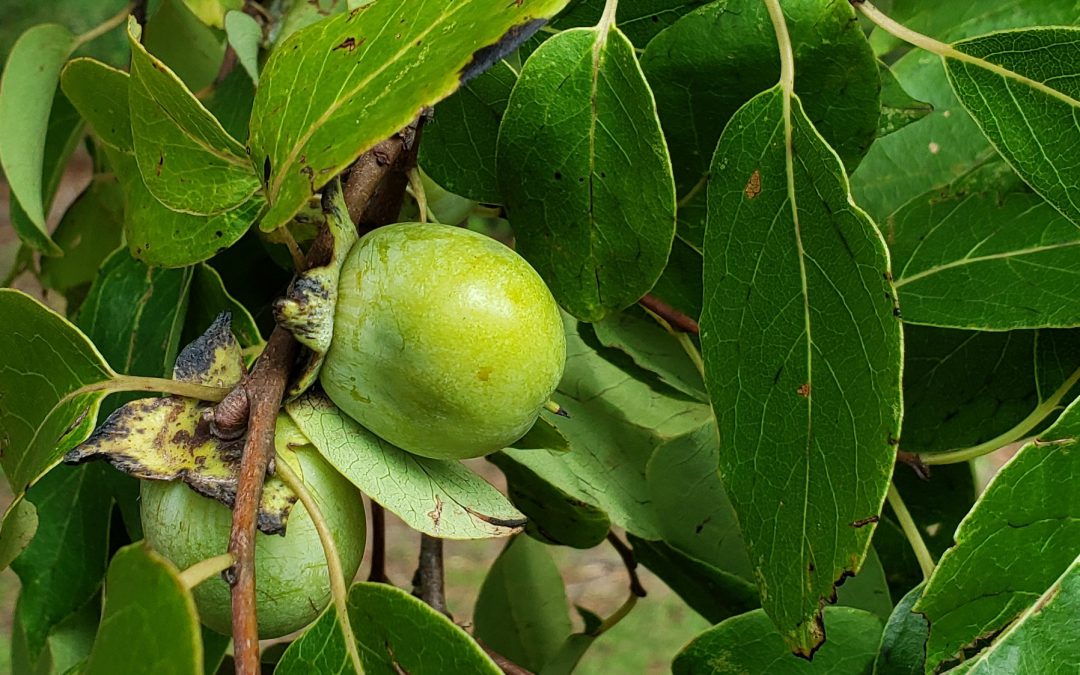
Protecting and promoting plants that produce soft mast, like this wild persimmon, can be a crucial step in improving wildlife habitat. Note: This time of year persimmons will be orange, the picture was taken earlier in the summer.
Photo Credit: Mark Mauldin
Landowners frequently prioritize wildlife abundance and diversity in their management goals. This is often related to a desired recreational activity (hunting, bird watching, etc.).
In order to successfully meet wildlife related management goals, landowners need to understand that animals frequent specific areas based largely on the quantity, quality and diversity of the food and cover resources available. Implementing management strategies that improve wildlife habitat will lead to greater wildlife abundance and diversity.
Herbivorous wildlife feed on plants, mostly in the form of forages and mast crops. All wildlife species have preferences in terms of habitat, especially food sources. Identifying these preferences and managing habitat to meet them will promote the abundance of the desired species.
Herbaceous plants, leaves, buds, etc. – serve as forages for many wildlife species. Promoting their growth and diversity is essential for improving wildlife habitat. Three common habitat management practices that promote forage growth include:
1) Create forest openings and edges; forested areas with multiple species and/or stand ages, areas left unforested allowing for increased herbaceous plant growth.
2) Thinning; open forest canopy allowing more light to hit the ground increasing herbaceous plant growth and diversity.
3) Prescribed fire; recycle nutrients, greatly improve the nutritional quality of herbage and browse, suppress woody understory growth.
Mast – the seeds and fruits of trees and shrubs – is often one of the most important wildlife food sources on a property.
Hard mast includes shelled seeds, like acorns and hickory nuts and is generally produced in the fall and serves as a wildlife food source during the winter.
Soft mast includes fruits, like blackberries and persimmons, and is generally produced in the warmer months, providing vital nutrition when wildlife species are reproducing and/or migrating.
Making management decisions that protect and promote mast producing trees will encourage wildlife populations.
Landowners can make supplemental plantings to increase the quantity and quality of the nutrition available to wildlife. These supplemental plantings (food plots/forage crops and mast producing trees) can be quite expensive and should be well planned to help maximize the return on investment.
Key points to remember to help ensure the success of supplemental wildlife plantings.
- Select species/varieties that are well adapted to the site.
- Take soil samples and make recommended soil amendments prior to planting.
- Make plantings in areas already frequented by wildlife (edges, openings, etc.).
- Food plots should be between 1 and 5 acres. Long, narrow designs that maximize proximity to cover are generally more effective.
Habitat management and other wildlife related topics are being featured this year in the UF/IFAS building at the Sunbelt Ag Expo. Make plans to attend “North America’s Premiere Farm Show” and stop by the UF/IFAS building, get some peanuts and orange juice and learn more about Florida’s Wildlife.
 If you have any questions about the topics mentioned above, contact your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Office or check out the additional articles listed on the page linked below.
If you have any questions about the topics mentioned above, contact your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Office or check out the additional articles listed on the page linked below.
EDIS – Wildlife Forages
A significant portion of this article was summarized from Establishing and Maintaining Wildlife Food Sources by Chris Demers et al.

by Mark Mauldin | Sep 2, 2018

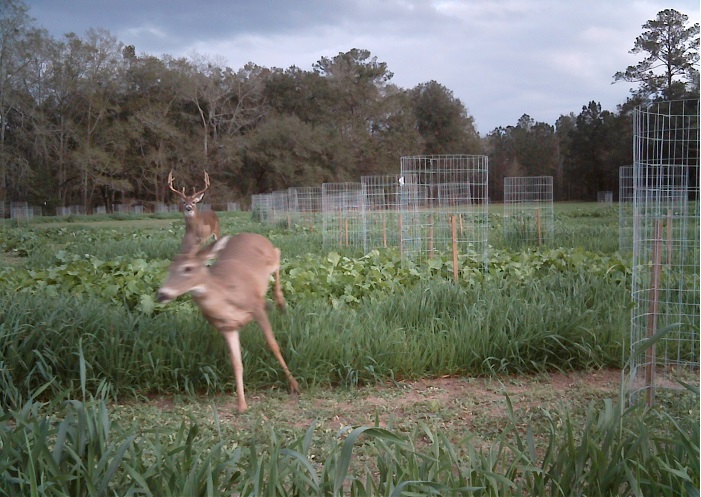
A buck chases a doe through plots of wildlife forages being evaluated at the University of Florida’s North Florida Research and Education Center. Photo Courtesy of Holly Ober
I know it feels too hot outside to talk about hunting season or cool-season food plots, but planting time will be here before you know it and now’s the time to start preparing. The recommended planting date for practically all cool-season forage crops in Northwest Florida is October 1 – November 15. Assuming adequate soil moisture, planting during the first half of the range is preferred. Between now and planting time there are several factors that need to be considered and addressed.
Invasive and/or Perennial Weed Control – Deer and other wildlife species utilize many soft/annual “weeds” as forage so controlling them is usually not a major concern. But from time to time unwanted perennials (grasses and woody shrubs) need to be controlled. An unfortunate and all too common example of and unwanted perennial is cogongrass – a highly invasive grass that should always be controlled if found. Effective control of perennial weeds, like cogongrass generally involves the use of herbicides. Late summer/early fall is a very effective time to treat unwanted perennials. Fortunately, this coincides well with the transition between warm-season and cool-season forages. If you have unwanted, perennial weeds in your food plots get them identified now and controlled before you plant your cool-season forages.

Cogongrass shown here with seedheads – more typically seen in the spring. If you suspect you have cogongrass in or around your food plots please consult your UF/IFAS Extension Agent how control options.
Photo credit: Mark Mauldin
Soil Fertility Management – In my experience, the most common cause for poor plant performance in food plots is inadequate soil fertility. Before planting time collect and submit soil samples from each of your food plots. Laboratory analysis of the samples will let you know the fertilizer and lime requirements of the upcoming cool-season crop. It is very important to have the analysis performed prior to planting so performance hindering issues can be prevented. Otherwise, during the growing season, by the time you realize something is wrong, it will likely be too late to effectively address the problem. This is particularly true if the issue is related to soil pH. To affect soil pH in a timely manner lime needs to be incorporated into the soil. Incorporation is impossible after the new crop has been planted. Soil analysis performed at the University of Florida’s Extension Soil Testing Lab cost $7 per sample. Your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Agent can assist you with the collection and submission process as well as help you interpret the results.
Variety Selection & Seed Sourcing – Sometimes it takes some time to find the best products/varieties. Just because forage seeds are sold locally doesn’t mean that the crop or specific variety is well suited to this area. The high temperatures and disease pressure associated with Florida, even in the “cool-season” mean that many products that do very well in other parts of the country may struggle here. Below are some specific forages that are favored by wildlife (specifically white-tailed deer) and generally well adapted to Florida. You may discover that these varieties are not sitting on the shelf at the local feed & seed. Often local suppliers can get specific varieties, but they must be special ordered, which adds time to the process. Hence the need to start planning and sourcing seed early.
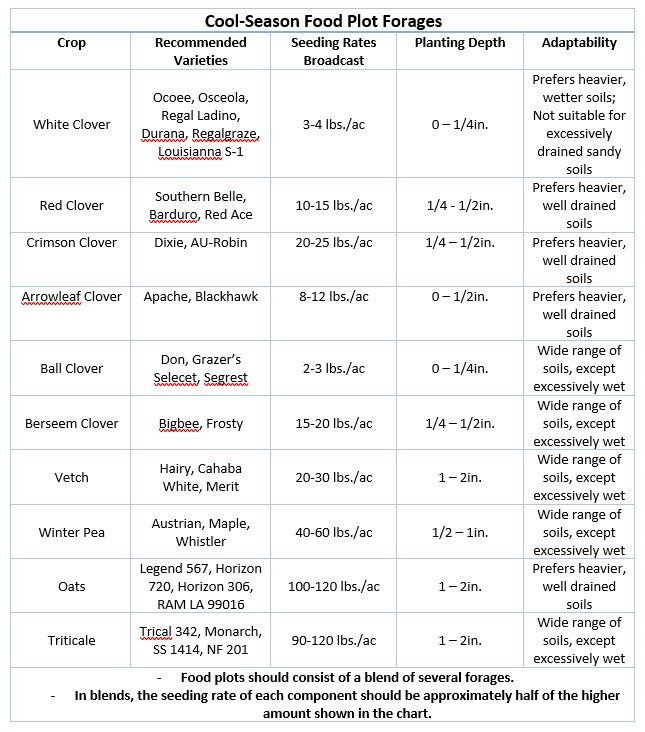
If you are debating trying food plots on your property for the first time, please carefully consider the following. Food plots are not easy – Making productive food plots that provide a measurable, positive impact to the wildlife on your property takes considerable time, effort, and money. Considering this, food plots really only make sense when viewed as habitat improvements that provide long term benefits to multiple wildlife species. If you are looking for nothing more than a deer attractant during hunting season food plots are not a very practical option. For more information on getting started with food plots contact your county’s UF/IFAS Extension Office and check out the reference below.

by hollyober | Dec 16, 2016

Christmas trees can provide benefits to wildlife long after they have served as holiday decoration indoors. Credits: IFAS photo database.
Americans purchased approximately 30 million live Christmas trees last year. If you plan to have a live tree this winter, and you’re wondering what you could do with your tree once it has finished its role as holiday decoration in your home, read below. Rather than simply dragging your tree to the curb for the waste disposal truck to pick up, you could prolong the life of your holiday tree by repurposing it to benefit wildlife.
YOUR TREE COULD PROVIDE FOOD FOR WILDLIFE
Many of the needles may have dropped from your Christmas tree as it dried out while indoors, but the branches should still be intact. This means your tree could be used as a frame to present food for wildlife. After removing your indoor decorations, consider propping the tree up in your yard (perhaps using the same stand you used indoors), and adorning the branches with food enjoyed by wildlife visitors. Some low-budget options include mesh bags filled with bird seed (black oil sunflower seed, safflower seed, and thistle (nyjer) are favorites of many common backyard birds), pine cones smeared with peanut butter, home-made suet cakes, and strings of fruit such as apple slices, orange slices, or grapes. If you choose this option, beware that you may attract not only birds, but mammals such as squirrels, raccoons, opossums, and others.
If you’d like to watch your wildlife visitors, be sure to attach the food items with string so that the animals must eat the food at the site of the tree rather than carrying it away to eat or store elsewhere out of view. Consider using a biodegradable string (i.e., cotton) to secure the food items to your tree so you can eventually compost the tree without worrying about needing to remove the string.
YOUR TREE COULD PROVIDE SHELTER FOR WILDLIFE
If you’re tired of seeing your holiday tree in its upright position, consider taking it outdoors, laying it down, and heaping other vegetative debris loosely on top to form a ‘brush pile’. Brush piles are mounds of woody vegetation created specifically to provide shelter for wildlife.
The lower portions of a brush pile can offer cool, shaded conditions that allow small mammals such as rabbits to hide from the weather and from predators. Meanwhile, the upper portions can serve as perch sites for songbirds. The entire pile may be used as resting sites for amphibians and reptiles. In yards with few understory trees or shrubs, and at times of year when many trees and shrubs have limited foliage, these brush piles can provide much-appreciated cover for many kinds of wildlife.
YOUR TREE COULD PROVIDE SHELTER FOR FISH
Your retired Christmas tree could be used to make long-lasting habitat improvements for fish. In artificial ponds with little submerged vegetation, the addition of one or more Christmas trees could upgrade the quality of refuge and feeding areas for fish. Small fishes may hide among purposely submerged Christmas trees for protection, and larger fishes may follow them. If you’ve got an artificial pond on your property, consider adding discarded trees to create a place where fish can hide and find food, and also to concentrate fish for angling. Simply secure a cinder block to your holiday tree using heavy wire or thin cable and place it far enough from shore that water covers the top of the tree by a couple of feet. When constantly submerged, Christmas trees can persist for many years underwater.
Not only can your tree offer enjoyment to you when decorated with lights and ornaments indoors, but it can also allow you to provide post-holiday gifts to the wildlife and fish on your property.



















